

About TNSThe proceedings series Theoretical and Natural Science (TNS) is an international peer-reviewed open access series which publishes conference proceedings from a wide variety of disciplinary perspectives concerning theoretical studies and natural science issues. TNS is published irregularly. The series publishes articles that are research-oriented and welcomes theoretical articles concerning micro and macro-scale phenomena. Proceedings that are suitable for publication in the TNS cover domains on various perspectives of mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, agricultural science, and medical science. The series aims to provide a high-level platform where academic achievements of great importance can be disseminated and shared. |
| Aims & scope of TNS are: ·Mathematics and Applied Mathematics ·Theoretical Physics ·Chemical Science ·Biological Sciences ·Agricultural Science & Technology ·Basic Science of Medicine ·Clinical and Public Health |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Malaysia

Al Kharj, Saudi Arabia

Turkey

Spain
Latest articles View all articles
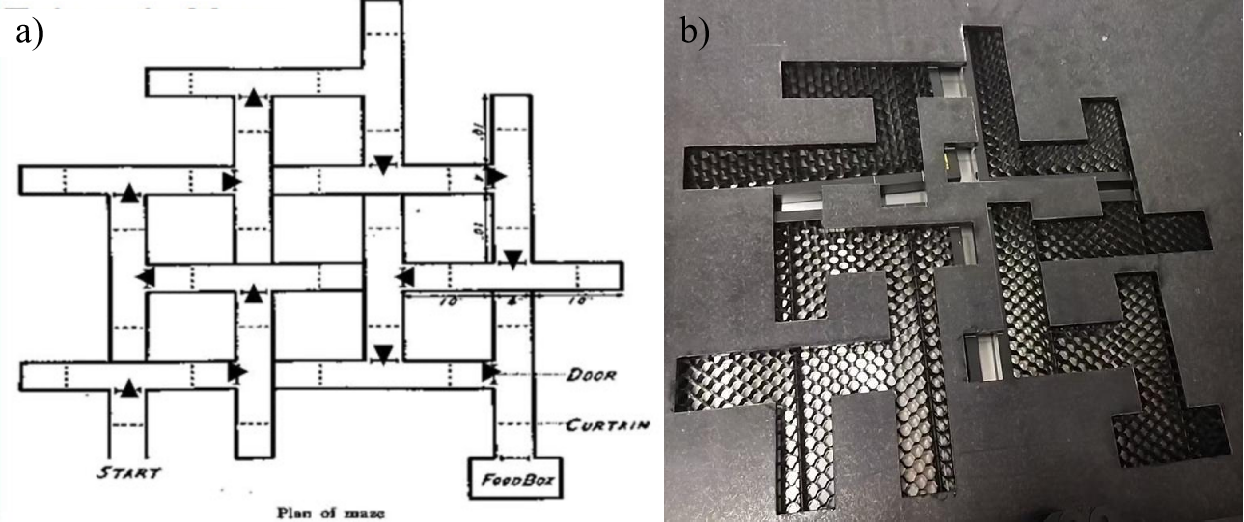
When we drive into a supermarket, navigate in a large shopping mall or find our way in an unfamiliar city, we utilize our attention and spatial memory to reach our goal. Previous research shows that the integration of memory, perception, and executive functions is essential for efficient navigation, and its capacity can vary greatly among individuals. It is unclear what specific factors drive individual differences in navigation abilities and spatial cognition. This study investigates the neural and behavioral mechanisms underlying landmark and map-based learning during goal-directed navigation. Our main contributions in this project contain two parts: 1) up to our best knowledge, I successfully developed the first novel goal-directed navigation research platform, NeuroNav, for investigating the neural mechanism in navigation. The maze design of NeuroNav is inspired by Tolman's multiple T-junctions. During testing, participants can observe the environment in the maze via a built-in camera and control their view and location via screw-driven linear slides, a gamepad controller, and an Arduino microcontroller; 2) I systematically examined how individual differences in attention, working memory, and spatial familiarity influence navigation performance. Participants navigated to different goal locations both with and without a map while behavioral metrics (e.g., time to goal, heading changes) and EEG signals (concentration, theta, beta, gamma bands) were recorded. Results showed that familiarity and map use significantly improved navigation efficiency and reduced cognitive load, as reflected in both behavior and neural activity. EEG recordings revealed increased theta and gamma activity during novel landmark encoding and decision-making phases. These findings highlight the interplay between attention, memory, and environmental cues in spatial learning, with implications for assistive navigation technologies and populations with spatial memory deficits.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Bornean orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) is one of the world's most endangered primates and holds a crucial position in the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia. However, rapid deforestation, large-scale palm oil plantation expansion, infrastructure development, climate change, and poaching have led to a dramatic population decline. This study reviewed existing literature and conservation reports to analyze the current status of the Bornean orangutan, identify the key drivers of habitat loss, and assess conservation measures at the international, national, and community levels. The findings indicate that while initiatives such as protected areas, sustainable palm oil certification, legal reforms, and community-based ecotourism projects provide valuable foundations, their effectiveness is limited by insufficient enforcement, low certification coverage, unstable funding, and conflicts between conservation and economic interests. This paper argues that a holistic approach integrating ecological conservation, sustainable industrial development, and community livelihoods is crucial to ensuring the long-term survival of the orangutan. Additionally, future research should address existing limitations by integrating primary ethnographic data, evaluating the long-term impacts of conservation policies, and exploring transboundary ecological corridor initiatives aimed at strengthening cooperation between Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei.

 View pdf
View pdf


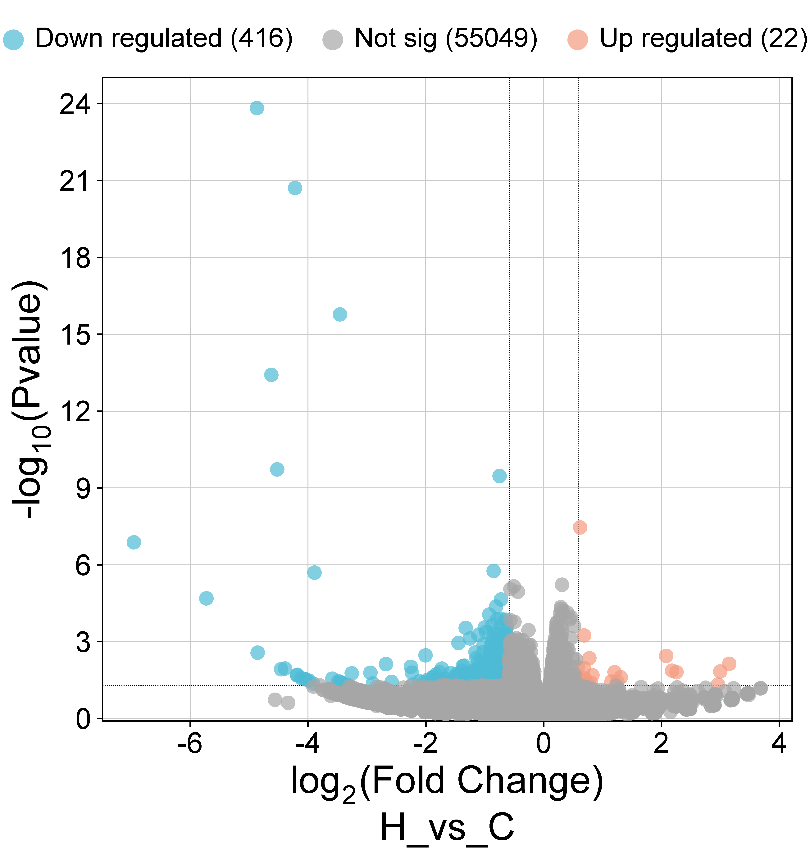
Depression is a highly heterogeneous neuropsychiatric disorder. The poor therapeutic efficacy, limited treatments, and persistently high relapse rates underscore the urgent need to explore new therapeutic methods. Growing evidence shows that inflammation in the brain plays a vital role in depression. Current treatments for depression tend to overlook this diet-inflammation link. This study examines the genomic and transcriptomic patterns of brain inflammation induced by high-fat diets(HFD). Based on high-throughput sequencing data from the GEO database, we revealed the transcriptional characteristics of neuroimmune imbalance in depression through differential expression analysis, GO, KEGG, and other analyses. We screened for Medicine-Food Homology (MFH) with potential antidepressant effects by integrating multi-omics analysis with network pharmacology. We found that an HFD induces alterations in brain gene expression and affects the process or biological function of monoamine neurotransmitter transport. We identified six MFH substances with potential therapeutic effects against depression, whose mechanisms may involve modulating the activity of membrane transporters and neural signalling. This work supports the idea that what we eat can profoundly shape brain health. These molecular patterns may provide a new idea of more accurate and personalised treatment for mood disorders related to a high-fat diet, to prevent and treat depression more effectively.

 View pdf
View pdf


Upper-limb motor impairment is most commonly caused by nerve damage, i.e., stroke, traumatic injuries, and neurological diseases, requiring innovative assistive devices to aid recovery and rehabilitation. Current upper-limb exoskeletons, particularly those controlled by surface electromyography (sEMG), often face issues related to signal variability and muscle fatigue, reducing their real-world reliability. This study developed a low-cost, non-invasive, AI-empowered, brain–computer interface (BCI)–controlled upper-limb exoskeleton to assist rehabilitation for patients with upper-limb motor impairments (e.g., stroke or neurological disease), responding to the clinical need for accessible assistive devices. The system uses EEG signals recorded through a conventional cap and preprocessed in MATLAB to remove noise and artifacts. Motor intentions are classified by a novel AI algorithm, EEGNet, using a custom dataset (flexion–extension, pronation, pull, resting), and are then translated into control signals to actuate the exoskeleton's movements. Experimental results show that the system can translate EEG signals into basic exoskeleton motion commands in real time (flexion–extension, arm pronation, arm pull, and resting), exhibiting stable model training behavior and real-time responsiveness. This AI-empowered and BCI-controlled upper-limb exoskeleton system has the potential to be applied in home rehabilitation, enhancing upper-limb mobility-impaired patients' quality of life.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
Volume 152December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of ICMMGH 2026 Symposium: Biomedical Imaging and AI Applications in Neurorehabilitation
Conference website: https://www.icmmgh.org/auckland.html
Conference date: 14 November 2025
ISBN: 978-1-80590-565-3(Print)/978-1-80590-566-0(Online)
Editor: Sheiladevi Sukumaran, Alan Wang
Volume 151December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of CONF-CIAP 2026 Symposium: Applied Mathematics and Statistics
Conference website: https://www.confciap.org/chicago.html
Conference date: 27 January 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-559-2(Print)/978-1-80590-560-8(Online)
Editor: Marwan Omar
Volume 150December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
Conference website: https://www.confciap.org/
Conference date: 30 January 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-537-0(Print)/978-1-80590-538-7(Online)
Editor: Marwan Omar
Volume 149December 2025
Find articlesProceedings of ICMMGH 2026 Symposium: Environmental Engineering and Climate Change
Conference website: https://www.icmmgh.org/petalingjaya.html
Conference date: 16 January 2026
ISBN: 978-1-80590-501-1(Print)/978-1-80590-502-8(Online)
Editor: Sheiladevi Sukumaran, Alan Wang
Announcements View all announcements
Theoretical and Natural Science
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Theoretical and Natural Science
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Theoretical and Natural Science (TNS) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:






