1 Introduction
The innovation-driven development strategy is a long-term national strategy in China. Innovation, as one of the primary sources of core competitiveness for major global economies, is crucial for seizing the initiative in development by mastering the high ground of innovation [1].President Xi, in his report at the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China and in multiple significant speeches, has emphasized the importance of cultivating innovative entities, optimizing the growth environment for tech-based small and micro enterprises, and forming an open innovation ecosystem with global competitiveness. With the advancement of new-generation artificial intelligence technologies, data, known as the “new oil of the era”, has become a core resource for high-quality development in the digital and national economies. It is a key driving force for the integration of the digital and real economies. Data empowerment involves applying big data and artificial intelligence technologies to critical aspects such as technological research and development, business process reengineering, and business model innovation [2]. This application extends the original capabilities of relevant entities and generates new capacities, continuously fostering new industrial patterns and models [3]. Data empowerment provides new momentum for industrial innovation, effectively optimizing production processes, improving energy efficiency, reducing production costs, minimizing resource wastage, and promoting technological research and development to achieve industrial innovation. Therefore, exploring the internal mechanisms and pathways of data-empowered industrial innovation is of great significance for cultivating new momentum and advantages in industrial integration and advancing high-quality socialist economic development.
Existing research indicates that data empowerment can promote industrial innovation through multiple pathways. First, it optimizes resource allocation and reduces costs. By leveraging the integration and analytical advantages of big data technology, resource misallocation can be effectively minimized [4]. Additionally, the information carried by data can optimize decision-making in production and operations, promote intelligent manufacturing and production model upgrades, and reduce resource waste in industrial production processes, further lowering innovation costs [5]. Second, it promotes the collaborative creation within and outside the industry. Data can flow between different entities within and outside the industry, transmitting and linking their needs [5], thereby improving the accuracy of information search and analysis and achieving precise demand matching. Data empowerment enables diverse entities within and outside the industry to engage in cross-time and cross-regional collaborative innovation, absorbing knowledge spillovers through R&D cooperation, thus realizing internal and external knowledge synergy and enhancing the industry's innovation capabilities [6]. Third, it enhances the capability levels of relevant entities within the industry. Data technology enhances entities' abilities to acquire, control, and manage resources [7], aiding in the development of more innovative resources. Additionally, digital technology can help organizations implement emerging business models such as virtual teams, facilitating resource collaboration and innovation among different organizations within the industry [8]. Consequently, data empowerment can significantly improve the ability of entities within the industry to integrate innovative resources, unleash their potential in the innovation process, and ultimately enhance innovation efficiency within the industry.
Overall, although existing literature acknowledges the crucial role of data empowerment in industrial innovation, it often broadly and descriptively highlights the enabling role of big data technology or data itself in individual aspects such as human resources, production, and dynamic resource allocation. There is a lack of comprehensive discussion on the internal mechanisms of data empowerment. Given the unique characteristics of data-driven industrial innovation, it is essential to conduct in-depth analyses based on specific cases to understand the empowerment effect on industrial innovation in local contexts. Addressing the gap between reality and theory, this paper focuses on the "internal mechanisms of data-driven industrial innovation," using the Machine Tool Industry Brain in Taizhou as a case study to elucidate these mechanisms. The aim is to provide theoretical and practical references for the development of industrial innovation.
2 Literature Review
2.1 Industrial Innovation
In 1912, Schumpeter first proposed the concept of innovation, defining it as the introduction of new products, processes, or systems, such as producing new products or using new technologies to produce old products [9]. Industrial innovation refers to the process within or across industries where technical, product, model, and service iterations and changes occur [10], optimizing industrial structure, improving efficiency, and increasing value [11]. With the deepening of digital transformation within industries, data has increasingly penetrated various stages of production and manufacturing, becoming a critical factor in industrial innovation development. It can promote technological, model, business format, and institutional innovation within industries [12]. Li Ying (2021) argue that data resources are crucial for industrial R&D, production, and operation [13]. By fully exploiting data resources, dual innovation combining breakthrough and incremental innovation can be achieved, linking traditional industry upgrading and transformation. Additionally, the development of digital technology has gradually become the mainstream of industry "intelligence." The cross-penetration of various technologies not only reshapes industries, contributing to the construction of collaborative industrial innovation systems but also fosters the emergence of new industries such as digital manufacturing, industrial internet platforms, and industrial robots [13].
Although scholars have noted the significant role of data in industrial innovation, most analyses focus on data resource utilization and the driving force of data technology, lacking a comprehensive examination of both aspects. Current research on industrial innovation tends to emphasize macro-logical perspectives and lacks detailed studies on the micro-mechanisms and implementation pathways of innovation. This paper integrates the impact of data resources and data technology on industrial innovation, exploring the internal mechanisms of industrial innovation from the perspective of data empowerment to enrich theoretical research in this area.
2.2 Data Empowerment
The concept of data empowerment originally stems from the empowerment concept in human resource management theory [14], which refers to the decentralization of authority from top to bottom within enterprises to provide employees with additional information and resources, aiming to enhance their work capabilities [15]. In the era of big data, empowerment has once again become a hot topic in academia. With the rapid development of data mining and machine learning technologies, static stored data has become a research focus, with scholars gradually recognizing the potential value space within massive data sets [16]. In theoretical research, data empowerment covers a wide range of topics, including agricultural production, tourism, healthcare, e-commerce, and manufacturing [17]. The key to data empowerment lies in the innovative application of data scenarios and the utilization of skills and methods, thereby enhancing the overall capabilities of specific systems and ultimately realizing the value of data empowerment [17].
Although data empowerment is an emerging concept, scholars at home and abroad have conducted extensive research on it, which can be divided into four areas: data empowerment and value co-creation, data empowerment and manufacturing upgrading, data empowerment and community issues, and data empowerment and disadvantaged groups. Domestic scholars tend to focus on the outcomes of empowerment, emphasizing the realization of data empowerment value through innovative data application scenarios and technologies [17]. For instance, Sun Xinbo and Su Zhonghai (2018) explored how data empowerment drives agile manufacturing in manufacturing enterprises through case studies [18]. In contrast, international research on data empowerment often inherits the concept of empowerment within organizations, emphasizing the distribution of rights among disadvantaged employees. When transitioning to data empowerment, international scholars focus more on empowering organizational teams through data and data technologies [17], especially the empowerment of disadvantaged groups. Spreitzer (2007) explicitly pointed out that the essence of empowerment is to stimulate the initiative of organizational members [19].
Based on the above research, this paper identifies two characteristics of data empowerment: first, providing data resource services. Relevant entities utilize digital technologies to acquire, analyze, and mine data resources, aiming to create new data capabilities previously unavailable, thereby generating new value [20]. Data resources are diverse, capable of intelligent combination [21], and highly valuable, making their use, development, and management significantly different from traditional resources. Hence, suitable data resource application service systems must be constructed based on different goals and needs [22]. Second, realizing data capability spillover among enterprises. Data capability refers to enhancing relevant entities’ ability to create value through data analysis and information utilization by linking people, objects, and information [23,24]. The existence of data resources alone does not automatically grant data capabilities, the flow of data resources is crucial for unlocking their value [17]. The development of sensors and the Internet of Things promotes the flow of data resources among enterprises, enabling them to innovate not solely based on internal resources and capabilities but by crossing technical, organizational, and geographical boundaries to acquire knowledge elements and absorb knowledge spillovers from partners [6], thereby promoting data capability spillover among enterprises.
2.3 Research Review
Industrial innovation involves creative changes in products, organizations, technologies, and markets to increase industrial added value, competitiveness, and sustainability. Data empowerment extends the connotation of industrial innovation within the context of deep digital transformation by exploring industrial innovation from the perspectives of data resource services and data capability spillover. Although existing literature has extensively explored industrial innovation and gradually acknowledged the importance of data, it often merely mentions data as a driver of industrial innovation without deeply analyzing the internal mechanisms by which data empowerment drives industrial innovation. In light of these research gaps, this paper integrates previous studies on industrial innovation, examines data empowerment from the perspective of industrial innovation, and explores the internal mechanisms and implementation pathways of data-empowered industrial innovation to better promote the development of industrial innovation. Thus, this paper holds significant theoretical and practical implications for industrial innovation.
3 Reaserch Design
3.1 Selection of Reaserch Method
This paper intends to explore how data empowers industrial innovation and discusses from which levels it empowers, which belongs to the category of "How" questions [25]. The aim is to open the "black box" in the process of the generation of the internal mechanism of data empowering industrial innovation. For this, this study decides to adopt exploratory single case study. On one hand, longitudinal case studies help to tell a good story, can better help identify the phenomena and truth behind the problem, and analyze the internal mechanism of process changes [26]. On the other hand, the rich and detailed materials of a single case can better ensure the depth and breadth of the research, help to explain complex phenomena, and refine the laws and mechanisms behind the phenomena [25].
3.2 Case Selection
This article takes the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry Brain in Zhejiang Province as the research sample for the following reasons: Firstly, Taizhou City is an important base for manufacturing in China, and its machine tool equipment industry is one of the pillar industries. The Taizhou Machine Tool Industry originated in the 1970s, initially focusing on repairing and maintaining old machine tools. With the recommendation of reform and opening up, a group of talents with management and technical experience took advantage of their own strengths and market opportunities to start businesses, producing machine tool parts and imitation machine tools. After many years of development, Taizhou has formed a machine tool equipment mainly in Wenling and Yuhuan City, and a large number of large-scale CNC machine tool companies such as Heideman and Eastern CNC have emerged. Although the machine tool industry in Taizhou started late, it has now achieved a transition from producing single simple instrument lathes to producing a variety of CNC machine tools, improving the scale of the industry and product technology, and taking a "specialized and new" path with Taizhou characteristics; Secondly, in 2021, Zhejiang Province proposed for the first time the goal and significance of building an "industry brain", and the machine tool equipment industry in Taizhou actively responded and established the Machine Tool Industry Brain at the end of the year. The Machine Tool Industry Brain is led by the government, facing enterprises in the industry, and jointly with universities, research institutes, financial institutions, upstream and downstream of the industrial chain and other advantageous resources, to form an organization system that can provide public services and optimize the industrial ecology for the common needs of industry development and enterprise collaborative creation. The industry brain takes data linkage as the core, allowing industry data and related enterprises to organically combine on the chain, promoting the value fission of the machine tool industry. Up to now, the Machine Tool Industry Brain has 24.9073 million pieces of data and 130 million pieces of enterprise data, providing more than 2,000 chain-finding services for more than 1,000 enterprises, saving more than 1 million yuan in costs. In summary, the development path of the machine tool equipment industry in Taizhou is typical, and its mode of empowering industry innovation with the Machine Tool Industry Brain has replicable potential, which can be promoted to other industries to help industry innovation and upgrade. Based on this, this article will discuss from which levels data empowers industry innovation based on the case of the Machine Tool Industry Brain, and try to clarify the generation process of the underlying innovation mechanism, aiming to provide some reference for the innovation of the machine tool industry and manufacturing industry in our country.
3.3 Data Collection and Analysis
The data collection for this study mainly relies on field research and in-depth interviews, supplemented by secondary sources such as official website information and policy documents, ensuring data triangulation. The data collection is divided into two stages: In the first stage, the research team made multiple field visits to the Taizhou Machine Tool Industrial Park in Zhejiang Province, conducting in-depth interviews with various stakeholders such as those responsible for the industrial brain, machine tool engineers, and chairmen of machine tool companies. In the second stage, the research team used the internet to collect a large amount of secondary information related to the "Machine Tool Industry Brain", such as press releases, official website information, and broker reports. The release time of these materials is concentrated from the end of 2021 to 2023, which is the time when the industrial brain started, was built, and operated, ensuring timeliness and authenticity. Finally, the team collated interview materials, research materials, and secondary materials totaling 80,000 words, deeply mined case materials, refined the underlying mechanism of data-driven innovation and development of the machine tool industry, and further verified the research theme of this article based on relevant literature on data empowerment and manufacturing transformation.
3.3.1 Open Coding
Open coding is the primary step in refining materials, which is a process of conceptualizing and abstracting the materials. The specific steps are as follows: Firstly, this study was conducted by two researchers using a "back-to-back" coding form to induct and label the original case materials; then another researcher carefully read the original materials and compared the coding results until theoretical saturation. Finally, this study formed 24 subcategories, and part of the coding process is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Example of Open Coding
Excerpt from Raw Data |
Subcategory |
Integrate data resources from various sectors of the industry to establish three major data warehouses for enterprises, industries, and government, facilitating the organic integration and circulation of more data and related enterprises on the chain. |
Construction of Government-Enterprise Data Warehouses |
Utilize cloud storage for data related to production, inventory, sales, design, and management, establishing an enterprise-level big data analysis platform that enables lightweight, personalized, and modular services, thus addressing the issues of data silos and integrated applications at low cost. |
Cloudification of Resources |
Integrate resources from the supply-demand chain, equipment chain, and policy chain to build a think tank service system that integrates an expert database, knowledge database, and model database, providing industry data mapping services to small and medium-sized enterprises. |
One-Click Resource Linkage |
On the enterprise side, build comprehensive connections across all elements, the entire industrial chain, and the entire value chain based on an industrial internet platform, enhancing the efficiency of economic and social operations and the allocation of resource elements. |
Comprehensive Chain Connection |
The "Industrial Brain of the CNC Machine Tool Industry" has intelligently pushed over 100,000 pieces of industrial chain data, saving more than 20 million yuan in comprehensive digital application costs for 13 enterprises. |
Intelligent Data Push |
3.3.2 Spindle Coding
The axial coding is a further development of open coding, based on the intrinsic connection between initial categories, further mining deeper relationships, and thus inducing the main category. Axial coding presents the organic connection and pattern logic in the initial categories through the structural framework of "condition-action-result", constantly comparing data, so as to grasp the essence of the phenomenon [27]. This article uses axial coding to induce 24 sub-categories into 9 main categories, including the networking of production resources, the sharing of data development capabilities, and the win-win of collaborative creation, etc. Specific coding examples are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Example of Axial Coding
Dimension |
Main Category |
Subcategory |
Resource Empowerment |
Networking of Production Resources |
Construction of Government-Enterprise Data Warehouses, Cloudification of Resources |
Diffusion of Data Integration Capabilities |
Intelligent Data Push, One-Click Resource Linkage, Comprehensive Chain Connection |
|
Efficient Resource Allocation |
Streamlined and Efficient Financing, Accurate Demand Matching, Supply Chain Assurance |
|
Production Empowerment |
Intelligent Production Scenarios |
Algorithm Optimization, Production Digital Twinning |
Sharing of Data Openness Capabilities |
Overcoming Technical Challenges, Interoperability of Manufacturing Technologies, Shared R&D Services |
|
Upgrading of Smart Manufacturing |
Real-Time Production Monitoring, Intelligent Solutions, Enhancing Production Efficiency Through Research |
|
Ecosystem Empowerment |
Two-Way Integrated Sharing |
Value Chain Sharing, Common Industrial Services |
Radiation of Data Dissemination Capabilities |
Collaborative R&D Between Industry and Academia, Think Tank Platform Services |
|
Collaborative Creation for Mutual Benefits |
Co-opetition Among Enterprises, Efficient Cross-Sector Collaboration, Integration and Co-Creation Between Industry and Urban Areas |
3.3.3 Selective Coding
Selective coding is a deep refinement and high abstraction of the main categories, drawing out the development context of the "story", and constructing the core concepts that summarize all the main categories. This study conducts a deep refinement and high abstraction of 9 main categories, and the core categories obtained are data resource services, data capability spillover, and industrial innovation realization. The story line described by this core category can be summarized as: data empowerment provides personalized and customized data resource services for related subjects, thereby realizing the spillover of data capabilities between related subjects, and ultimately promoting the realization of industrial innovation. For the specific coding process, see Table 3.
Table 3. Example of Selective Coding
Core Category |
Definition |
Main Category |
Data Resource Service |
Various resources are presented in digital form, offering services such as digital transformation, intelligent production scenarios, and data resource sharing. |
Networking of Production Resources, Intelligent Production Scenarios, Two-Way Integrated Sharing |
Data Capability Spillover |
The digital platform generates data capabilities in value creation through the connection, sharing, and analysis of data resources. By leveraging data technology to overcome spatial and temporal limitations, these data capabilities produce spillover effects, thereby breaking down technical and knowledge barriers between different entities. |
Diffusion of Data Integration Capabilities, Sharing of Data Openness Capabilities, Radiation of Data Dissemination Capabilities |
Industrial innovation realization |
Within the industry, iterations and transformations in production, models, and services are realized. |
Efficient Resource Allocation, Upgrading of Smart Manufacturing, Collaborative Creation for Mutual Benefits |
3.3.4 Theoretical Saturation Test
During the coding process, the research team always adhered to the principle of "data-theory-model" iterative adjustment, ultimately achieving theoretical saturation [28]. At the same time, this study coded and analyzed the reserved materials and supplementary texts. The results obtained were consistent with the above, and no new concepts or categories were generated. Therefore, it can be considered that the theory has passed the saturation test and no new theoretical revisions will occur for the time being. In this regard, based on previous research and grounded theory, the data obtained in this study empowers the integrated theoretical model of industry innovation as shown in Figure 1.
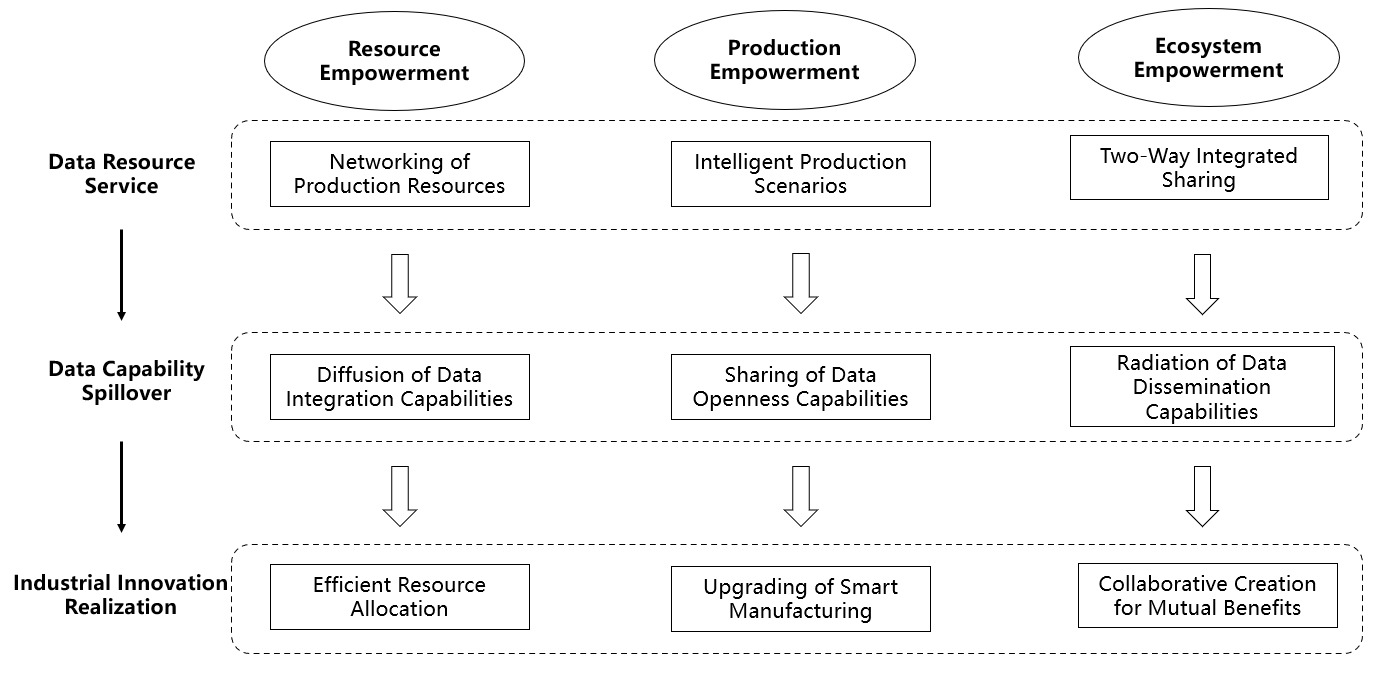
Figure 1. Integrative Theoretical Model of Data Empowerment Driving Industrial Innovation
4 Research Found
4.1 Data Resource Service
Resource service refers to the adoption of corresponding resource processing methods to promote the transformation of an organization from resources to capabilities in response to different scenario needs [29]. With the development of artificial intelligence technology, data resources have gradually become a key element in realizing industrial innovation [19]. This study believes that data resource service refers to the use of big data technology and digital platforms to "twin" physical resources, forming a one-to-one corresponding data resource, and providing specific data resource services for different scenario needs. In the practice of Taizhou Machine Tool Industry Brain, data resource services are presented in two aspects. First, with the help of the Industrial Brain platform and big data technology, the production resources of the machine tool industry are mapped into corresponding data resources. This twinning process not only includes the digital transformation of physical resources, but also uses cloud computing to "network" data resources, enabling data resources to be stored, circulated and shared in the cloud. In the "Cloud Warehouse Data Fusion" module developed by the Industrial Brain, different business systems such as enterprise resource management systems and manufacturing execution systems have been docked, storing production, inventory, sales, design, etc. into the cloud, promoting data interconnection between factories. Secondly, in response to service needs in different scenarios, the Industrial Brain can provide targeted data resource services. The Taizhou Machine Tool Industry Brain has built a digital twin space, providing a virtual processing environment model and digital model library through modules such as "Twin Tool Library", "Virtual Product" and "Virtual Factory", helping engineers to debug, design, and test production lines online virtually, optimize production line performance and avoid production risks in advance. At the same time, the Industrial Brain platform also provides personalized algorithm customization services, customizing algorithms to optimize production processes according to the production requirements of different factories, in order to improve the timeliness and accuracy of order completion, thereby solving the pain points of production and operation management. Data resource services have successfully promoted the circulation, interaction and sharing of resources within and outside the industry, improved the efficiency of resource utilization and production, and promoted the construction of a two-way interactive ecosystem in the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry. The Machine Tool Industry Brain is a platform for data resource exchange, realizing the interconnection of multi-source data between different production systems and equipment through standardized interfaces. At the same time, the Industrial Brain also promotes the connection of the innovation chain and value chain of the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry, in order to realize the value creation of data resources. On the government side, the Industrial Brain focuses on building sub-scenes such as industry knowledge libraries, third-party testing platforms, and industry maps, integrating government and enterprise business scenarios, providing public services for enterprises, and promoting the common sharing of resources within and outside the industry. In summary, data resource services, through the application of big data technology, realize the "digital twinning" of physical resources, provide differentiated data resource services for different scenarios, promote the formation of a two-way interactive industrial ecosystem, and provide prerequisite support for industrial innovation.
4.2 Data Capability Overflow
Data capability spillover refers to the enhancement or generation of corresponding value creation data capabilities by relevant entities through the processing, utilization, and analysis of data resources [30]. This capability, supported by digital platforms and data technologies, is purposefully transmitted within or outside the industry through transmission, sharing, and diffusion. In the process of industrial innovation, data capability spillover becomes a key driving force. Data capability spillover is not limited to between enterprises, but involves multiple entities within the industry, including universities, research institutes, etc. These organizations can fully utilize data capabilities to achieve resource, technology, and knowledge sharing, forming a community of collaborative creation within and outside the industry. Specifically, data capability spillover includes data integration capability diffusion, data opening capability sharing, and data dissemination capability radiation. The industrial brain plays a guiding and collaborative role in this process, promoting the spillover process of data capabilities.
Firstly, data integration capability diffusion refers to the machine tool industry brain collecting and organizing originally scattered and fragmented data resources, forming three major data warehouses of industry, enterprise, and government, and promoting the integration and fusion of data resources. The machine tool industry brain realized the basic data of more than 600,000 enterprises in the upstream, midstream, and downstream of the national machine tool industry chain at the initial stage of construction, and built a comprehensive connection mode of all elements, full industry chain, and full value chain, providing relevant entities with abundant and diverse data resources, enhancing their data integration capabilities. At the same time, powerful platform infrastructure, such as the provincial industrial brain comprehensive support system, supET/OS base capability, Taizhou Industrial Internet platform, etc., provide strong underlying technical support for the diffusion of data integration capabilities of relevant entities, realizing data sharing and efficient data analysis and processing among entities. Secondly, data development capability sharing refers to the machine tool industry brain improving the ability to develop data resources through various functions and services, and realizing the sharing of this ability among various entities, thereby promoting the construction of a wide cooperation network within the industry: (1) Construction of a technical exchange platform. Enterprises can connect with relevant industry experts and engineers through the "Intelligent Chain Finding" module, using autonomous search or algorithmic precise recommendation methods, to solve technical problems in the production process. At the same time, during the entire problem-solving process, the industrial brain will continuously follow up the problem, promote the solution of the problem, and thus promote technical interaction between enterprises. (2) R&D of shared laboratories. The shared laboratory platform mainly provides various public services such as application analysis, technical design, sample testing, invention patent transactions, etc., for the numerical control system and machine tool parts field, providing help in terms of experimental scenarios, testing needs, professional technical support, etc., for small and medium-sized enterprises, thereby realizing the sharing of R&D experience and promoting the improvement of R&D capabilities within the industry. Data dissemination capability radiation is the machine tool industry brain radiating valuable data capabilities from within the industry to inside and outside the industry. Taizhou machine tool enterprises and various research institutes have accumulated a large amount of professional knowledge and technical experience in the process of R&D. The machine tool industry brain actively gathers this information, forms a machine tool knowledge database, integrates professional knowledge and patent services of the machine tool industry at home and abroad, and promotes the storage and circulation of machine tool production and manufacturing knowledge. The machine tool industry brain radiates this knowledge inside and outside the industry through its own technical advantages, further laying the foundation for integration and co-creation inside and outside the industry.
Overall, as a key element in promoting industrial innovation, data capability spillover has achieved significant results in the innovative development of Taizhou machine tools. Through data capability spillover, not only is knowledge circulation and sharing realized, but cooperation between different entities is also promoted, providing strong support for the sustainable development of the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry.
4.3 Industrial Innovation Realization
The realization of industrial innovation refers to the use of data resource services and data capability spillover to promote the emergence of new technologies, new products, new models, and new business forms within the industry, enhancing the competitiveness and development level of the industry. The realization of industrial innovation is the purpose of data empowerment, and data empowerment drives the realization of industrial innovation mainly from three aspects. Firstly, the efficient allocation of resources aims to improve the utilization efficiency of resources within the industry, by realizing the automated response of resources, helping various entities to manage resources efficiently, coordinated, sustainable, and accurately. In the machine tool industry brain, the function of "linking and finding links" provides personalized digital services for enterprises, meeting the needs of enterprises of different scales. Large enterprises can open procurement to upstream enterprises on the platform, medium-sized enterprises can accurately match demands through "enterprise portraits", and small and micro enterprises can tap into customer resources to achieve dislocation competition. This personalized service helps enterprises of different scales to operate in a better coordinated manner, forming an efficient allocation of resources. Secondly, the upgrade of intelligent manufacturing aims to promote the intelligent transformation of the production level within the industry. Intelligent production scenarios can be monitored in real time, engineers can remotely view production lines, equipment, etc., and at the same time, the industry brain platform uses digital twin technology to generate intelligent production workshops, providing intelligent solutions for factory production. This also helps to shorten the cycle from enterprise R&D to market application, reduce R&D costs, and promote the development of new production technologies, thereby promoting the technological progress and production upgrade of the industry. Finally, collaborative creation for win-win aims to promote the integration of the industry. The industry brain platform builds a two-way shared ecological model to support the complementarity and efficient collaboration between enterprises. The machine tool industry brain provides sharing of various resources, forming a community of collaborative innovation in industry, academia, and research. At the same time, the construction of the industry brain has strengthened the integration of industry and city, promoted the clustering and chaining of the industry, and achieved efficient collaboration and co-creation between different fields and industries. In general, the goal of data empowerment of the industry is to achieve industrial innovation, through mechanisms such as efficient resource allocation, intelligent manufacturing upgrade, and collaborative creation for win-win, to provide solid support for industrial innovation and development.
4.4 The Inherent Mechanism of Data Empowerment Driving Industrial Innovation
The "Machine Tool Industry Brain" is a platform for the digital transformation and intelligent upgrade of the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry. It follows the data empowerment mechanism path of "data resource service - data capability spillover - industrial innovation realization" in the process of promoting industrial innovation development. It integrates resources, production, and ecological levels to create an advantage for the overall innovation development of the data-empowered industry. In the role of data empowerment at the resource level, the internal resources of the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry are presented in a digital form, and are networked through "resource clouding", promoting the high-speed flow of resources within the industry, improving the efficiency and potential value of resources, and providing a richer resource base and combination method for the industry. In the role of data empowerment at the production level, the blessing of computing power and algorithms has improved the level of automation and intelligence in production. Through deeper analysis, mining, and application of data resources, a more efficient production mode is provided for industrial innovation. In the role of data empowerment at the ecological level, by building a two-way interactive ecosystem, it promotes the efficient integration of industry, academia, and research, improves the synergy and innovation level of the ecosystem, and provides a broader ecological environment and opportunities for industrial innovation. Resource empowerment, production empowerment, and ecological empowerment are not completely independent, but are interdependent and mutually promoting. Data empowerment of resources is the basis and premise of production and ecological empowerment. High-quality, diversified, and networked data resources support the development of data-empowered production and ecology, improving the efficiency and value creation ability of data use; data-empowered production is the core of industrial innovation development, and the level of production determines the ability of high-quality development and innovation in the industry. The Machine Tool Industry Brain has realized the networking and intelligence of internal production in the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry, enhancing the competitiveness and creativity of the industry; data-empowered ecology is the driving force for industrial innovation development [31]. The Machine Tool Industry Brain platform provides a broader space for the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry, breaking the spatial and geographical limitations of knowledge spillover, and promoting collaborative innovation within and outside the industry. At the same time, the development of data-empowered production and ecology can promote the optimization and growth of data resources, forming a virtuous cycle.
5 Conclusion and Discussion
5.1 Main Conclusion
From the perspective of data empowerment, this article examines the inherent mechanism and path realization of innovation in the machine tool industry, and extracts the data empowerment industry innovation model of "Data Resource Service—Data Capability Spillover—Industry Innovation Realization". The core conclusions of this article are as follows:
First, the inherent mechanism of data empowerment driving industry innovation is achieved through the effects of resources, production, and ecology, providing comprehensive support and promotion for industry innovation. The interaction between these three levels not only has an impact at specific moments, but also forms a dynamic cycle. Resource empowerment is the basis for production and ecological empowerment, and the empowerment of production and ecology in turn promotes the optimization and growth of data resources, further promoting the efficiency and value creation of resources. This cyclical effect emphasizes the sustainability and evolution of data empowerment industry innovation.
Second, the path realization of data empowerment driving industry innovation follows the logic of "Data Resource Service—Data Capability Spillover—Industry Innovation Realization". Among them, data resource services and data capability spillover are not independent, but act in sync, complementing each other to achieve data empowerment. The data resource service process generates corresponding data capabilities, and the existence of the machine tool industry brain allows this data capability to circulate and share within the industry, breaking spatial and geographical restrictions to promote the spillover of enterprise data capabilities, and gradually empowering industry innovation.
Third, data empowerment is an important driving force for industry innovation, giving the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry a significant innovation advantage. Data empowerment improves the mobility and utilization of resources, optimizes production models, promotes collaborative innovation, and thereby enhances the competitiveness and creativity of the machine tool industry. This path of action reflects the key role of data empowerment in promoting industry upgrading and achieving sustainable development, highlighting the comprehensiveness and comprehensiveness of data empowerment in industry innovation, and laying a solid foundation for the future innovative development of the Taizhou Machine Tool Industry.
5.2 Theoretical Contribution
This article expands the theoretical boundaries and connotations of industrial innovation, and is a beneficial supplement and improvement to the research of industrial innovation. The theoretical contributions of this study are mainly reflected in the following three points: First, it deeply explores the inherent mechanism and path of data enabling industrial innovation. Although existing scholars have noticed the enabling role of big data technology or data itself in industrial innovation [32], the inherent mechanism of how data enables and then promotes the upgrade of industrial innovation is not clear. This study digs out the mechanism path of data enabling industrial innovation following the "data resource service—data capability spillover—industrial innovation realization", fully responding to the call of existing scholars for how data potential is transformed into actual social and economic value [22]. Second, it discusses industrial innovation from the perspective of data enabling, enriches and expands the research content of industrial innovation, and the connotation of data enabling is further expanded and extended. Existing research believes that data enabling is the process of applying data application scenarios, skills and methods to enhance the subject's ability and realize the value of data enabling [17]. This study is based on the background of industrial innovation, discusses the ways of data enabling, further subdivides data enabling into data resource services and data capability spillover, enriches the theory and connotation of data enabling, and supplements the research perspective of industrial innovation. Third, from a systemic perspective, it analyzes the inherent conditions for promoting the realization of industrial innovation. Existing research focuses more on the impact of data and its technology or application scenarios on a specific field of industrial innovation, such as industrial innovation efficiency analysis [33], etc., and lacks a generative discussion on the digitalization of industrial innovation. This study integrates the enabling mechanism of promoting the realization of industrial innovation from the perspectives of industrial resources, production, and ecology, and analyzes the role of data enabling at different levels in the realization of industrial innovation. Among them, resource enabling is the basis of production enabling and ecological enabling, production enabling is the key to the realization of industrial innovation, and ecological enabling is an important support for the realization of industrial innovation.
5.3 Management Suggestions
Facing the increasingly fierce global market competition and rapidly changing technological environment, industrial innovation is no longer a simple choice, but a necessary strategic deployment. In terms of the process of industrial innovation, the management suggestions in this article mainly focus on the following four aspects:
First, adapt to the requirements of the big data era, accelerate the digital construction and transformation of the industry. Actively promote the development of digital platforms, realize the sharing and utilization of data, resources, knowledge, and technology on the platform. Digital platforms can not only serve as hubs for information exchange, but also become incubators for innovation, by mining shareable processes in the production process, forming a comprehensive and dynamic knowledge database, realizing "process sharing", thereby promoting collaborative creation within the industry, and enhancing the industry's innovation ability and competitiveness.
Second, fully explore and release the potential of data in industrial innovation, and realize the efficient use and value creation of data resources. In the production process, conventional resources should be digitized for "twin" reproduction, corresponding one-to-one with physical resources, realizing the synchronous update and interaction of physical resources and data resources. At the same time, provide specific data resource services for different scenarios, provide data support for enterprises, generate corresponding data capabilities, and realize the spillover of capabilities supporting industrial innovation, promoting the upgrade and transformation of the entire industrial chain.
Third, build a good industrial ecology, promote the formation and development of industry-university-research collaboration alliances. Industrial ecology is an important environment and guarantee for industrial innovation. In this regard, the government should actively call on universities, research institutions, professional talent teams, financial institutions and other organizations to explore the operation mechanism of industry-university-research collaboration alliances, build a perfect industrial ecological system and enterprise development support system. Through industry-university-research collaboration alliances, rapid innovation in the industry can be achieved, the level of industrial technology can be improved, and "zero distance" between industry and innovation can be achieved.
Fourth, play the leading role of core enterprises in the industry, and achieve collaborative innovation and win-win development of the industrial chain. Core enterprises are important nodes in the industrial chain and important subjects of industrial innovation. Therefore, core enterprises should be based on the needs of forward-looking technology, actively play the role of "chain master" enterprises and leading enterprises, explore and promote the formation of joint forces of industry alliances, technology innovation alliances and other carriers, integrate high-quality resources in the upstream and downstream of the industry, and drive the cooperation and development of upstream and downstream enterprises. Through collaborative innovation within the industry, the optimization and upgrading of the industrial chain can be achieved, the value of the industrial chain can be enhanced, and the stability and sustainable development of the industrial chain can be promoted.
5.4 Research Limitations and Prospects
As an exploratory study, this article has certain limitations. First, this article is a single case study of the machine tool industry brain, which may lead to deficiencies in the universality of existing conclusions, and further multi-case studies should be carried out in the future to improve and verify the practical conclusions; second, it only explores the internal mechanism of industrial innovation under data empowerment from the aspects of industrial resources, production, and ecology, and lacks more in-depth research on the mutual influence and relationship of empowerment effects at different levels; finally, this article only proposes an integrated theoretical model of data empowerment for industrial innovation, and in the future, cross-level quantitative empirical tests should be carried out based on this research foundation to continuously revise and improve this theoretical model.
References
[1]. Zhang, K., Yu, L., Zhang, H., & others. (2023). Study on the impact mechanism and effect of digital transformation on innovation in high-tech industries. Statistical Research, 40(10), 96–108.
[2]. Beltagui, A., Rosli, A., & Candi, M. (2020). Exaptation in a digital innovation ecosystem: The disruptive impacts of 3D printing. Research Policy, 49(1), 103833.
[3]. Ou, C., Shao, Y., Cao, Y., & others. (2024). Research on the evolution process of the offshore wind power industry innovation ecosystem under digital and intelligent empowerment: A grounded analysis based on Mingyang Smart. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 41(15), 128–137.
[4]. Shi, B., & Li, J. (2020). Has the internet promoted specialization: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Management World, 36(4), 130–149.
[5]. Xia, J. (2023). Data elements empowering the high-quality development of China’s real economy: Theoretical mechanisms and path choices. Jiangxi Social Sciences, 43(7), 84–96+207.
[6]. Yang, Z., & Li, D. (2010). Innovation in Chinese manufacturing enterprises: Industry competition, social capital embedded in clusters, and technology strategy choices. Finance & Trade Economics, (6), 98–105+136.
[7]. Leong, C., Pan, S. L., & others. (2016). The emergence of self-organizing e-commerce ecosystems in remote villages of China: A tale of digital empowerment for rural development. MIS Quarterly, 40(2), 475–484.
[8]. Chi, M., Ye, D., Wang, J., & others. (2020). How can small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises in China improve new product development performance: A perspective based on digital empowerment. Nankai Business Review, 23(3), 63–75.
[9]. Eriksson, T., & Heikkilä, M. (2023). Capabilities for data-driven innovation in B2B industrial companies. Industrial Marketing Management, 111, 158–172.
[10]. Mendoza-Silva, A. (2020). Innovation capability: A systematic literature review. European Journal of Innovation Management, 24(3), 707–734.
[11]. Sun, T., Yang, D., & others. (2022). Recent research progress and prospects of emerging industries: A literature review. Industrial Economy Review, (1), 105–122.
[12]. Jiao, Y. (2020). Digital economy empowering manufacturing transformation: From value reshaping to value creation. Economist, (6), 87–94.
[13]. Li, Y. (2021). Study on the relationship between industry concentration and technological innovation in China’s high-tech manufacturing industry [Doctoral dissertation, Capital University of Economics and Business].
[14]. Eylon, D. (1998). Understanding empowerment and resolving its paradox: Lessons from Mary Parker Follett. Journal of Management History, 4(1), 16–28.
[15]. Kanter, R. M. (2010). Column: Powerlessness corrupts. Harvard Business Review.
[16]. Johanson, M., Belenki, S., Jalminger, J., & others. (2014). Big automotive data: Leveraging large volumes of data for knowledge-driven product development. In 2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) (pp. 736–741).
[17]. Sun, X., Su, Z., Qian, Y., & others. (2020). Current status and future prospects of data empowerment research. Research and Development Management, 32(2), 155–166.
[18]. Sun, X., & Su, Z. (2018). Data empowerment driving agile manufacturing in manufacturing enterprises: A case study. Management Science, 31(5), 117–130.
[19]. Spreitzer, G. (2007). Giving peace a chance: Organizational leadership, empowerment, and peace. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 28(8), 1077–1095.
[20]. Gupta, M., & George, J. F. (2016). Toward the development of a big data analytics capability. Information & Management, 53(8), 1049–1064.
[21]. Lu, M. (2023). Research on the path of data elements empowering high-quality development of the real economy under the new development pattern. Social Sciences Journal, (2), 143–151.
[22]. Günther, W. A., Rezazade Mehrizi, M. H., Huysman, M., & others. (2017). Debating big data: A literature review on realizing value from big data. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 26(3), 191–209.
[23]. Zhou, W., Deng, W., & Chen, L. (2018). Research on the process of value co-creation facilitated by platform enterprise data empowerment: A case study of Didi Chuxing. Journal of Management Sciences, 15(8), 1110–1119.
[24]. Chen, G., Zeng, D., Wei, Q., & others. (2020). Decision paradigm shift and enabling innovation under big data environment. Management World, 36(2), 95–105+220.
[25]. Phelan, S. (2011). Case study research: Design and methods. Evaluation & Research in Education, 24, 221–222.
[26]. Mao, J., & Li, G. (2014). Reflection on the “techniques” and “principles” of case study: A review of the China Business Management Case and Qualitative Research Forum (2013). Management World, (2), 111–117.
[27]. Talmar, M., Walrave, B., Podoynitsyna, K. S., & others. (2020). Mapping, analyzing and designing innovation ecosystems: The Ecosystem Pie Model. Long Range Planning, 53(4), 101850.
[28]. Pan, S. L., & Tan, B. (2011). Demystifying case research: A structured–pragmatic–situational (SPS) approach to conducting case studies. Information and Organization, 21(3), 161–176.
[29]. Sirmon, D. G., Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & others. (2011). Resource orchestration to create competitive advantage: Breadth, depth, and life cycle effects. Journal of Management, 37(5), 1390–1412.
[30]. Zhang, L., Zhao, S., Chang, Q., & others. (2019). Bridging the organizational hierarchy gap: Research on the dynamic construction mechanism of enterprise innovation capability. Management Review, 31(12), 287–300.
[31]. Jiang, X., & Zhang, L. (2023). Research on the path of digital transformation promoting green development in high-end manufacturing industry. Contemporary Finance & Economics, (9), 16–27.
[32]. Yin, Q., & Tian, Y. (2021). Mechanism of digital transformation affecting innovation efficiency in high-tech industries. China Science and Technology Forum, (3), 103–112.
[33]. Zhang, C., & Zhu, X. (2022). Research on the impact of digital finance on innovation efficiency in high-tech industries. Modern Management, 42(5), 105–112.
Cite this article
Yang,X.;Zhou,Y.;Guo,J. (2024). Case Study on the Inherent Mechanisms Driving Industrial Innovation through Data Empowerment. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,11,30-40.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang, K., Yu, L., Zhang, H., & others. (2023). Study on the impact mechanism and effect of digital transformation on innovation in high-tech industries. Statistical Research, 40(10), 96–108.
[2]. Beltagui, A., Rosli, A., & Candi, M. (2020). Exaptation in a digital innovation ecosystem: The disruptive impacts of 3D printing. Research Policy, 49(1), 103833.
[3]. Ou, C., Shao, Y., Cao, Y., & others. (2024). Research on the evolution process of the offshore wind power industry innovation ecosystem under digital and intelligent empowerment: A grounded analysis based on Mingyang Smart. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 41(15), 128–137.
[4]. Shi, B., & Li, J. (2020). Has the internet promoted specialization: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Management World, 36(4), 130–149.
[5]. Xia, J. (2023). Data elements empowering the high-quality development of China’s real economy: Theoretical mechanisms and path choices. Jiangxi Social Sciences, 43(7), 84–96+207.
[6]. Yang, Z., & Li, D. (2010). Innovation in Chinese manufacturing enterprises: Industry competition, social capital embedded in clusters, and technology strategy choices. Finance & Trade Economics, (6), 98–105+136.
[7]. Leong, C., Pan, S. L., & others. (2016). The emergence of self-organizing e-commerce ecosystems in remote villages of China: A tale of digital empowerment for rural development. MIS Quarterly, 40(2), 475–484.
[8]. Chi, M., Ye, D., Wang, J., & others. (2020). How can small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises in China improve new product development performance: A perspective based on digital empowerment. Nankai Business Review, 23(3), 63–75.
[9]. Eriksson, T., & Heikkilä, M. (2023). Capabilities for data-driven innovation in B2B industrial companies. Industrial Marketing Management, 111, 158–172.
[10]. Mendoza-Silva, A. (2020). Innovation capability: A systematic literature review. European Journal of Innovation Management, 24(3), 707–734.
[11]. Sun, T., Yang, D., & others. (2022). Recent research progress and prospects of emerging industries: A literature review. Industrial Economy Review, (1), 105–122.
[12]. Jiao, Y. (2020). Digital economy empowering manufacturing transformation: From value reshaping to value creation. Economist, (6), 87–94.
[13]. Li, Y. (2021). Study on the relationship between industry concentration and technological innovation in China’s high-tech manufacturing industry [Doctoral dissertation, Capital University of Economics and Business].
[14]. Eylon, D. (1998). Understanding empowerment and resolving its paradox: Lessons from Mary Parker Follett. Journal of Management History, 4(1), 16–28.
[15]. Kanter, R. M. (2010). Column: Powerlessness corrupts. Harvard Business Review.
[16]. Johanson, M., Belenki, S., Jalminger, J., & others. (2014). Big automotive data: Leveraging large volumes of data for knowledge-driven product development. In 2014 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) (pp. 736–741).
[17]. Sun, X., Su, Z., Qian, Y., & others. (2020). Current status and future prospects of data empowerment research. Research and Development Management, 32(2), 155–166.
[18]. Sun, X., & Su, Z. (2018). Data empowerment driving agile manufacturing in manufacturing enterprises: A case study. Management Science, 31(5), 117–130.
[19]. Spreitzer, G. (2007). Giving peace a chance: Organizational leadership, empowerment, and peace. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 28(8), 1077–1095.
[20]. Gupta, M., & George, J. F. (2016). Toward the development of a big data analytics capability. Information & Management, 53(8), 1049–1064.
[21]. Lu, M. (2023). Research on the path of data elements empowering high-quality development of the real economy under the new development pattern. Social Sciences Journal, (2), 143–151.
[22]. Günther, W. A., Rezazade Mehrizi, M. H., Huysman, M., & others. (2017). Debating big data: A literature review on realizing value from big data. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 26(3), 191–209.
[23]. Zhou, W., Deng, W., & Chen, L. (2018). Research on the process of value co-creation facilitated by platform enterprise data empowerment: A case study of Didi Chuxing. Journal of Management Sciences, 15(8), 1110–1119.
[24]. Chen, G., Zeng, D., Wei, Q., & others. (2020). Decision paradigm shift and enabling innovation under big data environment. Management World, 36(2), 95–105+220.
[25]. Phelan, S. (2011). Case study research: Design and methods. Evaluation & Research in Education, 24, 221–222.
[26]. Mao, J., & Li, G. (2014). Reflection on the “techniques” and “principles” of case study: A review of the China Business Management Case and Qualitative Research Forum (2013). Management World, (2), 111–117.
[27]. Talmar, M., Walrave, B., Podoynitsyna, K. S., & others. (2020). Mapping, analyzing and designing innovation ecosystems: The Ecosystem Pie Model. Long Range Planning, 53(4), 101850.
[28]. Pan, S. L., & Tan, B. (2011). Demystifying case research: A structured–pragmatic–situational (SPS) approach to conducting case studies. Information and Organization, 21(3), 161–176.
[29]. Sirmon, D. G., Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & others. (2011). Resource orchestration to create competitive advantage: Breadth, depth, and life cycle effects. Journal of Management, 37(5), 1390–1412.
[30]. Zhang, L., Zhao, S., Chang, Q., & others. (2019). Bridging the organizational hierarchy gap: Research on the dynamic construction mechanism of enterprise innovation capability. Management Review, 31(12), 287–300.
[31]. Jiang, X., & Zhang, L. (2023). Research on the path of digital transformation promoting green development in high-end manufacturing industry. Contemporary Finance & Economics, (9), 16–27.
[32]. Yin, Q., & Tian, Y. (2021). Mechanism of digital transformation affecting innovation efficiency in high-tech industries. China Science and Technology Forum, (3), 103–112.
[33]. Zhang, C., & Zhu, X. (2022). Research on the impact of digital finance on innovation efficiency in high-tech industries. Modern Management, 42(5), 105–112.









