

Volume 18 Issue 8
Published on September 2025
Based on sample data from A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges from 2011 to 2022, this study systematically examines the impact of new quality productive forces on organizational resilience in enterprises. The findings indicate that improvements in the level of new quality productive forces significantly enhance organizational resilience, and a robust positive correlation exists between the two. This effect is primarily realized through three mechanism pathways: alleviating financing constraints, improving investment efficiency, and promoting digital transformation. Heterogeneity analysis further reveals that the positive impact of new quality productive forces on organizational resilience is more pronounced among state-owned enterprises, large-scale enterprises, and enterprises located in regions with a well-developed technology market. This study adopts a micro-level perspective to explore how new quality productive forces affect organizational resilience at the enterprise level, enriching the relevant research in this domain. It provides both theoretical guidance and practical pathways for enhancing organizational resilience and offers scientific evidence and practical references for government policy-making aimed at supporting the development of new quality productive forces and strengthening enterprise resilience.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the dual drivers of deep global economic interconnection and the digital technology revolution, the complexity and uncertainty of international trade and capital flows have significantly intensified. Since China's reform of the exchange rate formation mechanism in 2005, the marketization of the RMB exchange rate has progressed steadily, leading to a significant increase in exchange rate flexibility. However, the problem of enterprises' exchange rate risk management capabilities lagging behind market development has become increasingly prominent. This paper focuses on the exchange rate risk management practices of two multinational enterprises, Apple and Toyota. Through case analysis and literature research, it systematically sorts out their four core strategies: supply chain regionalization, portfolio hedging with financial instruments, tax coordination, and digital-driven approaches. The study finds that Apple reduces its reliance on foreign currencies through global supply chain layout and dynamic hedging tools, while Toyota diversifies risks by relying on regional closed-loop production and multi-source supply networks. Both have achieved a reduction of over 85% in the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their profits. The research conclusions indicate that Chinese enterprises need to make breakthroughs in four aspects—strengthening supply chain resilience, applying derivative portfolios, integrating cross-border cash pools, and enhancing intelligent risk control—to promote the transformation of risk management from passive response to proactive prevention and control. This paper provides a reusable framework for foreign-related enterprises to address exchange rate fluctuations and holds important reference value for optimizing the risk management system under the "dual circulation" pattern.

 View pdf
View pdf


Earnings communication conferences (ECCs) have emerged as a critical interactive platform for information dissemination in China’s capital market, playing a pivotal role in mitigating information asymmetry between firms and investors. This paper conducts a systematic literature review of 15 key studies on ECCs published in top journals from 2020 to 2024, aiming to synthesize existing research and identify future directions. The review focuses on three core dimensions: the structure and functions of ECCs (with particular attention to the information-rich question-and-answer session), methodological approaches (including textual analysis of management tone, Q&A semantic similarity via BERT, and measurements of managerial traits (humor and narcissism), and theoretical frameworks (predominantly information asymmetry theory and signaling theory). Empirical findings highlight the impact of ECCs on market reactions, such as stock price dynamics and analysts’ forecast accuracy, as well as the influence of corporate characteristics (e.g., CSR performance) and managerial behaviors on communication quality. This review addresses the scarcity of comprehensive syntheses in extant literature, providing foundational insights for scholars exploring ECC-related topics and outlining avenues for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


To effectively prevent the outbreak of financial crises, constructing a resilient early-warning mechanism now constitutes a core mandate in macroprudential supervision. This paper employs literature review methods, combined with case analysis and the macroprudential regulatory framework, to explore optimization methods for early warning indicators of financial crises under new trends in financial regulation, and proposes innovative approaches. The paper investigates how to identify and quantify the three key drivers of financial crises: macroeconomic imbalances, market over-speculation, and financial institution risks; innovative approaches leveraging high-frequency financial datasets with ensemble learning algorithms to enhance the real-time accuracy of early warning indicators; the synergistic effects of cross-level regulatory information sharing, multi-stakeholder collaborative processes, and two-way feedback mechanisms; and demonstrates that constructing a multi-dimensional indicator system covering macro, market, and institutional levels can comprehensively reflect the accumulation and propagation of systemic risks. The utilization of big data feature engineering and machine learning models has significantly improved the prompt detection of warning signals, resulting in a marked decrease in false alarm rates. Information sharing and multi-party collaborative warning processes, combined with two-way feedback between market participants and regulators, have achieved closed-loop management and synergistic efficiency gains in the warning system.

 View pdf
View pdf


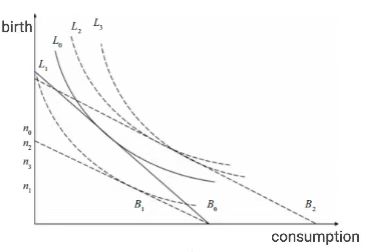
The current policy of delayed retirement in China is a hot topic, with many focusing on it to observe its potential impacts. This paper examines the mechanism through which China's progressive delayed retirement policy affects household fertility intentions. From the perspective of labor economics, this paper systematically analyzes the policy's dual effects using tools such as budget constraint lines and indifference curves. The study finds that the net effect of the policy on fertility intentions depends on the sophistication of supporting measures. Corresponding countermeasures are proposed: developing inclusive childcare services to fill the gap in intergenerational care, and strengthening policy support such as fertility subsidies, tax incentives, and protection of women's employment rights. This paper addresses the deficiency in existing research on the interaction mechanism between delayed retirement and fertility intentions, providing a theoretical reference for balancing responses to aging and long-term balanced population development.

 View pdf
View pdf


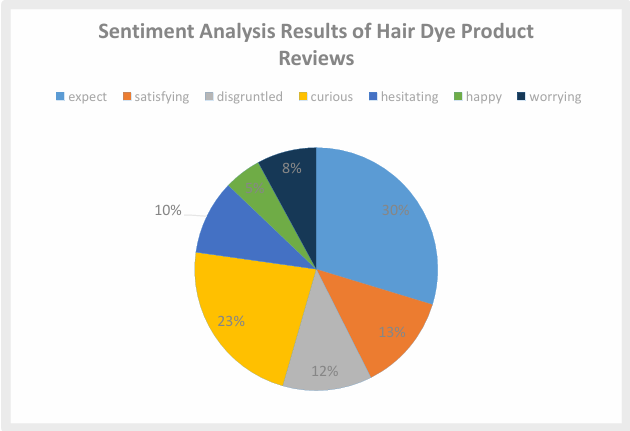
In the current digital era, consumer behavior on social media has become a key topic of research. An increasing number of scholars have found that consumers’ purchase intention in social media environments is influenced by multiple factors; however, more specific studies on young consumer groups with high consumption potential and distinctive consumption concepts remain insufficient. Therefore, this study focuses on the factors influencing the purchase intention of undergraduate students in Beijing with respect to social media. Using questionnaire surveys and online comment data, and applying sentiment analysis and correlation analysis, this study investigates the factors affecting the purchase intention of the undergraduate cohort in Beijing within social media contexts. The findings indicate that social media addiction influences purchase intention with mental health level as a mediating variable. In addition, the commenting environment on social media exerts a positive effect on purchase intention. These insights can help enterprises achieve precise targeting and content delivery. Enterprises may design interactive marketing activities on social media and build brand social communities, making effective use of users’ reliance on social media to provide communication platforms and cultivate a favorable social media environment, thereby promoting purchase behavior. Meanwhile, in terms of guidance for consumers themselves, the conclusions of this study can remind society and schools to actively carry out mental health courses and education on consumption concepts, thereby fostering a positive consumer culture and sound consumption values within the target group.

 View pdf
View pdf


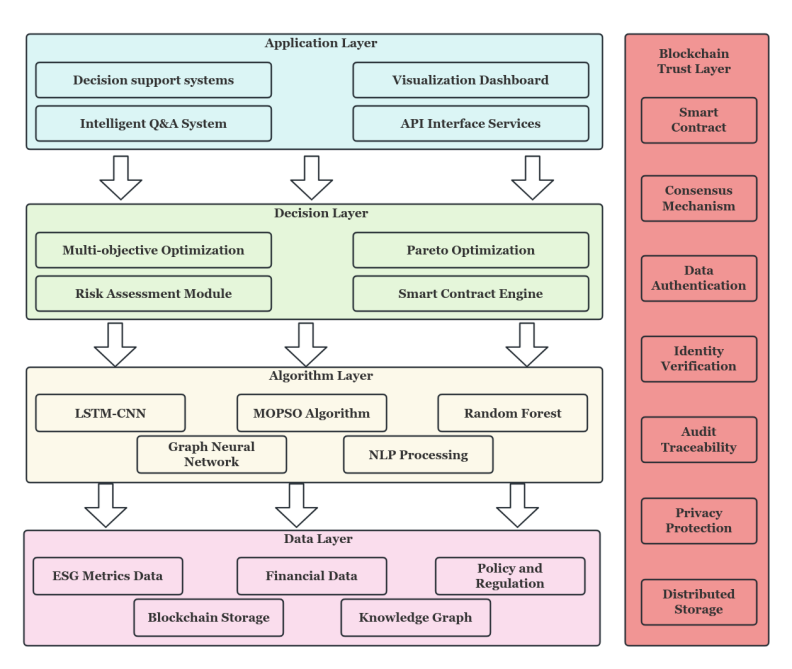
With the progressive advancement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), corporations encounter increasingly stringent Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance mandates. Conventional supply chain finance paradigms exhibit significant limitations in effectively integrating ESG considerations for decision-making optimization. While blockchain and artificial intelligence technologies are widely recognized as pivotal technological pathways for enhancing ESG transparency and achieving intelligent supply chain decision-making, a systematic integration framework remains absent. This study constructs an intelligent green supply chain finance framework grounded in ESG reporting standards. The research employs a sample of 120 enterprises from the CSI 300 constituent stocks, incorporating their ESG reporting data spanning 2019-2023. Through the application of deep learning and multi-objective optimization algorithms, a four-tier intelligent decision-making architecture encompassing data, algorithmic, decision-making, and application layers has been designed. Regarding technical implementation, this research employs a Long Short-Term Memory-Convolutional Neural Network (LSTM-CNN) hybrid model for ESG risk assessment, develops a supply chain finance resource allocation algorithm based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization, and constructs an ensemble learning prediction model integrating Random Forest and Gradient Boosting Decision Trees. The framework incorporates blockchain distributed storage technology to ensure data immutability, while utilizing knowledge graph and graph neural network technologies to achieve supply chain relationship modeling. Empirical investigations validate the framework's effectiveness and practicality, providing theoretical foundations and practical guidance for the profound integration of green finance and supply chain management. This research holds substantial value in promoting corporate sustainable development and facilitating the green transformation of the economy.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the development of modern information technology, digital transformation has become an inevitable trend for enterprise development. As a natural data center, the finance department is the primary point of breakthrough and a key focus of digital transformation. This paper employs an empirical analysis method, using the accounts receivable turnover rate of A-share non-heavy-polluting manufacturing listed companies from 2021 to 2023 as the dependent variable and the degree of enterprise digital transformation as the independent variable for regression analysis. Through research, it is concluded that digital transformation will inhibit the accounts receivable turnover of enterprises by affecting the sales expense ratio and the proportion of R&D investment. After replacing the explained variable twice with different data collection methods, the robustness test still holds. This study shows that the digital transformation process has an undeniable negative impact on enterprises, and enterprises should enhance their crisis prevention awareness to reduce transformation costs.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study focuses on eight cities within the Nanjing Metropolitan Area (NMA) and takes the manufacturing industry of the NMA as the research object. Using data from 2015 to 2020, we apply the orderliness model and the coupling coordination model. Ten manufacturing sectors within the NMA are selected, and a two-level evaluation index system for the NMA’s manufacturing industry is established to measure the development level of the sector and to explore its development trends. The results indicate that high-level advantageous industries overlap among the cities in the NMA; the external orderliness of the metropolitan manufacturing sector exhibits heterogeneity in the secondary subsystem; and the coupling and coordination among the manufacturing industries of the cities within the metropolitan area show relatively small differences. Based on these findings and the functional positioning of the eight cities, targeted recommendations are proposed for the future development of the NMA’s manufacturing industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


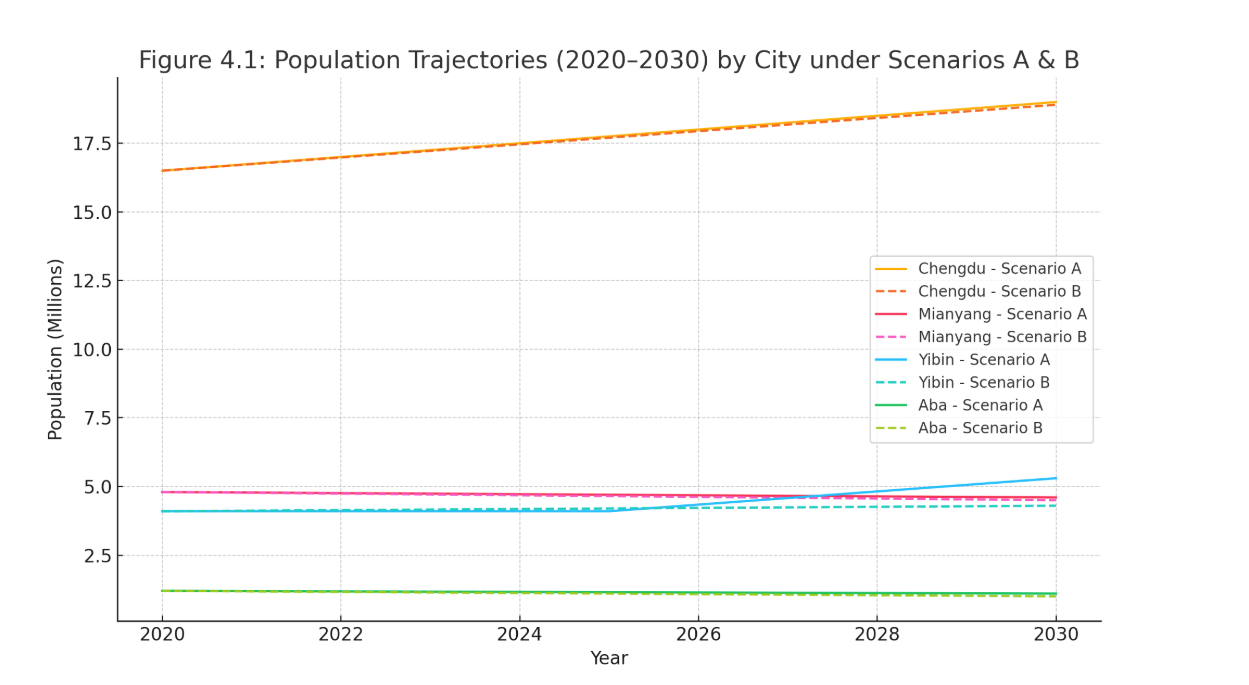
The research question guiding this paper is: How does education investment, as a knowledge-based investment, affect intra-provincial population migration within a regional modeling framework that examines the city of Yibin in Sichuan Province and its surrounding cities of Chengdu, Mianyang, and Aba, within China? We construct a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) to simulate migration flows under two policy scenarios: one featuring significant educational investment in Yibin, and the other assuming minimal intervention. The framework includes measurable socioeconomic variables and city-level characteristics to reflect the impacts of the changes in education infrastructure on migration patterns. The computational modelling based on MATLAB indicates that a specific and recurrent investment in education would have the prospective effect of slowly enhancing the demographic retention capacity of Yibin in terms of appealing to young families. The findings emphasize the need for education policy to be combined with overall urban development strategies. As a conclusion, we set some policy recommendations depending on the regions with regard to Yibin's structural limits and demographic characteristics.

 View pdf
View pdf




