1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Unemployment rate is an important economic indicator to measure the proportion of unemployed labor force. However, people usually only consider the natural rate of unemployment, the normal rate of unemployment based on economic fluctuations. Economists analyze unemployment to determine its root causes and help strengthen public policies that can affect the unemployed. These policies cover a range of approaches. For example, job training programs are designed to help individuals find employment, while unemployment insurance provides support to alleviate challenges faced by the unemployed[1]. In addition, it is believed that laws enforcing higher minimum wages could lead to increased unemployment among the least skilled and least experienced individuals in the workforce. By forecasting the unemployment rate, economists can gain valuable insight into the future state of the labor market and make informed decisions. Additionally, people can use this forecast to make informed career choices, seek necessary skills and training, and plan for potential job market volatility.
1.2. Motivation
Unemployment helps people judge the performance of the labor market, and the risk of unemployment is closely related to everyone. Catastrophic events, and national or global catastrophic events may lead to mass unemployment. "Catastrophic events" have happened many times: the oil crisis in 1973 and 1979, which led to a surge in global oil prices, which eventually triggered inflation and economic recession, we just went through the global pandemic of COVID-19, which eventually led to a severe recession in the global economy. Understanding the unemployment rate is not only helpful for government policy decisions, future business planning for private companies, personal judgment on future employment prospects and formulation of related work plans, but also research on the entire national economy[2]. For college students, most are likely to enter the workforce in recent years. If college students know how to analyze the characteristics of the current labor market, and even make a rough forecast of the future trend of the labor market, they will be able to make the most suitable career choice for them or at least gain some career advice.
1.3. Procedure
In the World Bank database, this article will use China's 11-year unemployment rate from 2012 to 2022 and conduct research on it. This article will use the ARIMA model in statistics to analyze this section of data, and then establish several models with different parameters. After obtaining the various values, compare the values given by different models, and then select the optimal model for prediction. Researchers will operate in RStudio. Finally, analyze the causes of such results according to the prediction results. As well as the limitations of this study and the suggestions and prospects for the future after analyzing the forecast results, and finally a summary of this study.
2. Methodology
2.1. Model
ARIMA model will be used in the research. The full name of ARIMA is Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model, which can also be written as ARIMA(p,d,q), the most common model used in statistical models for time series prediction. ARIMA is good at building trends and seasonal data A model that can handle non-stationary data and provides flexibility in its structure to capture different patterns. AR(p) model is an autoregressive model of order p, and it is a multiple regression that replaces the predictor variable with the historical value of the target variable.
\( {y_{t}}=c+{ϕ_{1}}{y_{t-1}}+{ϕ_{2}}{y_{t-2}}+…+{ϕ_{p}}{y_{t-p}}+{ε_{t}} \) (1)
Moving average model uses historical forecast errors to build a regression-like model, which is known as MA(q) model with a moving average model of order q.
\( {y_{t}}=c+{θ_{1}}{ε_{t-1}}+{θ_{2}}{ε_{t-2}}+…+{θ_{q}}{ε_{t-q}} \) (2)
And the differencing time is d.
2.2. Data
The 11-year data of Chinese unemployment rate from 2012 to 2022 in the World Bank database will be used(Figure 1). According to gglagplot(unem, do.lines = F), these points hardly present a diagonal line, so the data is consistent with white noise, and it also shows that the data is stationary. Most points barely cluster along the diagonal y=x, which cannot conclude an autocorrelation. This indicates that these data points are not significantly correlated to their lagged versions, and the time series of the unemployment rate might be consistent with white noise(Figure 2).
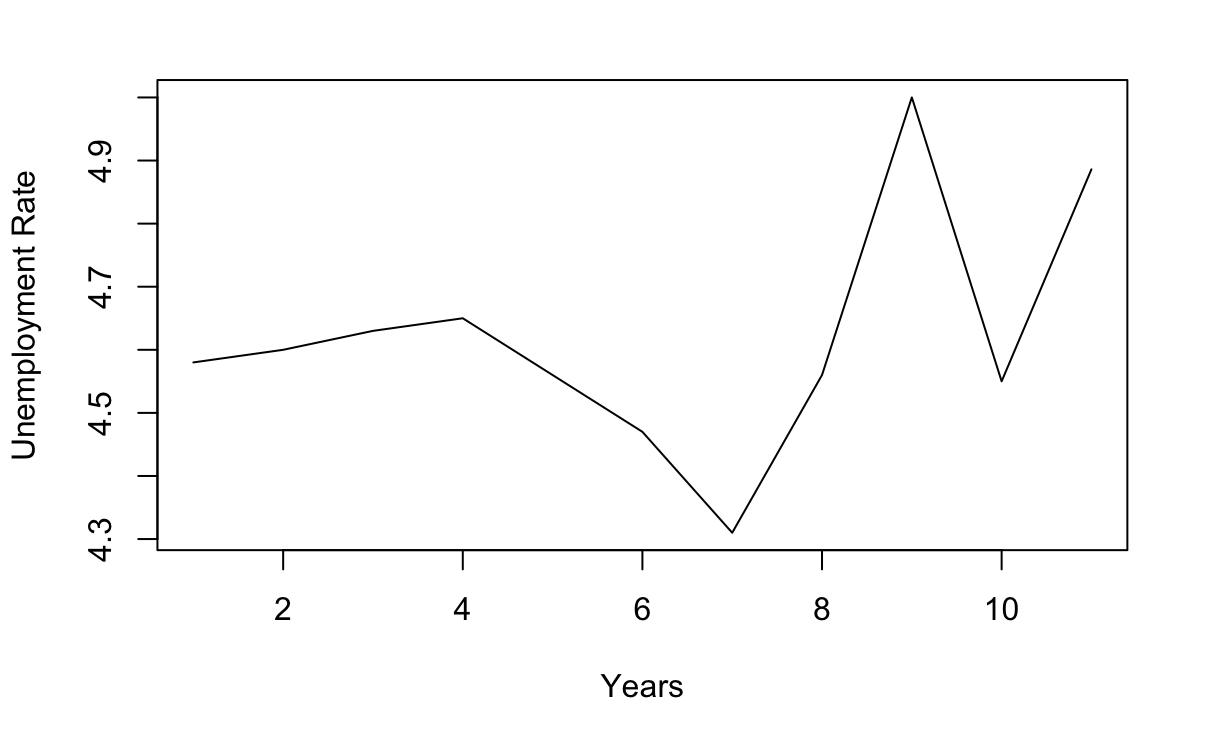
Figure 1: Line chart of unemployment rate for each year.
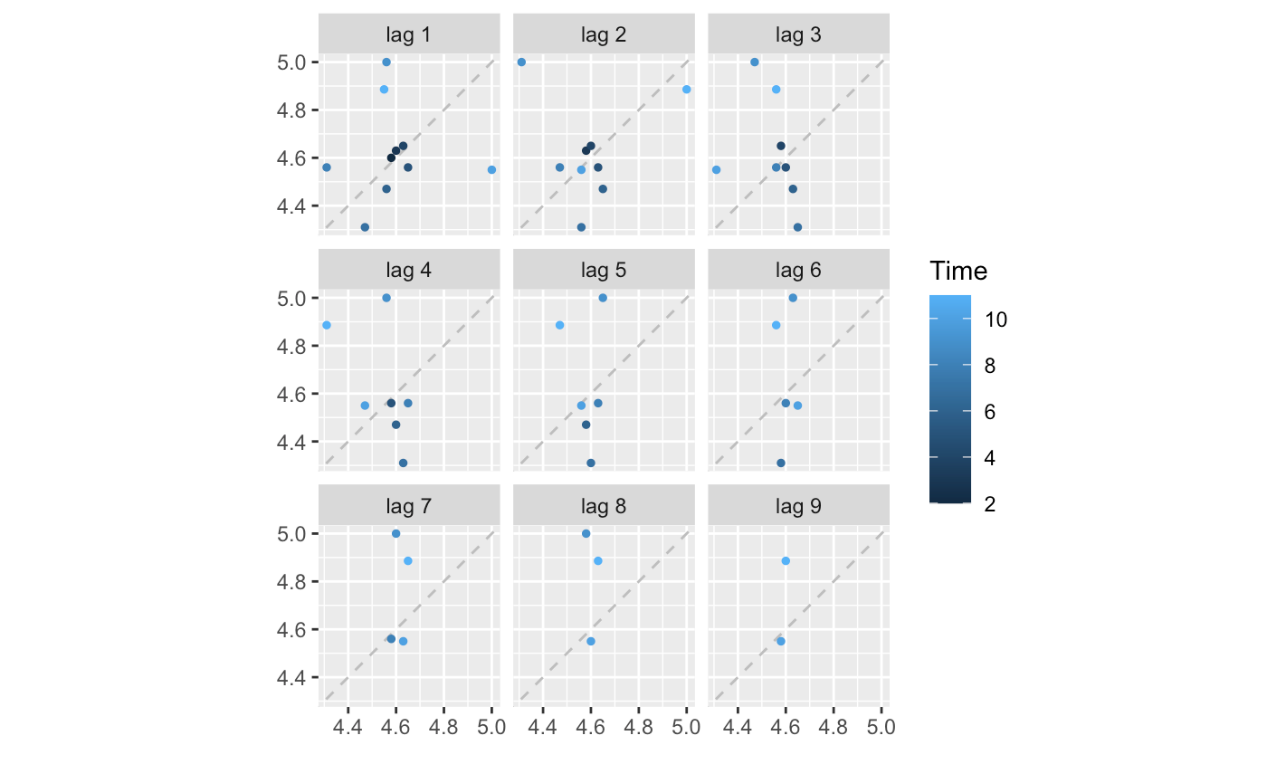
Figure 2: Lag plot.
3. Result
The code ndiffs(unem) gives a value of 0 for d. Next the values of p and q need to be confirmed. By ggtsdisplay(unem,xlab="Years", main = "Unemployment Rate") giving the ACF graph and PACF graph. It is known from the images that none of the lags in the two graphs exceeds the boundary range, so p and q are both 0(Figure 3).
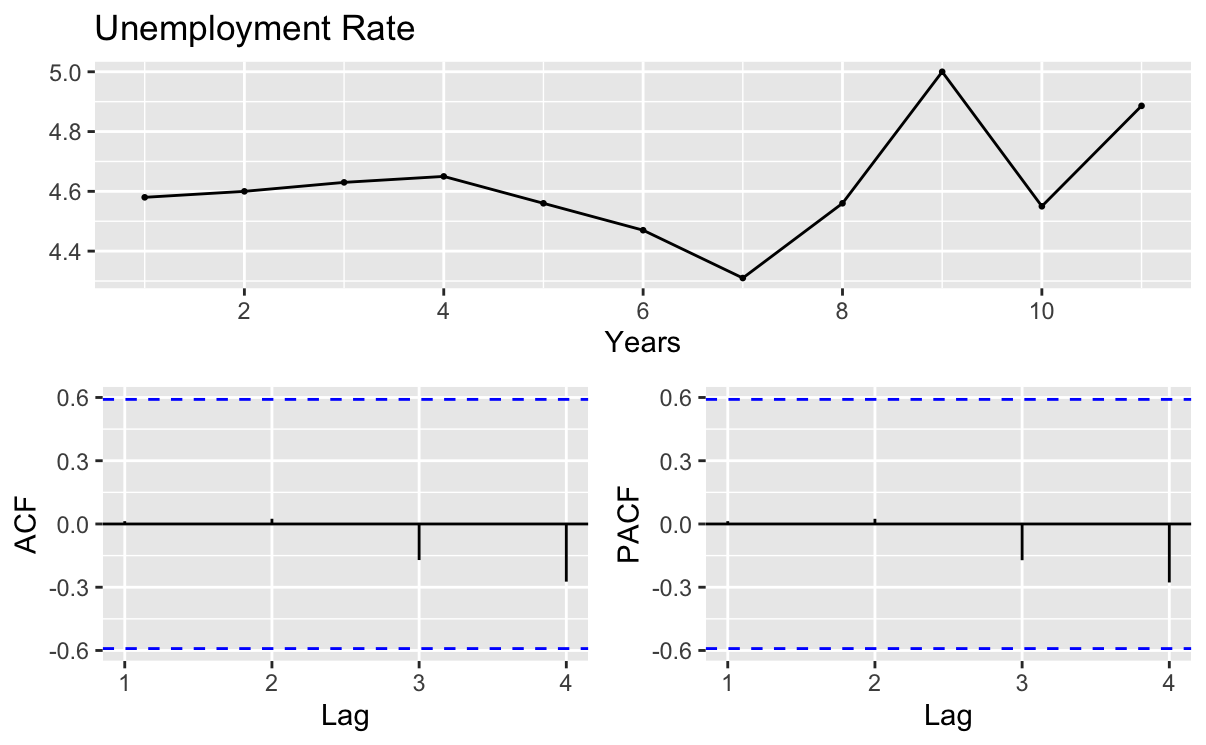
Figure 3: PACF.
Arima(unem,order=c(0,0,0)) build ARIMA(0,0,0) model, in this model AIC=-2.75, AICc=-1.25, and BIC=-1.95. Continue to build Several different ARIMA models check whether the arima(0,0,0) model is the optimal model.
ARIMA (0,0,0) with non-zero mean is obtained by auto.arima(unem), and all values are the same as the model established above.
AIC=-0.75, AICc=2.68, and BIC=0.45 are obtained by Arima(unem,order=c(1,0,0)). In this model, AIC, AICc, and BIC are all larger than the first model , this model is not optimal and will not be used.
AIC=-0.75, AICc=2.68, and BIC=0.45 are obtained by Arima(unem,order=c(0,0,1)). In this model, AIC, AICc, and BIC are all larger than the first model, this model is not optimal and will not be used.
The Point Forecast of ARIMA (0,0,0) is 4.617818, and the upper bound and lower bound of 95% confidence interval are (4.25177, 4.983867), and these forecast values have not changed in the next nine years(Figure 4).
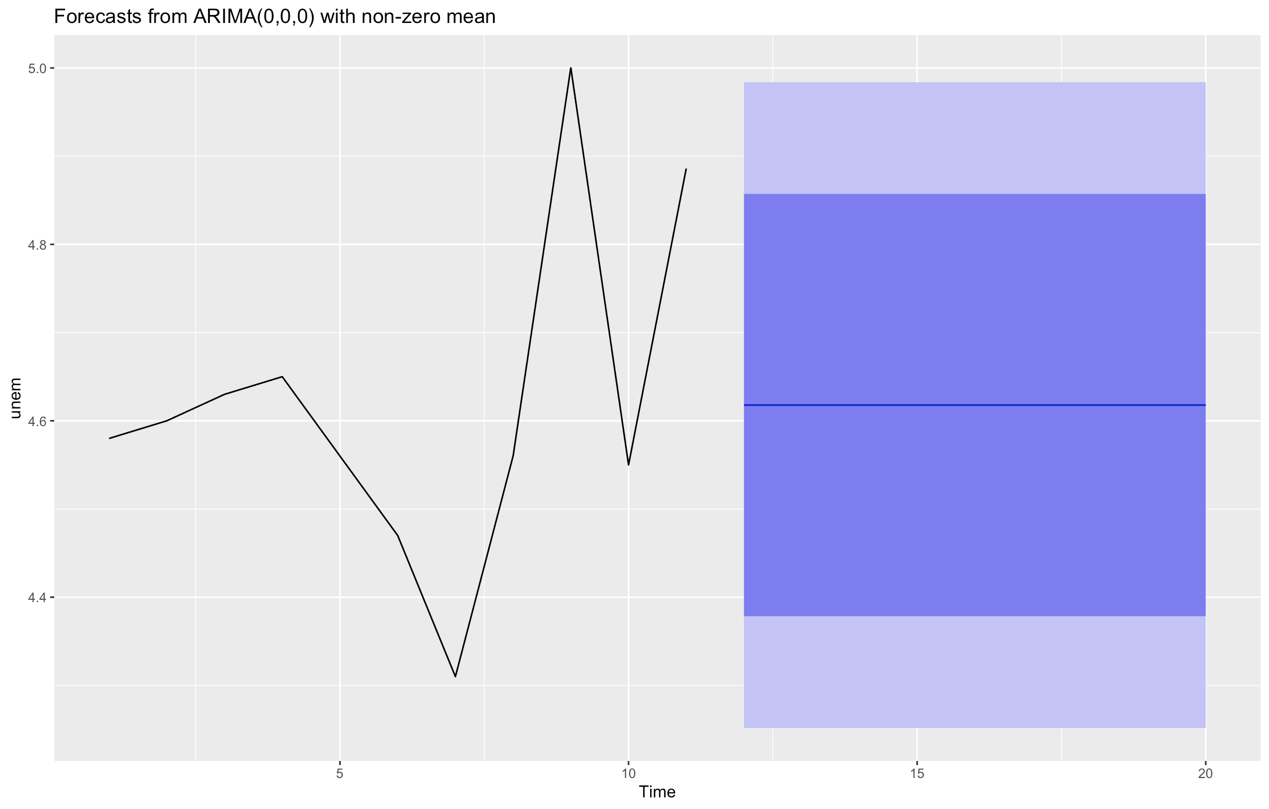
Figure 4: Prediction given by ARIMA.
4. Discussion
4.1. Cause Analysis
Too low an unemployment rate will lead to a shortage of reserve labor, which will also lead to difficulties in recruiting workers in the future, and the high cost of labor will affect the long-term economic development. At the same time, it will cause a decline in laborers' sense of competition, affect the improvement of work skills, and lead to low work efficiency. The low efficiency of production labor will not be conducive to the further development of the industry, technology, and society. But if the unemployment rate is too high for a long time, a large amount of labor will be idle and wasted. This will lead to a decline in economic growth, degradation of job skills of the unemployed, widening of the gap between the rich and the poor, difficulty in living for low-income groups, and even affect social stability. People's daily living environment and security will deteriorate. Therefore, the country and the government intervene in the unemployment rate at the macro level, such as finance, investment, government expenditure, monetary policy, deepening financial system reform, taxation, and other policies, and even introduce new regulations or norms for enterprises. ‘The effect of monetary policy on the unemployment rate is greater and more stable. This result may be since the part of monetary policy tools that can directly affect the development of enterprises and personal disposable income and thus employment is relatively obvious, while the part of fiscal policy that is directly used to solve employment problems The proportion is small. However, the adjustment of monetary policy and fiscal policy is not the main reason for reducing the unemployment rate.’ [4] Education expenditure A branch of municipal government expenditure. ‘The increase in education expenditure has improved the level of national knowledge and skills. From the perspective of the economy, on the premise that the economic structure remains unchanged, the higher the level of national education, the more likely it is to improve their employability, thereby reducing the overall unemployment rate. From the perspective of the distribution of the global industrial chain, the higher the level of national education, the more conducive it is to enhance the global competitiveness of mid-to-high-end industries and increase the employment of mid-to-high-end industries in the country by squeezing the total employment of mid-to-high-end industries in other economies The total amount, so as to achieve the effect of reducing the long-term unemployment rate. Obviously, for an economy in a downward economic cycle, increasing education expenditure will have a better employment effect in both the short term and the long term, especially the long-term effect is a key factor in combating structural unemployment [5].
Under the intervention of the government, as well as the influence of macro policies on micro behaviors, China's unemployment rate was gradually controlled after the catastrophe and gradually decreasing. And after the resumption of offline production activities, it will help the unemployment rate return to the original changing level. With the help of policies, the employment situation of college graduates tends to improve, and the employment situation of migrant workers (who got unemployed the most) gradually improves. This is the data for 2020 [6-7]. ‘The surveyed urban unemployment rates in July and August were 5.7% and 5.6% respectively; as the graduation season ended and college graduates gradually found jobs, the unemployment rate fell back to 5.4% in September.’ Compared with the 2020 data, the unemployment rate has been reduced in the 2023 data. ‘In the first quarter, the effects of stabilizing economic policies continued to emerge, which strongly supported the gradual recovery of the employment situation. 2.97 million new urban jobs were created, a year-on-year increase of 120,000. The surveyed urban unemployment rate in March was 5.3%, down 0.5 percentage points year-on-year. The demand for offline recruitment is warming up, and the activity of the job market is gradually increasing [3].
The purpose of these measures is to reduce the unemployment rate at this stage, and the change in the unemployment rate will gradually reach a relatively stable level within the forecast range.
4.2. Suggestion
To relatively stabilize the future unemployment rate, at the national level (a macro-position), the economy needs to recover from COVID-19, and the higher unemployment rate must gradually decline [8]. Employment needs to be placed in a prominent position in macroeconomic policies, and employment policies are jointly promoted with fiscal, monetary, investment, industrial, government expenditure, and regional policies. Encourage local conditions to develop different labor-intensive industries and increase the breadth of employment scope. Relevant departments should closely track and monitor the employment situation, strengthen the prevention and control of large-scale unemployment risks, and take practical measures to help enterprises solve difficulties and rescue them, which can encourage enterprises to recruit more employees and increase employment [9-10]. On the personal side, people can improve their working ability in various ways, try to learn a variety of skills through the Internet and other ways, and enhance their competitiveness in the labor market.
According to the research results, in order to control the unemployment rate, the government can formulate monetary policy and appropriately increase the money supply. The greater the amount of money in circulation, the greater the supply than the demand, lowering interest rates and lowering unemployment. The government can formulate fiscal policies and appropriately increase fiscal expenditures.
It can be directly used for social security and employment, stimulate aggregate demand and increase jobs. The more fiscal expenditures, the lower the unemployment rate. Compared with fiscal policy, monetary policy uses a larger proportion, and monetary policy is more effective and stable. It mainly uses the regulation of government expenditure, such as education expenditure, which not only directly increases jobs, reduces frictional unemployment and cyclical unemployment, but also increases aggregate demand to improve people's livelihood. The increase in education expenditure will not only reduce the unemployment rate in the short term and improve the ability of citizens to participate in employment, but also continuously upgrade the domestic industrial structure, occupy a dominant position in the competition of global high-end industries, increase the large amount of exports of domestic high-end industrial products, and make the middle and high-end industries more competitive. The proportion of high-end industry employment in total employment has increased, thereby achieving the goal of promoting the decline in the long-term unemployment rate. Local governments should formulate local policies according to different situations. The government can adopt an expansionary monetary policy and increase fiscal spending. The main reason is to increase government spending, such as the branch of education spending, which not only reduces the unemployment rate in the short term, but also helps people acquire more job skills and increases people's competitiveness in the workplace, which is also related to the low unemployment rate.
4.3. Limitation
COVID-19 is a worldwide historical event, it has brought global and catastrophic impact on the economy, and it will bring extremely extreme unemployment data, and the government's response to the unemployment rate will also be different from the It will be different than usual, and the stimulus to the economy and employment will be stronger than usual. But COVID-19 and similar events are sudden and unpredictable, and sudden events will affect the accuracy of predictions.
5. Conclusion
Unemployment helps us determine how the labor market behaves, and the risk of unemployment affects virtually everyone. Any kind of catastrophic event, whether national or global, can lead to job losses. Unemployment rate is the main indicator reflecting the unemployment status of a country or region. According to the unemployment rate in China from 2012 to 2022 in the World Bank database, this paper analyzes the data and constructs the ARIMA model. After comparing the values of AIB, AICc and BIC, ARIMA (0, 0, 0) is the best Perfect model. Based on ARIMA (0,0,0), this paper predicts the unemployment rate for the next nine years and finds that the result has not changed. The Point Forecast of ARIMA (0,0,0) is 4.617818, and the upper bound and lower bound of 95% confidence interval are (4.25177, 4.983867). The reason for this result is the intervention of various policies issued by government agencies, such as finance, investment, monetary policy, deepening financial system reform, taxation, etc., especially government expenditure (like education investment).
References
[1]. World Bank Data China Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate).
[2]. Zhang, Yi. An Empirical Test of the Effectiveness of Main Variables of Economic Policy in Controlling China's Unemployment Rate. China Information News. 2020 Oct 21. 003.
[3]. Han, Xin. The employment situation gradually recovers and is generally stable. People's Daily. 2023 April 25. 007.
[4]. Jia, LIjun. And Wang, Rong. An empirical test of the effectiveness of the main variables of economic policy in controlling China's unemployment rate. Economic Research Guide. 2014. 222.
[5]. Ye, Ting. Research on fiscal policy promoting the reduction of unemployment rate in the declining economic cycle. Master's thesis of Kunming University of Science and Technology. 2018 Nov.
[6]. Ji Bicong,Zhang Pinyi. Financial time series forecasting based on ARIMA-LSTM model[J]. Statistics and Decision Making,2022,38(11):145-149.
[7]. Jia Qianying. Empirical analysis of domestic carbon financial transaction risk based on financial time series analysis[D]. Shandong University,2022.
[8]. Liu H,Sun Z,Liu X. Research on Financial Market Price Direction Based on ARIMA Model[J]. Academic Journal of Business & Management,2022,4.0(5.0).
[9]. Shiwei S. Nonlinear ARIMA Models with Feedback SVR in Financial Market Forecasting[J]. Journal of Mathematics,2021,2021.
[10]. Sun Yi,Zhou Longlong. Teaching financial time series ARIMA modeling based on Python[J]. Modern Information Technology,2021,5(10):192-195.
Cite this article
Li,M. (2024). Analysis and Forecast of China's Unemployment Rate. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,60,9-15.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. World Bank Data China Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate).
[2]. Zhang, Yi. An Empirical Test of the Effectiveness of Main Variables of Economic Policy in Controlling China's Unemployment Rate. China Information News. 2020 Oct 21. 003.
[3]. Han, Xin. The employment situation gradually recovers and is generally stable. People's Daily. 2023 April 25. 007.
[4]. Jia, LIjun. And Wang, Rong. An empirical test of the effectiveness of the main variables of economic policy in controlling China's unemployment rate. Economic Research Guide. 2014. 222.
[5]. Ye, Ting. Research on fiscal policy promoting the reduction of unemployment rate in the declining economic cycle. Master's thesis of Kunming University of Science and Technology. 2018 Nov.
[6]. Ji Bicong,Zhang Pinyi. Financial time series forecasting based on ARIMA-LSTM model[J]. Statistics and Decision Making,2022,38(11):145-149.
[7]. Jia Qianying. Empirical analysis of domestic carbon financial transaction risk based on financial time series analysis[D]. Shandong University,2022.
[8]. Liu H,Sun Z,Liu X. Research on Financial Market Price Direction Based on ARIMA Model[J]. Academic Journal of Business & Management,2022,4.0(5.0).
[9]. Shiwei S. Nonlinear ARIMA Models with Feedback SVR in Financial Market Forecasting[J]. Journal of Mathematics,2021,2021.
[10]. Sun Yi,Zhou Longlong. Teaching financial time series ARIMA modeling based on Python[J]. Modern Information Technology,2021,5(10):192-195.









