1. Introduction
As the global community faces unprecedented environmental challenges, the architectural field is undergoing a significant transformation, with sustainability at its core. This shift towards sustainable architectural practices encompasses the integration of green building designs, the incorporation of smart technologies, and the pursuit of ultra-low energy consumption. These practices are not isolated phenomena but interconnected strategies that collectively aim to reduce environmental footprints, enhance operational efficiency, and promote occupant well-being. The urgency for this integration arises from the critical need to address climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation. Green buildings focus on minimizing the impact on the natural environment through efficient use of resources and reduced pollution. Smart technologies offer the potential to optimize building operations and energy use, making buildings more responsive to the needs of occupants and the environment. Ultra-low energy buildings go a step further, aiming to drastically reduce or even eliminate net energy consumption. This paper explores the synergy between these practices, highlighting how their integration can lead to the creation of sustainable, efficient, and livable spaces. Through an examination of empirical studies, quantitative analyses, and case studies, we delve into the environmental, economic, and technological aspects of sustainable architectural practices [1]. The challenges of implementing these practices, including higher initial costs and technological complexities, are also discussed. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced operational costs, increased property values, and a significant reduction in environmental impact, present a compelling case for their adoption. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the integration of green design, smart technologies, and ultra-low energy concepts in architecture stands as a testament to the field’s evolution and its role in addressing global environmental challenges.
2. Benefits and Challenges
2.1. Environmental Impact
The integration of green, smart, and ultra-low energy practices into building design dramatically reduces environmental footprints through several key strategies. Firstly, the utilization of renewable materials such as bamboo, recycled steel, and low-emission concrete substitutes reduces resource extraction and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a life cycle assessment (LCA) of a building constructed with these materials can show a 25% reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional buildings. Furthermore, smart systems, when integrated with energy-efficient designs, can optimize the use of natural light and air, reducing the need for artificial heating, cooling, and lighting by up to 40%. Waste minimization strategies, such as modular construction and on-site recycling, further exemplify sustainable development by reducing landfill contributions by up to 50% [2]. The challenge, quantitatively speaking, involves an initial cost increase of approximately 10-20% for green materials and smart technologies, which can be offset by a 30-40% reduction in operational costs over the building’s lifecycle.
2.2. Economic Considerations
Economically, the fusion of green, intelligent, and ultra-low energy practices presents a compelling case for long-term savings. A detailed quantitative analysis comparing the lifecycle costs of traditional versus green, smart buildings indicates that the initial investment in sustainable buildings is recuperated within 5 to 10 years through reduced utility bills, maintenance costs, and increased property values. For instance, a simulation model incorporating energy pricing, maintenance costs, and tax incentives over a 30-year period demonstrates that green, smart buildings offer a net present value (NPV) 20% higher than that of traditional buildings [3]. This economic viability is further enhanced by government incentives for sustainable development and increased market demand for green buildings, underpinning the economic model’s robustness.
2.3. Technological Integration
On the technological front, integrating smart systems with green and ultra-low energy designs requires advanced, innovative solutions that harness the power of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics. For instance, IoT devices can be employed to continuously monitor energy usage, indoor air quality, and occupancy patterns, feeding data into AI algorithms that optimize building performance in real-time. A mathematical model of this system’s energy flow might incorporate differential equations to predict energy consumption patterns and adjust systems accordingly, potentially reducing energy use by up to 30% [4]. However, the complexity of these integrated systems necessitates a workforce highly skilled in IT, data analytics, and sustainability principles. The implementation challenge is quantitatively significant, as the initial cost of smart technologies can be high. Still, with a projected increase in efficiency leading to a reduction in energy costs by approximately 25-30%, the long-term benefits are clear. This integration not only contributes to substantial energy savings but also enhances the functionality and adaptability of living and working spaces, aligning with the principles of sustainable urban development.
3. Design Principles and Implementation
3.1. Sustainable Materials and Construction Techniques
The selection of sustainable materials and the employment of environmentally friendly construction techniques are not just beneficial but essential for reducing the global carbon footprint and combating climate change. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) models serve as critical tools in this endeavor, offering a quantifiable measure of the environmental impact of building materials and methods from cradle to grave, as shown in Figure 1. These models consider various factors including energy consumption, water use, material extraction impacts, and end-of-life decommissioning. For instance, the use of recycled steel reduces the need for iron ore extraction, thereby saving energy and reducing GHG emissions associated with mining and processing [5]. Bamboo, a rapidly renewable material, serves as an excellent substitute for traditional hardwoods, significantly reducing deforestation rates and carbon emissions. Hempcrete, made from the hemp plant’s inner fibers, acts as a sustainable alternative to conventional insulation materials, offering excellent thermal mass and moisture regulation while sequestering carbon throughout its lifecycle. Employing construction techniques such as modular building can drastically reduce waste and energy consumption. This method allows for components to be prefabricated in a controlled factory setting, improving efficiency, and reducing material waste. On-site, the impact is minimized through precise assembly processes that require less energy and generate fewer emissions compared to traditional construction methods.
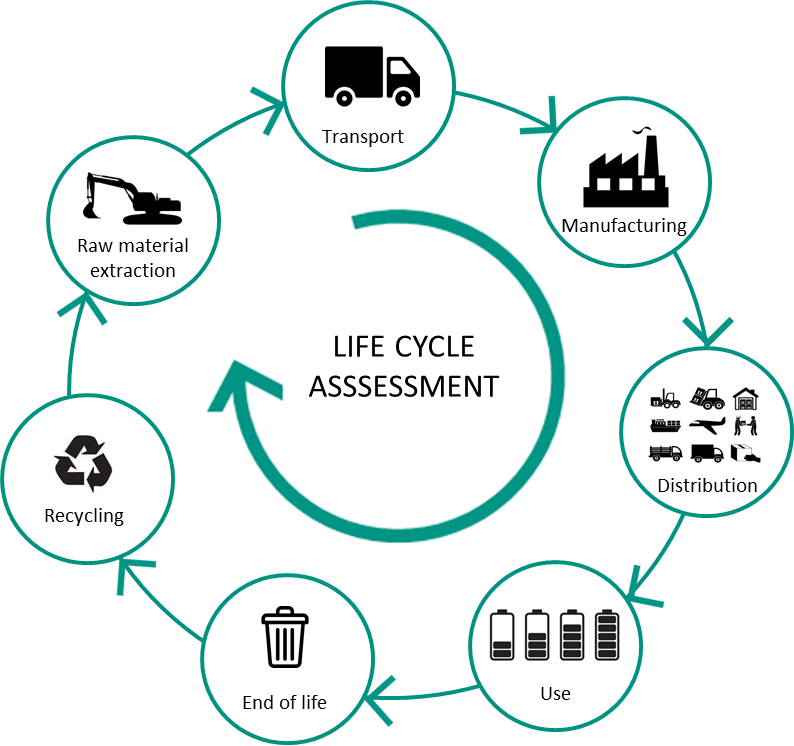
Figure 1. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), the key to a sustainable energy storage
By integrating LCA models in the design and construction phases, architects and engineers can make informed decisions that favor materials and techniques with lower environmental impacts. For example, a comparative LCA of traditional concrete and fly ash concrete shows that replacing a portion of cement with fly ash (a byproduct of coal combustion) can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of concrete without compromising structural integrity.
3.2. Energy Efficiency Through Design
Achieving energy efficiency through design necessitates a holistic approach, incorporating passive solar design principles, optimal thermal mass, and high-performance insulation. Mathematical models play a pivotal role in this process, enabling designers to simulate and optimize the interaction between a building and its environment. For example, by utilizing thermal mass models, architects can determine how materials like concrete or brick can be used to absorb and store heat from the sun during the day and release it at night, thus maintaining a more constant indoor temperature. This reduces reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems, leading to substantial energy savings [6]. Simulation of sunlight exposure through software like Radiance can help in designing window placements and overhangs that maximize natural lighting while minimizing overheating and glare. This not only reduces the need for artificial lighting but also prevents excessive heat gain, further reducing energy consumption for cooling [7]. The incorporation of natural ventilation models assists in designing building layouts and window placements that enhance airflow, eliminating the need for air conditioning during cooler months. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations can predict airflow patterns within and around buildings, allowing for the design of ventilation systems that optimize indoor air quality and thermal comfort.
4. Case Studies and Real-world Applications
4.1. Analysis of Existing Green Buildings
The empirical study of existing green buildings across the globe reveals distinct patterns of energy savings, water conservation, and enhanced indoor environmental quality, offering a blueprint for future sustainable construction. A notable example is the Edge in Amsterdam, which has been hailed as one of the most sustainable office buildings worldwide. The building boasts a BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) score of 98.4%, the highest ever awarded. It achieves significant energy savings through an innovative facade that maximizes daylight while minimizing solar gain, coupled with the use of energy-efficient LED lighting controlled by occupancy sensors. The quantitative analysis reveals that the building’s energy consumption is approximately 70% lower than that of typical office buildings [8]. Furthermore, the Edge utilizes rainwater harvesting and gray water recycling, reducing its water usage by 60% compared to conventional buildings. The indoor environment is enhanced through the use of natural ventilation systems and CO2 sensors that adjust air quality, ensuring optimal conditions for occupants.
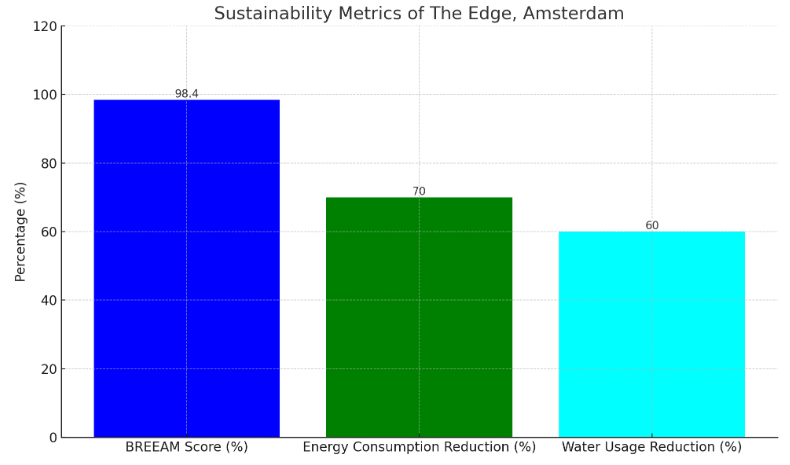
Figure 2. Sustainability Metrics of The Edge, Amsterdam
4.2. Smart Technology in Action
The deployment of smart technologies in buildings has transformed operational efficiency and energy management strategies. An exemplary case is the Salesforce Tower in San Francisco, which leverages the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and artificial intelligence to optimize its energy use and provide a dynamic work environment. The building is equipped with thousands of sensors that monitor temperature, occupancy, light levels, and even air quality in real-time. This data feeds into an AI system that predicts energy needs and adjusts the building’s systems accordingly, achieving a 30% reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional office buildings [9]. The Salesforce Tower also features an advanced water recycling system that treats and reuses greywater and rainwater, significantly reducing the building’s overall water demand. Quantitative analyses indicate that the tower saves approximately 7.8 million gallons of water annually, contributing to its LEED Platinum certification, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Quantitative Performance Analysis of Salesforce Tower: Embracing Smart Technologies for Sustainability
Metric | Value | Description |
Energy Consumption Reduction | 30% | Reduction in energy consumption compared to traditional office buildings, achieved through the use of IoT, data analytics, and AI. |
Annual Water Savings | 7.8 million gallons | Amount of water saved annually through the use of an advanced water recycling system that treats and reuses greywater and rainwater. |
LEED Certification Level | Platinum | Highest level of LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification achieved, indicating superior environmental performance. |
4.3. Ultra-Low Energy Building Achievements
Ultra-low energy buildings, striving for net-zero energy consumption, exemplify the zenith of sustainable architectural endeavors. The Bullitt Center in Seattle stands as a paragon of this approach, having achieved net-zero energy status through a combination of passive design, energy efficiency, and renewable energy production. From Figure 2, the building’s design minimizes energy demand through high-performance insulation, triple-glazed windows, and a tight building envelope, resulting in a heating and cooling demand 90% lower than that of typical office buildings [10]. The roof’s solar panel array generates more electricity than the building consumes annually, with the surplus energy fed back into the grid. Detailed quantitative analysis of the Bullitt Center’s performance over several years confirms its net-zero energy status, with the building producing an average of 10% more electricity than it uses. This excess energy production not only offsets the embodied carbon from the construction materials but also supports the city’s grid during peak demand times, showcasing the potential of integrated design and technology in achieving sustainable architectural solutions.
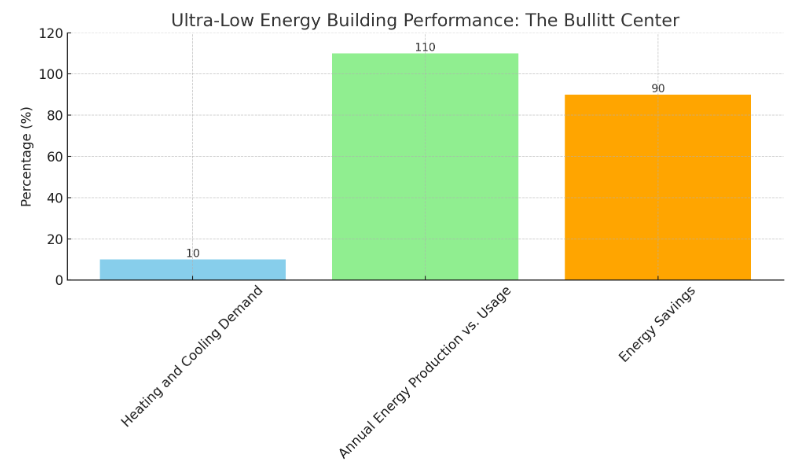
Figure 3. Ultra-Low Energy Building Performance: The Bullitt Center
5. Conclusion
The integration of green building practices, smart technologies, and ultra-low energy strategies represents a pivotal advancement in the field of architecture, aiming to address the pressing environmental challenges of our time. This study has illuminated the substantial benefits of such integrated approaches, including significant reductions in environmental impact, enhanced operational efficiency, and improved occupant comfort. The environmental benefits, underscored by reduced carbon emissions and conservation of water resources, align with global sustainability goals. Economically, the adoption of these practices offers long-term savings and potential for increased property values, making a strong case for their initial investment. Technologically, the integration of smart systems presents a forward-looking approach to building management, optimizing performance and energy use. Despite the challenges, including higher upfront costs and the complexity of technological integration, the compelling evidence presented through quantitative analysis and case studies underscores the feasibility and effectiveness of sustainable architectural practices. As the architectural field continues to evolve, the lessons learned from current implementations of green, smart, and ultra-low energy buildings will undoubtedly guide future developments. The transition towards more sustainable practices is not merely a trend but a necessary shift to ensure the long-term viability of our built environment. In concluding, this paper not only advocates for the continued exploration and adoption of these integrated approaches but also calls for a collective effort among architects, engineers, policymakers, and the public to embrace and advance sustainable architecture for the betterment of our planet and future generations.
References
[1]. Sangmesh, B., et al. “Development of sustainable alternative materials for the construction of green buildings using agricultural residues: A review.” Construction and Building Materials 368 (2023): 130457.
[2]. Şirin, Ceylin, Jamie Goggins, and Magdalena Hajdukiewicz. “A review on building-integrated photovoltaic/thermal systems for green buildings.” Applied Thermal Engineering (2023): 120607.
[3]. Goubran, Sherif, et al. “Green building standards and the united nations’ sustainable development goals.” Journal of Environmental Management 326 (2023): 116552.
[4]. Ullah, Muneeb, et al. “Smart technologies used as smart tools in the management of cardiovascular disease and their future perspective.” Current Problems in Cardiology 48.11 (2023): 101922.
[5]. Mansurjonovich, Joraev Muzaffarjon, and Nishonov Akmal Obidovich. “The Importance Of Smart Technologies In The Modern Integrated Digital Learning Environment.” CEMJP 31.4 (2023): 667-670.
[6]. Lee, Khai Loon, et al. “Digital supply chain transformation: The role of smart technologies on operational performance in manufacturing industry.” International Journal of Engineering Business Management 16 (2024): 18479790241234986.
[7]. Khanday, Mudasir A., Shazia Rashid, and Farooq A. Khanday. “1T Spiking Neuron Using Ferroelectric Junctionless FET with Ultra-Low Energy Consumption of 24 aJ/Spike.” Neural Processing Letters 55.8 (2023): 11527-11539.
[8]. Kumar, Abhash, et al. “Ultra Low Energy Charge Trapping MOSFET With Neuro-Inspired Learning Capabilities.” IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology (2023).
[9]. Mishra, Ayaskanta, and Arun Kumar Ray. “Multi-Access Edge Computing assisted ultra-low energy scheduling and harvesting in multi-hop Wireless Sensor and Actuator Network for energy neutral self-sustainable Next-gen Cyber-Physical System.” Future Generation Computer Systems 141 (2023): 298-324.
[10]. Rane, Nitin. “Integrating leading-edge artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IOT), and big data technologies for smart and sustainable architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) industry: Challenges and future directions.” Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry: Challenges and Future Directions (September 24, 2023) (2023).
Cite this article
Mi,Z. (2024). Sustainable architectural practices: Integrating green design, smart technologies, and ultra-low energy concepts. Theoretical and Natural Science,48,62-67.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Geoscience and Earth Ecology
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Sangmesh, B., et al. “Development of sustainable alternative materials for the construction of green buildings using agricultural residues: A review.” Construction and Building Materials 368 (2023): 130457.
[2]. Şirin, Ceylin, Jamie Goggins, and Magdalena Hajdukiewicz. “A review on building-integrated photovoltaic/thermal systems for green buildings.” Applied Thermal Engineering (2023): 120607.
[3]. Goubran, Sherif, et al. “Green building standards and the united nations’ sustainable development goals.” Journal of Environmental Management 326 (2023): 116552.
[4]. Ullah, Muneeb, et al. “Smart technologies used as smart tools in the management of cardiovascular disease and their future perspective.” Current Problems in Cardiology 48.11 (2023): 101922.
[5]. Mansurjonovich, Joraev Muzaffarjon, and Nishonov Akmal Obidovich. “The Importance Of Smart Technologies In The Modern Integrated Digital Learning Environment.” CEMJP 31.4 (2023): 667-670.
[6]. Lee, Khai Loon, et al. “Digital supply chain transformation: The role of smart technologies on operational performance in manufacturing industry.” International Journal of Engineering Business Management 16 (2024): 18479790241234986.
[7]. Khanday, Mudasir A., Shazia Rashid, and Farooq A. Khanday. “1T Spiking Neuron Using Ferroelectric Junctionless FET with Ultra-Low Energy Consumption of 24 aJ/Spike.” Neural Processing Letters 55.8 (2023): 11527-11539.
[8]. Kumar, Abhash, et al. “Ultra Low Energy Charge Trapping MOSFET With Neuro-Inspired Learning Capabilities.” IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology (2023).
[9]. Mishra, Ayaskanta, and Arun Kumar Ray. “Multi-Access Edge Computing assisted ultra-low energy scheduling and harvesting in multi-hop Wireless Sensor and Actuator Network for energy neutral self-sustainable Next-gen Cyber-Physical System.” Future Generation Computer Systems 141 (2023): 298-324.
[10]. Rane, Nitin. “Integrating leading-edge artificial intelligence (AI), internet of things (IOT), and big data technologies for smart and sustainable architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) industry: Challenges and future directions.” Engineering and Construction (AEC) Industry: Challenges and Future Directions (September 24, 2023) (2023).









