1. Introduction
The major topic this paper will focus on is the effect of emotions on sports performances. Emotion plays an important role in human behavior. Broadly, emotions are the affective states of mind people may encounter. Emotions can directly affect how a person thinks, perceives, and acts. For example, people are more likely to act without thinking of consequences when furious. There are numerous pieces of evidence that show emotions have an impact on sports performance. Since it is important in competitions for athletes to improve their performance, this paper will focus on examining the mechanism of how emotions affect sports performance and how to improve it.
Specifically, emotion also plays an important role in sports behavior. Sports have become highly valued daily, and athlete percentages have risen with the admiration of sport. During and before competitions, emotions play a significant part in impacting the athlete’s sports performance. By evaluating specifically emotion’s impact on athletes, sports coaches and teams may understand how to train their athletes for better performances; athletes may know what to avoid and what to encourage during and before games. Also, to avoid potential dangers for athletes working in a high-pressure and extremely competitive environment. This paper will be separated into four sections. The first section will introduce specifically on emotions as it is an abstract and broad topic. The second section discusses how emotions impact sports performance. The third section provides methods to improve sports performance based on previously discussed impacts. Last but not least, the final section will present future directions in the field of sport psychology.
2. Emotion
To begin with, “emotion” needs more clarification than only a state of mind for people. Human beings may experience up to 400 emotions per day with at least 27 distinct emotions.[1] Several emotions may appear at the same time on a person and thus make identification of a person’s emotion difficult. Past studies have categorized emotions using two categories: valence, which informs the positive or negative of an emotion, and activation, which claims the emotion intensity, usually low or high.[2] By using this binary form of categorization, psychologists were able to separate emotions by their characteristics. For example, in Lazarus’s paper, he separated emotion into six specific emotions: Anger, Anxiety, Guilt and shame, Relief, Happiness, and Pride. For each of these emotions, Lazarus analyzes each’s effect on sport performance.[3] In Yuri’s study, he classified emotions into emotional states. He uses five dimensions: form, content/quality, intensity, time and context of emotions.[4] Overall, in this field of study, researchers generally use the binary form of judgement on emotional categories.
In addition, emotional intelligence is also important in affecting sport performances. Emotional intelligence is defined as the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own and others emotions. In day to day life, emotional intelligence is important in helping people learn more about themselves and manage how they respond to others.
3. How does emotion impact sports performance?
After introductions for emotions, the impacts of emotions on sports performance can be explained. Emotions influence subcomponents including perception, attention, memory, decision-making, and judgment.[2] This section would be split into two parts. First, the IZOF model would be introduced. Second, the model would be applied to positive and negative emotions to discuss each’s impact on sports performance. By segmenting this section into these three parts, a clear correlation can be built between emotions and sports performances.
3.1. IZOF Model
Before all else, the most important model in the field of sports psychology is the IZOF model. The Individual Zones of Optimal Functioning(IZOF) model introduces the idea that all athletes have an optimal range of emotional states that maximize their sports performances. According to this model, emotions within this range would benefit athletes, while emotions outside of this range would most likely negatively affect their sports performances. This model have been used for developments of individualized self-regulation programs. [4]
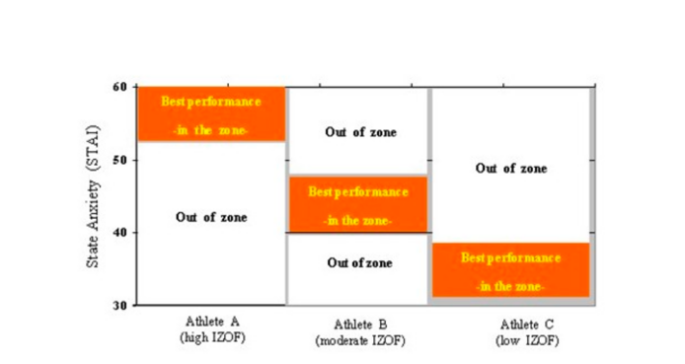
Figure 1: IZOF model in three athletes.
Figure 1 shows the difference in three kinds of athletes depending on their IZOF. Athlete A has high IZOF and will maximize their sports performance under higher state anxiety. Athlete B has a middle level IZOF and will maximize their sports performance under a moderate state of anxiety. Athlete C has a lower IZOF and will maximize their sports performance under lower levels of state anxiety. It will be important for individuals to understand their own IZOF position and avoid cases like being athlete A but experiencing lower or medium level of anxiety.
The IZOF model also shows one of the important concepts when looking at the correlation between emotions and sports performances. The bi-directionality of this study evaluates that pre-event emotions can affect performance and on-going performance affects mid-event and post-event emotions.[5]
3.2. Positive emotions
Furthermore, splitting emotions into binary parts, positive and negative, could more specifically identify the impacts on sports performances. When people experience positive emotions, they broaden their attention, which fosters openness, flexibility, and efficient integration of information.[2] The positive emotions most oftenly play the “positive” role towards sports performances, it is easy to estimate that with higher positive intensity, there would be higher sports performances. The concept “challenge state” is used to explain when a person perceives sufficient resources to meet situational demands, positive emotions are more likely to emerge and reach a benefit to performance. However, there is a limit to which further increases in emotional intensity may even cause a decrease in the level of sports performance. In cases of overly high positive emotions, people may experience the opposite effect on sport performances. To sum up, positive emotions are usually linked with psychological well-being. A controlled amount of such emotions would be beneficial for athletes both of sports performances and of releasing stress and anxiety under high competitive pressure.
3.3. Negative Emotions
On the other hand, negative emotions negatively affect sports performances. In the category of negative emotions, stress and anxiety is especially emphasized. With higher levels of emotional tension(level of uncertainty and level of anxiety), observations of not coordinated distribution of blood and appearance of red and pale spots on face and body in general.[6] Also, performance is affected negatively by emotional struggles that interfere with attention and concentration. Lowering of motivation so that competitors all but give up when they have been doing badly.[3] However, a certain level of negative emotions may be beneficial towards sport performances. For example, anger was associated with enhanced gross muscular peak force performance, while happiness did not. Interestingly, a difference between extroverts and introverts was also shown as that extroverts, when angry, increased more peak force than introverts.[7] For another example, stress can manifest physiological, behavioral and cognitive stressors which affects an individual’s performance which makes it problematic for athletes. Athletes may be unfocused, and it is easier to experience muscle fatigue. Researchers would argue that under circumstances, certain levels of stress can be defined as “challenge”. Challenges can be appraised as increasing athlete’s sports performances.[8] While taking situations like “Challenges” into consideration, it can be argued that certain levels of negative emotions would just as well be beneficial for athletes and does not need complete avoidance.
4. Training to improve sport performance
As the result of all previous concepts and conclusions drawn, the impact it has on the study of sports psychology weighs on the influences it could have on athletes. Methods of training can be introduced to coaches and individuals for their benefit towards performances both in competition and daily practice.
4.1. Emotion Recognition, Monitor and Alteration
Training in regards toward better sports performance should recognize the importance of emotion recognition, monitor and alteration in athletes and coaches.
First of all, to utilize the IZOF model, previously discussed, from an athlete’s perspective, it is necessary for him or her to be aware of his or her optimal and dysfunctional zones, able to distinguish optimal from less than optimal states; and able to enter and stay in the optimal zone during performance. This would help athletes maintain an healthy emotion tension during and before competitions to maximize their sports performance.
Second, specifically in team sports, coaches should lead teams to build an team identity. Group-based emotions lead to adoption of specific action tendencies that improve behavior prediction “above and beyond the relatively weak predictive power of individual-level emotions”.[9]
Last, it is important for athletes to recognize both positive emotions and negative emotions. Mental training strategies should be emphasized by teams, which would optimize precompetitive psychological states and to improve competition performance. For most cases, athletes should be aiming to optimize their positive emotions towards engaging their sport performances and decreasing distracting factors. However, on the other hand, competitive athletes are typically under pressure to meet performance expectations. It is also incumbent upon them to determine the strategies, routines, and thought processes that can aid them in using a pressure situation to enhance their performance.[8]
4.2. Emotion Intelligence
In addition to emotion recognition, monitor and alteration, emotion intelligence is also important towards optimizing sport performances. The basic structure of emotion intelligence is to first recognize emotion, then understand the emotion and lastly manage your emotions. Emotion intelligence relates to emotions, physiological stress responses, successful psychological skill usage and more successful athletic performance.[10] It is assumed that with higher emotion intelligence, athletes may be able to make more accurate action anticipations, which further increases their performance in competitive sports. This assumption leads sport teams to engage in special trainings to enhance emotion intelligence levels and make use of action anticipation skills.
5. Future Directions
After discussing the theories and studies of the relationship between emotion and sports performance, the clear trend of the importance of recognizing the role that emotion plays in sports is shown. The studies mentioned in this paper are usually based on a single sport and the question is whether they could be generalized to all other sports. Future research should emphasize the integration of technologies into individualized training programs for athletes and maintaining a healthy emotional state after competitions. Additionally, some factors that also contribute to the correlation between emotion and sports have not been discussed in this paper and may be important to be future evaluated, such as the cultural and contextual backgrounds of individual athletes in shaping their emotional experiences. The future of research on emotion and sports performance contains impactful innovations and improvements, creating a more interesting but also stabilized sports environment.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, emotions play a pivotal role in shaping athletic performance, as demonstrated through various theoretical and practical insights. The exploration of positive and negative emotional states using the Individual Zones of Optimal Functioning (IZOF) model illustrates that performance is optimized when athletes remain within their unique emotional ranges. While positive emotions generally foster openness and enhance performance, their excessive levels can be counterproductive. Conversely, negative emotions, particularly stress and anxiety, can impair focus and motivation, yet, when strategically harnessed, may act as performance enhancers under “challenge” states.
Practical applications, such as emotional monitoring, team identity building, and mental training, emphasize the need for emotional intelligence and recognition. These strategies are vital for athletes and coaches to maintain optimal performance and manage emotions effectively. The development of emotional intelligence, specifically, underscores its impact on enhancing psychological skills and competitive resilience.
Future directions in this field call for integrating technological advancements in personalized emotional training and addressing cultural contexts to better support athletes in diverse environments. By continuing to research and innovate in emotion-based sports psychology, practitioners can build more comprehensive, adaptive training regimens that maximize athletic potential and well-being.
References
[1]. Bradberry, T., & Antonakis, J. (2015). Is emotional intelligence a good measure of leadership ability. HRMagazine, 60(9), 22-23.
[2]. McCarthy, P. J. (2011). Positive emotion in sport performance: current status and future directions. International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 4(1), 50–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/1750984x.2011.560955
[3]. Lazarus, R. S. (2000). How Emotions Influence Performance in Competitive Sports. The Sport Psychologist, 14(3), 229–252. https://doi.org/10.1123/tsp.14.3.229
[4]. Hanin, Y. L. (2003, January). Performance related emotional states in sport: A qualitative analysis. In Forum qualitative sozialforschung/Forum: qualitative social research (Vol. 4, No. 1).
[5]. Robazza, C., Pellizzari, M., & Hanin, Y. (2004). Emotion self-regulation and athletic performance: An application of the IZOF model. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 5(4), 379–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1469-0292(03)00034-7
[6]. Malakhov, V. A., Puhach, Y. I., Serebrjakov, A. M., Bakanova, A. F., & Druz, V. A. (2014). Influence of the emotional state on behavior in extreme conditions of competitive sports activities. Physical education of students, 18(2), 25-32.
[7]. Woodman, T., Davis, P. A., Hardy, L., Callow, N., Glasscock, I., & Yuill-Proctor, J. (2009). Emotions and sport performance: An exploration of happiness, hope, and anger. Journal of sport and exercise psychology, 31(2), 169-188.
[8]. Frame, M. C., & Reichin, S. (2019). Emotion and sport performance: Stress, anxiety, arousal, and choking.
[9]. Campo, M., Champely, S., Louvet, B., Rosnet, E., Ferrand, C., Pauketat, J. V., & Mackie, D. M. (2019). Group-based emotions: Evidence for emotion-performance relationships in team sports. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 90(1), 54-63.
[10]. Kopp, A., & Jekauc, D. (2018). The influence of emotional intelligence on performance in competitive sports: A meta-analytical investigation. Sports, 6(4), 175.
Cite this article
Ma,C. (2025). How Does Emotion Impact Sports Performances?. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,83,1-5.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Global Politics and Socio-Humanities
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Bradberry, T., & Antonakis, J. (2015). Is emotional intelligence a good measure of leadership ability. HRMagazine, 60(9), 22-23.
[2]. McCarthy, P. J. (2011). Positive emotion in sport performance: current status and future directions. International Review of Sport and Exercise Psychology, 4(1), 50–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/1750984x.2011.560955
[3]. Lazarus, R. S. (2000). How Emotions Influence Performance in Competitive Sports. The Sport Psychologist, 14(3), 229–252. https://doi.org/10.1123/tsp.14.3.229
[4]. Hanin, Y. L. (2003, January). Performance related emotional states in sport: A qualitative analysis. In Forum qualitative sozialforschung/Forum: qualitative social research (Vol. 4, No. 1).
[5]. Robazza, C., Pellizzari, M., & Hanin, Y. (2004). Emotion self-regulation and athletic performance: An application of the IZOF model. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 5(4), 379–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1469-0292(03)00034-7
[6]. Malakhov, V. A., Puhach, Y. I., Serebrjakov, A. M., Bakanova, A. F., & Druz, V. A. (2014). Influence of the emotional state on behavior in extreme conditions of competitive sports activities. Physical education of students, 18(2), 25-32.
[7]. Woodman, T., Davis, P. A., Hardy, L., Callow, N., Glasscock, I., & Yuill-Proctor, J. (2009). Emotions and sport performance: An exploration of happiness, hope, and anger. Journal of sport and exercise psychology, 31(2), 169-188.
[8]. Frame, M. C., & Reichin, S. (2019). Emotion and sport performance: Stress, anxiety, arousal, and choking.
[9]. Campo, M., Champely, S., Louvet, B., Rosnet, E., Ferrand, C., Pauketat, J. V., & Mackie, D. M. (2019). Group-based emotions: Evidence for emotion-performance relationships in team sports. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 90(1), 54-63.
[10]. Kopp, A., & Jekauc, D. (2018). The influence of emotional intelligence on performance in competitive sports: A meta-analytical investigation. Sports, 6(4), 175.









