1. Introduction
The Silk Road Economic Belt, also known as the Silk Road, is a network of pipelines and railways connecting China to Central Asia and Europe.The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road is a project that runs from the coast of China to ports in East Africa and the northern Mediterranean, via Southeast Asia and South Asia (One Belt, One Road) (D.W. Larson, 2015, p.343). The BRI aims to link Asia, Europe, Africa and other regions for economic cooperation and development. It also aims to improve political relations between countries along the BRI route through China's substantial investment in transport and other supporting infrastructure in these countries. In addition to attracting more FDIs from Chinese enterprises, the Belt and Road Initiative will support structural changes in the Chinese economy, reduce domestic overcapacity, and promote better connectivity and more stable and deeper economic integration. (NDRC, MOF and MOC, 2015) Through geopolitical and geo-economic theories, the BRI also has a huge impact on the international order. This initiative not only creates new opportunities and impetus for China's economic development, but also provides a platform for countries around the world to strengthen cooperation and exchange. In this paper, I will study the quantitative analysis of the impact of the BRI on trade from cultural, economic and political perspectives, and based on the empirical case of the China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline (CCAGP), I will explore how the BRICS Initiative embodies China's rise and its impact on the global political and economic arena, as well as its impact on China's development trend and international relations.
2. BRI and the Rise of China
2.1. One Belt, One Road Reflects China's Economic Rise
As China's reform and opening-up process continues, the country is being closely watched by many other countries who want a glimpse at the policies that helped it move from poverty into prosperity in such a short space. But the way China's economy grows is changing. Some scholars refer to China's reform and opening up as the "China Way" or "China Model", mainly because of its economic success: it relied heavily on cheap labour. As China's economy developed, labour costs rose and labour-intensive industries moved to Southeast Asia, making it difficult for the economy to maintain medium- to high-speed growth (Wu, J.,2019).The gradual accumulation of excess productivity at the beginning of the 21st century led to overcapacity (mainly concentrated in the iron and steel, coal, cement, electrolytic aluminium, and flat glass industries); the external environment was affected by geopolitical factors, the international trade situation tensions, the rise of trade barriers, and the implementation of many measures unfavourable to China's foreign trade and investment, restricting the investment of domestic enterprises (Hofman, B. 2018, p1). BRI can, firstly, boost domestic demand by increasing exports and exporting excess capacity. Secondly, it can break the bottleneck of energy resources supply. Most of China's neighbours are energy-poor and rich, but vertical cooperation with China's industries and cooperation with neighbouring countries can achieve mutual benefits. Third, BRI can improve the efficiency of China's foreign exchange reserves. China has $3 trillion in foreign exchange reserves, more than half of which are in U.S. dollars, most of which are U.S. Treasury bonds with low yields. Investing in infrastructure, industry, trade and distribution along the Belt and Road will yield higher returns than U.S. Treasuries (Zheng Xinli, Deputy Director of the China Centre for International Economic Exchanges, 2015).
China has turned its advantages in capacity, technology, capital, experience and model into market advantages. With the "Silk Road Economic Belt" as a link, China has driven economic development in Asia, Europe and Africa, expanded foreign trade and promoted international trade, while eliminating overcapacity by supplying various products to countries along the Silk Road. At the same time, it has driven the economic development of Asia, Europe and Africa, expanded foreign trade and promoted international trade.
The BRI is of great economic significance worldwide. The BRI spans more than 60 countries in Asia, Europe, the Middle East and Africa, and aims to boost the global economy by opening up new trade routes and investment opportunities." All countries along the "Belt and Road" route will be involved. Two initiatives in the region, SREB and MSRI, continue China's "open-door" policy, with six land-based economic cooperation corridors and one maritime economic cooperation corridor supporting Chinese companies' overseas expansion, domestic industrial upgrading, outward foreign direct investment (OFDI), foreign trade and RMB internationalisation. (Li Xiang, Mengqi Shao and May Tan-Mullins, 2021). These six economic corridors connect China with cities in Russia, Europe, Turkey, Iran, West Asia, South Asia and Southeast Asia via railways.
The BRI promotes regional connectivity and China's domestic development. According to Figure 1, China's trade with countries along the BRI grew from 5 trillion yuan to 13.83 trillion yuan between 2014 and 2022. China's outward foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to countries along the BRI rose from $12.63 billion in 2013 to $24.15 billion in 2021 (Statistical Bulletin of China's Outward Foreign Direct Investment, 2021, page 19). By 2021, China's investment in Belt and Road countries will total about US$59.5 billion (WANG, C. N, 2022). Since 2013, Chinese companies have set up 56 economic and trade cooperation areas in Belt&Road countries, generating almost $1.1 billion in local tax revenues and 180,000 jobs. (Liu W, 2018).
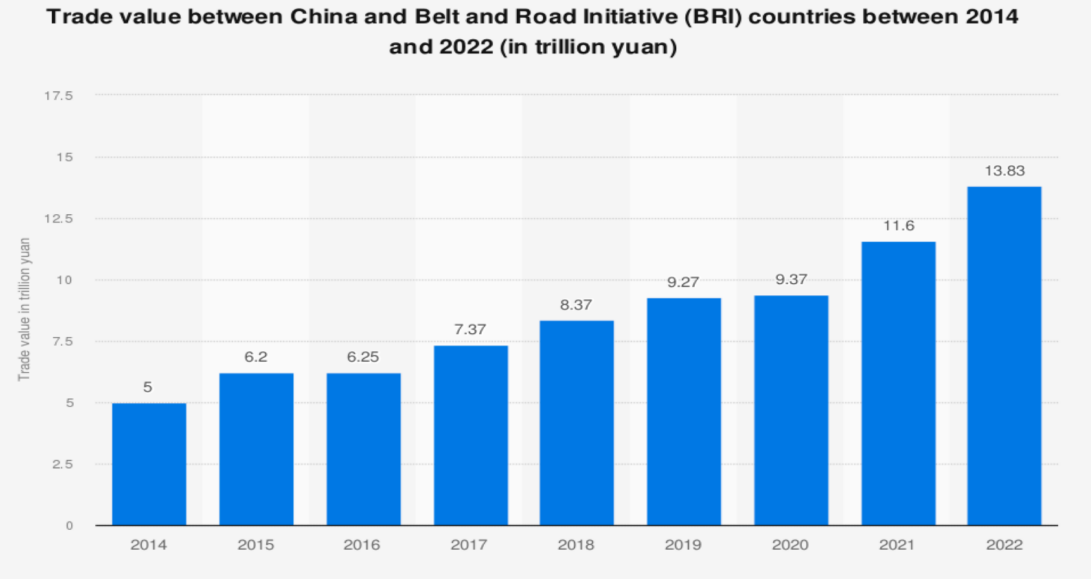
Figure 1: China's trade with Belt and Road countries, 2014-2022 (Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China)
In a report published on 17 May 2015, the Valdai Club for International Debate, a Russian think tank, said that China's Silk Road Economic Belt strategy will promote a common development zone in central Eurasia, which will be integrated like the European Union. The Silk Road Economic Belt, which includes transport transit, infrastructure, industry, trade and service development projects, is an overall strategy to drive the economic development of the countries along the route, the Valdai Club said at an international conference in Astana on the same day. This strategy maximises the potential of the region and ensures its stability. At the seminar, Giaudin Magomedov, chairman of the Russian Suma Group, said that the Silk Road Economic Belt allows for large-scale infrastructure development along the route, which will increase the flow of goods along the Siberian Main Line (Valdai International Debate Club, Russian think tank, 2015).
As the Belt and Road enters its tenth year, its integration with domestic priorities is becoming more systematic. The development of Xinjiang and the globalisation of the West are closely linked to the land-based Belt and Road. The maritime Belt and Road is linked to China's maritime expansion in the east and Hong Kong's Greater Bay Area strategy. China's state-owned enterprises are also investing more in the green economy, digital infrastructure, construction and railways. Reactions to Belt and Road in the West have been mixed. However, it has been a key component of the global political economy over the past decade and is likely to remain so.
2.2 "BRI" Reflects the Rise of Chinese Politics
Over the past four decades, China's growing economy has increased its power and influence in the U.S.-dominated global order. As of 2022, a total of 149 countries have signed documents to join China's BRI, about nine more than in January 2021, according to official announcements by China (Belt and Road Portal, 2022). In April 2019, the Belt and Road Summit on International Cooperation was attended by 140 countries, 80 international organisations, more than 30 heads of state and more than 1,600 participants. (Deng Y, 2021). China has played an important role in international affairs and is at the forefront of the world. Its influence, attractiveness and impact are growing, and the Belt and Road Summit Forum hosted by China is the largest and highest-level diplomatic event since its inception.
In terms of global governance, China's BRI has been continuously improved. Globalisation and regionalisation have created global value chains (Gereffi, G., & Fernandez-Stark, K, 2016, p.8), based on comparative and absolute advantages and the gradual international division of labour, where developed countries are at the top of the chain as a result of their use of monopoly advantages, research and development and intellectual property rights, pricing power, and industrial transfers, and where they integrate developing countries and poor countries Integration into the global value chain puts developing and poor countries at a disadvantage. China is still at the bottom of the global value chain, but the BRI aims to achieve mutual benefits for countries along the route, encouraging value chain creation and optimisation, and BRI is a form of regionalised cooperation. Establishing the Belt and Road regional value chain will help manage China's industrial chain, division of labour and value chain in the world. "One Belt, One Road" is a response to the rise of China and Asia, a process of de-localisation in which Western-centred theories are localised to suit Asian history and practice, and local historical and cultural constructions are combined with contemporary practices from abroad to universalise policies and intra-regional relations and project them onto the global arena (Acharya, 2014).
China's BRI has further strengthened its position in the world. Some developing and developed countries see the BRI as geopolitical. The BRI could challenge peace under the United States, shift strategic and commercial focus from neighbouring waters to Eurasia, and weaken the United States' naval hegemony. The BRI has raised China's political profile. India opposes the Belt and Road because the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor passes through Kashmir, which India claims sovereignty over but is occupied by Pakistan. (Li, M ,2020).
The United States has responded with a "free trade" strategy. Some scholars see the BRI as a counter to the Obama administration's Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and a way to improve security after the 2009-2012 conflict in the South China Sea. Chinese scholars and policymakers see the BRI as an initiative. However, some of the BRI's measures to promote economic co-development cannot be separated from their geopolitical implications. (Flint, C., & Zhu, C., 2019, p.100).
2.3 The BRI Reflects the Rise of China's Cultural Soft Power
Announced in 2013, the BRI initiative is an ambitious multi-year programme in China. The "Belt and Road" promotes China's discourse. International discourse is not only a country's right to 'speak' in the world, but also its power and effectiveness in doing so, essentially reflecting a country's position and influence in the power structure of the international community, and a reflection of the reality of international political power relations." In the current reality of international development, international discourse has become an important part of a country's cultural soft power competition. In terms of international discourse, China is currently facing major challenges. Since September 2013, the BRI has led to increasingly close economic ties between China and countries along the route through the application of a number of portfolios such as the ADB, the Silk Road Fund and the BRICS Bank. The Belt and Road concept has been widely discussed in neighbouring countries and even in the West. Through the BRI, China is able to transform its huge market and production capacity into a broader international presence. Today, we can see China's international influence from a variety of perspectives, for example, when China entered Africa, a continent long neglected by the West after the Cold War, countries began to take a new look at Africa and play a bigger game of influence with China in Africa, which is, of course, in the direct interest of African countries (Zhao L, 2015).
The BRI is the spirit of the Silk Road of "peace and cooperation, openness and inclusiveness, mutual learning and appreciation, and mutual benefit and win-win", and it is an important way to explore the common values of humanity in the 21st century, build a community of common destiny for humanity, and demonstrate the wisdom of the East (Xi Jinping, 2013). On 17 March 2017, the UN Security Council unanimously adopted Resolution 2344, which urges the international community to strengthen regional economic cooperation through initiatives such as the construction of the BeltRoad, create a safe and secure environment for the construction of the BeltRoad, improve development policies and strategies, and promote the construction of the BeltRoad. (Wang Y.M., 2017).
"The New Silk Road University Consortium (NSRU) is a private, non-profit, open and internationalised higher education cooperation platform for academic exchanges and cooperation among higher education institutions in countries and regions along the "Belt and Road". Since its establishment in 2015, it has nearly 100 universities in 22 countries and regions. It promotes academic exchanges, talent training, scientific research, cultural exchanges, policy consultation, health care and other exchanges and cooperation among higher education institutions in countries and regions along the Belt and Road, and promotes the sharing and development of Chinese culture. (Introduction-University Alliance of the Silk Road, n.d.).
3. Empirical Analysis and Findings
The question discussed in this paper is how the BRI affects the rise of China, and this paper decides to choose the most obvious trade relations from an economic perspective to verify the impact of the BRI on the growth of China's exports to the countries along the Belt and Road.
3.1 Hypothesis:
The regression results of the BRI and the value of China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road are positively correlated
3.2 Operationalization
In order to test the impact of Belt and Road on China's exports, the following econometric model is constructed in this paper:
\( Y1=α+{β_{1}}X+{ε_{it}} \) (1)
where denotes country and year. The explanatory variable Y denotes China’s exports to countries along the Belt and Road in USD million, using constant 2010 prices; X is a dummy variable measuring the BRI, set to 1 if the BRI has been proposed in that year, otherwise set to 0; is a random disturbance term; is the core coefficient of interest in this paper, whose estimation results can indicate the effect of the proposal of the BRI on China's exports to the actual relationship of China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road. If it is significantly positive, it indicates that the BRI will positively affect China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road, and if it is significantly negative, it indicates that the BRI will negatively affect China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road.
3.3 Data Sources and Measurement Issues
This paper selects data related to China's export value to countries along the Belt and Road from 2010-2018, for Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan; West Asia: Iran, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates; Central and Eastern Europe: Bulgaria, Croatia, Romania, Poland, Serbia All data in this study are from the World Bank and are expressed in US dollars, using 2010 constant prices.
Since the World Bank data, calculated with data provided by the countries themselves, their data may be influenced by political games and there may be some exaggerations, but at present, the World Bank data is considered the most official source of secondary data.
3.4 Research Design and Preliminary Analysis
In this paper, regression estimation is performed using the least squares method, which is a common mathematical optimization method whose core idea is to estimate by minimizing the sum of squares of the residuals. Specifically, the original data are some scatter points with which we wish to fit an optimal straight line, and such an optimal line is obtained when the sum of squares of the distances between the scatter points and the fitted line is minimized. That is, the residual sum of squares is minimized.
In order to eliminate the fluctuation of data and reduce the influence of extreme data on the regression results, the natural logarithm is taken for China's export value. The descriptive statistics table is as follows:
Table 1: Descriptive statistics
Variables | Sample size | Mean value | Maximum value | Minimum value | Standard deviation |
Export quota | 152 | 3.776 | 7.762 | 1.04 | 1.173 |
The regression results are presented below. Column (1) shows the regression results of the proposed BRI on the value of China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road. The results show that the regression results of the BRI and China's export value to countries along the Belt and Road are significantly positively correlated with a relatively large regression coefficient of 1.347. This implies that the BRI will significantly increase the export value of China to countries along the Belt and Road, and the regression results hold at the 1% significance level.
Table 2: Regression Results
(1) | |
China's exports to countries along the Belt and Road | |
BRI | 1.347*** |
(0.74) | |
_cons | 6.7244*** |
(68.09) | |
N | 152 |
r2 | 0.049 |
*、**、***denote statistical significance at 10%, 5% and 1%, respectively
The conclusion of this study is that the BRI has a significant growth effect on China's exports to countries along the route. However, only 19 countries were selected for this study, and there may be cases that the export volume of some countries did not change much; after all, foreign trade is influenced by multiple factors, and the researcher may consider increasing the sample size by various data searches in future studies.
4. Case Study--Central Asia-China Gas Pipeline (CACGP)
In the third part, this paper takes the Central Asia-China gas pipeline as an empirical case study to analyse in detail how China has implemented the BRI initiative and increased its international influence through the BRI initiative.
4.1 Project Introduction
The China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor is one of the six major economic corridors under the BRI and plays an important role in the construction of the BRI. The China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor is an important node of the Belt and Road, starting from China, passing through Central Asia and extending to the Arabian Peninsula. This economic corridor starts from Xinjiang in China and extends to the Persian Gulf, the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Peninsula, connecting five Central Asian countries (Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan) with Iran and Turkey (South Caucasus and Central Asia - The Belt and Road Initiative, 2020, p.6). The Central Asia Gas Pipeline (CAGP) is a key project of BRI's Sino-foreign energy co-operation, which is of landmark significance and an important supporting force for ensuring national energy security. The China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline starts from the border between Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan on the right bank of the Amu Darya River, passes through the centre of Uzbekistan and the south of Kazakhstan, and enters China from Khorgos, becoming the "Second West-East Natural Gas Pipeline". The approximately 10,000-kilometre pipeline, which includes 188 kilometres from Turkmenistan, 530 kilometres from Uzbekistan, 1300 kilometres from Kazakhstan and 8,000 kilometres from China, is China's first cross-border pipeline. Pipelines A, B and C were fully commissioned in December 2016, while pipeline D is in the laying phase. From the start of operations in 2009 until the end of 2022, the pipeline will have delivered 423.2 billion cubic metres of natural gas to China (China's Economic & Trade Cooperation with Central Asia - Silk Road Briefing, n.d.). At present, the China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline D-Line is under construction, including Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, China. After the completion of the D-Line, China can achieve an annual gas transmission capacity of more than 85 billion cubic metres, making it the first major gas transmission channel in Central Asia (Aminjonov, 2021).
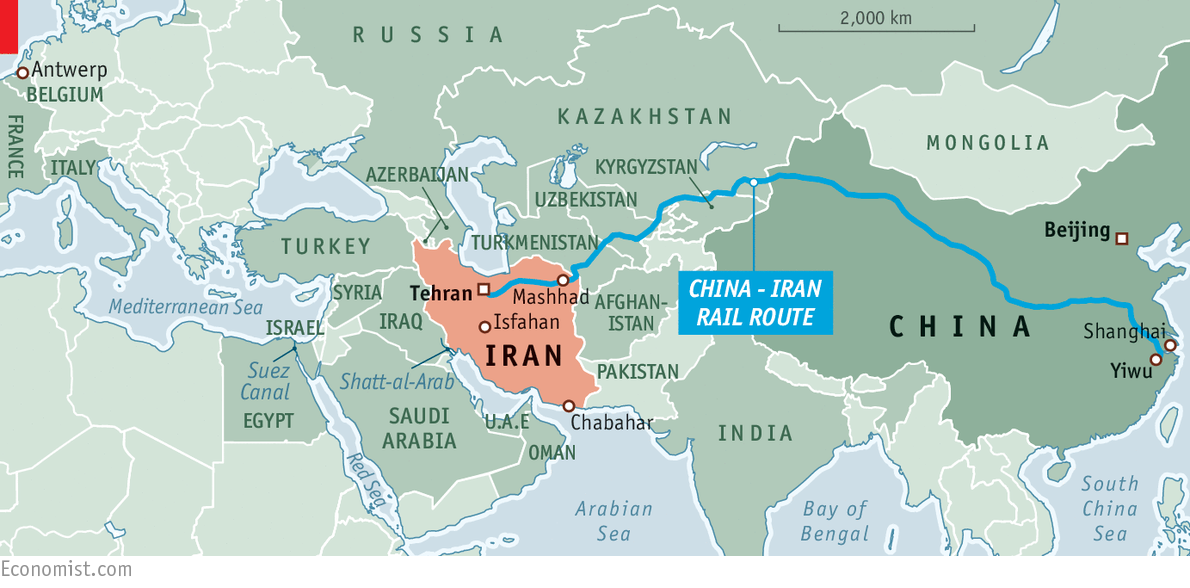
Figure 2: China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor Route (Source: Google Images)
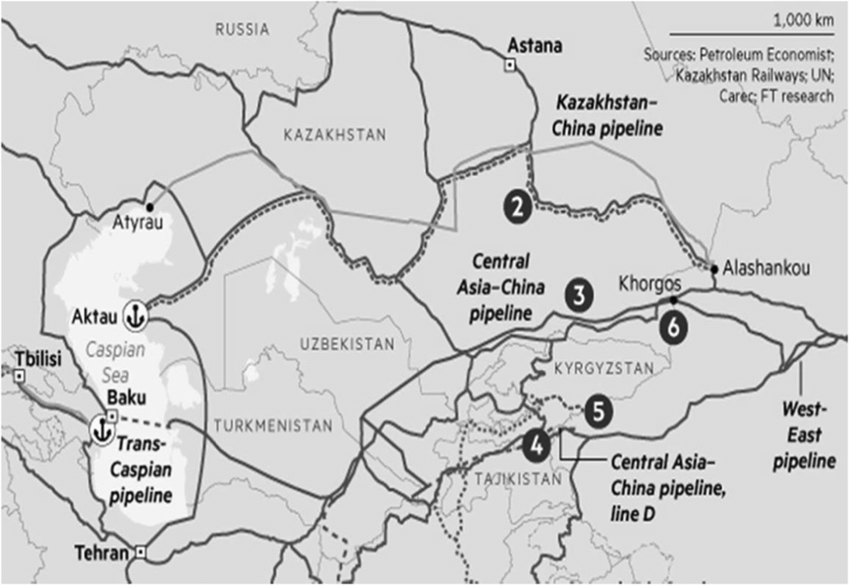
Figure 3: China-Central Asia gas pipeline network line (Source: Google Images)
4.2 Implications for China and the World
The massive and continuous growth of China's economy over the past three decades has created a huge demand for imported energy, and China's urbanisation has made it the world's largest energy consumer, as shown in Figure 4. China’s natural gas consumption began to rise after 2000, and since 2008 natural gas production has been less than consumption. China’s growing energy demand has expanded the amount of energy it imports, including from Central Asia. China has become heavily dependent on a number of politically unstable countries in the Middle East and Africa: in 2011, the Middle East, including Iran, supplied China with 2.6 million barrels per day (bpd), Africa with 1.2 million bpd, and the Asia-Pacific region with 173,000 bpd. Developing a Sino-Central Asian Gas Pipeline could reduce this dependency and provide access to more stable and proximate energy resources, helping to ensure energy security through energy diplomacy.
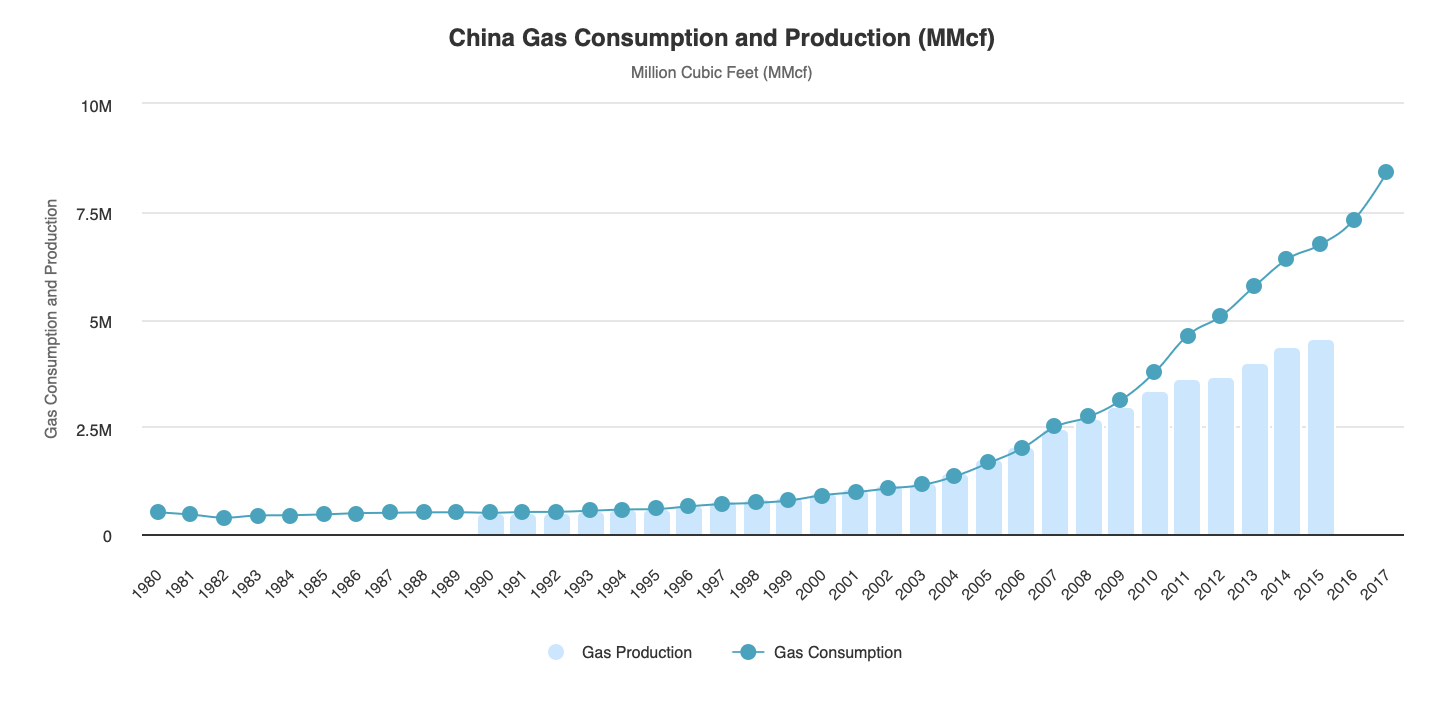
Figure 4: Natural gas consumption and production in China (1980-2017) (Source: Statistical Review of World Energy - British Petroleum)
According to the Oil & Gas Journal, Turkmenistan is one of the world's largest natural gas exporters, with proven natural gas reserves of approximately 265 trillion cubic feet in 2012. The Turkmenistan-China gas pipeline project is a product of this energy cooperation. It has doubled Turkmenistan's oil exports to China, bypassing its biggest competitors, Iran and Russia, while providing China with additional energy supplies and Turkmenistan with infrastructure development. According to a report in the Oil & Gas Journal, Uzbekistan, another Central Asian country, discovered 65 trillion cubic metres of natural gas in 2012, the fourth largest discovery in Eurasia, and the China-Uzbekistan gas pipeline crosses this pipeline, which has helped to further strengthen energy cooperation between the two sides (Chen & Fazilov, 2018). Uzbekistan is a beneficiary of Chinese investment in the country's energy sector, which has spillover effects on other sectors. In contrast, Kazakhstan's natural gas resources are concentrated in the north-western region, while consumption is concentrated in the densely populated and relatively economically developed southern region. The implementation of the South Kazakhstan Gas Pipeline Project has improved the country's gas pipeline network facilities, effectively solved the problem of the misalignment of gas supply and consumption areas, and completely changed the situation in the southern region of Kazakhstan, which was dependent on imported gas. By investing in the construction of the gas pipeline, CNPC has provided more than 10,000 temporary jobs for countries along the route. In addition, the project will bring thousands of long-term stable jobs and tens of billions of dollars in tax revenues to the country during the pipeline's operation. For China, the natural gas supplied to China from Central Asian countries through the China-Central Asia Pipeline accounts for more than 15 per cent of China's total natural gas consumption and serves more than 20 provinces and municipalities, which will play a very important role in diversifying China's energy imports and improving the structure of domestic energy consumption (One Belt, One Road, One Humanity: Witness to the Central Asia Natural Gas Pipeline Project, China-International Gas Network, n.d.).
CNP officials describe the Central Asia-China natural gas pipeline as a symbol of solidarity and mutually beneficial cooperation. China relies on natural gas from Central Asia to enhance its energy security, and the import of resource outlets is expected to boost socio-economic development in the region (South Caucasus and Central Asia - The Belt and Road Initiative, 2020).
5. Conclusion
In summary, BRI is actively participating in regional economic cooperation, promoting China's development, improving global relations, enhancing international cooperation and creating a win-win situation. Under the influence of geo-economics and geopolitics, the BRI has had a great impact on the countries along the route and improved international discourse. According to the case study of the China-Central Asia Gas Pipeline, it can be found that China's BRI is mainly based on the construction of infrastructure to safeguard its own national interests and security, as well as to promote the co-operation and development between countries. China is also becoming a world power. Therefore, the BRI is crucial to both China and the world, bringing both new development opportunities and new challenges. China's international influence has been enhanced through cultural exchanges, infrastructure development, trade and investment, and the establishment of cooperative relationships with BRI participating countries.
References
[1]. Acharya, A. (2014). International Relations Theory and the “Rise of Asia.” In S. M. Pekkanen, J. Ravenhill, & R. Foot (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of the International Relations of Asia (p. 0). Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199916245.013.0007
[2]. Aminjonov, F. (2021). Central Asia-China Gas Pipeline (Line D) Spanning from Turkmenistan to Basic Information Project Outline / BRI - The People’s Map of Global China.
[3]. Belt and Road Humanities: Central Asia Gas Pipeline Project Witnesses China-International Gas Network. (n.d.).
[4]. https://gas.in-en.com/html/gas-3673121.shtml
[5]. Belt and Road Portal. (2022). China: Number of BRI partner countries by region 2022. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1347393/china-number-of-bri-partner-countries-by-region/
[6]. China’s Economic & Trade Cooperation With Central Asia—Silk Road Briefing. (n.d.). https://www.silkroadbriefing.com/news/2023/05/18/chinas-economic-trade-cooperation-with-central-asia/
[7]. Chen, X., & Fazilov, F. (2018). Re-centering Central Asia: China’s “New Great Game” in the old Eurasian Heartland. Palgrave Communications, 4. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-018-0125-5
[8]. Deng, Y. (2021). How China Builds the Credibility of the Belt and Road Initiative. Journal of Contemporary China, 30(131), 734–750. https://doi-org.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/10.1080/10670564.2021.1884958
[9]. Flint, C., & Zhu, C. (2019). The geopolitics of connectivity, cooperation, and hegemonic competition: The Belt and Road Initiative. Geoforum, 99, 95–101.https://doi-org.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/10.1016/j.geoforum.2018.12.008
[10]. Gereffi, G., Humphrey, J., Sturgeon, T. (2005). The governance of global value chains. Review of International Political Economy, 12(1), 78-104. doi10.108009692290500049805
[11]. *Hofman, B. (2018). “Reflections on 40 years of China’s reforms,” in Cai Fang, Ross Garnaut, Ligang Song, (eds.)., China’s 40 Years of Reform and Development, 1978–2018, Canberra: Australian National University Press.
[12]. Introduction-University Alliance of the Silk Road. (n.d.). http://uasr.xjtu.edu.cn/About_UASR/Introduction.htm
[13]. Larson, D. W. (2015). Will China be a New Type of Great Power? The Chinese Journal of International Politics, 8(4), 323–348.
[14]. Li, M. (2020). The Belt and Road Initiative: geo-economics and Indo-Pacific security competition. International Affairs, 96(1), 169–187. https://doi-org-s.elink.xjtlu.edu.cn:443/10.1093/ia/iiz240
[15]. Li, X., Shao, M., & Tan-Mullins,M. (2021). China’s Belt and Road Initiative: Debates, Impacts, and Trends. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190846626.013.674
[16]. Liu W. (2018). The Belt and Road Initiative: A Bellwether of China’s Role in Global Governance. Carnegie Endowment for International Peacerom.
[17]. https://carnegieendowment.org/2018/09/10/belt-and-road-initiative-bellwether-of-china-s-role-in-global-governance-pub-77204
[18]. NDRC, MOF and MOC. (2015). Visions and Actions on Jointly Building Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road . Belt and Road Initiative.Hong Kong. https://www.beltandroad.gov.hk/visionandactions.html
[19]. South Caucasus and Central Asia—The Belt and Road Initiative. (2020). World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/34121
[20]. Wu, J. (2019). “Soul Searching on China’s 70-Year Economic Evolution”, Caixin Global, https://www.caixinglobal.com/2019-10-14/wu-jinglian-soul-searching-on-chinas-70-year-economic-evolution-101470780.html
[21]. WANG, C. N. (2022). Brief: China Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) Investment Report 2021 – Green Finance & Development Center. https://greenfdc.org/brief-china-belt-and-road-initiative-bri-investment-report-2021/
[22]. Wang Y.M. (2017). Wang Yimian: "One Belt, One Road" is the world's role in China's rise, from NPCA website: http://www.rmzxb.com.cn/c/2017-05-12/1532457.shtml
[23]. Zheng X.L., Vice President, China Center for International Economic Exchanges. (2015). "One Belt, One Road" is a major strategy to improve the open economic system,State Council Information Office. http://www.scio.gov.cn/31773/35507/35515/35523/document/1530264/ 1530264.htm
[24]. Zhao L. (2015). "One Belt, One Road" boosts China's civilizational rise, from State Council Information Office website: http://www.scio.gov.cn/31773/35507/35515/35523/Document/1530436/1530436. htm
Cite this article
Li,X. (2023). How Does the BRI Reflect China's Rise and Its Influence in World Politics?. Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies,1,1-11.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Journal:Journal of Applied Economics and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Acharya, A. (2014). International Relations Theory and the “Rise of Asia.” In S. M. Pekkanen, J. Ravenhill, & R. Foot (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of the International Relations of Asia (p. 0). Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199916245.013.0007
[2]. Aminjonov, F. (2021). Central Asia-China Gas Pipeline (Line D) Spanning from Turkmenistan to Basic Information Project Outline / BRI - The People’s Map of Global China.
[3]. Belt and Road Humanities: Central Asia Gas Pipeline Project Witnesses China-International Gas Network. (n.d.).
[4]. https://gas.in-en.com/html/gas-3673121.shtml
[5]. Belt and Road Portal. (2022). China: Number of BRI partner countries by region 2022. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1347393/china-number-of-bri-partner-countries-by-region/
[6]. China’s Economic & Trade Cooperation With Central Asia—Silk Road Briefing. (n.d.). https://www.silkroadbriefing.com/news/2023/05/18/chinas-economic-trade-cooperation-with-central-asia/
[7]. Chen, X., & Fazilov, F. (2018). Re-centering Central Asia: China’s “New Great Game” in the old Eurasian Heartland. Palgrave Communications, 4. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-018-0125-5
[8]. Deng, Y. (2021). How China Builds the Credibility of the Belt and Road Initiative. Journal of Contemporary China, 30(131), 734–750. https://doi-org.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/10.1080/10670564.2021.1884958
[9]. Flint, C., & Zhu, C. (2019). The geopolitics of connectivity, cooperation, and hegemonic competition: The Belt and Road Initiative. Geoforum, 99, 95–101.https://doi-org.ez.xjtlu.edu.cn/10.1016/j.geoforum.2018.12.008
[10]. Gereffi, G., Humphrey, J., Sturgeon, T. (2005). The governance of global value chains. Review of International Political Economy, 12(1), 78-104. doi10.108009692290500049805
[11]. *Hofman, B. (2018). “Reflections on 40 years of China’s reforms,” in Cai Fang, Ross Garnaut, Ligang Song, (eds.)., China’s 40 Years of Reform and Development, 1978–2018, Canberra: Australian National University Press.
[12]. Introduction-University Alliance of the Silk Road. (n.d.). http://uasr.xjtu.edu.cn/About_UASR/Introduction.htm
[13]. Larson, D. W. (2015). Will China be a New Type of Great Power? The Chinese Journal of International Politics, 8(4), 323–348.
[14]. Li, M. (2020). The Belt and Road Initiative: geo-economics and Indo-Pacific security competition. International Affairs, 96(1), 169–187. https://doi-org-s.elink.xjtlu.edu.cn:443/10.1093/ia/iiz240
[15]. Li, X., Shao, M., & Tan-Mullins,M. (2021). China’s Belt and Road Initiative: Debates, Impacts, and Trends. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190846626.013.674
[16]. Liu W. (2018). The Belt and Road Initiative: A Bellwether of China’s Role in Global Governance. Carnegie Endowment for International Peacerom.
[17]. https://carnegieendowment.org/2018/09/10/belt-and-road-initiative-bellwether-of-china-s-role-in-global-governance-pub-77204
[18]. NDRC, MOF and MOC. (2015). Visions and Actions on Jointly Building Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road . Belt and Road Initiative.Hong Kong. https://www.beltandroad.gov.hk/visionandactions.html
[19]. South Caucasus and Central Asia—The Belt and Road Initiative. (2020). World Bank. https://doi.org/10.1596/34121
[20]. Wu, J. (2019). “Soul Searching on China’s 70-Year Economic Evolution”, Caixin Global, https://www.caixinglobal.com/2019-10-14/wu-jinglian-soul-searching-on-chinas-70-year-economic-evolution-101470780.html
[21]. WANG, C. N. (2022). Brief: China Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) Investment Report 2021 – Green Finance & Development Center. https://greenfdc.org/brief-china-belt-and-road-initiative-bri-investment-report-2021/
[22]. Wang Y.M. (2017). Wang Yimian: "One Belt, One Road" is the world's role in China's rise, from NPCA website: http://www.rmzxb.com.cn/c/2017-05-12/1532457.shtml
[23]. Zheng X.L., Vice President, China Center for International Economic Exchanges. (2015). "One Belt, One Road" is a major strategy to improve the open economic system,State Council Information Office. http://www.scio.gov.cn/31773/35507/35515/35523/document/1530264/ 1530264.htm
[24]. Zhao L. (2015). "One Belt, One Road" boosts China's civilizational rise, from State Council Information Office website: http://www.scio.gov.cn/31773/35507/35515/35523/Document/1530436/1530436. htm









