1. Introduction
1.1. Historical and cultural connotation
Acupuncture boneless lanterns originated in the Tang Dynasty. Emperor Taizong Li Shimin of the Tang Dynasty issued an edict to pay tribute to Xianju "Wantan Lanterns" ten pairs every year, which means "perfect and perfect". Later, the Song, Yuan, Republic and Qing dynasties followed this example to pay tribute to the court[1] . In its early stages, it was nurtured by the Tang and Song dynasties, which was the initial period of acupuncture boneless lanterns, and then gradually matured and prospered in the Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasties, and then declined from the founding of the People's Republic of China to the Cultural Revolution and after the reform and opening up. recovery period. Quanzhou lanterns have a long history and splendid culture. "Acupuncture boneless lanterns" are regarded as a unique and exquisite craft in southern Fujian. People use them to reward gods and pray for good weather in the coming year. It is a treasure of Chinese folk culture. This kind of lantern is unique, exquisite, finely made and gorgeous and dignified, showing the distinctive, bright and crystal regional cultural characteristics of southern Fujian.
1.2. Artistic Expressions
The needle-punched boneless lantern absorbs and integrates art forms such as painting, embroidery, architecture, etc. The shape of the lamp is very exquisite and beautiful. The acupuncture boneless lamp is mainly based on the flat and hollow pattern, so its shape is more sophisticated. There are usually lychee lamps, longan lamps, gem lamps, vase lamps, hydrangea lamps, mother and child lamps and so on. There are nearly five types of lamps. There are ten types of lamps. The main body is generally made of geometric frames such as squares, triangles, polygons, etc., which are folded front and back and fit together[2]. The whole has a strong sense of three-dimensionality and space, and the structure is delicate and changeable. Through the shape, size, radius, relaxation and soothing of the lanterns, the unique charm and charm inherent in the work are expressed. The color is bright and translucent, the saturation is high, and it has the characteristics of southern Fujian. The unique craftsmanship and beautiful shape it presents are both artistic expressions. The pattern on the lamp surface does not use ink, and the light is transmitted to leave a shadow. The perforation technology of piercing the lamp paper is used to achieve a fine pattern grid. It is a masterpiece derived from the traditional red needlework technique. Then the inner wick is illuminated, making it dazzling and beautiful. A lantern is a story, which has high aesthetic appreciation and artistic research value.
2. Extraction element
2.1. The refinement of geometric shapes
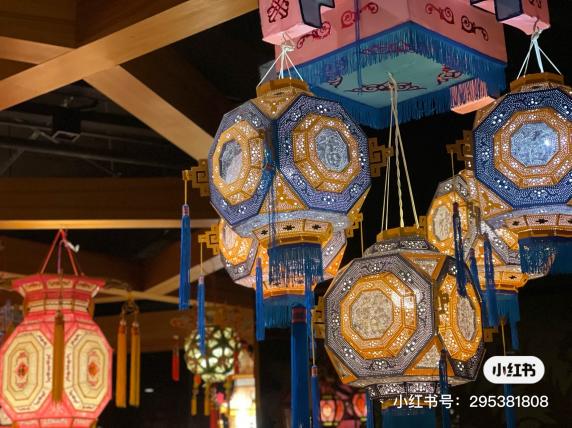
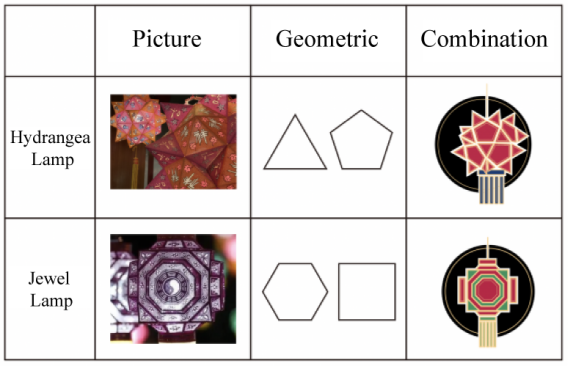
The needle-punched boneless lanterns do not rely on external force when making them. They use boneless technology and are made by folding and splicing flat pieces of paper. The modeling elements with geometry as the main body undergo repeated changes, visually showing a regular and measured order. This form is mainly manifested in block lamps and spherical lamps, such as lychee lamps and gemstone lamps (Figure 1), etc., which reflect a strong sense of fastness, square shape, and tough outline lines. In modern brands, the geometric expressions of lanterns are refined and decomposed, such as starting from hydrangea lanterns and gem lanterns (Figure 2), and simplifying and extracting its fast-face elements into irregular triangles to create a flat style. On the basis of the plane, the geometric figures are spliced together, with different sizes but regular and orderly, and finally create a simple and intuitive brand visual graphics with oriental culture.
|
Figure 1: Acupuncture boneless lantern |
|
Figure 2: Extraction element |
2.2. Simplification of acupuncture techniques
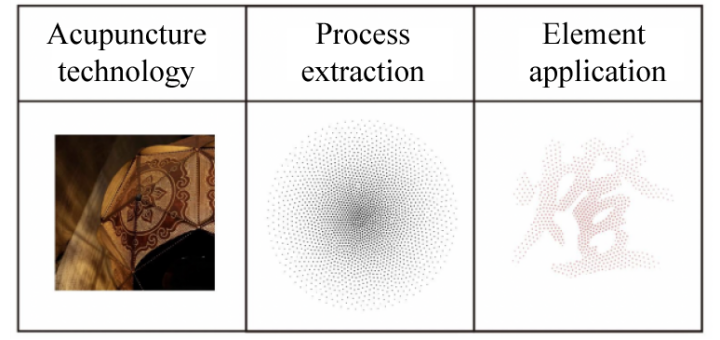
Acupuncture, which was called "Nvhong" in ancient times[3], is the most critical task in the production of acupuncture boneless lanterns. It takes the longest time and tests the skill and patience of the maker. The craftsmanship is fine, the needle eyes are exquisite and clear, and the stitches are even and orderly. This special technology is used on the lanterns to produce a bright and charming effect, twinkling like stars at night, with light and shadow flickering. And its pattern method of "gathering points to form a surface" (Figure 3) uses the composition method of points, lines and surfaces to create a unique composition effect, which has a certain sense of depth. Inspired by the drill-hole carving technique of acupuncture boneless lanterns (Figure 4), we simplified it and used it in the brand design in a radial composition, so that the acupuncture boneless lanterns can be integrated into people's lives in innovative ways. , and have the effect of promoting and inheriting folk culture.
|
Figure 3: Gathering points into an area |
|
Figure 4: Got the answer |
2.3. Lantern feelings
Nowadays, the "national trend" is at the moment, which shows that traditional culture is increasingly recognized by the public. We must continue to dig out excellent traditional culture and make innovative changes. John Eaton was one of the most important teachers in the early days of the German Bauhaus School of Design. He liked to apply Chinese traditional culture into course practice. When teaching, he has quoted ancient Chinese philosophical thoughts many times and applied them to course experiments, such as "When heaven assigns great responsibilities to people, they must first work hard to achieve their goals", etc. This shows that the application of traditional Chinese culture is very important. widely. Nowadays, many brands integrate traditional culture into modern brands, such as the domestic cosmetics brand "Hua Xizi"[4]. The brand's main colors, relief techniques, and hundreds of birds facing the phoenix interpret oriental exquisite aesthetics in the design, and all aspects reflect unique national feelings. . It starts with reviving oriental culture and ends with creating the ultimate product.
As one of the intangible cultural heritages, Quanzhou lanterns inherently imply auspiciousness and joy, and are full of fireworks in the world. The Ming Dynasty's Xie Zhaozhe recorded in "Wuzazu" that "the number of lamps and candles in Shangyuan in the world is no greater than that in central Fujian." "The lamps range from colorful beads to paper paintings, fish, dragons, and fruit trees. Yes. Tourists and women, noisy carriages and horses, dispersed at night" [5]. The lights are friendly, and wherever there are lights, there are people. In the Hokkien language, "deng" has the same pronunciation as "ding", which means more children, more blessings, and a prosperous population. The creations of ordinary working people are the source of the production of needle-punched boneless lanterns. They improvise spontaneously based on their own imagination and life scenes, thereby expressing the joy after the harvest, the materialization of this ideal, and the result of human beings' will to create the world. . The traditional cultural sentiments and folk customs contained in the lanterns are given to the catering brand design to enhance the rural atmosphere and profound cultural heritage. The excellent traditional culture is integrated into the brand design to refresh the public's eyes and is also a welcome addition to the African continent. Inheritance and promotion of material cultural heritage.
3. The application practice of acupuncture boneless lanterns in modern brands
3.1. Design concept
Starting from the acupuncture boneless lanterns, we started to extract inspiration. From the perspective of brand design, we transformed and expressed the artistic expression form of the lanterns, acupuncture technology, and human cultural heritage to form a local catering brand with exquisite commoner flavor. The design started with scene differentiation, and the Southern Fujian culture and Quanzhou lanterns have obvious regional recognition, which is also one of the brand's selling points. The scene uses acupuncture boneless lanterns as the first visual transmission, and the atmosphere of human fireworks is also the focus of the depiction. Comprehensive culture and amplifying concepts are the core of this brand building.
3.2. Designing process
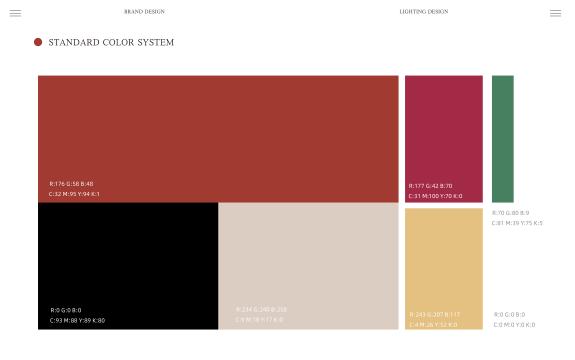
This themed work is called "Light-On Restaurant" and is an application design that integrates Quanzhou lanterns - acupuncture boneless lanterns and modern catering brands. In this trendy era, people are constantly pursuing the essence of traditional culture, and the public is more and more inclined to their own national culture. In design, it is necessary to keep up with the times, perform it in a timely manner, and combine it reasonably. In the design of the brand graphics, the geometric shape of the lanterns is extracted, simplifying it and making it small and cute; then paired with the acupuncture round hole graphics, and using equally radiant design expression techniques to match the lanterns; the color is combined with the psychological effect, using the best The intuitive festive red is the main color of the brand, set off by green, which means good luck and good luck. It is supplemented by the light retro and elegant paper texture, which embodies the local flavor of the city, is very friendly, and brings visual impact to people (Figure 5).
In the design of the brand logo, it fully absorbs the cultural heritage and feelings of the lanterns and grasps "people" as the core design point. Nowadays, the trend of nostalgia continues to prevail. In the context of consumption upgrading and consumer demands becoming increasingly personalized and emotionally diversified, injecting the nostalgic and retro human fireworks atmosphere into catering brands may also be a powerful means to increase sales. The old Republic of China-style big-character poster format is used, paired with the print-textured "curtain" font background. On the other side, hanging English is used to simplify the eaves of traditional Minnan buildings (Figure 6), highlighting the Minnan area where the catering brand is mainly engaged. Local private cuisine(Figure 7).
|
|
Figure 5: Standard color system | Figure 6: Brand standard words |
| |
Figure 7: Visual effect | |
4. Summary
In the preliminary research theory part of this article, through the analysis of acupuncture boneless lanterns, we extracted its unique characteristics as follows: the boneless three-dimensional modeling characteristics of being folded into a body without the help of external force, the hollow pattern characteristics of chiseling and needling, and the light-transmitting and shadowing characteristics. Multi-level spatial features. This is the difference between acupuncture boneless lanterns and other colored lanterns. In the practical innovation part, the artistic expression shape of southern Fujian lanterns and its unique acupuncture technology are used as the main research objects, and the local feelings contained behind the lanterns are explored. Based on the artistic characteristics and craftsmanship of lanterns, the application practice in modern brands is carried out. Through the use of geometric splicing, point, line and surface composition, traditional folk customs and multi-dimensional divergent and extended techniques, the needle-punched boneless lanterns are shown in the current brand design. application in.
5. Conclusions
In today's globalized world, intangible cultural heritage handicrafts are increasingly able to shine on the world stage, combining traditional culture and modern design in a timely manner to show the unique beauty of Chinese traditional culture in more fields, making traditional culture truly "alive" stand up. Integrating excellent traditional folk customs into brand design can not only increase the brand's own benefits, but also adapt to current development trends. As students majoring in design, we must follow the trend of the times. We must pay attention to form, but not copy it mechanically. We must carefully study the connotation behind traditional culture, conduct exploration and analysis, and let more people understand and love Chinese culture.
References
[1]. Zhang Jing, Tao Yu. The art of night—a preliminary study on the production and decoration techniques of Quanzhou lanterns [J]. Chinese Art, 2022(03):109-118.
[2]. Zhang Baodan. Research on the cultural implications of the acupuncture patterns of Xianju boneless lanterns [J]. Cultural and Educational Materials, 2017(13):70-71.
[3]. Shen Shabai. Research on the application of the artistic characteristics of acupuncture boneless lanterns in clothing design [D]. Zhejiang Science and Technology University,2021.DOI:10.27786/d.cnki.gzjlg. 2021.000011.
[4]. Gao Qian. A brief discussion on the integration and development of traditional culture and brand design - taking Hua Xizi as an example [J]. Western Leather, 2022, 44(04): 101-103.
[5]. See "Wuzazu·Volume 2·Tianbu 2" by Xie Zhaozhe.
Cite this article
Chen,X. (2024). The Application Practice of Acupuncture Boneless Lanterns in Modern Brands. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,42,166-171.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Social Psychology and Humanity Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang Jing, Tao Yu. The art of night—a preliminary study on the production and decoration techniques of Quanzhou lanterns [J]. Chinese Art, 2022(03):109-118.
[2]. Zhang Baodan. Research on the cultural implications of the acupuncture patterns of Xianju boneless lanterns [J]. Cultural and Educational Materials, 2017(13):70-71.
[3]. Shen Shabai. Research on the application of the artistic characteristics of acupuncture boneless lanterns in clothing design [D]. Zhejiang Science and Technology University,2021.DOI:10.27786/d.cnki.gzjlg. 2021.000011.
[4]. Gao Qian. A brief discussion on the integration and development of traditional culture and brand design - taking Hua Xizi as an example [J]. Western Leather, 2022, 44(04): 101-103.
[5]. See "Wuzazu·Volume 2·Tianbu 2" by Xie Zhaozhe.