

Volume 132
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-APMM 2025 Symposium: Simulation and Theory of Differential-Integral Equation in Applied Physics
Proper time and time dilation, though well-established in special relativity, are predominantly analysed for point particles. Much less attention has been given to how proper time behaves across spatially extended rigid bodies in inertial motion. Existing studies have explored differential aging effects under relativistic rigid motion, but primarily in scenarios involving acceleration. Therefore, this paper aims to investigate how proper time varies across different points of an extended object experiencing purely inertial motion, focusing on how the different clock synchronisation conventions affect the overall desynchronisation in proper time. This paper uses classical formulations of special relativity in order to contribute to a new perspective on the role of simultaneity in distributed time frames. This paper discovered that the two primary clock synchronization conventions— the Einstein convention and slow clock transport—produce comparable desynchronization in proper time; however, each method presents distinct advantages and disadvantages in practical contexts, necessitating a complementary approach to effectively address desynchronization in applications like satellite communication.

 View pdf
View pdf



The advent of relativity theory, initiated by Albert Einstein in the early 1900s, ushered in the era of modern physics by reshaping fundamental concepts of space, time, and gravity. This framework emerged in response to the shortcomings of Newtonian mechanics, particularly its failure to account for the invariance of the speed of light and anomalies in Mercury’s orbital path. The paper, through a method of literature review, analyzes and summarizes the historical development and core concepts of both special and general relativity. It explores key background events, major breakthroughs, and their lasting influence on modern science. The paper concludes that the two main contributions of relativity are the famous equations: the mass-equivalence equation in special relativity and the Einstein field equations in general relativity, both of which continue to shape physics today.

 View pdf
View pdf


Option pricing is one of the core problems in modern financial mathematics. This paper systematically reviews the mathematical models used in option pricing, including classical models (Black-Scholes model, binomial tree model), modern stochastic models (Heston model, Merton jump-diffusion model), numerical methods (Monte Carlo simulation, finite difference method), and machine learning techniques. Through theoretical analysis and empirical comparisons, the study reveals the mathematical principles, applicability, and limitations of these models. Furthermore, the study discusses model optimization directions in the context of real financial markets, particularly for special cases such as China's A-share market. The research shows that the evolution of mathematical models has always balanced market incompleteness and computational efficiency. Future trends will focus on hybrid models integrating stochastic analysis and data science.

 View pdf
View pdf


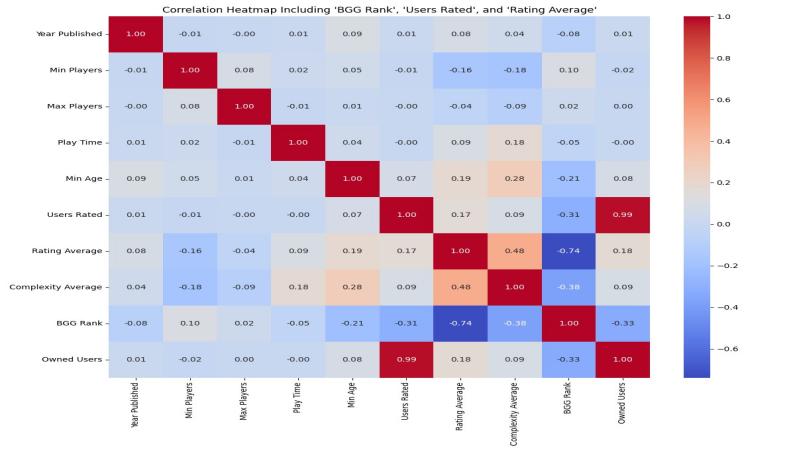
This study investigates the factors influencing board game ownership using a comprehensive dataset from BoardGameGeek. By applying statistical techniques such as correlation analysis, Lasso regression, Random Forest, and a Gradient Boosting Model (GBM), the paper explores how variables such as user ratings, complexity, playtime, age rating, and year of publication affect ownership. The analysis reveals that user engagement metrics—particularly the number of users who rated a game—are the strongest predictors of ownership. However, when visibility metrics are excluded, intrinsic attributes like game complexity, playtime, and accessibility (minimum age) emerge as significant drivers. The Gradient Boosting Model, trained with log-scaled ownership values, achieves a high score of 0.975 on the validation set, confirming its strong predictive performance. These findings provide actionable insights for developers, highlighting the importance of both marketing efforts and thoughtful design choices. The study contributes to the understanding of consumer behavior in the board game industry and offers a data-driven framework for optimizing game appeal and commercial success.

 View pdf
View pdf


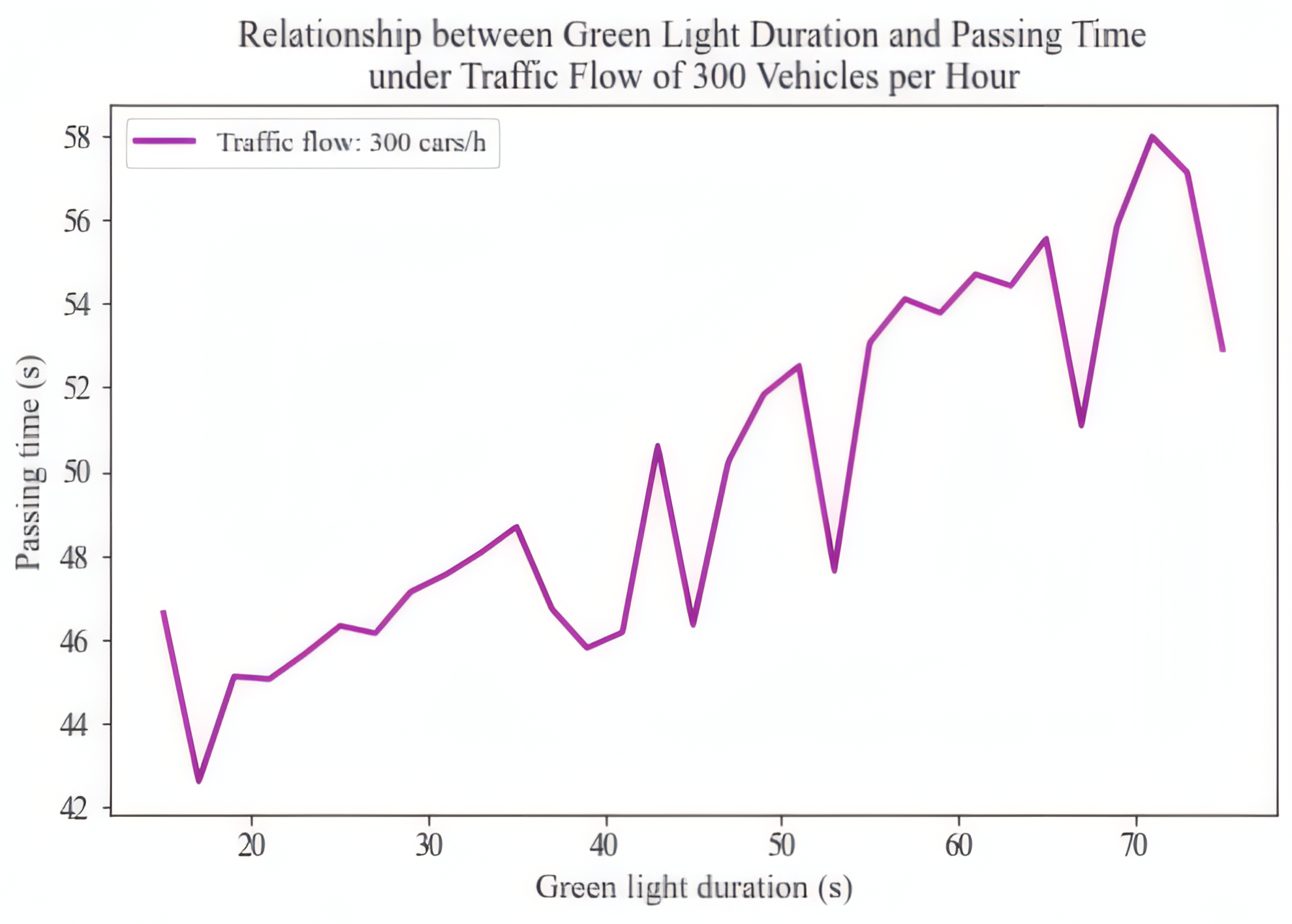
Traffic congestion is an escalating issue in modern cities, which impacts the quality of life, economic productivity, and causes unnecessary harm to the environment. As urbanization moves on, the increasing traffic flow makes traditional management methods using fixed green light duration struggle to cope. Mathematical modeling and computer simulation act as effective tools for analyzing and optimizing traffic light controlling systems. This study focuses on using these techniques to explore traffic flow behavior and propose model-based optimization strategies. In addition to the Nagel-Schreckenberg (NaSch) model, the author incorporates a signal-vehicle interaction mechanism to better represent the realistic urban traffic conditions. The extended model is validated through computer simulations, and the result demonstrates its capability to simulate the effects of traffic signals on vehicle movement and congestion. Moreover, this study explores the optimization of traffic light control strategies based on this extended model. Simulation results indicate that the extended model can effectively boost the efficiency of the traffic system and facilitate the development of more efficient signal control schemes. This model also offers a technical reference for the intelligent and meticulous management of urban traffic signal systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper investigates the numerical stability of QR decomposition, Singular Value Decomposition (SVD), and Cholesky decomposition in least squares problems. Through theoretical analysis and numerical experiments, the computational errors and efficiency of the three decomposition methods are compared for matrices with different condition numbers. The experimental results show that SVD decomposition exhibits the best robustness for ill-conditioned matrices, while Cholesky decomposition is the most efficient for well-conditioned matrices. Additionally, this paper compares the performance of direct solving (without decomposition) with decomposition methods, demonstrating that decomposition methods significantly outperform direct solving in terms of numerical stability and computational efficiency. To further validate the findings, we conduct experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets, covering a range of matrix sizes and condition numbers. The results highlight the trade-offs between accuracy and computational cost, providing practical insights for selecting the appropriate decomposition method based on specific problem requirements. This study not only reinforces the theoretical understanding of matrix decompositions but also offers actionable guidelines for their application in scientific computing and data analysis

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of global climate change and energy crises, the energy sector, which accounts for over 70% of global greenhouse gas emissions, has become a key focus for climate change mitigation. While renewable energy investments are growing, fossil fuels still dominate the global energy mix, especially in developing countries, highlighting the urgency of optimizing energy allocation for sustainable development. The paper adopts a mathematical modeling approach, specifically linear programming, and utilizes data from open energy databases such as those of the IEA and Our World in Data. It constructs a national-level energy allocation model involving five energy sources (coal, natural gas, nuclear, wind, and solar) to explore the optimal energy mix that balances total cost and CO₂ emissions under constraints like capacity limits, renewable portfolio requirements, and emission caps. Additionally, scenario analyses with different carbon prices and emission caps are conducted to derive policy insights. The paper finds that an energy mix excluding coal, consisting of nuclear, wind, solar, and natural gas, can meet emission targets at a reasonable cost. Scenario analyses reveal that carbon pricing and emission caps significantly influence the energy configuration and the trade-offs between cost and emissions, emphasizing the effectiveness of mathematical optimization in balancing economic and environmental goals in energy planning.

 View pdf
View pdf


Contextual multi-armed bandit (CMAB) algorithms have become a cornerstone of modern recommendation systems owing to their ability to effectively manage the exploration-exploitation trade-off in dynamic and uncertain environments. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive empirical comparison of three advanced CMAB algorithms: Double Explore-Then-Commit (DETC), Feel-Good Thompson Sampling (FG-TS), and Multinomial Logit Upper Confidence Bound (MNL-UCB). Leveraging the MovieLens 1M dataset, we constructed a realistic experimental setting by encoding detailed user profile features, including demographic and behavioral attributes, and generating low-dimensional movie embeddings using truncated singular value decomposition (SVD). We employed a logistic regression framework that captures the probabilistic nature of user preferences. The algorithms behaved markedly differently under long-term (10,000 rounds) and short-term (200 rounds) recommendation scenarios. It indicates that MNL-UCB achieves the lowest cumulative regret and shows strong performance stability across varying contexts in the long-term experiment. And FG-TS demonstrates robust adaptability in highly dynamic environments, making it particularly effective in scenarios with unpredictable behavior. However, DETC tends to underperform in complex contextual settings because of its lack of adaptability, leading to increased regret and fluctuating performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


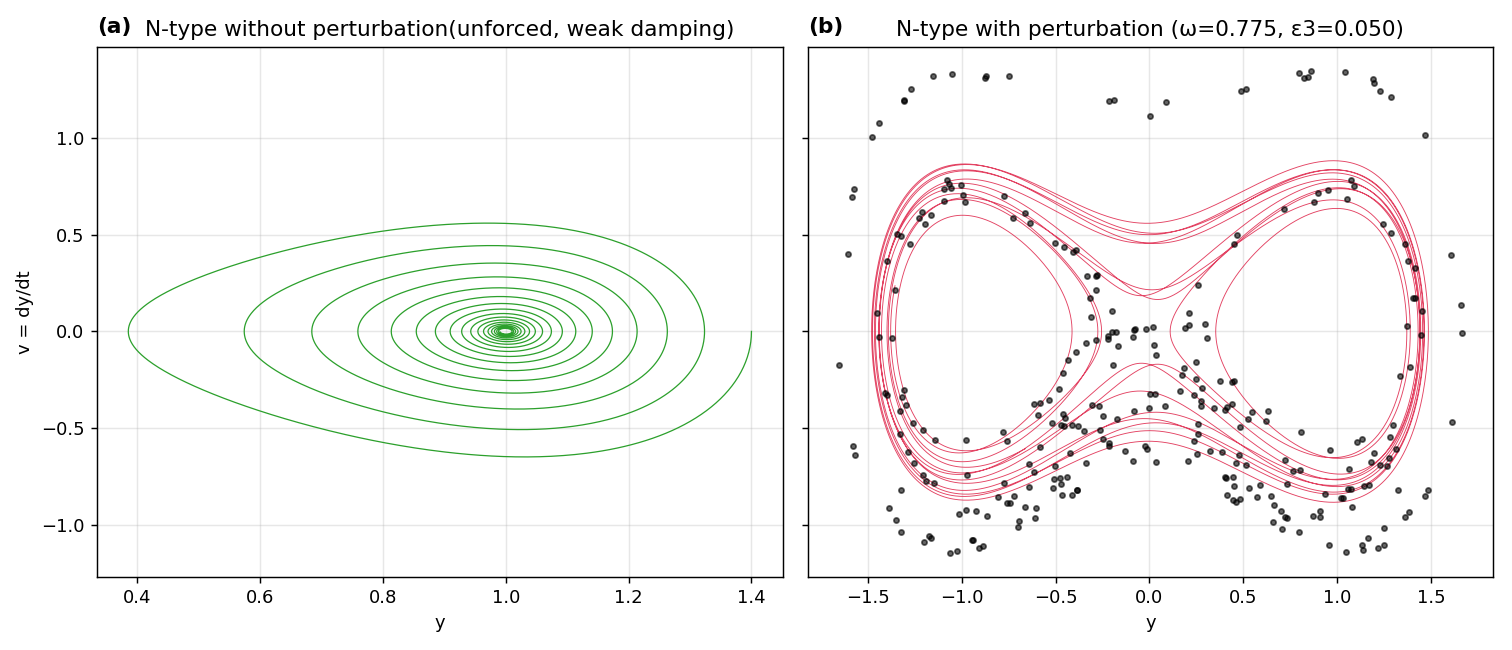
The study presents a unified Duffing-type framework to analyze how physiological perturbations can cause irregular wall motions in coronary arteries. The model incorporates linear and nonlinear wall recoil, flowmediated feedback, viscoelastic (derivative) coupling, periodic cardiaclike forcing, singular constriction terms that mimicking nearocclusive narrowing, and saturating compliance. Direct numerical simulations—including phase portraits, Poincaré sections, and longtime integrations—corroborate this theory: unforced systems relax regularly into single or doublewell equilibria, whereas modest periodic inputs tuned near Melnikov thresholds produce interwell transport, thickened invariantset remnants, broadband Poincaré scattering, and intermittent largeamplitude wall excursions. Extended Stype formulations featuring singular and saturating terms further enrich the route to chaos and highlight the sensitizing role of viscoelastic memory. This framework establishes a mathematically transparent bridge between vascular biomechanics and nonlinear dynamical diagnostics, suggesting earlywarning metrics for transition to pathological oscillations in coronary vessels.

 View pdf
View pdf


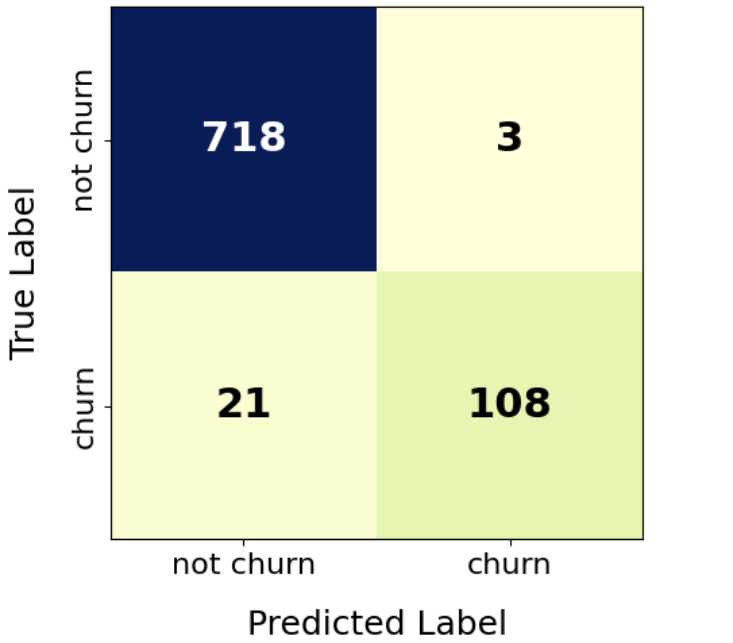
Customer churn prediction benefits the telecom company in retaining churning customers. Various methods, from traditional data analysis to advanced deep learning, were introduced in previous research, while there is little research on boundary data processing and combining advanced deep neural network architectures and traditional data-driven machine learning algorithms. This essay proposed the SDB model, selecting boundary data using SVM and making predictions using a stacked ensemble model where DNN and XGBoost made independent predictions, and logistic regression was used to fit the two predictions into a final prediction. Based on the dataset provided by Kaggle, the SDB model with various augmentation rates and several single models was trained to compare the accuracy, F1-score, recall and precision. Comparison showed that it obtained higher accuracy and F1-score than single models and an ensembled model without boundary augmentation. Meanwhile, the augmentation rate should be carefully chosen to control the trade-off between absorbing attention in boundary data and shifting data distribution, and more real-world datasets could be used on this model to assess its practical utility in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf




