1.Introduction
In the current era of globalization and informatization, the dynamism of cultural dissemination is increasingly enhanced[1,2].Elite culture, as a special aspect of the social and cultural structure, not only carries historical inheritance and values, but also plays a key role in the process of cultural dissemination. With the advent of modern society, the boundary between elite culture and popular culture is gradually blurred, and the interaction and influence between the two have become more complex[3].Elite culture spreads through education, media, art, and other channels, exerting a profound impact on public awareness, social values, and cultural identity. At the same time, the dynamic nature of cultural dissemination also means the constant changes in cultural forms and dissemination modes[2], which pose new challenges to the status and role of elite culture. Through the study of the cultural transmission of elite culture, we can break the barriers of internal the construction of culture and understand the process of the internal construction and empowerment of culture. Secondly, it can break away from the study of postmodern culture in the cultural circle and pull cultural research back to the track of culture and society research. Furthermore, this research topic holds practical significance and provides guidance for the development of society, particularly in the context of an increasingly globalized and diversified society. So, studying the changing link between elite culture and cultural dissemination is very important for figuring out how cultures change, predicting how they will grow, and making cultural policies. The rest of this paper is structured as follows: the first part is a literature review, the second part is to elaborate on the research methods, and analyze the relevant literature in the past ten years. The third part describes the analysis results and future prospects.
2.The development and characteristic of elite culture
In his article, Jiang Yilin proposed that the reproduction process of elite culture and elite status is transnational, that is, the children of elites who are born and educated in one country may also obtain important positions in other countries in the future. Therefore, other cultures will undoubtedly influence elites motivated by this drive [4].In the era of globalization, elite culture has also become a bridge of cultural transmission. Therefore, elite culture is the product of internationalization. To take a simple example, at the end of the 19th century, British elite culture was dominated by aristocratic activities, including shooting, hunting, equestrian and other activities, which gradually declined over time. In the early 20th century, high culture (such as theater, classical music, literature, opera, and art) began to rise, reaching a peak in the mid-20th century, and then gradually declining. In recent decades, elite cultures have begun to blend high culture with everyday cultural engagement, such as spending time with family, friends, and pets, a model that emphasizes everyday cultural practices [5]. And this cultural symbol of the elite has gradually gone abroad with the United Kingdom and been recognized by the elites of other cultural backgrounds in the world. Cultural symbols such as theatre, literature and classical music are also sought after by other cultures. British culture, especially before the Industrial Revolution, was heavily influenced by elite culture. British scholars such as Arnold and Levison believe that "elite culture" education should be carried out. Then, around the 20th century, there emerged the school of cultural Studies, which opposed elite cultural narratives in favor of mass cultural communication. They also believe that mass culture is influenced by elite culture. Examples include the "critical paradigm" of education and the life value of literature [6]. Therefore, elite culture is an important part of social culture, but also has the characteristics of The Times.
3.Review of the relevant studies
The role of elite culture in cultural communication is a familiar and unfamiliar research direction. Although the academic circles often put forward the theoretical topic of the dynamic connection between elite culture and cultural communication, it is rarely studied independently from the cultural context. But at the same time, elite culture is a very important part of cultural background, so it is very necessary to conduct independent demonstration and analysis.
Via research, we found that the number of articles published in different years is different. Although articles are published almost every year, the number of published articles varies greatly from year to year, and the analysis shows that the academic discourse of elite culture and cultural communication is dynamic and fluid. Learning is not continuous, there are so-called peaks and valleys. This can reveal the dynamic nature of the research topic.
It can be observed that the same article may revolve around multiple keywords as themes for discussion and analysis. For example, in Article 4, which is by Jiang Yilin, cultural dissemination is studied as an important influencing factor in the formation of professional elites [4]. At the same time, there are many articles on elite individuals in different regions, which indicates that many researchers study individuals as carriers of culture. However, due to the limitations of research difficulty, they mostly focus on a certain region and do not mention the flow between different cultures. Only a few researchers have linked elite culture and cultural dissemination for analysis. In addition, there are some other research directions on elite culture, such as political elite research, but their numbers are very small, and will not be elaborated here.
At the same time, the paper's topic seems to correlate with time. Earlier papers, especially those from 2014-2016, tended to explain the connection between elite culture and cultural communication from the perspective of political economy or cultural anthropology. For example, from the perspective of art, religion, academia and even merchandise retailing. In Richard's article, based on the research of Peterson and Simkus, he analyzes the relationship between elite culture and cultural transmission from the perspective of meat retailing. He created a concept called "cultural omnivore”[7].The elite culture is absorbing the culture they previously rejected, such as the consumption of meat in some retail stores, which represents the dynamic flow of culture that is constantly relying on the carrier of elite culture. Later papers, especially those after 2019, prefer to explain the relationship between elite culture and cultural communication from the perspective of communication itself. For example, in An wei's article, from the perspective of localization, the article connects with the popular Chinese TV program called Thirteen Invitations (a TV interview program).As mentioned in the article, elite culture has a special influence on TV programs, especially interview. Audiences prefer to see the ordinary side of the elites, which objectively promotes the spread and flow of culture[8].In addition, we can find that a number of papers are related to communication or cultural communication while studying elite culture, and almost all of them mention key words such as cultural communication or cross-cultural communication. However, they only mentioned the term rather than digging deeply into it, and most of the articles explained the profound influence of elite culture from other perspectives.
Previous studies have adopted many research methods to analyze the effect of elite culture on cultural communication, and provided evidence of the influence of elite culture on cultural communication. According to the articles of Adam Howard and Jane Kenway, due to the understanding of the research topic, the methodology issues are often ignored in the research on elite and elite education, and researchers pay more attention to the application of theoretical resources, while the discussion of research methods and techniques is insufficient .Researchers tend to reuse familiar methodological frameworks and practices, and this repetition limits methodological vision and innovation. At the same time, researchers studying elite and elite educational institutions face challenges at all stages, from entering the field of research to disseminating results[9]. Therefore, this paper employs both quantitative and qualitative analysis methods to examine the data from the article.
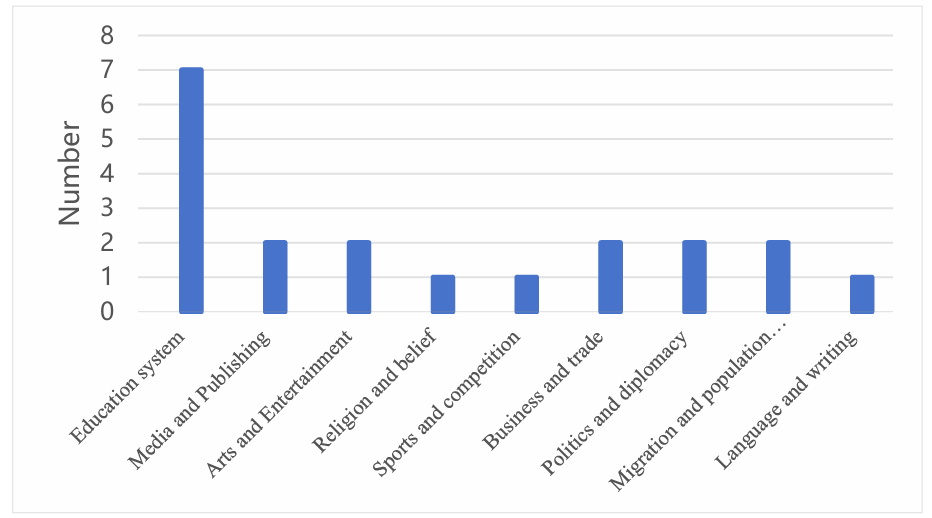
Figure 1: The transmission path of culture
In the study of the transmission path of elite culture, we can see that the biggest transmission path is education. Media, art, business, politics, and population mobility have similar effects on communication, while religion, movement, and language have the weakest effects. But overall, the gap is small. It shows that the communication effect of education is far greater than that of other ways. Elite culture is changing dynamically, and its cultural symbols and cultural carriers are also changing dynamically. The influence of elite culture on cultural transmission is sometimes explicit and sometimes implicit. However, it has always been an important part of cultural content, and this study fills a research gap and summarizes the missing areas of research. Firstly, this paper makes a holistic study of the communication path of elite culture, reveals the relationship between the communication path and elite culture, and its impact on the communication of elite culture.
4.The analysis of dynamic connection between elite culture and cultural dissemination
Elite culture and cultural dissemination are closely related to the development of social culture itself. In the traditional feudal society, due to the appearance of the aristocracy, there came into being the elite cultural view, which advocated the sense of social mission and emphasized that literature must have realistic life value. Elite culture flowed with the aristocratic classes, introducing cultural symbols such as hunting to other cultures. Then during the Industrial Revolution, due to the decline of the aristocracy, critical paradigms emerged in elite culture. At this time, the symbols of elite culture gradually changed to opera and poetry. However, elite culture still influences mass culture through cultural symbols and other factors, and has a profound impact on the spread and exchange of culture [6]. From Arnold and Reeves to Hoggart and Hall, the study of elite culture and cultural communication has been a long-term research direction, but it lacks the analysis and connection within the cultural framework, and the connection of The Times and mobility.
4.1.Research fluidity and dynamics
Traditional elite culture studies and intercultural communication theories mainly discuss how to effectively transmit information between different cultures, reduce cultural misunderstanding and promote mutual understanding between cultures. In the context of the accelerated development of globalization, cross-cultural communication has gradually become an important way to connect different cultures. However, with the development of new media technology and the increasing frequency of global cultural exchanges, the traditional cross-cultural communication theory is facing new challenges and opportunities for development. Through the quantitative analysis of the research methods of the article, I found some rules. Due to the particularity of cultural studies, a large number of researchers are more inclined to adopt traditional ethnographic research and field investigation methods, which can more accurately sample the embodiment of elite culture in individuals. For example, Jiang Yilin's theology takes this approach. Jiang tells about the social competition of children from elite families in Beijing's top middle schools from high school to the future[4]. This research method undoubtedly enhances the rigor and rationality of the logic of literary research. However, due to the long research time and in-depth research, researchers often draw established research conclusions, ignore the epochal nature of culture, and lose the dynamic connection between elite culture and cultural communication research. At the same time, it can be found that there is a certain relationship between time and the object of study. Early articles, for example, are based on elite cultural analysis of the meat retail industry[7], or Elite cultural analysis of elite athletes and the dynamics of cultural communication [10]. This kind of research is generally based on interdisciplinary research methods, and its research logic is more like the investigation and research mode of sociology or statistics, rather than the systematic narration of cultural construction, which is mostly integrated interdisciplinary research combined with other disciplines. Most of the later articles are comprehensive studies within the cultural framework of culture itself. For example, the interview with Erdoghan mentioned above explores the role of Turks in cultural transmission in both elite and civilian culture [11]. Most of these studies focus on the formation and development of a country's elite and popular culture, and are also related to political science, but only a few chapters are devoted to exploring its connection to cultural exchanges between different cultural backgrounds. The research object of the article also reflects that in different times, the cultural expression symbols and carriers of elite culture are different. As the research of Sam Friedman and Aaron Reeves reveals, earlier elites maintained their status by developing expensive and sophisticated tastes, while contemporary elites emphasized commonality, authenticity, and cultural connection by openly emphasizing everyday cultural practices [5].
4.2.The transmission path of elite culture
In the study of the transmission path of elite culture, we can find that the most important export port of elite culture is education. As an important way of personnel training, education is rarely influenced by elite culture. No matter what country, education is a very important channel for the advancement of social strata. Therefore, education has become the most important transmission carrier and path of elite culture. Then it can be found that because culture-related issues, especially elite culture and cultural communication, are a broad field with high research depth and few research gaps, researchers have pointed out different transmission paths of elite culture. Even in addition to education, elite culture has its transmission channels in all fields, and the enhancement effect of each field is very similar. So, it can be seen that research on the transmission path of elite culture is mostly cross-disciplinary, and that academics have made strong connections between their own research and research from other fields.
It is also surprising that the media and publishing industries do not play a major role in the transmission of elite culture. This is quite different from what we have been told. Media has always been regarded as an important carrier of communication. McLuhan said that information is the medium, and mass media, as a carrier of information, has always been regarded as an important channel and means of cultural communication. But when it comes to elite culture, it seems that mass media are not playing their proper role. The media can transform individual worries into guidance, dispel the mental anxiety of the public, break and bridge the barriers between elite culture and mass culture in this way, expand the audience, so as to grasp the dual benefits of social and economic programs, and realize the public recognition of elite programs[8]. In my opinion, the enhancement of the media in the dissemination of elite culture needs further study by the academic circle. At the same time, elite culture is often studied as a contrastive argument against populism, For example, in Burak's article, he conducts a study of elite culture and populism in Turkey, using Dirili. Ertu tu rul as an entry point. In the course of the research, the author interviewed Erdo Prime an of the National Cultural Commission of the Third World. He said the people, who are the dominant color of our nation are far away from the cultural power[11]. Through interviews, the author learned that Turkey has a strong cultural background, but it is difficult for the public to have a profound understanding of it, so it needs elite culture as a carrier to carry out cultural dissemination and communication. This type of research, in turn, is linked to politics or population mobility, the most important dynamic element in the era of globalization. Population flow has a strong effect on the dissemination and enhancement of elite culture, so the relationship between population flow and elite culture should be further discussed. There are also articles that do not focus on the transmission path but on the methodology of elite cultural studies, for example, in the work of Adam Howard and Jane Kenway, Certainly, a rare few papers in the field of elite studies in education have focused on methodology itself[9].This may be caused by the particularity of cultural issues research itself.
5.Conclusion
Aiming at the theme of cultural construction and the research direction of elite culture and cultural communication in the last ten years, this study systematically summarizes the research contents, methods and research gaps of previous researchers.
However, there are some research problems in this paper. First of all, due to the limitations of time and material conditions, the number of articles that can be collected is not enough, and most of them are concentrated in the past 10 years, and the representation is not strong enough. Secondly, the research method is relatively simple, the lack of field investigation and ethnographic research, cannot avoid the academic ethical problems brought by this research method. Finally, it is impossible to collect some internal data, such as the enrollment rate and employment rate of elite English schools, and the representative symbols of elite culture. There is a lack of questionnaire surveys and the support of key data.
Based on the above research problems, it is necessary to collect data and literature for a long time in the later research. Fieldwork and ethnographic research probably require a long period of time to follow the life development of certain elite groups. Large-scale questionnaires and interviews will be conducted to interview some cultural officials to enhance the authoritativeness and consensus of the article. These methods can effectively improve the representativeness of the article.
References
[1]. Li,Huiting.“Cultural Changes in the Global Information Age.”Proceedings,2020, p.48
[2]. Wang,Qiangchun.“Research on cross-cultural communication strategies and paths of Black Myth: Wukong.”Academic Exploration,2024,p.1-7
[3]. Chen,Huahui.“Insights from the Norman Rockwell Phenomenon: A Shift in the Relationship between Popular Culture and High Art.”Art Journal,2023,p.141-145
[4]. Jiang,Yilin.“Study Gods:How the New Chinese Elite Prepare for Global Competition.” Citic Publishing Group,China,2024.
[5]. Sam Friedman,Aaron Reeves.“From Aristocratic to Ordinary: Shifting Modes of Elite Distinction.”American Sociological Review,2020,p.323-350
[6]. Zhang,Huanyi.“British cultural Studies at the end of the twentieth century Influence on media literacy education.”News Dissemination,2023,p.54-56
[7]. Richard E. Ocejo.“Show the animal: Constructing and communicating new elite food tastes at upscale butcher shops.”Poetics,2014,p.106-121
[8]. An,Wei.“On the talk show Thirteen Invites The construction of the mass line of elite culture -- from Xu Zhiyuan, the host of the program.”SHENG PING SHI JIE ,2023, p.36-38
[9]. Adam Howard,Jane Kenway.“Canvassing conversations: obstinate issues in studies of elites and elite education.”International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education,2015,p.1005-1032
[10]. Michael McDougall, Mark Nesti, David Richardson.“The Challenges of Sport Psychology Delivery in Elite and Professional Sport: Reflections From Experienced Sport Psychologists.”The Sport Psychologist,2015,p.265-277
[11]. Burak Özçetin.“The show of the people’ against the cultural elites: Populism, media and popular culture in Turkey.”European Journal of Cultural Studies,2019,p.942-957
Cite this article
Zhang,C. (2025). The Dynamic Connection Between Elite Culture and Cultural Dissemination. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media,85,140-145.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social Psychology and Humanity Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li,Huiting.“Cultural Changes in the Global Information Age.”Proceedings,2020, p.48
[2]. Wang,Qiangchun.“Research on cross-cultural communication strategies and paths of Black Myth: Wukong.”Academic Exploration,2024,p.1-7
[3]. Chen,Huahui.“Insights from the Norman Rockwell Phenomenon: A Shift in the Relationship between Popular Culture and High Art.”Art Journal,2023,p.141-145
[4]. Jiang,Yilin.“Study Gods:How the New Chinese Elite Prepare for Global Competition.” Citic Publishing Group,China,2024.
[5]. Sam Friedman,Aaron Reeves.“From Aristocratic to Ordinary: Shifting Modes of Elite Distinction.”American Sociological Review,2020,p.323-350
[6]. Zhang,Huanyi.“British cultural Studies at the end of the twentieth century Influence on media literacy education.”News Dissemination,2023,p.54-56
[7]. Richard E. Ocejo.“Show the animal: Constructing and communicating new elite food tastes at upscale butcher shops.”Poetics,2014,p.106-121
[8]. An,Wei.“On the talk show Thirteen Invites The construction of the mass line of elite culture -- from Xu Zhiyuan, the host of the program.”SHENG PING SHI JIE ,2023, p.36-38
[9]. Adam Howard,Jane Kenway.“Canvassing conversations: obstinate issues in studies of elites and elite education.”International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education,2015,p.1005-1032
[10]. Michael McDougall, Mark Nesti, David Richardson.“The Challenges of Sport Psychology Delivery in Elite and Professional Sport: Reflections From Experienced Sport Psychologists.”The Sport Psychologist,2015,p.265-277
[11]. Burak Özçetin.“The show of the people’ against the cultural elites: Populism, media and popular culture in Turkey.”European Journal of Cultural Studies,2019,p.942-957









