1. Introduction
Currently, the booming rise of artificial intelligence(AI) technology is infiltrating and reshaping multiple industry sectors at an unprecedented speed, greatly affecting human life and improving efficiency in many fields, and the education sector is no exception [1]. This revolutionary force, extending from basic computer technology to intelligent network platforms, highly interactive chatbots, and even complex humanoid robot systems, profoundly changes the teaching paradigm, learning ecology, and management mode of schools [2]. Its widespread application not only substantially enriches the educational experience, but also significantly improves the overall quality of education and accessibility of resources. It fosters a learning environment that is tailored to individual needs, efficient in operation, and characterized by dynamic interaction for students [3]. With the ongoing development of AI, it is expected to have a considerable bearing on the roles of students, teachers, schools, and educational leaders.
As AI becomes increasingly common daily, it influences the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects of human functioning [4]. Current research shows that the trend of college students using AI tools is increasing. A study encompassing over 6,300 university students in Germany indicates that approximately two-thirds of the participants have utilized or are currently utilizing AI assisted tools in their academic pursuits. Specifically, nearly 50% of the students surveyed explicitly identified ChatGPT or GPT-4 as their preferred AI tools. Notably, students majoring in engineering, mathematics, and natural sciences are the most frequent adopters of AI-based learning tools. [5]. Similarly, at Sampoerna University in Indonesia, AI tools have become a commonly used tool for academic support, with grammar checking being the most common application [6]. Efficacy is significantly affected after the use of AI, and the integration of AI affects individual initiative, employee performance, and system acceptability [7]. In the field of education, AI literacy may affect teachers' self-efficacy beliefs, thereby potentially impacting their performance and student outcomes [8]. For students, their perception of the difficulty of AI will affect their sense of efficacy in AI courses [9]. In the field of writing, generative artificial intelligence tools have the potential to bolster authors' perceived competence by offering support, creative stimulation, and tailored advice [10]. Undoubtedly, the impact of AI may have exceeded the original scope of understanding. Currently, most academic research in this field focuses on qualitative analysis, theoretical construction, and phenomenon interpretation. More quantitative research is needed to solidify the theoretical foundation and verify the universality and accuracy of previous findings. Therefore, promoting the deepening of AI research towards quantitative analysis and systematically exploring the complex relationships and causal mechanisms between many dependent variables is of great value.
Anxiety, as a profound psychological response, significantly affects the public's psychological state and constitutes an important and far-reaching dimension of the multidimensional psychological impact brought about by the introduction of AI technology [11].Currently, two main theories have been proposed to explore the influence of AI on college students' anxiety during their educational pursuits.
On the one hand, one viewpoint suggests that AI assisted learning has shown promising prospects in reducing anxiety and enhancing the educational experience of college students. AI models, as "mentors" and "math partners," can provide personalized support and step-by-step explanations, helping to alleviate math anxiety and enhance confidence [12,13]. In language learning, teaching based on AI chatbots has been found to reduce anxiety in English writing classes by providing instant feedback and enabling a personalized learning pace for students [14]. This AI provides customized content and timely feedback in a way that empowers students and promotes their self-regulation of learning patterns and growth mindset during the learning process [15,16]. AI mainly relies on big data information assistance and intelligent personalized assistance in learning, helping students to master academic knowledge more efficiently and reduce anxiety caused by academic difficulty.
On the other hand, a widely held view posits that the advent of AI in educational contexts has generated a dual-edged sword for college students, presenting them with new opportunities and challenges, as well as bringing new forms of anxiety. Johnson and Verdicchio identified three factors that contribute to "AI anxiety": a focus on AI programs without a human background, confusion about autonomy, and a misunderstanding of technological development [17]. In addition, this anxiety also stems from various factors, including concerns about job loss, social and technological illiteracy, and concerns about the ramifications of AI on societal interactions [18]. The misunderstanding of the nature and potential of AI exacerbates this concern, which is often triggered by alarmist rhetoric and confusion about technological autonomy.
This study proposes a core viewpoint: the impact of AI intervention on individual anxiety is not simplified as a single enhancement or attenuation effect. On the contrary, this psychological phenomenon exhibits a high degree of complexity and dynamism, and its trajectory is deeply influenced by multiple factors such as students' specific motivations and duration for using AI. In exploring the impact of the use of AI on human psychological factors, it is necessary to further quantify experiments based on previous research, and explore the complex psychological processes involved.
In the academic process of college students, research has consistently shown that anxiety emotions will affect academic self-efficacy. Academic self-efficacy, as a belief in students' ability to complete academic tasks, is positively associated with academic achievements and is an effective indicator for predicting students' academic performance [19-21].
This study will focus on exploring the impact of the use of AI on college students' academic self-efficacy, and introduce anxiety emotions to explore its mediating role, in order to explore the internal mechanism of the impact of AI on college students' academic psychology in the college student population, and contribute new theoretical perspectives and empirical evidence to the existing research on the psychological impact mechanism of AI. In terms of research methods, this study will strictly follow the standardized scientific experiment paradigm, and use the fully validated scale with good reliability and validity as the research tool to ensure the rigor of the experimental process and the effectiveness of the results.
2. Method
2.1. Participants
After the first two weeks of the new semester, questionnaires were distributed to college students from different majors through the online platform, and selection of participants was based on the principle of voluntary participation. In the end, 437 questionnaires were actually collected. After all questionnaires are collected, the work of removing invalid questionnaires is carried out, excluding questionnaires with long or short response time, almost identical response items, and highly regular response items. Finally, 368 valid questionnaires were obtained. The age range of participants is between 17 and 28, with an average age of 19.99 years (standard deviation=1.59), including 211 males, accounting for 57.34%; 157 women, accounting for 42.66%; 338 individuals hold a bachelor's degree, accounting for 91.85%; 30 people have a postgraduate degree or above, accounting for 8.15%.
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.2.1. AI anxiety questionnaire
This study used the AI Anxiety Questionnaire to measure the anxiety caused by college students' use of AI. The scale was developed by Wang, and referenced and reviewed multiple relevant literature, including studies on anxiety caused by the use of AI, robot anxiety, and computer anxiety. The scale consists of 21 questions and four dimensions, measuring learning, career replacement, socio technical blind spots, and AI configuration. The internal consistency coefficients of each dimension are 0.974, 0.917, 0.917, and 0.961, respectively. The overall internal consistency coefficient of the scale is 0.964, indicating good internal consistency. There is a significant correlation between the four dimensions, indicating the existence of a common AIA structure. The scale uses a seven-point Likert scale for scoring, with higher scores indicating stronger feelings of AI anxiety. The reliability and validity of the scale have been verified, with good reliability and validity, and a standard correlation coefficient of 0.864.
2.2.2. Academic self-efficacy questionnaire
This study used the Academic Self Efficacy Questionnaire, which was developed by Liang Yusong and Zhou Zongkui from Central China Normal University. They referred to the articles of Pintrich and De Groot and revised the relevant dimensions in the table for this questionnaire. This scale consists of two parts, measuring self-efficacy in learning ability and self-efficacy in learning behavior. By measuring learning efficacy through two dimensions, students' self-efficacy can be comprehensively and effectively understood. Each dimension has 11 test questions, for a total of 22 test questions (Cronbach's alpha=0.89). Using a five-point Likert scale for scoring, the higher the score, the higher the sense of efficacy. The questionnaire has high reliability and validity. Two dimensions can explain a total variation of 85.6%, with coefficients of 0.820 and 0.752, respectively. The internal consistency coefficient in the questionnaire is 0.92. Throughout many studies on academic self-efficacy, many have adopted this questionnaire, ensuring its wide applicability and consistency. In the process of writing, the author strives to conform to the learning characteristics of college students, which is consistent with the research object of this study.
3. Results
Common method deviation test: using Harman single factor test method, the results show that there are 7 factors with eigenvalue greater than 1, the maximum eigenvalue is 16.3, the maximum interpretation percentage is 33.3%, which is lower than the critical standard of 40%.There are no factors with excessive explanatory power, indicating that there is no serious common method deviation problem.
Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis: the results of bivariate person test are shown in the Table 1. Age and subject categories are significantly correlated with AI use anxiety and academic self-efficacy, and these variables will be used as control variables in subsequent regression analysis;Gender and education are not significantly correlated with the three variables.
Table 1: Mean, standard deviation and correlation of variables.
Variable |
M |
SD |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
1.Gender |
1.43 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.Age |
19.99 |
1.59 |
-0.15** |
|
|
|
|
|
3.Qualifications |
4.02 |
0.29 |
-0.01 |
0.51** |
|
|
|
|
4.Discipline |
3.66 |
2.95 |
-0.04 |
0.01 |
-0.08 |
|
|
|
5.AI use |
21.62 |
4.55 |
-0.09 |
-0.04 |
0.01 |
-0.09 |
|
|
6.AI anxiety |
77.28 |
31.51 |
-0.02 |
-0.14** |
-0.09 |
0.05 |
0.04 |
|
7.Academic self-efficacy |
77.92 |
15.18 |
-0.02 |
-0.04 |
0.01 |
-0.12* |
0.40** |
0.17** |
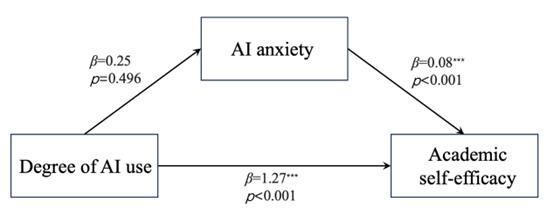
Figure 1: The mediating effect of AI anxiety on the degree of AI use and academic self-efficacy
In order to explore the internal mechanism of the influence of AI use on academic self-efficacy, anxiety was introduced into the structural equation model as a mediator. The mediating effect was tested by using model4 in SPSS macro process, and the mediating effect of anxiety between AI use and academic self-efficacy was verified and analyzed by using the bootstrap method provided by Hayes. The path coefficient of AI anxiety between AI use and academic self-efficacy is shown in the Figure1.
According to Table 2, the mediation model had a total effect of 1.29 (p<0.001), a direct effect of 1.27 (p<0.001), and a path profile effect of 0.02 (95% CI = [-0.03, 0.10]) with AI anxiety as the mediating variable. The upper and lower bounds of the bootstrap 95% confidence interval of AI use(95%CI = [0.96,1.58]) and AI anxiety(95%CI = [0.03,0.12]) on academic self-efficacy do not contain 0, indicating that AI use and AI anxiety have a direct effect on College Students' academic self-efficacy. The upper and lower bounds of the bootstrap 95% confidence interval of AI use on AI anxiety path include 0, indicating that AI use has no effect on AI anxiety.
Table 2: Breakdown of total, direct and mediated effects.
|
Effect size |
se |
LLCI |
ULCI |
Magnitude of Effect |
Total effect |
1.29 |
0.16 |
0.98 |
1.61 |
|
Direct effect |
1.27 |
0.16 |
0.96 |
1.58 |
98.44% |
Mediation effect |
0.02 |
0.01 |
-0.03 |
0.10 |
1.55% |
4. Discussion
The introduction of AI into the field of education will have an impact on students' psychological factors. This investigation examines the influence of AI utilization on the academic self-efficacy of university students via a survey questionnaire, providing a powerful empirical supplement to its integration into society. To some extent, it makes up for the shortcomings of existing research, and also provides necessary reference data for AI utilization in universities. The research results mainly reveal two points: 1. the degree of AI use and AI anxiety positively affect students' academic self-efficacy; 2. AI anxiety does not play a mediating role between AI use and academic self-efficacy.
In alignment with prior scholarly findings, the deployment of AI is anticipated to exert a beneficial influence on students' psychological well-being, which is consistent with the results of this study [22]. However, some studies posit that a detrimental effect of artificial intelligence on students' psychology, which is contrary to the conclusion of this study [23]. Analysis shows that there are two main reasons:
First of all, AI brings personalized learning experience to students, thereby enhancing students' academic productivity and engagement. By leveraging AI to scrutinize students' educational data, it becomes feasible to deliver tailored learning content and pathways, and give timely feedback [24]. This customized learning method helps students master knowledge and skills faster, so as to enhance students' academic self-efficacy. AI technology is capable of helping students find curricular resources more conveniently and quickly, and furthermore,it aids them in completing learning tasks more efficiently. When students can master more knowledge in a shorter time, their academic self-efficacy will be significantly improved. Secondly, AI currently plays an auxiliary tool rather than a substitute role within the domain of education [25]. If the introduction of AI mainly leads to the replacement of human jobs, this is likely to trigger a series of negative emotions [26]. On the other hand, if AI is carefully designed and applied as a “superior assistant” to enhance human capabilities and work efficiency, it is much less likely to trigger anxiety, so in the process of using AI, it has little impact on students' negative psychology [27].
In the conclusion of the study, it is found that the mediating model of AI anxiety as a mediator affecting AI use on academic self-efficacy is not tenable. Specifically, the impact of AI use on AI anxiety is not significant. Analyzing the reasons, the use of AI has a complex path for the generation of AI anxiety, and there may be potential variables that affect this path insignificantly. Research has shown that technology readiness inhibitors are positively correlated with a variety of AI anxiety factors and that misconceptions about the nature and potential of AI contribute to anxiety [17,18], which can be potential variables. Meanwhile, the impact on AI anxiety is not only its degree of use, but also different individuals' cognition and understanding of AI technology, which may lead to different perceptions of the impact of AI technology. Some people may view their potential risks more rationally due to their in-depth understanding of AI technology, while others may have excessive concerns due to lack of understanding. In addition, the adaptability and coping ability of different individuals in the face of new technologies are also different. Some individuals with coping abilities may be able to rapidly adjust to the technical advancements introduced by AI technology, consequently reducing their anxiety. On the contrary, individuals with weak adaptability or conservatives may be more likely to feel anxiety.
At the same time, the study found that both the degree of AI use and AI anxiety contributed positively to academic self-efficacy. The previous research believed that anxiety would cause a decline in academic self-efficacy [19-21]. The reason why this study is contrary to previous studies is that this study uses the AI anxiety scale rather than the general anxiety scale, which is different from previous studies, so it may lead to different results. Secondly, combined with the above analysis of AI anxiety path, it may be that individuals are prone to cognitive bias in the face of uncertainty [28]. When individuals have limited knowledge or misconceptions about AI technology, they are prone to cognitive bias, which further tends to lead to high anxiety measures. Finally, college students pay particular attention to their competitive position in society,which may be even more so in the era of AI [29]. When individuals feel the competitive pressure from AI technology, they may evaluate their competitiveness by comparing their academic performance. This comparative psychology may cause them to feel anxious, but it may also stimulate their academic drive and academic self-efficacy.
The limitations of this research can be outlined as follows: first, this study adopts a cross-sectional design, only gathering data at a singular time period, thereby precluding the observation of the variables' temporal dynamics. Future research can adopt longitudinal design and collect data for many times to explore the development, change and causal relationship among AI tool use, anxiety and academic self-efficacy. Second, the focus of this investigation is solely on the impact of AI engagement on academic self-efficacy. In fact, college students' use of AI to solve different types of problems, some may only be used for simple translation, while others are used for copywriting editing. Different use intentions may also affect academic self-efficacy. This study does not make an experimental analysis of the types of problems college students use AI to solve and their intention to use AI. Future research can further explore the self-efficacy of college students' use of AI in different periods.
5. Conclusion
Through the research, this paper found that with the increase of college students' use of AI assisted learning in the academic process, their academic self-efficacy also increased significantly. AI anxiety did not play a mediating role in its impact path, but also significantly affected college student’s academic self-efficacy. Therefore, it is suggested that college students can appropriately use AI to assist their studies during the course of study to boost their perception of skill development and self-belief in the learning process. AI in the learning process of college students may help college students alleviate the anxiety caused by the academic process by providing information, auxiliary computing and other ways, so as to enhance students' academic self-efficacy. Certain research in the field suggests that AI engagement might alleviate anxiety and enhance students' confidence, potentially through cultivating self-regulated learning mode and growth mentality. However, the specific reflection mechanism between the use of AI and anxiety remains to be studied and explained.
This study provides the quantitative results of college students' psychological changes after using AI, confirms the view that the use of AI shows a good prospect for students' academic development, and provides a practical basis for exploring the use strategies of AI within the domain of education, which is conducive to formulating more reasonable AI assisted teaching strategies in university education. However, this study did not consider more potential control variables. The influence mechanism of the use of AI on college students' psychological factors is complex. Future research can further tap more potential variables, build a more comprehensive and in-depth theoretical model, and provide a more solid theoretical basis and practical guidance for optimizing the application of AI in the field of education.
References
[1]. Aggarwal, N. (2019). Study of AI and its Applications. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology.
[2]. Dhyani, S., Ahmad, I., Gupta, A., Singh, S., Pathak, A. K., & Yamsani, N. (2024, January). Role of Artifical Intelligence in Education Sector. In 2024 IEEE 1st Karachi Section Humanitarian Technology Conference (KHI-HTC) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
[3]. Begum, I. U. (2024). Role of AI in Higher Education-An Empirical Investigation. International Research Journal on Advanced Engineering and Management (IRJAEM), 2(03), 49-53.
[4]. Ojha, A.K. (2024). Psychological Impact of AI: Understanding Human Responses and Adaptations. Feb-Mar 2024.
[5]. Von Garrel, J., & Mayer, J. (2023). AI in studies—use of ChatGPT and AI-based tools among students in Germany. humanities and social sciences communications, 10(1), 1-9.
[6]. Rahim, N. A., Hanum, A. Z. A., Bhakti, M. A. C., & Wandy, W. (2023). AI Tools in Higher Education Students Usage Analysis–Case Study: Sampoerna University. Jurnal Teknologi, 16(2), 137-145.
[7]. Pagliari, M., Chambon, V., & Berberian, B. (2022). What is new with AI? Human–agent interactions through the lens of social agency. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 954444.
[8]. Oran, B. B. (2023). Correlation between AI in education and teacher self-efficacy beliefs: a review. RumeliDE Dil ve Edebiyat Araştırmaları Dergisi, (34), 1354-1365.
[9]. Straub, J., Kerlin, S., & Kim, E. (2017, May). Analysis of student characteristics and feeling of efficacy in a first undergraduate AI course. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT) (pp. 010-015). IEEE.
[10]. Washington, J. (2023). The Impact of Generative AI on Writer's Self-Efficacy: A Critical Literature Review. Available at SSRN 4538043.
[11]. Rodríguez, C. G. (2024). Anxiety in the face of AI. Between pragmatic fears and uncanny terrors/Ansiedad ante la Inteligencia Artificial. Entre temores pragmáticos y terrores ominosos. Studies in Psychology, 45(1), 123-144.
[12]. Inoferio, H. V., Espartero, M., Asiri, M., Damin, M., & Chavez, J. V. (2024). Coping with math anxiety and lack of confidence through AI-assisted Learning. Environment and Social Psychology, 9(5).
[13]. Toribio, N. F. (2023). Analysis Of Chatgpt And Other AI’s Ability To Reduce Anxiety Of Science-Oriented Learners In Academic Engagements. Journal of Namibian Studies: History Politics Culture, 33, 5320-5337.
[14]. Hawanti, S., & Zubaydulloevna, K. M. (2023). AI chatbot-based learning: alleviating students' anxiety in english writing classroom. Bulletin of Social Informatics Theory and Application, 7(2), 182-192.
[15]. Li, H. H., Liao, Y. H., & Wu, Y. T. (2019, August). AI to assist E-Learning. In 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE) (pp. 653-654). IEEE.
[16]. Edelblut, P. (2020). Realizing the promise of AI-powered, adaptive, automated, instant feedback on writing for students in grade 3-8 with an IEP. In Adaptive Instructional Systems: Second International Conference, AIS 2020, Held as Part of the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark, July 19–24, 2020, Proceedings 22 (pp. 283-292). Springer International Publishing.
[17]. Johnson, D. G., & Verdicchio, M. (2017). AI anxiety. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(9), 2267-2270.
[18]. Lemay, D. J., Basnet, R. B., & Doleck, T. (2020). Fearing the robot apocalypse: Correlates of AI anxiety.
[19]. Chairiyati, L. R. (2013). Hubungan antara Self-Efficacy akademik dan konsep diri akademik dengan prestasi akademik. Humaniora, 4(2), 1125-1133.
[20]. Basith, A., Syahputra, A., & Ichwanto, M. A. (2020). Academic self-efficacy as predictor of academic achievement. JPI (Jurnal Pendidikan Indonesia), 9(1), 163-170.
[21]. Brennan, M. B. (2015). Exploring a complex model of student engagement in middle school: Academic self-efficacy beliefs and achievement.
[22]. Shahzad, M. F., Xu, S., Lim, W. M., Yang, X., & Khan, Q. R. (2024). AI and social media on academic performance and mental well-being: Student perceptions of positive impact in the age of smart learning. Heliyon, 10(8).
[23]. Crawford, J., Allen, K. A., Pani, B., & Cowling, M. (2024). When AI substitutes humans in higher education: the cost of loneliness, student success, and retention. Studies in Higher Education, 49(5), 883-897.
[24]. Kaledio, P., Robert, A., & Frank, L. (2024). The Impact of AI on Students' Learning Experience. Available at SSRN 4716747.
[25]. Lampou, R. (2023). The integration of AI in education: Opportunities and challenges. Review of AI in Education, 4, e15-e15.
[26]. Prahl, A., & Van Swol, L. M. (2021). Out with the humans, in with the machines?: investigating the behavioral and psychological effects of replacing human advisors with a machine. Human-Machine Communication, 2, 209-234.
[27]. Shneiderman, B. (2022). Intelligent Agents and Supertools. Human-Centered AI.
[28]. Momeni, F., & Shibaei, A. (2022). Decision-making under Uncertainty: A Cognitive Approach. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Cognition, 1(1), 101-107.
[29]. Mulvey, B., & Wright, E. (2022). Global and local possible selves: Differentiated strategies for positional competition among Chinese university students. British Educational Research Journal, 48(5), 841-858.
Cite this article
Zhou,J. (2024). The Impact of AI Use on College Students' Academic Self-efficacy: Exploring the Mediating Role of Anxiety. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,75,139-146.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Global Politics and Socio-Humanities
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Aggarwal, N. (2019). Study of AI and its Applications. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology.
[2]. Dhyani, S., Ahmad, I., Gupta, A., Singh, S., Pathak, A. K., & Yamsani, N. (2024, January). Role of Artifical Intelligence in Education Sector. In 2024 IEEE 1st Karachi Section Humanitarian Technology Conference (KHI-HTC) (pp. 1-9). IEEE.
[3]. Begum, I. U. (2024). Role of AI in Higher Education-An Empirical Investigation. International Research Journal on Advanced Engineering and Management (IRJAEM), 2(03), 49-53.
[4]. Ojha, A.K. (2024). Psychological Impact of AI: Understanding Human Responses and Adaptations. Feb-Mar 2024.
[5]. Von Garrel, J., & Mayer, J. (2023). AI in studies—use of ChatGPT and AI-based tools among students in Germany. humanities and social sciences communications, 10(1), 1-9.
[6]. Rahim, N. A., Hanum, A. Z. A., Bhakti, M. A. C., & Wandy, W. (2023). AI Tools in Higher Education Students Usage Analysis–Case Study: Sampoerna University. Jurnal Teknologi, 16(2), 137-145.
[7]. Pagliari, M., Chambon, V., & Berberian, B. (2022). What is new with AI? Human–agent interactions through the lens of social agency. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 954444.
[8]. Oran, B. B. (2023). Correlation between AI in education and teacher self-efficacy beliefs: a review. RumeliDE Dil ve Edebiyat Araştırmaları Dergisi, (34), 1354-1365.
[9]. Straub, J., Kerlin, S., & Kim, E. (2017, May). Analysis of student characteristics and feeling of efficacy in a first undergraduate AI course. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Electro Information Technology (EIT) (pp. 010-015). IEEE.
[10]. Washington, J. (2023). The Impact of Generative AI on Writer's Self-Efficacy: A Critical Literature Review. Available at SSRN 4538043.
[11]. Rodríguez, C. G. (2024). Anxiety in the face of AI. Between pragmatic fears and uncanny terrors/Ansiedad ante la Inteligencia Artificial. Entre temores pragmáticos y terrores ominosos. Studies in Psychology, 45(1), 123-144.
[12]. Inoferio, H. V., Espartero, M., Asiri, M., Damin, M., & Chavez, J. V. (2024). Coping with math anxiety and lack of confidence through AI-assisted Learning. Environment and Social Psychology, 9(5).
[13]. Toribio, N. F. (2023). Analysis Of Chatgpt And Other AI’s Ability To Reduce Anxiety Of Science-Oriented Learners In Academic Engagements. Journal of Namibian Studies: History Politics Culture, 33, 5320-5337.
[14]. Hawanti, S., & Zubaydulloevna, K. M. (2023). AI chatbot-based learning: alleviating students' anxiety in english writing classroom. Bulletin of Social Informatics Theory and Application, 7(2), 182-192.
[15]. Li, H. H., Liao, Y. H., & Wu, Y. T. (2019, August). AI to assist E-Learning. In 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE) (pp. 653-654). IEEE.
[16]. Edelblut, P. (2020). Realizing the promise of AI-powered, adaptive, automated, instant feedback on writing for students in grade 3-8 with an IEP. In Adaptive Instructional Systems: Second International Conference, AIS 2020, Held as Part of the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark, July 19–24, 2020, Proceedings 22 (pp. 283-292). Springer International Publishing.
[17]. Johnson, D. G., & Verdicchio, M. (2017). AI anxiety. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 68(9), 2267-2270.
[18]. Lemay, D. J., Basnet, R. B., & Doleck, T. (2020). Fearing the robot apocalypse: Correlates of AI anxiety.
[19]. Chairiyati, L. R. (2013). Hubungan antara Self-Efficacy akademik dan konsep diri akademik dengan prestasi akademik. Humaniora, 4(2), 1125-1133.
[20]. Basith, A., Syahputra, A., & Ichwanto, M. A. (2020). Academic self-efficacy as predictor of academic achievement. JPI (Jurnal Pendidikan Indonesia), 9(1), 163-170.
[21]. Brennan, M. B. (2015). Exploring a complex model of student engagement in middle school: Academic self-efficacy beliefs and achievement.
[22]. Shahzad, M. F., Xu, S., Lim, W. M., Yang, X., & Khan, Q. R. (2024). AI and social media on academic performance and mental well-being: Student perceptions of positive impact in the age of smart learning. Heliyon, 10(8).
[23]. Crawford, J., Allen, K. A., Pani, B., & Cowling, M. (2024). When AI substitutes humans in higher education: the cost of loneliness, student success, and retention. Studies in Higher Education, 49(5), 883-897.
[24]. Kaledio, P., Robert, A., & Frank, L. (2024). The Impact of AI on Students' Learning Experience. Available at SSRN 4716747.
[25]. Lampou, R. (2023). The integration of AI in education: Opportunities and challenges. Review of AI in Education, 4, e15-e15.
[26]. Prahl, A., & Van Swol, L. M. (2021). Out with the humans, in with the machines?: investigating the behavioral and psychological effects of replacing human advisors with a machine. Human-Machine Communication, 2, 209-234.
[27]. Shneiderman, B. (2022). Intelligent Agents and Supertools. Human-Centered AI.
[28]. Momeni, F., & Shibaei, A. (2022). Decision-making under Uncertainty: A Cognitive Approach. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Cognition, 1(1), 101-107.
[29]. Mulvey, B., & Wright, E. (2022). Global and local possible selves: Differentiated strategies for positional competition among Chinese university students. British Educational Research Journal, 48(5), 841-858.









