1. Introduction
In recent years, short videos have become the most prominent content format in the global social media landscape, prompting major platforms to invest heavily in this domain. Among them, TikTok, launched by the Chinese company ByteDance, has achieved explosive user growth on a global scale, demonstrating remarkable penetration and momentum worldwide. Its rapid rise to the forefront of social media platforms within just a few years indicates that short video content is now driving industry trends, with TikTok emerging as one of the leading players in this space. TikTok’s performance in the North American market has been particularly noteworthy. As shown in Figure 1, as of March 2023, the platform had approximately 150 million Monthly Active Users (MAUs) in the United States alone, with user scale and engagement growth significantly outpacing those of other social media platforms in the U.S. during the same period. As a globally recognized short video phenomenon in recent years, TikTok’s success in North America has sparked strong interest from both academia and industry regarding its mechanisms of user attraction and retention [1]. In existing studies, various theoretical frameworks and analytical models have been employed to explore the factors behind TikTok’s success. Analyses based on the extended Technology Acceptance Model suggest that TikTok’s service features (such as informativeness, interactivity, and recommendation systems) and users’ personal attributes (such as innovativeness and self-efficacy) significantly influence their intention to continue using the platform. Additionally, some scholars have presented empirical findings indicating that information quality and system quality play decisive roles in user satisfaction and continued usage. These pioneering studies generally agree that technical factors such as TikTok’s recommendation algorithms and content quality contribute to user acquisition and platform establishment [2].
However, most existing research tends to focus primarily on general technology acceptance factors. In the highly competitive media environment of North America, how TikTok balances localized strategies with a global platform structure to achieve large-scale MAU growth has not been sufficiently explained. In particular, there is a lack of comprehensive analysis on how TikTok’s algorithm-based content distribution structure and content ecosystem interact with its marketing and localized communication strategies to facilitate the user journey from acquisition to activation and long-term engagement.
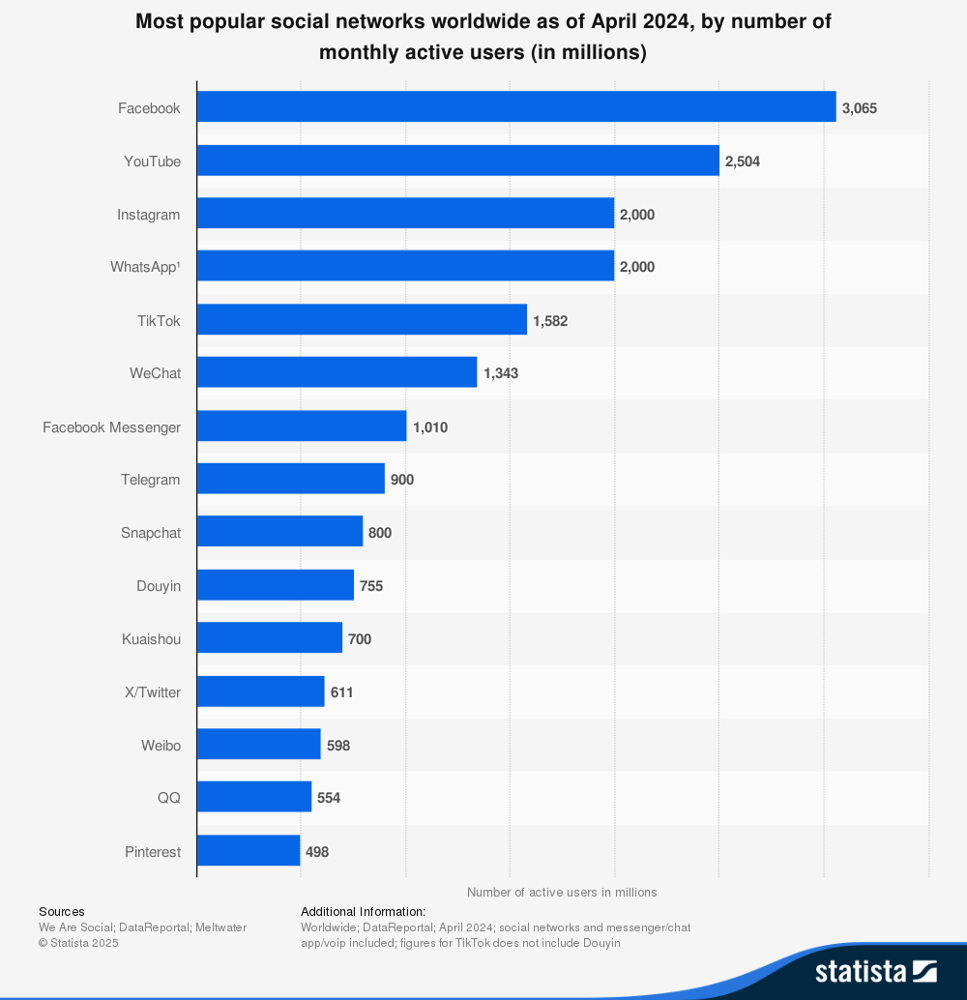
Figure 1. Comparison of monthly active users of major global social networking platforms as of April 2024 [3]
This paper analyzes the key factors and operational strategies behind TikTok’s rapid user expansion, exploring the unique advantages that have enabled it to thrive amid intense social media competition. On the other hand, this study contributes to the theoretical and case-based development in the field of user acquisition and social platform growth, offering valuable insights for industry practitioners in developing social media operation strategies and providing empirical references for academic exploration of success mechanisms in emerging short video platforms.
2. Literature review
This chapter establishes a knowledge foundation for analyzing TikTok’s user growth by reviewing theoretical frameworks and case studies. It summarizes existing research findings and theoretical underpinnings, providing contextual support for the subsequent analysis and highlighting both the general patterns and distinctive phenomena behind TikTok’s rise.
First, this section reviews literature related to user attraction theories, including models of user acquisition and retention, as well as factors influencing users’ choices of social platforms. For instance, prior studies have pointed out that platform ease of use, perceived usefulness and entertainment value, and social influence significantly affect users’ acceptance and continued use of new applications. These findings offer theoretical support for understanding how TikTok attracts users. Accordingly, this paper analyzes how TikTok’s feature design enhances users’ perceived value and ease of use—for example, how personalized recommendations provide useful experiences, and how simple content creation tools lower entry barriers, thereby increasing user acceptance. Moreover, network effect theory suggests that as the number of users increases, the value of the platform to each individual user also increases, creating a positive feedback loop. As TikTok’s base of creators and users expands, the richness of content and level of interaction rise, further attracting more users. Network effects thus play a key role in its growth [4].
Next, this section reviews research related to Monthly Active User (MAU) growth models for social platforms, including user growth mechanisms driven by network effects, viral diffusion models, and innovation diffusion theory. Studies show that user growth on social networks often follows an S-shaped diffusion curve: initial adoption is driven by early users, followed by exponential growth as network externalities strengthen, eventually reaching saturation. A key factor behind TikTok’s ability to surpass competitors in both user growth and retention lies in its algorithm-driven content distribution mechanism. TikTok employs a highly personalized “For You” recommendation algorithm, using artificial intelligence and collaborative filtering technologies to tailor content feeds for each individual user. The platform tracks every user action within the app—likes, comments, shares, and watch duration—and uses this behavioral data to build detailed user profiles in real time. It continuously learns users’ interests and pushes matching short videos accordingly. This feedback-based recommendation mechanism minimizes the role of social connections and follower lists in content distribution, shifting the core of information flow from being relationship-driven to interest-driven [5]. In addition to its core algorithm, TikTok’s product design also contributes to an immersive user experience, further reinforcing its user stickiness. On the one hand, TikTok adopts a vertical, full-screen video display format, allowing users to seamlessly browse the next video by simply swiping up or down. This single-stream content layout is described as “algorithm-friendly” design. Each time a user swipes past or lingers on a video, a clear positive or negative feedback signal is sent to the system, enabling the algorithm to rapidly adjust its recommendation strategy [6].
3. Research methodology
This study adopts a case study approach, selecting TikTok’s user growth in the North American market as a single case for in-depth analysis. By integrating both qualitative and quantitative methods, the research aims to explore the platform’s user acquisition mechanisms. Data sources include authoritative industry databases and reports, such as user scale and growth data from Statista, app download and usage statistics from Sensor Tower and App Annie, as well as user data released by TikTok and information from media coverage. By collecting relevant data and operational events from TikTok’s entry into the North American market in 2017 through 2024, the study outlines the key milestones and strategic initiatives in its user growth. The research focuses specifically on TikTok’s operations and user performance in the North American market—primarily the United States—during its recent phase of rapid growth. The analysis is grounded in the aforementioned theoretical framework to ensure the case study is theory-driven.
4. Case analysis
This chapter conducts a detailed, multi-dimensional analysis of TikTok’s user growth trajectory in the North American market based on collected data, with a focus on how its product and operational strategies attract and retain users. The specific areas of analysis are as follows:
4.1. Product function optimization
Continuous optimization of product features played a critical role in TikTok’s user growth in North America. By enhancing personalized recommendation mechanisms and user interface interaction, the platform significantly increased user engagement and stickiness. First, TikTok’s recommendation algorithm is highly technology-driven. The platform utilizes an AI-based “For You” recommendation system, which leverages deep learning and collaborative filtering technologies to analyze user behavior data in real time—such as watch time, likes, comments, and shares—and accurately delivers content aligned with users’ interests. This mechanism breaks away from the traditional reliance on social connections for content distribution and instead emphasizes “the intrinsic appeal of content,” thereby greatly improving the visibility and reach of ordinary users’ posts [7]. Second, TikTok’s innovations in interface design greatly enhance the user experience. Its vertical, full-screen immersive video display, combined with swipe-based browsing, provides an efficient and seamless content consumption journey. This design not only lowers the operational threshold for users but also creates a closed-loop system of “seamless viewing – instant feedback – algorithmic learning,” allowing the platform to quickly respond to user preferences and deliver accurate content recommendations. In addition, TikTok’s improvements in content creation tools significantly reduce the barriers to content production. The platform offers a wide range of filters, editing tools, subtitles, and background music, enabling ordinary users to participate in content creation without professional equipment or skills. This technology empowerment expands the base of content creators, laying the groundwork for a thriving content ecosystem and indirectly enhancing user engagement and platform stickiness [8]. Notably, TikTok’s global expansion is complemented by localized adaptations. For instance, in the North American version, TikTok supports over 70 languages and tailors local events and recommendation strategies based on regional cultures. This “global platform + local adaptation” approach not only enhances users’ cultural identification but also boosts the platform’s penetration across diverse cultural settings [9].
In summary, TikTok’s ongoing optimization of product features—especially its innovations in recommendation systems, user interface design, and content creation tools—has significantly enhanced user experience and platform appeal, laying a solid foundation for its user growth in the North American market.
4.2. Content ecosystem development
A rich and diverse content ecosystem is a key driver behind TikTok’s user appeal. Initially focusing on youth-oriented content such as music, dance, and lip-sync performances, TikTok gradually expanded into a broad community featuring themes including comedy, fashion, beauty, gaming, and education. The platform encourages high-quality content production through creator incentive mechanisms, such as the establishment of a “Creator Fund” and traffic support programs, allowing content producers to gain financial rewards or public recognition, thereby fueling their enthusiasm for content creation. TikTok manages its content ecosystem with an open and inclusive approach: on one hand, it continually refines its tools—adding features like subtitles, sound effects, and editing functions—to lower the barrier to creation and encourage ordinary users to contribute; on the other hand, it uses algorithmic support to boost emerging content types. For example, TikTok has intentionally reduced the weight of repetitive lip-sync music videos in favor of promoting content in genres such as magic, comedy, and sports, thereby enhancing content diversity. These efforts effectively attract users from various interest groups—users can always find content niches aligned with their preferences on TikTok. At the same time, new content creators have the opportunity to be discovered and gain popularity through the algorithm, creating a virtuous cycle between creators and fans that continually enriches the breadth and depth of the content ecosystem [10].
It is worth noting that TikTok’s content distribution prioritizes the appeal and quality of the content itself over traditional social graphs. Research indicates that in TikTok’s algorithmic weighting, “video content quality” far outweighs “user social relationships,” meaning that even creators with few followers can have their quality content widely recommended. This mechanism ensures that viral content can quickly gain exposure and reach large audiences, while also enabling creative newcomers to rapidly accumulate popularity and attention.
4.3. Localized marketing strategy and communication
TikTok employed a diverse range of marketing strategies to rapidly expand its influence during its user growth phase. Upon entering the North American market, TikTok initially relied heavily on advertising across platforms such as YouTube and Facebook, at one point becoming one of the largest advertisers on Meta’s platforms. This user acquisition strategy—centered on paid media—enabled TikTok to swiftly establish a foundational user base. Subsequently, the platform shifted its focus toward viral marketing and social dissemination, effectively leveraging celebrity influence and organically generated pop culture trends to attract users. For example, TikTok actively invited well-known celebrities and influencers to join the platform and produce content, collaborating with popular musicians and actors to launch challenges and hashtag campaigns. By tapping into the fan bases of these public figures, TikTok generated widespread buzz. In North America, activities such as dance challenges and comedic relays frequently trended on other social media and news outlets, greatly enhancing brand recognition and boosting conversion rates for new users. Furthermore, TikTok is adept at cultivating viral moments by algorithmically amplifying high-engagement trends and challenges to reach broader audiences, thereby maximizing marketing impact. Unlike traditional marketing, many of TikTok’s campaigns are powered by user-generated content, embodying a “users-as-marketers” model: as users participate in platform activities, they inadvertently contribute to TikTok’s outreach. This blend of officially orchestrated campaigns and spontaneous user creation has become a powerful engine for TikTok’s user growth in North America [11].
In terms of community operations, TikTok follows a “global product + localized operation” strategy, emphasizing alignment with local culture and user preferences in its activities. The North American TikTok team tailors content moderation standards and recommendation tendencies to suit U.S.-based users, ensuring that the platform ecosystem aligns with local cultural norms. In the U.S. market, TikTok actively hosts localized online and offline events—such as themed challenges tied to holidays and hashtag campaigns that tap into domestic pop culture—to foster a sense of participation and belonging among users. From a community management perspective, TikTok emphasizes a safe and inclusive environment. The platform has established mechanisms for content moderation and guidance, combats harmful content, protects teenage users, and promotes a positive creative atmosphere—all to strengthen user trust and platform loyalty [12]. Moreover, TikTok maintains active engagement with local creator communities via official accounts and operational teams, gathering feedback to continually refine product features (e.g., adjusting interface elements and enhancing privacy settings in line with North American user habits). This localized community management enables TikTok to establish emotional connections with users and deepen its roots in the North American market, ultimately boosting user retention. By integrating a unified global technological platform with region-specific operational strategies, TikTok has successfully created a model that combines scalability with local resonance—securing a distinct competitive advantage in the North American social media landscape.
5. Competitive analysis and crisis assessment
Through the above case analysis, we can distill the key drivers behind TikTok’s explosive growth in monthly active users in the North American market. First and foremost, product and technological advantages serve as the primary driving force: the highly engaging product experience (immersive short videos, intelligent recommendation system) significantly boosted user retention and activity, enabling TikTok to build a strong user stickiness barrier. According to statistics, the average usage time per TikTok user far surpasses that of its main competitors, reflecting the platform’s enhanced user engagement. In this regard, TikTok has maximized the “ease of use” and “usefulness (entertainment)” components of the Technology Acceptance Model, encouraging users to remain on the platform for extended periods spontaneously. Secondly, its content ecosystem and creator community ensure a continuous supply of high-quality content. Through incentive mechanisms and decentralized recommendations, TikTok has mobilized a large number of UGC (user-generated content) creators, resulting in a diverse and highly dynamic content pool that caters to a wide range of user interests. This is a major reason for both user retention and growth—each time users open TikTok, they encounter fresh and interesting content, leading to habitual usage. Furthermore, marketing efforts and network effects have jointly propelled user base expansion. In the early stages, TikTok quickly acquired users through advertising. Once it reached a critical mass, it achieved exponential growth through user sharing and viral social discussions. Notably, TikTok demonstrates a pronounced network effect: as friends or celebrities become active on the platform, more users are drawn in, who in turn generate more content to attract the next wave of users. In addition, localized operations ensured that TikTok could effectively penetrate the North American mainstream. Content planning and community management tailored to the North American market created a sense of localized care, reducing cultural barriers and enhancing user recognition of the platform [13].
This section also compares TikTok’s growth experience with that of other platforms to analyze its uniqueness. Compared with competing products such as Instagram and YouTube Shorts, TikTok shows several distinctions in user acquisition pathways:
(1) In terms of recommendation mechanisms, TikTok emphasizes interest-driven content distribution rather than social relationships. This allows ordinary users to see globally viral videos; in contrast, Instagram traditionally recommends content based on follow relationships, and its social graph somewhat limits content reach. Although Instagram enhanced its algorithmic recommendations after launching Reels, the overall atmosphere remains different.
(2) Regarding content creation and ecosystem, TikTok promotes widespread participation by offering easy-to-use creation tools and a music library to lower entry barriers, while directly incentivizing creators. This leads to extremely rapid content updates and frequent trending content. In comparison, YouTube Shorts relies on YouTube’s base of professional content creators, with limited participation from ordinary users, and Instagram’s creative ecosystem leans more toward fashion and lifestyle content with fierce competition.
(3) In terms of user engagement models, TikTok’s features like challenges and Duets facilitate interactive creation, forming new modes of social interaction. Instagram continues to rely primarily on traditional engagement forms like likes and comments, while YouTube Shorts is largely focused on viewing and sharing, with limited interactivity.
(4) As for market positioning, TikTok initially captured the needs of teenagers and Gen Z, quickly dominating the youth market before expanding to all age groups. Instagram, with its broad and established user base, must prevent user attrition in the short video space. YouTube Shorts, backed by the YouTube ecosystem, is better positioned to attract existing YouTube users for short-form content but is less appealing to new, younger users.
In summary, TikTok’s differentiated algorithms and product positioning enable it to engage in non-direct competition with its rivals, securing a favorable position in the battle for user attention. The analysis shows that TikTok’s success in North America is no coincidence but the result of multiple contributing factors: a deep understanding of user psychology and behavior, combined with precise strategic execution. These differentiating advantages have enabled it to maintain rapid growth amid competition with Instagram and YouTube Shorts [14].
Despite its remarkable success, TikTok faces numerous crises and challenges in North America, mainly in the following areas:
Regulatory Pressure and Potential Ban Risks: As a Chinese-owned social app, TikTok continues to face intense scrutiny and suspicion from North American governments. The U.S. government, concerned about national security threats, has repeatedly proposed banning or forcing the sale of TikTok’s U.S. operations. Notably, in 2024, the U.S. Congress passed a bill requiring TikTok’s parent company ByteDance to sell TikTok to a non-Chinese entity within a specified timeframe or face a nationwide ban. In April 2024, the Biden administration signed the Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act (PAFACA), delivering an ultimatum to TikTok. As of early 2025, political wrangling over the ban continues, with the U.S. Supreme Court debating its constitutionality. This suggests TikTok could face imminent removal from app stores or forced business divestiture. A ban would wipe out TikTok’s painstakingly accumulated user base and thriving community overnight. Similar incidents have occurred elsewhere: in 2020, following a border conflict, India abruptly banned TikTok and 58 other Chinese apps on security grounds, stripping TikTok of its largest overseas market—over 200 million users—overnight. Evidently, geopolitical tensions pose a significant threat to overseas operations of Chinese companies like TikTok, with policy uncertainty hanging over its North American expansion like the Sword of Damocles [15].
Data Security and Privacy Controversies: A direct trigger for heightened regulatory vigilance in the West is concern over the security of TikTok’s user data. U.S. policymakers fear the vast amount of American user data collected by TikTok could be accessed by the Chinese government or used for improper purposes, such as opinion manipulation or user surveillance. These suspicions have placed TikTok under heavy public scrutiny, prompting repeated reassurances of its independence and data protection measures. TikTok launched “Project Texas,” promising to store American user data on domestic servers monitored by a U.S. company (Oracle) to mitigate trust concerns. However, doubts about data privacy persist. In the context of strict privacy regulations in the U.S. and Europe (e.g., GDPR), TikTok must continually prove that its data handling practices are transparent, lawful, and compliant to avoid hefty fines or removal from app stores due to privacy violations [16].
Geopolitical Tensions and Image Challenges: TikTok’s challenges go beyond business competition—it is enmeshed in the geopolitical rivalry between China and the U.S. As one of the few Chinese internet products to achieve significant success in the West, TikTok has inevitably become a political target. In the U.S., security hearings and media reports on TikTok are often ideologically charged, portraying the platform as “controlled by the Chinese government.” This politicized public discourse undermines TikTok’s brand image and user trust. TikTok must maintain its positioning while cautiously navigating public relations challenges brought on by diplomatic tensions to avoid deeper political entanglements. Furthermore, geopolitical uncertainty may lead to sudden market exits (as seen in India) and cross-border operational hurdles (such as app store removals), requiring TikTok to formulate contingency plans to mitigate the impact of policy shifts in any single market on its global business.
In conclusion, regulatory risks, trust crises, and geopolitical tensions form the core challenges to TikTok’s future development in North America. These factors may not only constrain TikTok’s ability to acquire new users and monetize its platform, but also jeopardize its existing user base. To remain resilient amid external volatility, TikTok must continue refining its product and operations while proactively addressing these uncertainties to ensure steady progress through turbulent waters.
6. Conclusion and recommendations
Through an in-depth analysis of TikTok’s user growth in the North American market, this study reveals the internal mechanisms and unique strategies that enabled the platform to rapidly attract a massive number of monthly active users. As a benchmark case of a Chinese internet enterprise expanding overseas, TikTok’s success in North America offers important insights for other Chinese platforms pursuing internationalization. The findings indicate that TikTok’s success stems from a synergistic combination of four key factors: product technology, content ecosystem, marketing communication, and localized operations. Its “global + local” strategy ensured the platform could leverage economies of scale while maintaining local relevance; the innovative recommendation algorithm and user-friendly product experience significantly enhanced user stickiness; the diverse and rich content ecosystem met users’ continuous browsing demands; ingenious marketing strategies and network effects facilitated exponential user growth; and localized operational strategies further consolidated its user base. Together, these elements contributed to TikTok’s phenomenal growth and exceptional user retention. Compared with traditional social platforms, TikTok pioneered a user growth model centered on “content-driven and algorithm-powered” strategies, creating a differentiated advantage amid fierce competition in the social media landscape.
Based on the above conclusions, several recommendations and insights are proposed. For social platform operators, emphasis should be placed on personalized recommendation technology and product innovation to improve user experience and retention. Simultaneously, a healthy creator ecosystem should be nurtured by providing incentives and support tools to encourage user-generated content, thereby ensuring a steady supply of high-quality content. In terms of marketing, TikTok’s strategies can be used as reference, particularly its effective use of viral dissemination on social media, integration of trending cultural elements, and the influence of KOLs (Key Opinion Leaders) to expand reach. Furthermore, when entering new markets, attention should be paid to localized operations by tailoring content and activities to local user preferences to enhance user identification and engagement.
7. Future research directions
Limitations and prospects for future research: Given that TikTok’s rapid growth is intertwined with complex issues such as regulatory policies and social impact, future studies may further explore the relationship between platform governance, data privacy, and user growth, as well as the applicability of the TikTok model in different regional and cultural contexts. Comparative studies between TikTok and other types of platforms could also be conducted to deeply analyze the long-term impact of short video platforms on the evolution of social media. Overall, the case of TikTok’s user acquisition in the North American market offers valuable reference for innovation and development in the social platform domain. This study aims to provide new perspectives and insights for both industry and academia.
References
[1]. Sharabati, A. A., AlHamad, A. Q., & Al-Zoubi, R. M. (2022). The impact of TikTok user satisfaction on continuous intention to use the application. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8030125
[2]. Chen, X., Liu, T., & Wang, Y. (2023). The impact of e-service quality and e-satisfaction on users’ loyalty to TikTok in Russia and China. Journal of Marketing Communications. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2023.2166570
[3]. Sprout Social. (2024). TikTok stats: Updated data & trends for 2024. Retrieved April 22, 2025, from https://sproutsocial.com/insights/tiktok-stats/
[4]. Omar, B., & Dequan, W. (2020). Watch, share or create: The influence of personality traits and user motivation on TikTok mobile video usage. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 14(4), 121–137. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i04.12429
[5]. Centeno, D. (2020). Understanding TikTok: The platform’s features, uses, and popularity among Gen Z. Journal of Digital Media Studies, 12(3), 45–59.
[6]. Wang, S. Z. (2018, November 27). A look into TikTok’s success. Medium. https://medium.com/@seanzhiyangwangsk/a-look-into-tik-toks-success-6c12ebae572c
[7]. Chen, X., Liu, T., & Wang, Y. (2023). The impact of e-service quality and e-satisfaction on users’ loyalty to TikTok in Russia and China. Journal of Marketing Communications. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2023.2166570
[8]. Kaye, D. B. V., Chen, X., & Zeng, J. (2021). The co-evolution of TikTok and content creators: Platforms, labor, and global digital culture. International Journal of Communication, 15, 1147–1166.
[9]. Lee, J., & Lee, H. (2021). The effects of local adaptation strategy and global standardization strategy on user satisfaction in global social media services. Telematics and Informatics, 61, 101602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2021.101602
[10]. Omar, B., & Dequan, W. (2020). Watch, share or create: The influence of personality traits and user motivation on TikTok mobile video usage. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 14(4), 121–137. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i04.12429
[11]. Romano, A. (2018, December 10). TikTok explains why it’s the most valuable startup in the world — but you probably only know it for its memes. Vox. https://www.vox.com/culture/2018/12/10/18129126/tiktok-app-musically-meme-cringe
[12]. Shen, Z. (2023). Research on the current development and optimization of TikTok’s digital marketing strategies. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.54097/pqyn9177
[13]. Anderson, M., & Jiang, J. (2018). Teens, social media & technology 2018. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/05/31/teens-social-media-technology-2018/
[14]. De Veirman, M., Cauberghe, V., & Hudders, L. (2017). Marketing through Instagram influencers: The impact of number of followers and product divergence on brand attitude. International Journal of Advertising, 36(5), 798–828. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650487.2017.1348035
[15]. Al Jazeera. (2025, January 17). What you need to know about the upcoming U.S. TikTok ban. Al Jazeera. https://chinese.aljazeera.net/news/2025/1/17
[16]. Martin, K., & Shilton, K. (2022). TikTok and the tension between national security and digital rights. Journal of Cybersecurity, 8(1), tyac012. https://doi.org/10.1093/cybsec/tyac012
Cite this article
Xu,K.;Zhao,Y. (2025). Analysis report on TikTok’s monthly active user attraction (a case study of North America). Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,18(5),26-32.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Sharabati, A. A., AlHamad, A. Q., & Al-Zoubi, R. M. (2022). The impact of TikTok user satisfaction on continuous intention to use the application. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8030125
[2]. Chen, X., Liu, T., & Wang, Y. (2023). The impact of e-service quality and e-satisfaction on users’ loyalty to TikTok in Russia and China. Journal of Marketing Communications. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2023.2166570
[3]. Sprout Social. (2024). TikTok stats: Updated data & trends for 2024. Retrieved April 22, 2025, from https://sproutsocial.com/insights/tiktok-stats/
[4]. Omar, B., & Dequan, W. (2020). Watch, share or create: The influence of personality traits and user motivation on TikTok mobile video usage. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 14(4), 121–137. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i04.12429
[5]. Centeno, D. (2020). Understanding TikTok: The platform’s features, uses, and popularity among Gen Z. Journal of Digital Media Studies, 12(3), 45–59.
[6]. Wang, S. Z. (2018, November 27). A look into TikTok’s success. Medium. https://medium.com/@seanzhiyangwangsk/a-look-into-tik-toks-success-6c12ebae572c
[7]. Chen, X., Liu, T., & Wang, Y. (2023). The impact of e-service quality and e-satisfaction on users’ loyalty to TikTok in Russia and China. Journal of Marketing Communications. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527266.2023.2166570
[8]. Kaye, D. B. V., Chen, X., & Zeng, J. (2021). The co-evolution of TikTok and content creators: Platforms, labor, and global digital culture. International Journal of Communication, 15, 1147–1166.
[9]. Lee, J., & Lee, H. (2021). The effects of local adaptation strategy and global standardization strategy on user satisfaction in global social media services. Telematics and Informatics, 61, 101602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2021.101602
[10]. Omar, B., & Dequan, W. (2020). Watch, share or create: The influence of personality traits and user motivation on TikTok mobile video usage. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 14(4), 121–137. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v14i04.12429
[11]. Romano, A. (2018, December 10). TikTok explains why it’s the most valuable startup in the world — but you probably only know it for its memes. Vox. https://www.vox.com/culture/2018/12/10/18129126/tiktok-app-musically-meme-cringe
[12]. Shen, Z. (2023). Research on the current development and optimization of TikTok’s digital marketing strategies. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.54097/pqyn9177
[13]. Anderson, M., & Jiang, J. (2018). Teens, social media & technology 2018. Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/05/31/teens-social-media-technology-2018/
[14]. De Veirman, M., Cauberghe, V., & Hudders, L. (2017). Marketing through Instagram influencers: The impact of number of followers and product divergence on brand attitude. International Journal of Advertising, 36(5), 798–828. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650487.2017.1348035
[15]. Al Jazeera. (2025, January 17). What you need to know about the upcoming U.S. TikTok ban. Al Jazeera. https://chinese.aljazeera.net/news/2025/1/17
[16]. Martin, K., & Shilton, K. (2022). TikTok and the tension between national security and digital rights. Journal of Cybersecurity, 8(1), tyac012. https://doi.org/10.1093/cybsec/tyac012









