

Volume 133
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: AI for Healthcare: Advanced Medical Data Analytics and Smart Rehabilitation
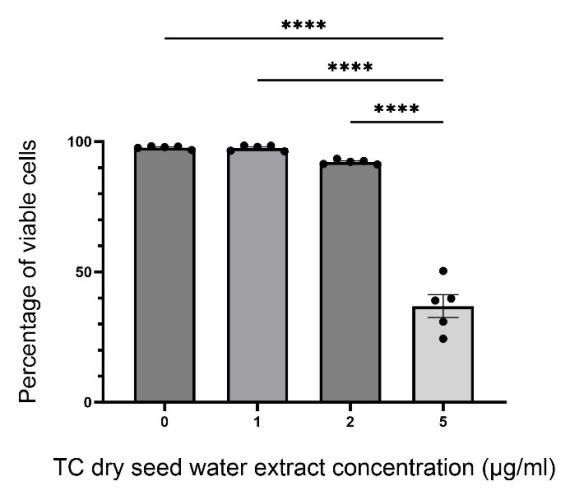
Evaluating the potential mediating effects of Tinospora cordifolia (TC) extracts on microglial phagocytosis is necessary to research on the therapeutic efficacy of this rarely studied plant on neurodegenerative diseases associated with underregulated microglial phagocytic activity. Research has demonstrated the extract’s impact on human neutrophil cells; however, experiments are still in need to include microglia, immune cells in the central nervous system that are tightly bound with various diseases. This research used the Trypan Blue exclusion test to evaluate the cytotoxicity of TC dry seed water extract’s influence on the viability of mouse microglia Bv2 cells, and adopted pH-sensitive fluorescent microspheres to evaluate the impact of various concentrations of TC extract on the phagocytic activity of microglia as measured by relative fluorescent units. Results indicate that 0.1 μg/ml – 1.0 μg/ml TC dry seed water extract did not show significant effects on both cell viability and microglial phagocytosis, while 2.0 μg/ml TC dry seed water extract demonstrated the ability to reduce microglial phagocytosis without exhibiting influential cytotoxicity. 5.0 μg/ml TC dry seed water extract revealed strong cytotoxicity and was therefore not tested subsequently. In conclusion, 2.0 μg/ml TC dry seed water extract serves as a potential agent for managing the phagocytic activity of microglia under inflammation, and therefore may be experimented with for further medical use.

 View pdf
View pdf


Stroke is one of the leading causes of long-term disabling illness in the world, resulting in persistent functional impairment in 75% of survivors. Traditional rehabilitation methods are often limited by their inability to effectively activate long-term neuroplasticity. This study investigated the use of brain-computer interface (BCI) technology in post-stroke rehabilitation and systematically assessed its clinical efficacy for limb function recovery by analyzing neural signal decoding mechanisms and classification (invasive/non-invasive). The results of this paper showed that a motor imagery (MI)-based BCI training program enhanced neural coupling between the motor cortex and the affected limb, reflecting clinical significance in hand grasp, joint range of motion, and motor coordination. For comorbid upper and lower extremity dysfunction, the BCI intervention yielded across-the-board benefits: walking speed improved by 0.15 m/s, spasticity scores (wrists, fingers, and ankles) were significantly reduced, and Barthel Index (BI) scores improved by 5.0 points. These synchronized improvements confirm the synergistic effect of BCI on motor function, spasticity control and activities of daily living. The integrated BCI robotic system incorporates Error-Related Negativity (ERN) decoding, enabling real-time detection of motor intent errors (8.5:1 detection-to-false-alarm ratio) and precise millisecond adjustment of assistive forces. This technological advancement permits early initiation of active neuroplasticity training in acute phase patients with complete loss of voluntary movement, confirming superior efficacy compared to conventional therapy alone. By facilitating active neural remodeling, BCI technology overcomes the limitations of passive rehabilitation and offers transformative potential for chronic patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


Steady-state visual evoked potential (SSVEP), as a non-invasive EEG signal, is widely used in brain-computer interfaces (BCI) due to its high signal-to-noise ratio and high temporal resolution. With advancements in neural engineering, SSVEP-BCI technology has become one of the important research directions in the fields of medicine, rehabilitation and human-computer interaction. Despite its potential, SSVEP-BCI systems still face challenges such as signal stability, individual variability, system portability and interaction naturalness. This paper explores the relationship between SSVEP and brain function, analyzes its role in cognitive tasks, and evaluates the mechanism, current status, and challenges of SSVEP-BCI systems across various fields. By reviewing relevant literature, it examines the mechanism of SSVEP generation, its application in cognitive neuroscience, and the integration of SSVEP-BCI with other EEG signals (e.g., P300, motor imagery (MI), and electrooculogram (EOG)). Studies have indicated that the SSVEP-BCI system has high application value in brain-computer interaction, especially in the medical field, where it has been widely used in the rehabilitation of patients with movement disorders and the control of assistive devices. However, current studies face challenges such as decoding accuracy, system stability, and individual variability. By focusing on multimodal integration, deep learning, and wearables, future SSVEP-BCI developments aim to enhance accuracy, stability, and user experience, broadening their applications in medicine, industry, and entertainment.

 View pdf
View pdf


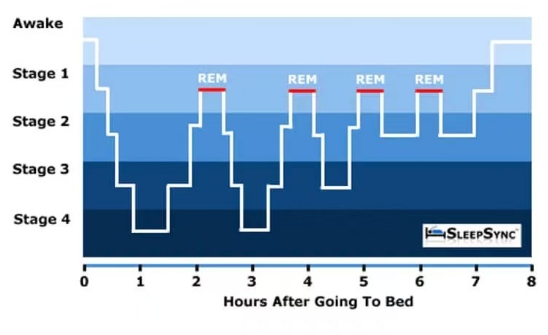
Sleepwalking, a prevalent parasomnia disorder characterized by complex motor activities during non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, affects individuals across the lifespan, with distinct developmental patterns. It is especially common among children. Their behaviors can vary from simple actions like sitting up or walking in bed to more complex ones such as dressing or opening doors. These actions are typically purposeless and mechanical, with reduced awareness of the environment and limited responses to external stimuli. In adults, sleepwalking behaviors are generally less frequent but can still involve similar mechanical and purposeless actions. Stress, irregular sleep patterns, and environmental factors often act as triggers. Both pediatric and adult populations require age-specific management strategies to address sleepwalking effectively. For children, ensuring regular sleep routines and avoiding forced awakenings are key, with professional help recommended if episodes occur frequently. For adults, maintaining consistent sleep habits, managing stress, and creating a safe environment is crucial, with medical intervention suggested if sleepwalking persists. This paper provides a comprehensive review of current literature to explore multifaceted aspects of sleepwalking, focusing on its epidemiological characteristics, triggering mechanisms, clinical manifestations, pathophysiological underpinnings, and tailored management approaches for both children and adults.

 View pdf
View pdf


Coenzyme Q10is a lipid-soluble quinone compound that functions both as a mitochondrial electron transport carrier and as an antioxidant. It is widely used in the fields of cardiovascular disease adjuvant therapy, health products, and cosmetics. However, its poor water solubility, low photothermal stability, and limited bioavailability constrain its practical applications. This paper systematically discusses three delivery systems for coenzyme Q10: nanoemulsions, which enhance water solubility and cellular permeability; nanoparticles, which enable particle size control and high encapsulation efficiency with targeted, sustained-release properties; and gel-based delivery systems, which improve the skin’s antioxidant capacity and storage stability. This research offers material design strategies and technological optimization approaches to address the bottlenecks in coenzyme Q10application, providing important academic reference value for improving the bioavailability of lipophilic active substances.

 View pdf
View pdf


Focusing on exercise rehabilitation for elderly patients with coronary artery disease after coronary angiography, this paper systematically analyzes the multifaceted significance of exercise rehabilitation in restoring physical function, improving mental health, and enhancing quality of life. The paper explores the mechanisms and clinical effects of rehabilitation modalities, including aerobic exercise to promote collateral circulation and cardiac function, resistance training to improve lipid profile by increasing muscle mass, flexibility training to prevent joint stiffness, and balance training to reduce the risk of falls. Key findings emphasize that exercise rehabilitation can promote the aerobic metabolism of myocardium, increase myocardial oxygen uptake, enhance myocardial contractility, improve cardiac pumping function, improve cardiac function, significantly reduce cardiovascular events and postoperative complications, and improve patients' quality of life. Meanwhile, early exercise rehabilitation has a positive impact on patients' psychological state through neurobiological mechanisms, improves psychological comfort, reduces anxiety and depression, and improves the negative psychological state of patients after coronary heart disease surgery. The study provides both theoretical frameworks and practical guidance for integrating scientific exercise programs into post-PCI rehabilitation, emphasizing its role in achieving comprehensive physical and psychological recovery for elderly patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a global pandemic imposing substantial health and economic burdens, highlighting the critical need for effective non-pharmacological management strategies beyond medication. This paper comprehensively examines the biological mechanisms underpinning the therapeutic effects of resistance training (RT) in T2D and translates this evidence into clinical applications. The results of this paper demonstrate that RT enhances glycemic control by upregulating skeletal muscle GLUT4 expression through AMPK/HDAC5-MEF2 and Akt/AS160 pathways, and activates mTORC1 signaling to promote protein anabolism. Clinically, structured RT significantly reduces HbA1c, attenuates postprandial glucose fluctuations, and mitigates major complications. The rationale is to improve the prognosis of diabetic foot by enhancing plantar pressure distribution and endothelial function, which is expected to reduce renal inflammation and oxidative stress in a preclinical diabetic nephropathy model, and in combination with aerobic exercise, improve nerve conduction velocity and pain in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Critically, RT demonstrates a unique "strength-metabolism coupling" effect, concurrently improving muscle strength and glycemic control, especially in elderly T2D patients with sarcopenia. This paper underscores RT as a potent, evidence-based cornerstone intervention for T2D management. It provides a crucial theoretical foundation for developing personalized RT prescriptions and integrating RT within multidisciplinary care models to optimize outcomes and reduce complication risks.

 View pdf
View pdf


Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) have fragmented identities, memory impairments, and emotional resistance, which seriously affect their physical and mental health. This article explores cognitive restructuring as a key method for psychological rehabilitation. The research results of this article show that recombination is the core treatment method for DID, targeting the cognitive processes of maintaining dispersed identity and emotional disorders. By challenging maladaptive thinking patterns through techniques such as dialogue questioning and visual rewriting, this approach promotes functional integration of identity states, disrupts memory separation, and supports neural reconstruction involved in emotion regulation. Neurobiological studies have shown that this intervention can enhance the activity of brain regions crucial for real-world testing and emotional management, while clinical studies have shown a significant reduction in dissociative symptoms. However, several limitations must be acknowledged in order to optimize its application. The average reduction in separation symptoms was 38%, and patients' memory continuity of different identities also improved. Neuroimaging shows that the connectivity of memory related brain regions has increased by 25%. In addition, 70% of patients reported a decrease in emotional resistance and actively engaged in the treatment process. These findings highlight the effectiveness of cognitive restructuring in promoting identity integration and emotional regulation, providing a promising direction for DID rehabilitation. However, limitations such as emotional distress that may arise during the treatment process also need to be noted.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Osa Peninsula has undergone a significant economic transformation, shifting from a primarily agriculture-based economy to one centered on ecotourism. As a critical representative of tropical rainforest ecosystems, the region is home to abundant and diverse flora and fauna. Historically, the peninsula experienced environmental degradation due to agricultural expansion and industrial activities. Today, it serves as a microcosm of broader ecological development trends. Recognized globally as a model for ecotourism and conservation, the Osa Peninsula has benefited from a series of national policies in Costa Rica that have contributed positively to its environmental protection. Nonetheless, despite its successes, ecotourism in the region faces several ongoing challenges that warrant critical attention and sustainable management strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf



Lipids are biomolecules that are important research topics in biology, energy use, and engineering. As organic compounds, lipids play a crucial role in biological systems and human activities. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the development of lipids in modern technologies (3D-printed food technology and biodiesel fuels) and prospects for future exploitation. It is shown that lipid-based 3D printing technologies enable customized food production, but face material and cost challenges. Biodiesel fuel blends offer environmental benefits, but struggle with low-temperature performance and high costs. Meanwhile, the combination of 3D printing technology with medical science offers great potential for personalized medicine and tissue engineering, but is also limited by protein stability and high-tech costs. By analyzing these technologies, this study provides a theoretical basis for advancing lipid-related technologies and addressing energy, food, and medical issues.

 View pdf
View pdf




