

Volume 18 Issue 10
Published on October 2025This study addresses the supply-demand mismatch in elderly meal assistance services, with a specific focus on the operational challenges within mountainous counties, using a cross-regional comparative analysis of Jinyun County in Zhejiang (a basic guarantee model) and Songyang District in Shanghai (a quality-oriented benchmark). A mixed-methods approach combining qualitative and quantitative analysis was employed, grounded in fieldwork and data collection including site visits to 20 elderly canteens, 76 menu samples, 238 price data points, 15 operational observations, and verification of financial documents. This was supplemented by analysis of 18 policy texts and official data from 2021-2023 within an analytical framework of “policy design – practical implementation – service efficiency.” The findings reveal significant regional differences in service layout, financing, and refinement. Jinyun County exhibits a “small and scattered” model constrained by terrain, whereas Songjiang District utilizes a “central kitchen + distribution point” approach characterized by high social participation, universal aging-friendly modifications, and intelligent supervision. Based on these empirical results, the study proposes optimization pathways such as establishing county-wide coordinated service networks, diversifying operational mechanisms, promoting digital technology adoption, and strengthening standardization, thereby offering actionable strategies to enhance service quality and efficiency in mountainous regions.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) crisis not only triggered fear in the financial market at that time but also led to a series of chain reactions—such as deposit outflows from other banks, which further heightened their risk of failure. Therefore, it is crucial for China to optimize its financial institution supervision system to reduce the risks in the financial market. Based on the literature measurement and case anatomy, this paper analyzes the implications of the Silicon Valley banking crisis for the banking supervision of Chinese financial institutions. Specifically, the authors analyze the direct and indirect causes of the banking crisis in Silicon Valley, and from a regulatory perspective, put forward insights for the banking supervision of Chinese financial institutions. Based on this crisis, the enlightenments for Chinese finance are empowerment in regulation with technology, strengthening the current system by including medium-sized banks in the dynamic assessment of the liquidity coverage ratio, and promoting international collaborative governance.

 View pdf
View pdf


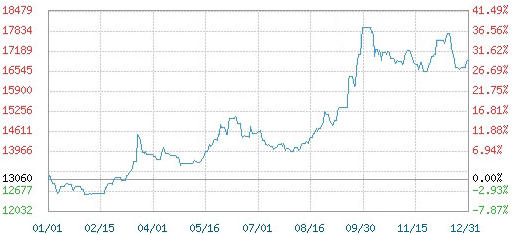
In recent years, the tire industry has faced a significant increase in trade barriers in the international market, and the situation of overcapacity in the domestic market has continued to deteriorate. China's tire industry has been under continuous pressure amid the dilemma of "revenue growth without corresponding profit increase". This paper elaborates on three aspects: an analysis of the current situation and a brief account of the causes of China's tire industry, an analysis of the risks faced by China's tire industry, and research conclusions and future trends of China's tire industry. The types of investment risks in China's tire sector are complex. The uncertainty caused by fluctuations in raw material prices: core raw materials such as rubber and carbon black are affected by multiple factors including global supply and demand, natural conditions, trade policies, and international situations, leading to significant price fluctuations. This has significantly increased production costs and eroded corporate profitability. Market competition is extremely fierce: overseas brands dominate the high-priced market, while local enterprises concentrate on competition in the mid-to-low-end sector. New entrants face challenges such as difficulties in market development and low brand recognition. Price competition and technological competition within the industry have further intensified market pressure. Although technological upgrading is the core driving force for progress, it involves high R&D costs, long cycles, and uncertain results. The industrialization of innovative technologies also needs to address challenges such as insufficient market recognition. If enterprises respond slowly, they may lose development opportunities or even be eliminated by the market. In addition, with the improvement of global environmental protection requirements and the strengthening of supervision, the environmental protection expenditures of tire manufacturers have increased accordingly, further compressing profit margins. Failure to adapt to regulatory adjustments in a timely manner may result in severe consequences such as penalties or production restrictions. When investing in this sector, investors need to comprehensively assess the above risks, formulate response plans, continuously pay attention to industrial trends and market dynamics, and dynamically optimize operational strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf




