1. Introduction
Parental involvement and parenting styles are the key factors influencing children's academic success. Students' education is not only shaped by peers and environments, but also affected by parents. Research has been shown that children are more likely to receive better grades, display greater motivation, and have higher graduation rate when their parents are actively engaged in their kids' education and providing help. Although it is commonly believed that parental involvement improves students' academic success, it is yet unknown how various parenting philosophies and kids' academic achievement relate to one another. A parent's parenting style can have numerous impacts on how the students perform academically. Parenting style is the methods they use to raise and educate their children, including attitudes, actions and expectations. Parenting styles vary from person to person, but the four parenting styles that are frequently discussed are authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved.
A study by Zahedani et al uses a correlation research method conducted at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences [1]. From a population of 1600 students, 310 were randomly selected as the sample. This study analyzes the relationship between parenting styles, academic achievement, and career path. Parenting styles have a strong connection with job pathways and academic success, the results show that authoritative parenting often leads to better outcomes. In contrast, authoritarian parents emphasize strict rules, affecting educational outcomes and career development negatively [2].
By examining the impact of different parenting styles on children's academic success, people can gain a better understanding of the ways that families support a kids' education, and discover solutions that strengthen more effective collaborations between home and school.
How do different parenting styles influence children's academic performance?
2. Cause
Every family has a different parenting style, which is influenced by a wide range of social, cultural, and individual factors that affect how parents engage with their kids. One of the most important factors is the cultural backgrounds of parents, parents who grow up in a collectivist society will place more emphasis on respect for authority, which may become an authoritarian parent. On the contrary, parents who live in an individualistic cultural background tend to emphasize independence and self-expression, supporting authoritative parenting. Parenting is also influenced by socioeconomic status (SES), while parents in higher incomes have more time and stability to employ authoritative techniques, parents in lower SES households often suffer a lot of pressure and have scarce resources, which can lead to tighter punishment. Additionally, education is one of the factors. Parents who received higher education tend to have broader visions and be more enlightened, whereas less educated parents may rely on traditional methods. In some contexts, some parents adopt permissive or uninvolved parenting styles. Permissive parents seem to think that reducing regulations and allowing more flexibility encourages independence and creativity, and they assume that children should take their own responsibilities, so they spend less energy on guiding and controlling. Last but not least, uninvolved parents are often under stress or facing financial difficulties. Long-term fatigue and mental health problems can destroy parents' physical energy to engage in their children's lives.
2.1. Authoritative
This type of parents always set high expectations for their kids to achieve while also supporting them by creating a trusting and emotionally nurturing atmosphere [3]. According to Jessup University, this approach is also recognized as "firm but nurturing" or "tough but fair." Within a certain framework, a youngster is allowed to make mistakes and is not judged for them [4]. Baumrind described authoritarian parents as aggressive without being overbearing or constrictive. Instead of using punitive measures, their disciplinary strategies are supportive. Along with being cooperative, they also want their kids to be self-reliant, socially conscious, and aggressive.
2.2. Authoritarian
This approach can be also regarded as high demands and low responsiveness. When the kids asked for reasons, authoritarian parents replied, "Because I said so!" and often without explanation or room for negotiation [2]. This style emphasizes tight rules and obedience, which focuses on control, rather than encouraging independence and critical thinking. There are harsh punishments for children who break the regulations that their parents set. Children in this type of home are expected to follow instructions without question and revolt, and are seldom allowed a say in their own business.
2.3. Permissive
Permissive parents, who are the complete opposite of authoritarian parents, don't impose rules or structures that could disappoint or annoy their kids. Instead, they allow them to do as they like. This method is characterized by the parent giving in to their child's requests almost instantly and attempting to behave more like a buddy or peer. This can be the result of that parent growing up with an authoritarian parenting style in their own household and not wanting to put their child through it.
2.4. Uninvolved
As the name would suggest, parents who fall into this category don't spend much time with their kids. The kids are mostly left on their own and receive no affection, structure, or regulations. Neglectful parents don't converse or interact with their children much, don't attend their children's activities or events and don't strive for any kind of emotional connection.
Figure 1 illustrates four parenting styles, categorized by levels of warmth/responsiveness and expectations/control, highlighting differences in parental approaches.
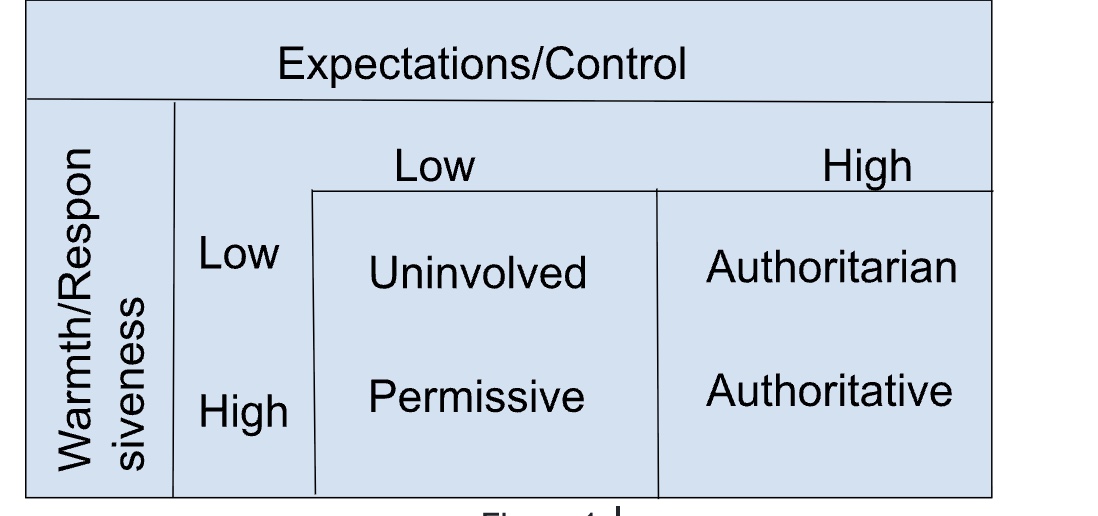
3. Effect
Parenting styles have a direct effect on kids' self-discipline, motivation, and self-control—all of which are critical in deciding how well kids perform in school.
Authoritative parenting is consistently associated with the best academic outcomes, they provide systematic guidance and emotional support by combining warmth and clear expectations. This encourages accountability, internal motivation, and better study habits. Zahedani, Rezaee, Yazdani, Bagheri, and Nabeiei found that students raised by authoritative parents demonstrated higher academic success and more defined career routes, proving the benefits of balanced parenting practices [1]. However, authoritarian parenting, which is typified by a high degree of control and a low amount of warmth, usually undermines children's long-term academic engagement, critical thinking, and self-confidence. Because they do not have the structure and boundaries, so it may lead to short-term conformity. Children who encounter permissive parenting—characterized by a high degree of warmth but a low amount of discipline which generally perform worse academically. Last but not least, uninvolved parenting—which exhibits low responsiveness and low control is most significantly associated with poor academic achievements because children receive no help, guidance, or tracking of their academic growth. The educational and psychological studies have shown that parenting style is a strong predictor of academic outcomes. The biggest support for achievement comes from authoritative parenting, whereas permissive and uninvolved parents can be harmful to students' academic motivation and performance. Together, these findings demonstrate how much children's academic achievement is influenced by the emotional climate and disciplinary strategies they learn at home.
The study Parenting Style as Correlates of Adolescents' Academic Achievement Motivation by Mihret, Dilgasa, and Mamo (2019) 4 investigates how different parenting styles affect adolescents' academic motivation in Ethiopia. The research involved 192 secondary school students and utilized standardized scales to assess parenting styles and academic motivation. Random selection was used to choose 110 female adolescents (n = 437) and 100 male adolescents (n = 415). The following table, which displays the correlation coefficients between all variables, displays the correlation matrix between the variables under study.
|
SN |
Parenting Styles |
Mean scores of academic achievement motivation |
|
1 |
Authoritative |
44 |
|
2 |
Authoritarian |
32 |
|
3 |
Permissive |
26 |
|
4 |
Neglectful |
21 |
According to Table 1, Educational success and career path are positively and significantly correlated with a firm and reassuring parenting style at the significance level of 0.01; conversely, there is a negative and significant correlation between educational success and career path and an authoritarian parenting style at the significance level of 0.05. These two factors do not significantly correlate with a permissive parenting style.
4. Solutions
Improving the negative impacts of permissive and uninvolved parenting styles requires a combination of family, school, and community interventions supported by research evidence. Previous studies emphasize that parental education programs are highly effective in encouraging healthier parenting practices.
The study by Zahed Zahedani et al. found that when parents were guided to adopt more structured and supportive approaches, children have much higher academic achievement [1]. Setting consistent boundaries, providing emotional support, and engaging actively in schoolwork are the key factors of authoritative parenting, so parents can attend workshops and training to learn these strategies. Schools can also act as key partners in strengthening parental involvement. According to Spoth, R., Randall, G. K., & Shin, C., strong school–family partnerships are consistently linked to improved academic outcomes [5]. Regular communication, progress monitoring, and parent-focused resources can help bridge the gap between home and school environments. Teachers who provide parents with simple tools to reinforce learning at home contribute to improved discipline and responsibility in students [6]. Addressing broader challenges such as socioeconomic stress is equally important. Research shows that financial strain often limits parents' ability to be engaged, increasing the likelihood of uninvolved parenting. Solutions include offering affordable childcare, counseling, and social support systems to ease stressors, allowing parents to increase their involvement in their kids' education. Finally, awareness campaigns and community initiatives can spread knowledge about the benefits of authoritative parenting. By promoting positive role models and sharing research findings, society can encourage healthier parenting styles that lead to long-term academic success [7,8].
5. Conclusion
Parenting practices have a substantial and complex impact on kids' academic achievement. This study shows that parental participation and the way parents interact with their children have a significant impact on academic performance by doing a meta-analysis of previous data. Of the four primary parenting theories, authoritative parenting is always the most effective because it finds a balance between structure and emotional support while promoting self-reliance, drive, and fortitude. Children who grow up in authoritative homes frequently perform better academically, have more self-control, and succeed more in school over the long run. On the other hand, authoritarian parenting tends to stifle creativity and critical thinking, which limits children's general academic development even when it occasionally encourages discipline and obedience. Meanwhile, permissive and uninvolved parenting styles generally undermine academic success due to a lack of boundaries, guidance, and consistent support.
However not all situations have the same correlation between parental practices and academic success. The success of parenting methods is greatly influenced by a number of factors, including parental education levels, cultural norms, socioeconomic situation, and psychological well-being. Although authoritative parenting offers a generally good model, this intricacy implies that it cannot be used as a one-size-fits-all strategy. Contextual and individual child requirements must also be taken into consideration by effective parents.
In the end, the results emphasize how crucial parental involvement in their children's education is. Programs that give parents the tools they need to adopt more structured, supportive, and balanced parenting techniques should be taken into consideration by educators and legislators. Fostering situations that promote cooperation between educators and families increases the likelihood that children will succeed academically and acquire the skills needed for lifelong learning. In conclusion, even though there are many different parenting philosophies, the ones that combine warmth, involvement, and clear expectations seem to offer the best prospects for future success in school.
References
[1]. Zahed Zahedani, Z., Rezaee, R., Yazdani, Z., Bagheri, S., & Nabeiei, P. (2016). The influence of parenting style on academic achievement and career path. Journal of Advances in Medical Education & Professionalism, 4(3), 130–134. https: //pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4927255/
[2]. Ansay, K. J. P. (2025). Parental involvement and teacher disciplinary strategies on student behavior and learning engagement: A basis for teacher and parent support program. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Publications, (Online), 2581-6187. http: //ijmrap.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/IJMRAP-V8N1P32Y25.pdf
[3]. Weicker, E. A. (2022). Parenting style and academic success: How can you help your child succeed? Caravel Undergraduate Research Journal. University of South Carolina, Office of the Vice President for Research. https: //sc.edu/about/offices_and_divisions/research/news_and_pubs/caravel/archive/2022/2022_parenting.php
[4]. Hayek, J., Schneider, F., Lahoud, N., Tueni, M., & de Vries, H. (2022). Authoritative parenting stimulates academic achievement, also partly via self-efficacy and intention towards getting good grades. PloS one, 17(3), e0265595. https: //doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265595
[5]. Spoth, R., Randall, G. K., & Shin, C. (2008). Increasing school success through partnership-based family competency training: Experimental study of long-term outcomes. School Psychology Quarterly: The Official Journal of the Division of School Psychology, American Psychological Association, 23(1), 70–89.
[6]. Jessup University. (2022, August 16). The psychology behind different types of parenting styles. Jessup University Blog. Retrieved 2025, August 17, from https: //jessup.edu/blog/academic-success/the-psychology-behind-different-types-of-parenting-styles/
[7]. Mihret, D., Dilgasa, D., & Mamo, F. (2019). Parenting style as correlates of adolescents' academic achievement motivation. ERIC. https: //files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1219553.pdf
[8]. Wilder, S. (2014). Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educational Review, 66(3), 377–397.
Cite this article
Li,T. (2025). The Impacts of Different Parenting Styles on Children's Academic Success. Communications in Humanities Research,89,42-47.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceeding of ICIHCS 2025 Symposium: Integration & Boundaries: Humanities/Arts, Technology and Communication
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zahed Zahedani, Z., Rezaee, R., Yazdani, Z., Bagheri, S., & Nabeiei, P. (2016). The influence of parenting style on academic achievement and career path. Journal of Advances in Medical Education & Professionalism, 4(3), 130–134. https: //pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4927255/
[2]. Ansay, K. J. P. (2025). Parental involvement and teacher disciplinary strategies on student behavior and learning engagement: A basis for teacher and parent support program. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Publications, (Online), 2581-6187. http: //ijmrap.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/IJMRAP-V8N1P32Y25.pdf
[3]. Weicker, E. A. (2022). Parenting style and academic success: How can you help your child succeed? Caravel Undergraduate Research Journal. University of South Carolina, Office of the Vice President for Research. https: //sc.edu/about/offices_and_divisions/research/news_and_pubs/caravel/archive/2022/2022_parenting.php
[4]. Hayek, J., Schneider, F., Lahoud, N., Tueni, M., & de Vries, H. (2022). Authoritative parenting stimulates academic achievement, also partly via self-efficacy and intention towards getting good grades. PloS one, 17(3), e0265595. https: //doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265595
[5]. Spoth, R., Randall, G. K., & Shin, C. (2008). Increasing school success through partnership-based family competency training: Experimental study of long-term outcomes. School Psychology Quarterly: The Official Journal of the Division of School Psychology, American Psychological Association, 23(1), 70–89.
[6]. Jessup University. (2022, August 16). The psychology behind different types of parenting styles. Jessup University Blog. Retrieved 2025, August 17, from https: //jessup.edu/blog/academic-success/the-psychology-behind-different-types-of-parenting-styles/
[7]. Mihret, D., Dilgasa, D., & Mamo, F. (2019). Parenting style as correlates of adolescents' academic achievement motivation. ERIC. https: //files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1219553.pdf
[8]. Wilder, S. (2014). Effects of parental involvement on academic achievement: A meta-synthesis. Educational Review, 66(3), 377–397.









