1. Introduction
Theories about goal setting have been around for decades, and most of them focus on external goal setting and the relationship between goal acceptance and performance. There are many studies explaining and discussing the goal-setting theory. They focus mainly on the factors that influence goal choice; the effect of learning goals and goal framing; macro-level goal setting; and conscious versus subconscious goals [1].
This paper, through a method of survey analysis, explores the factors that determine the goals' setting and performance and finds out that the inner factors play a more significant role in the course of goal achievement than external factors.
By knowing both the external and internal factors, more understanding about the mode of thinking can be gained. By combining surveys and theories, it is revealed that internal factors affect goal acceptance and goal choices more than external factors. Suggestions are given for future research.
2. Internal and External Factors
Everyone has goals when doing things, no matter if those goals are small or large. During different stages of people’s development, goals often vary from time to time. Goals can motivate people to pursue higher achievement. Many studies, including goal-setting theory in industrial/organizational psychology, have shown that high (hard) goals result in higher task performance than easy goals or vague, abstract goals [2]. From where the goals come from, goals can be classified into two categories: self-setting goals and external-setting goals. They have different impacts on people and, hence, different performances. According to Erez and Kanfer’s study, "people prefer choice and control over no choice or no control. Therefore, the effects of presented goals should be enhanced by the degree to which a worker perceives him/herself as participating in choosing the goal and maintaining control over the goal-directed behavior "[3]. However, what factors specifically contribute more to the accomplishment of goals?
A goal is a desired result that a person wishes to achieve. It is a target that a person wants to reach. "Goals represent an end state towards which a person strives and that they serve as immediate regulators of action" [3]. Once a goal is set, the story just begins. The performance then follows. However, the key to whether or not the goal can be achieved is to set a proper goal first. If a goal is not realistic and appropriate, it will just be a dream. There are many cases when people set a huge, general goal but they don’t know how to achieve it. For instance, a famous billionaire in China once made some suggestions to the young entrepreneurs in a live show: "As a young entrepreneur, having a dream is very common, but first of all, you have to set a small goal, such as earning one hundred million in 3 or 5 years." Admittedly, it seems like a reasonable goal for him, since he had already accumulated enough wealth to do whatever he wanted, but it's not that realistic or appropriate for other people, especially for those young entrepreneurs. They had little capital and resources to take too many adventures, and they lacked experience and skills. So a goal like this may cause the young entrepreneurs to feel anxious, and since this goal is nearly impossible to accomplish, these young men might as well just give up on doing it.
3. Internal and External Factors that Influence Setting Appropriate Goals
3.1. External Factors
Undoubtedly, external factors play a role in the goal-setting process. They are easily taken into account by people when they set their goals. To be more specific, external factors like money or the persuasion of others can affect the goals that one sets. For instance, most students set goals for their future career. Let’s say a student wanted to be a teacher who teaches primary classes. It is his dream career because he loves to spend time with children. However, he was told that being a primary teacher could not help him get a high salary. His parents and friends all suggested he study in medical school. After days of struggling, he switched his goal to becoming a doctor, and in turn, he chose biology as his major. In this case, it turns out that the desire for the external factors, namely the money and the suggestions from others, outweighs the influence of interest when setting goals.
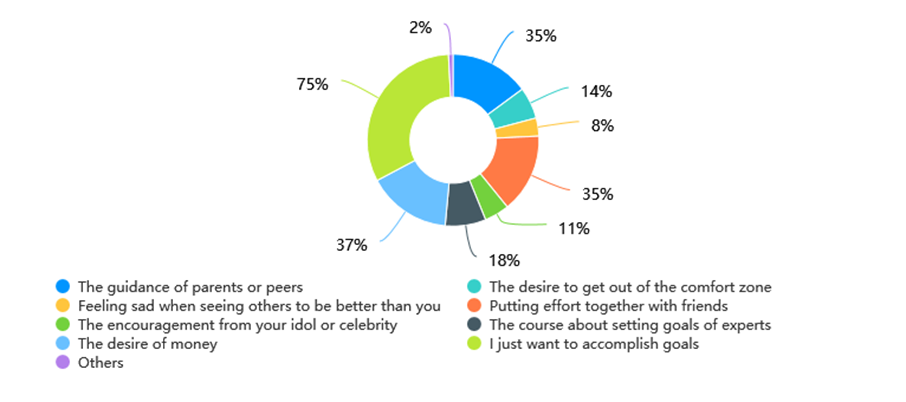
Figure 1: The factors that affect self-goal setting.
However, even though it seems like external factors get the bigger head, many studies actually indicate that the best way to set an appropriate goal is through self-setting rather than following those set by others. "A goal is more likely to be accepted when it is perceived to be under a person’s control than when it is perceived to be externally imposed" [3]. A self-setting goal is comparatively easier to achieve than an external-setting goal. There are many factors that affect the self-goal-setting process. To further explore this topic, 100 people were randomly selected to complete a survey about goal setting and goal accomplishment. When they were asked about what factors affect their decisions the most in the course of goal-setting, "the inner desire" got the most attention. 75% of the participants believe they follow their inner desires when setting goals. The option "the desire for money" got 37% of the votes (see fig. 1). Through this data, it was revealed that inner desire contributes the most when people set their goals. For further research, the answer to this question differs a lot by gender and age. Although about 70% of both males and females chose the option "my own willingness" as one of the most important factors in goal setting, they have a great divergence in other factors.
3.2. Internal Factors
Table 1: Which of the following factors can motivate you to set a goal? (can choose more than one answer).
X\Y | The guidance of parents or peers | The desire to get out of the comfort zone | Feeling sad when seeing others to be better than you | Putting effort together with friends | The encouragement from your idol or celebrity | The course about setting goals of experts | The desire of money | I just want to accomplish goals | Others | Sum |
male | 17 | 8 | 5 | 17 | 2 | 11 | 29 | 41 | 0 | 53 |
female | 18 | 6 | 3 | 18 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 34 | 2 | 47 |
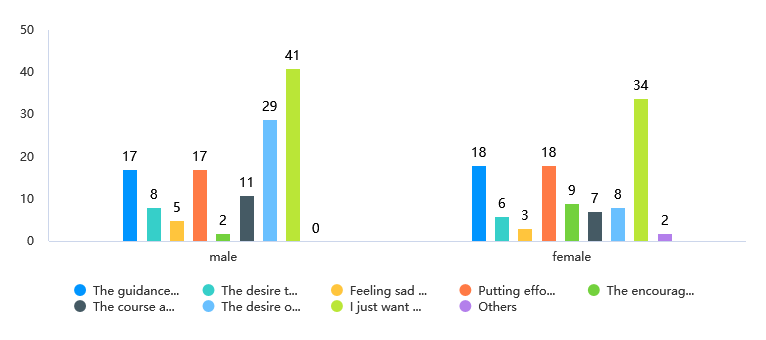
Figure 2: Gender and the factors that affect self-goal setting.
Statistics show that half of the male participants chose "the desire for money" as one of the most important factors that affect them when setting goals. In contrast, only 17.02% of the female participants chose this option. It implies that males generally carry more of an economic burden than females in modern society. Moreover, 14.89% of the female participants chose the option "the encouragement of an idol or celebrity". Only 3.77% of the male participants chose this option (see chart 1 and fig. 2), which implies that women are more likely to be affected by external factors when making decisions [4].
Similarly, different stages of age show divergence in the survey. Adolescents have a relatively scattered option, with similar proportions chosen in each section. In comparison, college students unanimously focus on their own desires rather than the affections of others. Office workers show more realistic characteristics. The top 3 factors on their list are: "my own willingness," "the desire for money," and "the guidance of parents or peers." The elderly tend to make more rational decisions based on their past experiences. They believe the guidance of parents or peers, working together with friends, and their own willingness are the most important factors (see fig.3). Through the data analysis, it can be revealed that as people age, they tend to make more rational and realistic decisions when setting goals.
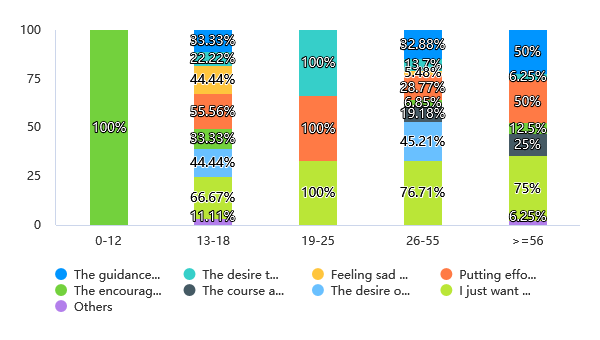
Figure 3: Age and the factors that affect self-goal setting.
4. Increasing the Chance of Achieving Goals through Internal and External Factors
In order to increase the chances of achieving the goals that people have set, it is better to downgrade them to the ground level, which means to narrow the gap between the goal and action. Breaking the macro goals into smaller pieces can reduce the mental stress as well as contribute to the overall progress [5]. Goals can be divided into personal goals, such as marriage, children, home, etc., and professional goals that are related to the professional aspect of life, such as job, career, and so on. Back to the same example as stated before, if young entrepreneurs want to earn money by starting a business themselves, they can set some specific goals like reading four books per month about how to start a business or finishing two programs in six months [5]. Unfortunately, not everyone has the ability to downgrade their goals and persistently push forward. Based on the data from the survey, only 43% of the participants chose "yes" when asked if they could always detail their goals. 34% said they "do not believe they are capable of making consistent efforts" (see fig. 4).
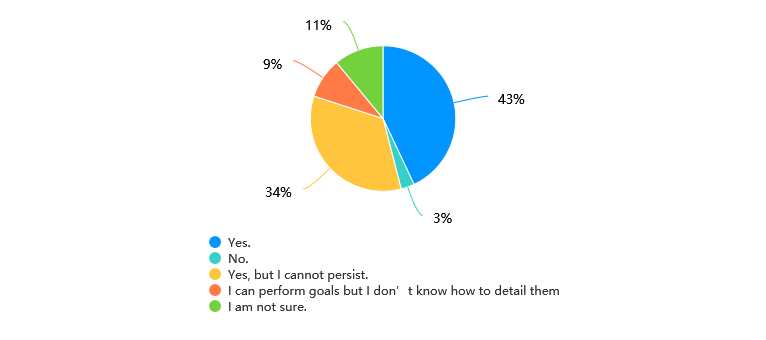
Figure 4: Answers of the question “Do you think that you can detail your goals and perform them?”
Once the detailed goal is clear, performing comes next. Another significant topic is how people can take this plan into action. In the survey, when asked about the motivation to achieve one’s goal, the inner factors again got more attention than external factors. More than half of the participants chose their self-interest as the most important factor that pushed them to persist. Among those external factors, 34% of the participants believed the reward for achieving that goal was another important motivator, but only 2% of them chose punishment as a main influencer (see fig.5). Inner factors play a more significant role in people’s actions [6].
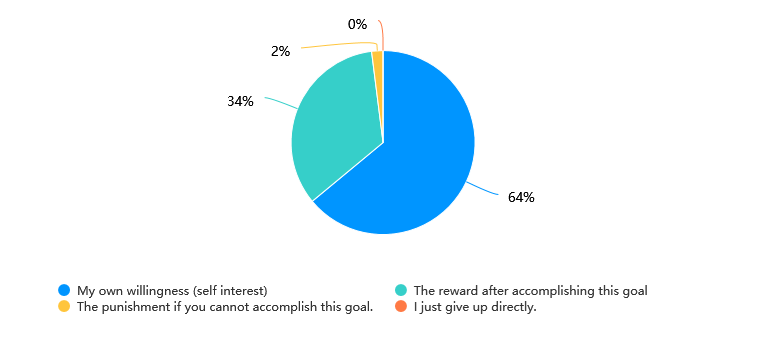
Figure5: factors can push you to accomplish the goals the most.
Among the external factors that affect the performance of goals, it seems like rewards may be one of the best motivators to drive the goal's accomplishment. In fact, to make sure the external factors are playing their roles, they have to be based on a person’s own willingness or desire. Sometimes, whether reward or punishment, may have some negative effect if the goal is against a person’s willingness [6]. It's true that rewards can motivate people and reinforce an action by providing a treat or removing an unfavorable event, and punishment can reduce the number of actions by presenting an unfavorable event or removing a favorable event". Rewarding for positive behavior can be tricky because you don’t want to create a generation that thrives only on rewards in order to behave well, and frequently rewarding a misbehaving person to raise his/her morale is also not fair to those who show good behavior without the stimulus of a reward" [4]. This contradicts the common belief that rewarding behavior is the best way to learn and achieve goals.
5. Conclusion
The survey shows a more clear idea when considering the factors that affect goal setting and achieving. Inner factors, mainly a person's inner desire, affect far more than external factors such as parental guidance, reward, or punishment. Unfortunately, there are still some weaknesses in this scientific survey. For instance, the participants are chosen randomly online, but one shortage is that there cannot be an equal number of participants in every age group, so the data result cannot fully represent the group that they’re in. Another shortage is that the survey only includes participants from China, mostly the east coast cities. As a result, the survey's findings cannot represent all people.
References
[1]. Adam Steel, Edward H. Silson, Charlotte J. Stagg & Chris I. Baker. “The impact of reward and punishment on skill learning depends on task demands”. Scientific Reports volume 6 Article number: 36056 (2016). https://www.nature.com/articles/srep36056/.
[2]. Edwin A. Locke and Gary P. Latham. “New Directions in Goal-Setting Theory.” Current Directions in Psychological Science. Vol.15, No. 5(Oct., 2006). JSTOR. www.jstor.org/stable/20183128.
[3]. Miriam Erez and Frederick H. Kanfer. “The Role of Goal Acceptance in Goal Setting and Task Performance”. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 8, No. 3(July., 1983) JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/257834.
[4]. Psychologenie. “Reward Vs. Punishment: Which One is More Effective? Let’s Discuss ”. https://psychologenie.com/reward-vs-punishment-which-one-is-more-effective.
[5]. Vina Silviani Marinda, and Agatha Rinta Suhardi. “Effects of Positive, Negative, and Punishment Reinforcement on Motivation at College's Students in Indonesia”. November 2021. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation 24(7):7211-7219. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356554702_Effects_of_Positive_Negative_andPunishment_Reinforcement_on_Motivation_at_College%27s_Students_in_Indonesia.
[6]. Gerard H. Seijts, Gary P. Latham, Kevin Tasa and Brandon W. Latham. “Goal Setting and Goal Orientation: an Integration of Two Different yet Related Literatures”. The Academy of Management Journal. Vol. 47, No.2 (Apr., 2004) JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/20159574.
Cite this article
Chen,S. (2023). The Factors That Affect Goals Setting and Performing. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,6,189-194.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the International Conference on Interdisciplinary Humanities and Communication Studies (ICIHCS 2022), Part 5
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Adam Steel, Edward H. Silson, Charlotte J. Stagg & Chris I. Baker. “The impact of reward and punishment on skill learning depends on task demands”. Scientific Reports volume 6 Article number: 36056 (2016). https://www.nature.com/articles/srep36056/.
[2]. Edwin A. Locke and Gary P. Latham. “New Directions in Goal-Setting Theory.” Current Directions in Psychological Science. Vol.15, No. 5(Oct., 2006). JSTOR. www.jstor.org/stable/20183128.
[3]. Miriam Erez and Frederick H. Kanfer. “The Role of Goal Acceptance in Goal Setting and Task Performance”. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 8, No. 3(July., 1983) JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/257834.
[4]. Psychologenie. “Reward Vs. Punishment: Which One is More Effective? Let’s Discuss ”. https://psychologenie.com/reward-vs-punishment-which-one-is-more-effective.
[5]. Vina Silviani Marinda, and Agatha Rinta Suhardi. “Effects of Positive, Negative, and Punishment Reinforcement on Motivation at College's Students in Indonesia”. November 2021. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation 24(7):7211-7219. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356554702_Effects_of_Positive_Negative_andPunishment_Reinforcement_on_Motivation_at_College%27s_Students_in_Indonesia.
[6]. Gerard H. Seijts, Gary P. Latham, Kevin Tasa and Brandon W. Latham. “Goal Setting and Goal Orientation: an Integration of Two Different yet Related Literatures”. The Academy of Management Journal. Vol. 47, No.2 (Apr., 2004) JSTOR, www.jstor.org/stable/20159574.









