1. Introduction
The share of global e-commerce retail sales in total global retail sales has been increasing, and the scale of the global cross-border e-commerce industry has continued to expand, as shown in Figures 1 and 2, with the transaction scale growing from 8.06 trillion yuan to 17.48 trillion yuan from 2017 to 2023 [1]. However, in recent years, uncertainties such as geopolitical conflicts and epidemic shocks have exacerbated the vulnerability of the global supply chain, causing cross-border e-commerce enterprises to face multiple challenges such as supply chain disruptions, logistical delays, and fluctuations in market demand [2].
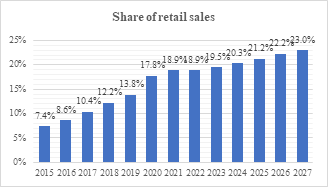
Figure 1. Global e-commerce retail sales account for an increasing share of total global retail sales
Data source: statista, GF securities development research center
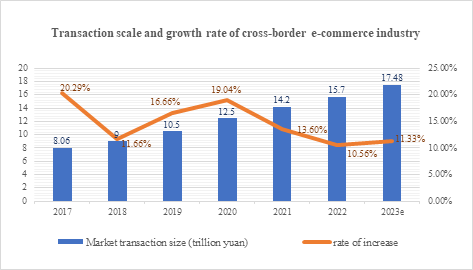
Figure 2. Transaction size and growth rate of cross-border e-commerce industry
Data source: network economy and social networks
In this context, enhancing cross-border e-commerce supply chain resilience (Supply Chain Resilience) has become a common focus of attention in both academic and practical circles. Supply chain resilience refers to the ability of enterprises to maintain operations and recover quickly in the face of internal and external shocks [3], and the rapid development of cross-border e-commerce provides a new perspective for supply chain resilience research.
This paper focuses on the construction of an evaluation system and exploration of improvement path of supply chain resilience of cross-border e-commerce enterprises. For cross-border e-commerce as a special industry, supply chain resilience is not only related to the stability of the enterprise's own operation, but also of strategic significance to guarantee the smooth flow of global trade and promote industrial upgrading. Meanwhile, supply chain resilience enhancement has multi-level needs and needs to be synergized at the regional and macro levels. Relevant scholars take cross-border e-commerce and logistics planning in Guangdong, China, as a case study, revealing problems in the synergistic development of the two, such as poor information sharing, and proposing the establishment of a mutual trust mechanism to enhance the level of synergy. This study emphasizes the relationship between logistics and e-commerce from the perspective of regional synergy [4]. Another part of scholars, from a more macroscopic perspective, analyzed the current development status of China's cross-border e-commerce supply chain and the problems of regulatory inconsistency, logistics imbalance, and imperfect payment and settlement, and further pointed out that the future supply chain will be developed in the direction of data-driven and intelligent [5]. This indicates that the optimization of supply chain management needs to be synergistically promoted from various aspects such as technology, regulations and operation mode.
Among the specific paths to address supply chain resilience enhancement, digital technology is seen as a key tool that can effectively complement the lack of policy synergy and regional synergy. Digital technology, as an important means to enhance supply chain resilience, has been highlighted in several studies. Relevant scholars proposed a blockchain-based cross-border e-commerce supply chain framework, demonstrating the potential of blockchain technology in supply chain security and efficiency enhancement, although its incentives and implementation difficulties remain challenges [6]. Meanwhile, bibliometric studies by related scholars show that the application of blockchain in cross-border e-commerce supply chain mainly focuses on platform construction and operation optimization, which provides a clear direction for subsequent research [7]. In addition, some scholars have studied the risk propagation of B2C cross-border e-commerce supply chain based on the viral propagation model and AHP method, and put forward risk control strategies both inside and outside the enterprise, which further enriches the application scenarios of digital technology in supply chains risk management [8], complementing with the research on blockchain technology framework.
The purpose of this paper is to systematically explore the evaluation dimensions and practice paths of supply chain resilience in cross-border e-commerce enterprises through a combination of literature review and case study analysis.
2. Cross-border e-commerce supply chain characteristics and risk identification
2.1. Supply chain structure characteristics
The cross-border e-commerce supply chain has unique and diverse characteristics that have a key impact on its resilience. At the structural level, compared with the traditional trade supply chain, which involves a long chain of manufacturers, traders, overseas buyers, distributors and retailers, the cross-border e-commerce supply chain has been streamlined into a direct consumer-facing one between the manufacturer and the cross-border e-commerce platform, which has greatly shortened the circulation path and reduced the uncertainty and risk transmission in the intermediate links, thus laying the foundation of the supply chain's resilience.
In terms of logistics support, there are different modes of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. The mainstream cross-border e-commerce non-standard supply chain relies on cross-border air transportation, which has a transportation cycle of about 1 day, plus 2-3 days for delivery by domestic merchants, 2-3 days for turnover processing in domestic warehouses, and about 2 days for delivery by logistics companies at overseas destinations, so that it can respond quickly to market demand, and is particularly suitable for non-standard commodities that are sensitive to the time limit and have large fluctuations in demand, which guarantees the resilience of the supply chain in the dimension of rapid delivery. While the traditional standard supply chain adopts cross-border shipping, although the transportation length is 15-30 days, it is suitable for large-volume stocking, relying on the turnover processing of overseas warehouses and subsequent delivery in about 2 days, which can improve the supply chain resilience in terms of stabilizing the supply and reducing the cost to meet the large-scale and relatively stable market demand for standard products. This diversified logistics and transportation mode provides strong support for cross-border e-commerce supply chain to cope with different market situations and risk impacts.
However, the cross-border e-commerce supply chain also has higher complexity compared with the traditional supply chain, and is more susceptible to the influence of the external environment. This complexity is mainly reflected in geographic distribution, laws and regulations, cultural differences and logistics networks. According to Statista data, the global cross-border e-commerce transaction volume reached $1.5 trillion in 2022, involving more than 200 countries and regions. The huge transaction scale and wide geographic distribution make it necessary for cross-border e-commerce supply chains to deal with multiple challenges such as laws and regulations, tax policies, tariff barriers, and cultural practices in different countries. In addition, there are significant differences in logistics infrastructure and transportation modes in different countries, making it difficult to guarantee the timeliness and reliability of cross-border logistics. According to the World Bank, the Global Logistics Performance Index (LPI) has large disparities between different countries and regions, which further exacerbates the complexity of cross-border e-commerce supply chains.
At the same time, the volatile and rapidly changing business environment and the increasing complexity of global supply chain networks have led to higher uncertainty in cross-border business, and unexpected and unavoidable risks are more likely to cause serious disruptions in the supply chains of cross-border e-commerce firms than in domestic supply chains [9][10].
2.2. Type of risk
Logistics risk is one of the most common risks in the cross-border e-commerce supply chain. It mainly includes transportation delays, cargo damage, loss, and customs clearance issues. According to DHL's report, the global annual loss of cross-border e-commerce due to logistics problems amounts to billions of dollars. According to COSCO Sea Control's financial report, in 2023, the China-US shipping timeframe will fluctuate ±15 days; in 2021, the global container shortage and port congestion will be a serious problem, resulting in a large number of cross-border e-commerce orders being delayed in delivery or even canceled. These problems not only increase the operating costs of enterprises, but also damage their brand image.
In addition, customs clearance issues are also an important logistics risk. According to the World Customs Organization, more than 10% of cross-border e-commerce shipments are detained or returned each year due to customs clearance issues, which directly affects the continuity and stability of the supply chain.
Policy risk refers to the adverse impact on the cross-border e-commerce supply chain due to policy changes in various countries. It mainly includes tariff policies, trade barriers, and foreign exchange controls. For example, during the US-China trade friction in 2018, the US government imposed 25% tariffs on Chinese goods, which led to a significant increase in costs for a large number of Chinese cross-border e-commerce companies, some of which were even forced to exit the market.
Demand fluctuation risk refers to supply chain uncertainty due to changes in market demand. Demand in the cross-border e-commerce market is volatile and is mainly affected by various factors such as seasonal factors, market trends and consumer behavior. For example, the surge in cross-border e-commerce orders during shopping festivals such as Black Friday and Double 11 has put tremendous pressure on the supply chain. According to Numerator data, the first day of Amazon Prime Day order amounted to $56.26 in 2023, an increase of 8% compared with 2022, but the average weekly order volume after the promotion dropped by 40%, and the supply chain upstream and downstream had to make timely adjustments in response to the huge gap in order volume.
3. Supply chain resilience assessment system construction
3.1. Evaluation dimensions and indicator system
This paper constructs a set of cross-border e-commerce enterprise supply chain toughness evaluation dimensions and indicators based on multi-dimensions such as response speed, resilience capacity, redundancy capacity, etc., which provides angles for analyzing cross-border e-commerce enterprise supply chain toughness enhancement paths in the later part of the paper.
Table 1. Dimensions of supply chain resilience assessment for cross-border e-commerce enterprises
Dimension | Indicator |
Speed of response | Order fulfillment cycle time (days) |
Resilience capability | Overseas warehouse coverage (%) |
Redundancy capability | Supplier concentration (CR5) |
Collaboration capability | Digital system penetration (%) |
3.1.1. Speed of response and order fulfillment cycle time
Against the backdrop of increasingly fierce competition in global cross-border e-commerce, response speed and order fulfillment cycle time have become key indicators of supply chain resilience. Response speed refers to the time interval from the time a customer places an order to the time a company begins to process the order, while order fulfillment cycle refers to the complete time chain from order generation to final delivery. The faster the response time, the higher the customer satisfaction, which in turn enhances the market competitiveness of the enterprise. Amazon has shortened its order fulfillment cycle to an average of 2-3 days through its highly efficient logistics system and advanced inventory management technology, significantly enhancing customer experience. According to the statistics of Guohai Securities, cross-border e-commerce enterprises with faster response times usually have an order fulfillment cycle of less than 5 days, while enterprises with slower response times may take more than 10 days.
3.1.2. Resilience capability and overseas warehouse coverage
Resilience refers to the supply chain's ability to adapt and recover in the face of unexpected events. Overseas warehouse coverage, on the other hand, measures the ability of companies to lay out their warehouses globally, which has a direct impact on the resilience of the supply chain. Overseas warehouses with high coverage can quickly deploy resources to guarantee timely delivery of orders in the event of a surge in demand or supply disruption. Taking Alibaba as an example, it has set up more than 100 overseas warehouses around the world, covering North America, Europe, Southeast Asia and other regions, which significantly improves the resilience of its supply chain.
3.1.3. Redundancy capacity and supplier concentration
Redundancy capacity refers to the reserve of back-up resources and alternatives in the supply chain that can be quickly substituted in the event of problems with the primary resource, guaranteeing the continuity of the supply chain. Supplier concentration, on the other hand, reflects the degree of risk associated with an enterprise's dependence on a single supplier. Research shows that the higher the supplier concentration, the higher the supply chain risk; on the contrary, firms with higher redundancy capacity and lower supplier concentration are able to switch suppliers quickly to ensure the stable operation of the supply chain in the face of similar risks.
3.1.4. Collaboration capability and digital system penetration
Collaboration capability refers to the level of coordination and cooperation between supply chain segments, while digital system penetration measures the application of information technology in supply chain management by firms. High collaboration capabilities and high digital system penetration can significantly enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency. For example, through its advanced digital supply chain management system, Jingdong has realized the visualization and management of the whole process from procurement, inventory to distribution, which significantly improves the collaborative efficiency of the supply chain.
3.2. Case studies of headline companies
Relying on the advantages of the Pearl River Delta garment industry cluster, SHEIN has built a distributed production network with Panyu, Guangzhou as the core, 300-400 core suppliers as the hub, and more than 1,000 small and medium-sized manufacturers on the periphery, realizing rapid response through the “small order quick return” mode (single quantity 100-500 pieces). Its self-developed MES intelligent system integrates design, production, and warehousing the whole chain of data, new clothing from production to the central warehouse in Foshan warehouse in just a few hours, the warehouse 30 million pieces of storage capacity and 400,000-500,000 SKU dynamic management capabilities to support the distribution of 95% of the global orders, logistics time limit compressed to the maximum of 14 days for overseas users to sign for the longest (courier delivery of 8 days), compared with the traditional fast-fashion brand efficiency significantly higher than that of traditional fast fashion brands.
SHEIN has established a three-tier warehousing system to spread risks. As of 2021, overseas warehouses cover more than 10 countries, including Belgium and India, and bear 5% of order shipments and continue to expand, with reverse logistics processing in Saudi Arabia and UAE transit warehouses, to strictly control the return cycle within 45 days. Its warehouse management system handles 30 million pieces of inventory dynamically deployed on a daily basis, with the inventory rate dropping to single digits and the demurrage rate (backlog of over 90 days of inventory) at only 6%, far lower than the industry's average of 30%-40%.Its 2022 inventory turnover days are shortened to 40 days (turnover rate of 9.0 times/year), compared to 80 days for ZARA's parent company Inditex (Figure 3). The on-demand production model (small batch trial production followed by additional orders) has stabilized the unsold inventory ratio in the low single-digit range, and the flexible replenishment mechanism during the epidemic effectively mitigated the impact of supply chain disruptions.
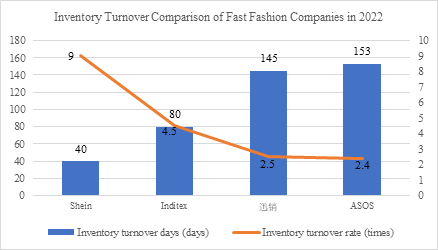
Figure 3. Inventory turnover comparison of fast fashion companies in 2022: SHEIN inventory turnover days of only 40 days
Data source: Guohai securities
By upgrading supplier capabilities through systematic renovation, SHEIN has completed more than 130 factory upgrades in 2022-2023, covering 430,000 square meters of production capacity, and has established 60,000 square meters of innovation centers to output standardized modules. In terms of digitization, SHEIN integrates 10 sets of sub-systems such as merchandise and production to realize full-process tracking through the cloud factory platform, and connects more than 300 raw and auxiliary material suppliers through the “SHEIN Amoy Material Network”, which compresses the material procurement cycle to 48 hours. The advantages of high-frequency orders and advanced cash flow drive suppliers to implement lean transformation, forming a positive cycle of supply and demand synergy.
SHEIN's domestic logistics adopts self-operated (1/3 capacity) in synergy with SF and Cross (2/3 capacity), and the cross-border segment unites DHL and UPS to build a global network. The system controls the logistics cost share at 8-10%, with an exception rate of less than 3%, and efficiently handles the industry's high return pressure of 20-30%. A geographic decentralization strategy coupled with a digital system shortens the production plan response time to 12 hours, and the inventory turnover rate is optimized to 24 times/year, which is 5.6 times higher than ZARA.
The above practice shows that SHEIN has constructed a supply chain resilience model adapted to the complex environment of globalization through the three-dimensional strategy of “industrial cluster integration - digital system embedding - risk buffer architecture”. Its operational data also verifies the effectiveness of the model in market demand fluctuations and external risks, providing a quantifiable practical reference for cross-border e-commerce enterprises to optimize their supply chain resilience.
4. Supply chain resilience improvement path
4.1. Multi-sourcing supply networks
4.1.1. Diversified supplier selection and management
In the context of globalization, cross-border e-commerce enterprises face the risk of supply chain disruption, especially the single-supplier model is particularly vulnerable in the face of unexpected events. Diversified supplier selection and management has become one of the key strategies to enhance supply chain resilience. In addition, effective supplier management is crucial. Cross-border e-commerce enterprises should establish a strict supplier evaluation system, including quality control, delivery capability, financial stability and other dimensions. By regularly evaluating and dynamically adjusting the supplier list, companies can ensure the stability and flexibility of the supply chain.
Take SHEIN as an example, the enterprise has more than 6,000 suppliers globally. It manages suppliers hierarchically through an intelligent supply chain system, dynamically adjusts order allocation according to suppliers' capacity, quality, delivery speed and other indicators, and effectively guarantees the supply of commodities during the epidemic by virtue of its diversified supplier system.
4.1.2. Geographic diversification of supply chain networks
Geographic diversification of supply chain networks is another important strategy to enhance supply chain resilience. Geographic diversification can effectively reduce the impact of regional risks such as natural disasters and political unrest on supply chains. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), disruptions in global supply chains cost the global economy trillions of dollars annually. By establishing warehousing and distribution centers in different regions, cross-border e-commerce companies can achieve geographic diversification of the supply chain, thus improving supply chain risk resistance. Amazon has multiple regional distribution centers around the world, and this geographically diverse supply chain network not only improves distribution efficiency, but also enhances the ability to respond to regional emergencies.
4.2. Digital technology empowerment
4.2.1. Application of blockchain technology in supply chain traceability
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized, tamper-proof and highly transparent features, shows great potential in cross-border e-commerce supply chain management. Through blockchain technology, enterprises can realize the full traceability of the supply chain and ensure that the information in each link is true and reliable. Walmart utilizes blockchain technology to track the food supply chain, where information about the entire process from farm to fork is recorded on the blockchain, greatly improving food safety and supply chain transparency. In addition, blockchain technology can improve supply chain efficiency and traceability, reducing human error and fraud.
4.2.2. Use of AI technology in demand forecasting
Traditional supply chain management relies on historical data and empirical judgment, making it difficult to respond to rapid changes in the market; the application of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in cross-border e-commerce demand forecasting can effectively improve the responsiveness and accuracy of the supply chain. Cross-border e-commerce enterprises can collect multi-dimensional information such as historical sales data, user browsing behavior data, social media data, macroeconomic data, etc., and use AI algorithms to build demand forecast models to analyze market trends and changes in consumer preferences, so as to facilitate the enterprises to reasonably arrange their production schedules, optimize their inventory management, avoid inventory backlogs or stock-outs, and improve the supply chain's responsiveness and operational efficiency.
4.3. Policy compliance synergy
Cross-border e-commerce enterprises need to strictly comply with the laws and regulations of various countries in their globalized operations, and policy compliance is not only the core embodiment of corporate social responsibility, but also the key to enhancing the resilience of the supply chain. For example, the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for corporate data management and privacy protection, and companies need to ensure compliance through technological upgrades and management optimization to avoid legal risks and economic losses. The practice of China's comprehensive cross-border e-commerce pilot zones suggests that domestic policy reforms (e.g., trade facilitation, tax incentives, etc.) can significantly enhance firms' supply chain resilience [11], highlighting the important role of policy design and implementation at the national level for supply chain structure optimization.
Regional agreements such as RCEP have reshaped the supply chain landscape through tariff reductions and simplified customs clearance. Firms can integrate resources within the region to optimize production, and research shows that such policy synergies increase supply chain resilience by 35% [12]. However, there is a need to balance the dividends of rules with the costs of compliance, such as the conflict between intellectual property protection and localized production requirements.
5. Conclusions
This paper constructs a cross-border e-commerce supply chain resilience evaluation system and proposes enhancement paths such as multi-sourcing supply network, digital technology empowerment and policy compliance synergy. The study shows that digitalization and localization are the core paths to enhance supply chain resilience, while policy risks need to be transformed into competitive advantages through proactive compliance.
Future research could further explore the potential of emerging technologies in supply chains and analyze the specific mechanisms and pathways of digitization and localization in enhancing supply chain resilience. For example, case studies and in-depth interviews can be used to analyze in detail the effectiveness of different types of digital technologies in different market environments and the implementation of localization strategies in different countries and regions. In addition, the synergies between digitalization and localization strategies can be studied to explore how the resilience and flexibility of the supply chain can be further enhanced through the organic combination of the two.
Policy risk is one of the important challenges faced by cross-border e-commerce firms. Future research could focus on how to turn policy risks into competitive advantages. For example, by analyzing the policy environments of different countries and regions, it is possible to explore how enterprises can take advantage of market opportunities arising from policy changes by adjusting their supply chain strategies. In addition, the innovative practices of enterprises in coping with policy risks can be studied to explore how policy risks can be transformed into competitive advantages through innovative means, such as establishing a diversified supply chain network and strengthening cooperation with government and industry associations. These studies will provide important theoretical support and practical guidance for cross-border e-commerce enterprises to realize sustainable development in the complex and changing international market.
References
[1]. Li, Y. X., Xu, C., & Zhu, P. (2023). Analysis of the Development Environment and Trend of Cross - Border E - commerce in China. Proceedings of Business and Economic Studies, 6(6), 30-38.
[2]. Zeng, J. (2024). Research on the Influencing Factors of Supply Chain Resilience in China's Cross-border E-commerce. Research on Business Economics, 2024(11), 26-29.
[3]. Cheng, J. H., & Zhang, J. (2020). Is tourism development a catalyst of economic recovery following natural disaster? Current Issues in Tourism, 23(20), 2602–2623.
[4]. Qi, X., Qin, W., & Lin, B. (2024). Case study on synergistic development strategy of cross-border e-commerce and logistics: An empirically model estimation. PLoS ONE, 19(6), e0304393.
[5]. He, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, S., & Du, X. (2024). Construction and implementation of cross-border e-commerce supply chain system under the background of green and low-carbon. Journal of Internet and Digital Economics, 4(1), 1-11.
[6]. Liu, Z., & Li, Z. (2020). A blockchain-based framework of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 102059.
[7]. Zhou, F., & Liu, Y. (2022). Blockchain-Enabled Cross-Border E-Commerce Supply Chain Management: A Bibliometric Systematic Review. Sustainability, 14(23), 15918.
[8]. Zhou, L., Wang, J., Li, F., Xu, Y., Zhao, J., & Su, J. (2022). Risk Aversion of B2C Cross-Border e-Commerce Supply Chain. Sustainability, 14(13), 8088.
[9]. Blackhurst, J., Craighead, C. W., Elkins, D., & Handfield, R. B. (2005). An empirically derived agenda of critical research issues for managing supply-chain disruptions. International Journal of Production Research, 43(19), 4067-4081.
[10]. Bakshi, N., & Kleindorfer, P. (2009). Co-opetition and investment for supply-chain resilience. Production and Operations Management, 18(6), 583-603.
[11]. Deng, F., Rao, F., & Ni, M. J. (2024). Impact of cross-border e-commerce reform on firms' supply chain resilience - a quasi-natural experiment from a comprehensive cross-border e-commerce pilot zone. Journal of Liaoning University (Philosophy and Social Science Edition), 52(5), 49-17.
[12]. Li, Y. (2024). Bilateral Free Trade Agreements and Supply Chain Resilience of Cross-border E-commerce Firms - The Moderating Role of Supply Chain Redundancy. Research in Business Economics, 2024(17), 143-146.
Cite this article
Du,J. (2025). Research on the evaluation of supply chain toughness and improvement path of cross-border e-commerce business: based on the integration perspective of multi-source supply, digital technology and policy synergy. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,18(5),12-18.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li, Y. X., Xu, C., & Zhu, P. (2023). Analysis of the Development Environment and Trend of Cross - Border E - commerce in China. Proceedings of Business and Economic Studies, 6(6), 30-38.
[2]. Zeng, J. (2024). Research on the Influencing Factors of Supply Chain Resilience in China's Cross-border E-commerce. Research on Business Economics, 2024(11), 26-29.
[3]. Cheng, J. H., & Zhang, J. (2020). Is tourism development a catalyst of economic recovery following natural disaster? Current Issues in Tourism, 23(20), 2602–2623.
[4]. Qi, X., Qin, W., & Lin, B. (2024). Case study on synergistic development strategy of cross-border e-commerce and logistics: An empirically model estimation. PLoS ONE, 19(6), e0304393.
[5]. He, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, S., & Du, X. (2024). Construction and implementation of cross-border e-commerce supply chain system under the background of green and low-carbon. Journal of Internet and Digital Economics, 4(1), 1-11.
[6]. Liu, Z., & Li, Z. (2020). A blockchain-based framework of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 102059.
[7]. Zhou, F., & Liu, Y. (2022). Blockchain-Enabled Cross-Border E-Commerce Supply Chain Management: A Bibliometric Systematic Review. Sustainability, 14(23), 15918.
[8]. Zhou, L., Wang, J., Li, F., Xu, Y., Zhao, J., & Su, J. (2022). Risk Aversion of B2C Cross-Border e-Commerce Supply Chain. Sustainability, 14(13), 8088.
[9]. Blackhurst, J., Craighead, C. W., Elkins, D., & Handfield, R. B. (2005). An empirically derived agenda of critical research issues for managing supply-chain disruptions. International Journal of Production Research, 43(19), 4067-4081.
[10]. Bakshi, N., & Kleindorfer, P. (2009). Co-opetition and investment for supply-chain resilience. Production and Operations Management, 18(6), 583-603.
[11]. Deng, F., Rao, F., & Ni, M. J. (2024). Impact of cross-border e-commerce reform on firms' supply chain resilience - a quasi-natural experiment from a comprehensive cross-border e-commerce pilot zone. Journal of Liaoning University (Philosophy and Social Science Edition), 52(5), 49-17.
[12]. Li, Y. (2024). Bilateral Free Trade Agreements and Supply Chain Resilience of Cross-border E-commerce Firms - The Moderating Role of Supply Chain Redundancy. Research in Business Economics, 2024(17), 143-146.









