

Volume 16 Issue 11
Published on November 2025
Synthetic fertilizers and herbicides are widely recognized for their harmful impacts on the environment. Lemna minor, a fast-growing aquatic plant, is a possible sustainable alternative due to its excellent absorption capacity and ability to be converted into green manure. Addtionally, it can serve as phytoremediator to absorb toxic chemicals in polluted water. In this study, Lemna minor or duckweed was exposed to ibuprofen, glyphosate, ibuprofen and glyphosate, and a control. Ibuprofen and glyphosate were used to test the duckweeds’ absorption capacity, as measured by duckweed biomass. The treated duckweed was converted into green manure by mixing it into a soil mixture. The manure, inorganic fertilizer, and a control group were then applied to kale. Duckweed-based green manure, which is an organic fertilizer, was studied to see if it could replace inorganic fertilizer. Unexpectedly, the green manure treated with glyphosate and, at times, both glyphosate and ibuprofen increased kale growth, contradicting glyphosate’s intended function as an herbicide to inhibit plant growth. These findings suggest duckweed as a possible solution to low-cost wastewater treatment and eco-friendly agriculture, though further research is needed to address long-term effectiveness.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of modern urbanization, excessive concentration of population and economic activities in core areas has intensified problems such as congestion, housing shortages, and environmental stress, prompting cities to evolve toward multi-centered spatial structures. This study explores the interaction between rail transit accessibility and urban spatial decentralization, using Boston as a representative case. Drawing on accessibility theory, decentralization theory, and the Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) model, the research combines theoretical analysis with empirical observation to examine how Boston’s century-long rail transit evolution has guided the redistribution of population, industry, and land use. The findings reveal that improved accessibility along rail corridors has fostered the emergence of new sub-centers—such as Kendall Square, Alewife, and Quincy Center—where innovation, residence, and commerce coexist, forming a balanced polycentric structure. The study concludes that rail transit acts not only as a transportation system but also as a structural mechanism for spatial reorganization, enhancing economic vitality, social equity, and environmental sustainability. Limitations include reliance on secondary data and contextual constraints of the Boston case. Future research should integrate GIS-based spatial modeling and comparative analyses across diverse urban contexts to further clarify the causal mechanisms linking transit development and spatial restructuring.

 View pdf
View pdf



(1) Background: To address the issues of tobacco flue-cured tobacco particles clogging sieve holes during vibration screening, which affects detection accuracy and causes material mixing, (2) Method: The CFD-DEM coupling method was employed to simulate the dynamic behavior of flexible tobacco particles during the cleaning process. By introducing a viscoelastic surface energy contact model, the influence of operational parameters on cleaning efficiency was systematically analyzed. (3) Results: Within the inlet velocity range of 12 m/s to 20 m/s, the optimal flow field structure was achieved at 16 m/s. At a vibration frequency of 50 Hz, the system reached optimal energy transfer efficiency with the most uniform particle velocity distribution. Although high-frequency vibration improves cleaning efficiency, it intensifies particle force fluctuations. (4) Conclusion: This study provides a theoretical basis for the intelligent design of tobacco flue-cured tobacco cleaning devices.

 View pdf
View pdf


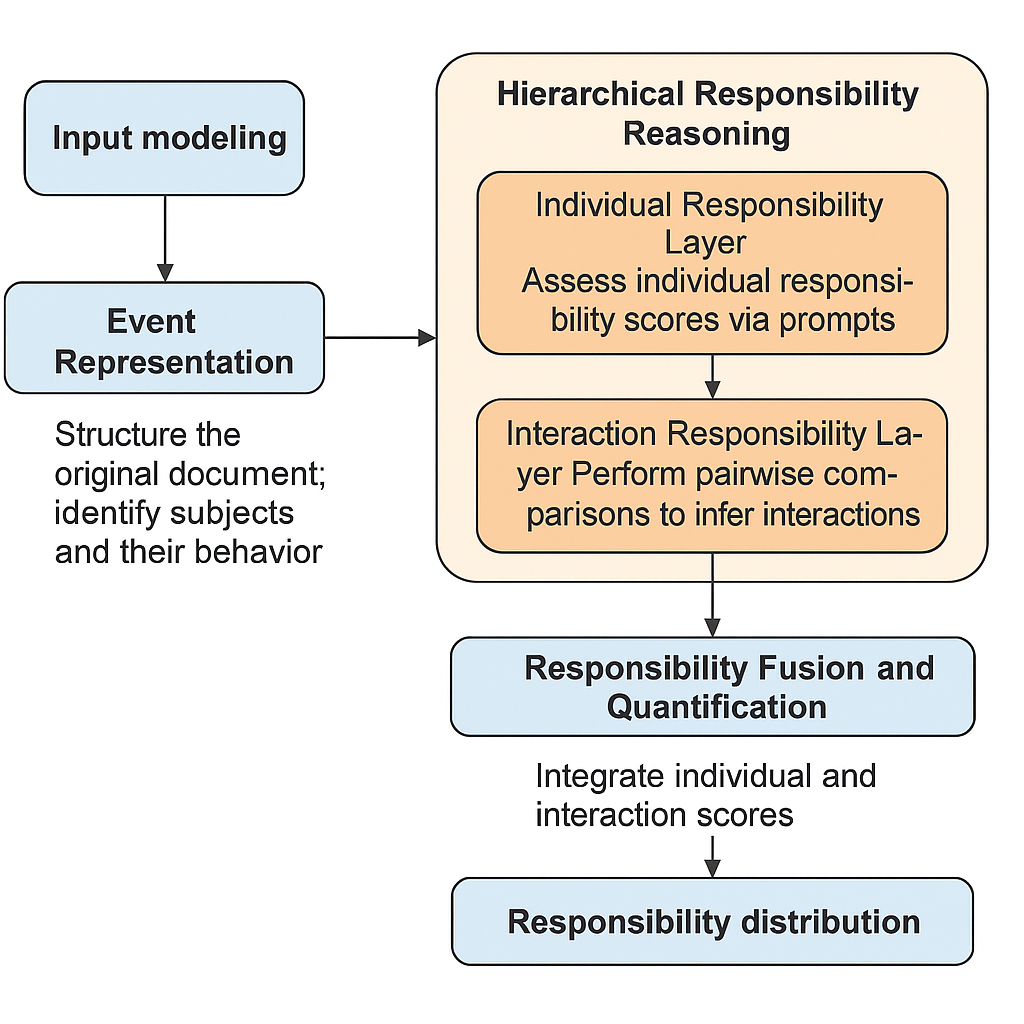
In response to the challenges of complex multi-agent responsibility division and low efficiency in manual judgment in telecommunications operators’ customer complaint handling, this paper proposes a multi-agent interaction responsibility determination method based on Large Language Models (LLMs) and Prompt Engineering. Taking complaint texts as input, the method constructs a hierarchical reasoning framework consisting of an individual layer and an interaction layer. The individual layer analyzes each agent’s responsibility fulfillment behavior, while the interaction layer depicts responsibility transfer relationships among agents. A responsibility fusion mechanism then integrates these analyses to generate a comprehensive responsibility distribution. This method achieves automated and interpretable multi-agent responsibility determination, offering a new technical approach and theoretical foundation for intelligent customer service, responsibility tracing, and service quality evaluation.

 View pdf
View pdf




