

Volume 3
Published on October 2023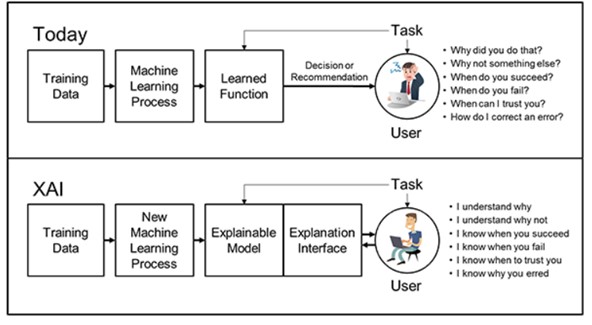
Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems, particularly deep learning models, have revolutionized numerous sectors with their unprecedented performance capabilities. However, the intricate structures of these models often result in a "black-box" characterization, making their decisions difficult to understand and trust. Explainable AI (XAI) emerges as a solution, aiming to unveil the inner workings of complex AI systems. This paper embarks on a comprehensive exploration of prominent XAI techniques, evaluating their effectiveness, comprehensibility, and robustness across diverse datasets. Our findings highlight that while certain techniques excel in offering transparent explanations, others provide a cohesive understanding across varied models. The study accentuates the importance of crafting AI systems that seamlessly marry performance with interpretability, fostering trust and facilitating broader AI adoption in decision-critical domains.

 View pdf
View pdf


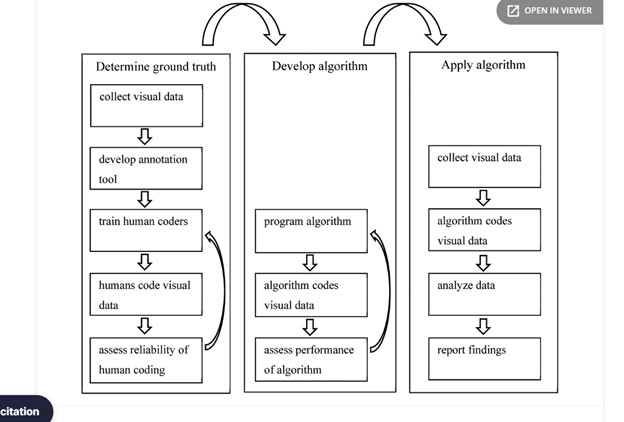
Computer vision, an interdisciplinary field bridging artificial intelligence and image processing, seeks to bestow machines with the capability to interpret and make decisions based on visual data. As the digital age propels forward, the ubiquity of visual content underscores the importance of efficient and effective automated interpretation. This paper delves deeply into the modern advancements and methodologies of computer vision, emphasizing its transformative role in various applications ranging from medical imaging to autonomous driving. With the increasing complexity of visual data, challenges arise pertaining to real-time processing, scalability, and the ethical implications of automated decision-making. Through an exhaustive literature review and novel experimentation, this research demystifies the multifaceted domain of computer vision, elucidating its potential and constraints. The study culminates in a visionary outlook, highlighting future avenues for research, including the fusion of augmented reality with computer vision, novel deep learning architectures, and ensuring ethical AI practices in visual interpretation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Vibroseis seismic acquisition technology is a method of acquiring seismic data utilizing correlation technology. Specifically, the seismic single shot record is obtained through correlation between the reference signal and the mother record. Specifically, the seismic single shot record is obtained through correlation between the reference signal and the mother record. Specifically, the seismic single shot record is obtained through correlation between the reference signal and the mother record. In line with pertinent technical regulations, greater correlation between the two signals equates to superior correlation outcomes. The reference signal is transmitted to the surface via the vibration of the vibrating plate. This is achieved using the vibroseis machine. However, due to the coupling relationship between the vibrating plate and the surface, the vibration signal output by the former is not equivalent to the vibration signal received by the latter. Consequently, the correlation between the reference signal and parent record fails to procure the best correlation result. In this paper, a technique is presented for establishing a correlation between the surface vibration signals captured by the geophone in proximity to the vibroseis and the reference record. This approach improves the quality of the correlated single shot, and holds significant potential for broad dissemination.

 View pdf
View pdf


The intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and software engineering marks a transformative phase in the technology industry. This paper delves into AI-driven software engineering, exploring its methodologies, implications, challenges, and benefits. Drawing from data sources such as GitHub and Bitbucket and insights from industry experts, the study offers a comprehensive view of the current landscape. While the results indicate a promising uptrend in the integration of AI techniques in software development, challenges like model interpretability, ethical concerns, and integration complexities emerge as significant. Nevertheless, the transformative potential of AI within software engineering is profound, ushering in new paradigms of efficiency, innovation, and user experience. The study concludes by emphasizing the need for further research, better tooling, ethical guidelines, and education to fully harness the potential of AI-driven software engineering.

 View pdf
View pdf


The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cloud computing heralds a transformative phase for the tech industry. As cloud infrastructures become more sophisticated, the potential of optimizing these services using AI has captured significant attention. This study aimed to explore how cloud providers can leverage AI to optimize resource allocation, enhance scalability, and offer innovative AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) solutions. Through a mixed-method approach, insights were gleaned from companies that have adopted AI in their cloud architectures. The findings elucidate that AI-driven methods have led to substantial operational savings and a reduction in downtimes. Moreover, the proliferation of AIaaS models is particularly beneficial for mid-level enterprises and startups. However, concerns around data privacy, potential biases, and integration costs emerge as significant challenges. Future work in this domain promises to delve deeper into these challenges, aiming for a harmonious synergy between AI and cloud computing.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the escalating complexity of IT networks and the surge in cyber threats, the need for advanced, real-time security solutions has never been more paramount. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) present promising avenues for enhancing the detection, analysis, and mitigation of threats in these intricate networks. The paper delves into the confluence of ML and DL techniques in the realm of cybersecurity, focusing on their application for real-time threat detection within IT infrastructures. Drawing from recent research and developments, the study underscores the potential of these techniques in outmaneuvering conventional security models, while also shedding light on the inherent challenges and areas for future exploration.

 View pdf
View pdf


As Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems increasingly weave into the fabric of diverse sectors, their intricate and often opaque decision-making processes pose challenges to users and stakeholders alike. The 'black box' nature of AI, especially deep learning models, highlights a pressing need for transparency and interpretability. This paper delves into the significance of making AI decisions transparent and provides a comprehensive exploration of methods aimed at demystifying AI processes. Through the lens of Explainable AI (XAI) and advanced visualization tools, we underscore the importance of bridging the chasm between sophisticated AI operations and human-centric understanding. By fostering transparency, it is anticipated that AI systems can not only enhance efficacy but also fortify trust, ensuring that decisions are both informed and explicable.

 View pdf
View pdf


Natural Language Processing (NLP), a branch of artificial intelligence, is gaining traction as a potent tool for business analytics. With the proliferation of unstructured textual data, businesses are actively seeking methodologies to distill valuable insights from vast textual repositories. The introduction of NLP in the realm of business analytics offers a transformative approach, automating traditional manual processes and fostering real-time, data-driven decision-making. From sentiment analysis to text summarization, NLP is facilitating businesses in deciphering consumer feedback, predicting market trends, and breaking down linguistic barriers in the age of globalization. This paper sheds light on the evolution of NLP techniques in business analytics, their applications, and the inherent challenges and opportunities they present.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of the widespread application of artificial intelligence technology, international Chinese language education is taking on new characteristics. The next generation of artificial intelligence is profoundly impacting the global education landscape and transforming the methods of knowledge production, driving the digitization of international Chinese language education and innovating all elements of education. It is systematically constructing a new ecosystem for the future of international Chinese language education, attracting extensive attention and lively discussions in the education field, including the domain of international Chinese language education. This paper, through a review of the application of computer technology in the field of Chinese language teaching and a discussion of the challenges and opportunities it currently presents, analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of artificial intelligence technology in the context of international Chinese language education. It offers strategies for Chinese language teachers to effectively utilize artificial intelligence technology, employ flexible teaching methods to address challenges, and enhance teaching effectiveness.

 View pdf
View pdf




