1. Introduction
In recent years, the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence technology has significantly transformed various sectors globally, leading to innovations that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making processes. As AI continues to evolve, its applications have expanded into multiple fields, including healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and finance. Among these, the financial sector has particularly benefitted from AI's ability to automate difficult jobs, forecast market trends, and analyze enormous volumes of data. The importance of studying AI applications in the financial sector cannot be overstated. The financial sector, characterized by vast amounts of data and complex decision-making requirements, is particularly poised to benefit from AI technologies. Financial institutions have increasingly adopted AI-driven solutions to optimize operations, mitigate risks, and deliver personalized services to clients. The ability of AI to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions offers significant advantages in areas such as fraud detection, algorithmic trading and document verification. These issues highlight the significance of conducting comprehensive research to understand the full impact of AI on the financial industry.
Despite the promising applications of AI in finance, there are substantial challenges that must be addressed to fully realize its potential. These include technical issues related to data quality and algorithm transparency, as well as ethical and legal concerns surrounding data privacy and financial liability. This research aims to explore the current applications of AI in finance, identify existing issues, and propose potential solutions. By reviewing the relevant literature, this study will provide a detailed overview of how AI technologies, such as machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision, are being utilized in financial services.
Furthermore, this study contributes significantly to the application of AI in the financial sector. The study identifies the key technical and ethical challenges facing the deployment of AI in the financial sector, providing insights into the complexities of integrating AI technologies into the industry. It also presents potential solutions and recommendations to address the identified challenges, aiming to guide financial institutions and policymakers to effectively utilise AI while mitigating the associated risks.
2. Artificial Intelligence Technology
2.1. Definition of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence can be summarized as a collection of analytical tools designed to mimic the cognitive functions of living beings. Over time, these tools have evolved into sophisticated instruments that address problems once considered difficult or impossible to solve [1]. AI involves the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think and learn. These intelligent machines are capable of doing tasks like speech recognition, language translation, visual perception, and decision-making that normally need human intellect. AI systems are made to become more accurate at their duties, learn from mistakes, and adjust to new inputs.
2.2. Major AI Technologies
The advancement of AI technologies—encompassing machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision—has created numerous opportunities across various domains. Understanding these technologies and their applications is essential for maximizing AI's potential in the financial sector and beyond. This knowledge is crucial for effectively leveraging AI to enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in diverse fields.
2.2.1. Machine Learning. Creating methods that let computers learn from data and make predictions is the main goal of the machine learning. It tackles the problem of developing automated systems that get better with use [2]. These models identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention. As shown in Figure 1, key types include supervised learning, which uses labeled data; unsupervised learning, which finds patterns in unlabeled data; and reinforcement learning, which trains an agent through rewards and penalties.
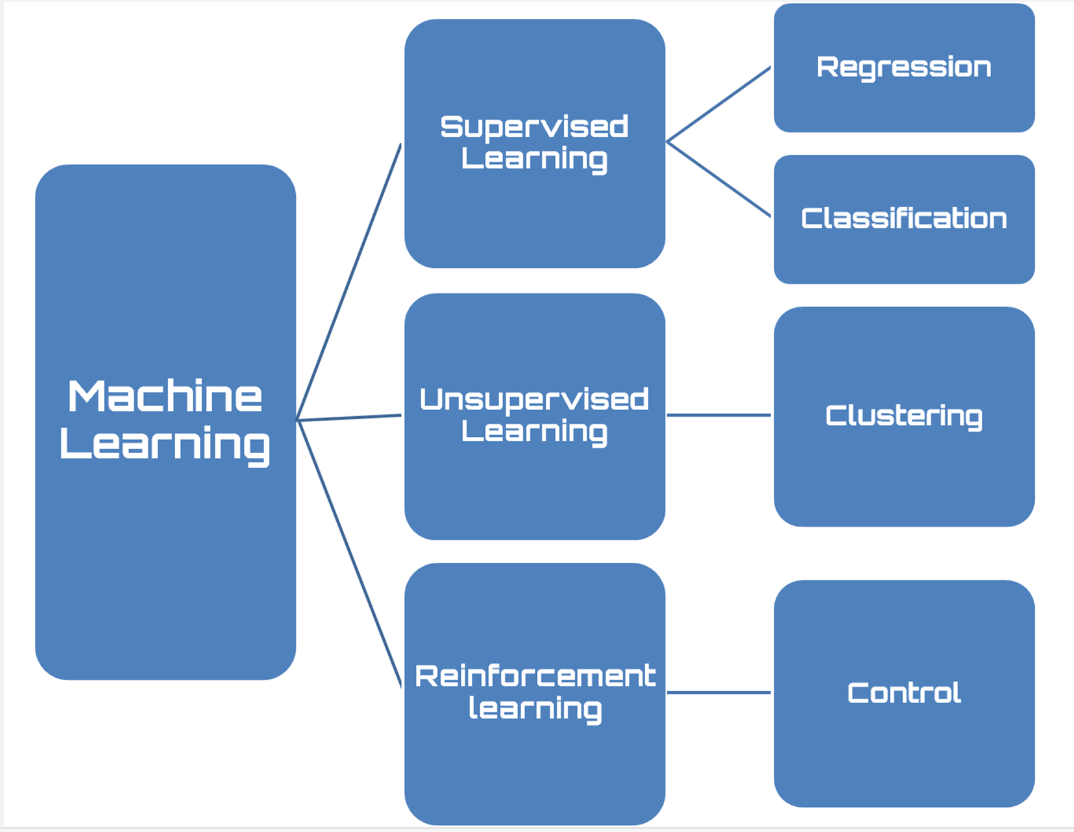
Figure 1. The key types of Machine Learning [3]
2.2.2. Deep Learning. Deep learning enables computational models with multiple processing layers to learn data representations with various levels of abstraction [4]. This approach has significantly advanced fields such as speech recognition, visual object recognition, object detection, drug discovery, and genomics. By employing multi-layered neural networks, deep learning effectively models complex relationships in data. Key components include Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image processing, a CNN architecture for handwritten digit recognition is shown in the figure 2. With such a multilayer architecture, CNN is able to extract and learn important features in an image, leading to efficient and accurate image classification.
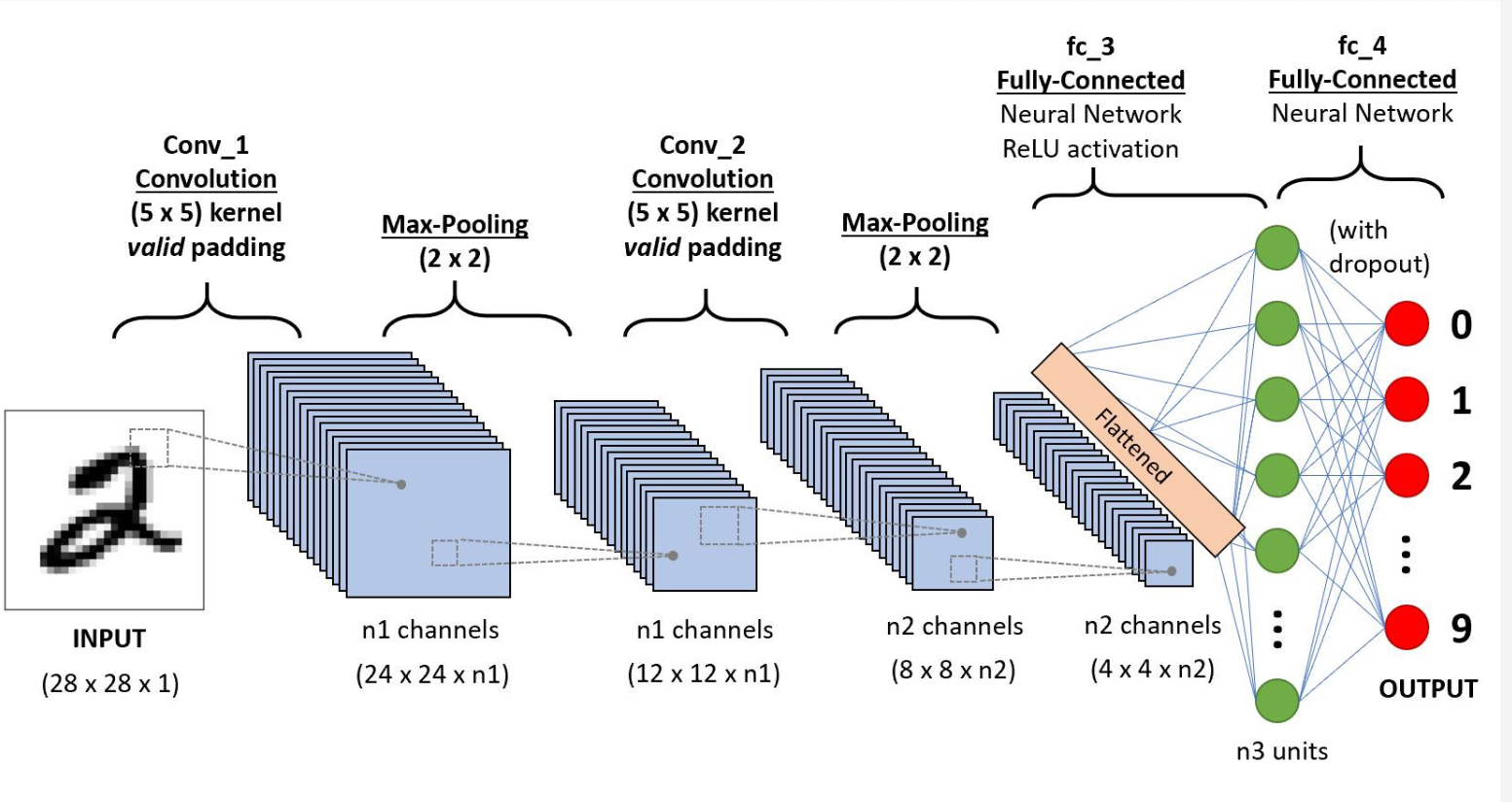
Figure 2. Flowchart of CNN [5]
2.2.3. Computer Vision. Computer vision enables computers to interpret visual data from the world. By establishing rules for pixel characteristics, relationships, and temporal changes, computer vision algorithms can automate the review of ecological images [6]. Applications include image classification, object detection and tracking, and image generation and enhancement. For example, the following figure 3 shows how a parallax image can be used for simple object detection, where objects in an image are distinguished into foreground and background by comparing pixel intensities with a set threshold. Such computer vision techniques can be used in autonomous driving to identify obstacles on the road, in medical imaging to help separate focal areas, and in surveillance to detect moving targets, thus enabling automated and intelligent image processing and analysis.
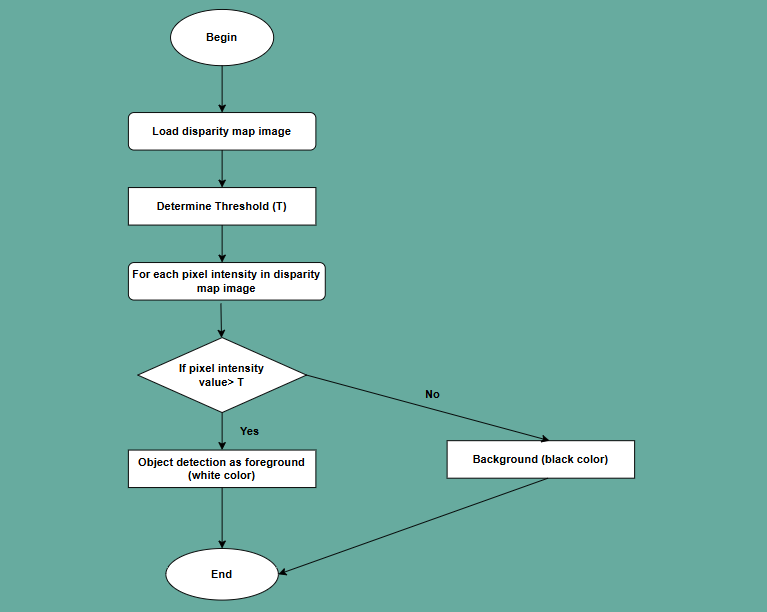
Figure 3. Flowchart for an Object Detection Process (Photo/Picture credit : Original)
3. Applications of AI in the Financial Sector
3.1. Machine Learning for Fraud Detection
Machine learning is revolutionizing fraud detection in the financial sector by utilizing sophisticated algorithms to analyze large volumes of transaction data and identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities. Banks and financial institutions use supervised learning models to detect known fraud patterns, such as decision trees and random forest, which play crucial roles in identifying fraudulent transactions.
3.1.1. Decision Trees. A machine learning approach called a decision tree may be applied to applications involving regression and classification [7]. It simulates choices and their potential results, including as utility, resource costs, and outcomes from random events. Nodes and branches make up the tree structure, as seen in Figure 4. Based on eigenvalues, each internal node represents a decision point, and each branch, up to the output result, which is a leaf, indicates a decision outcome and links to other nodes.
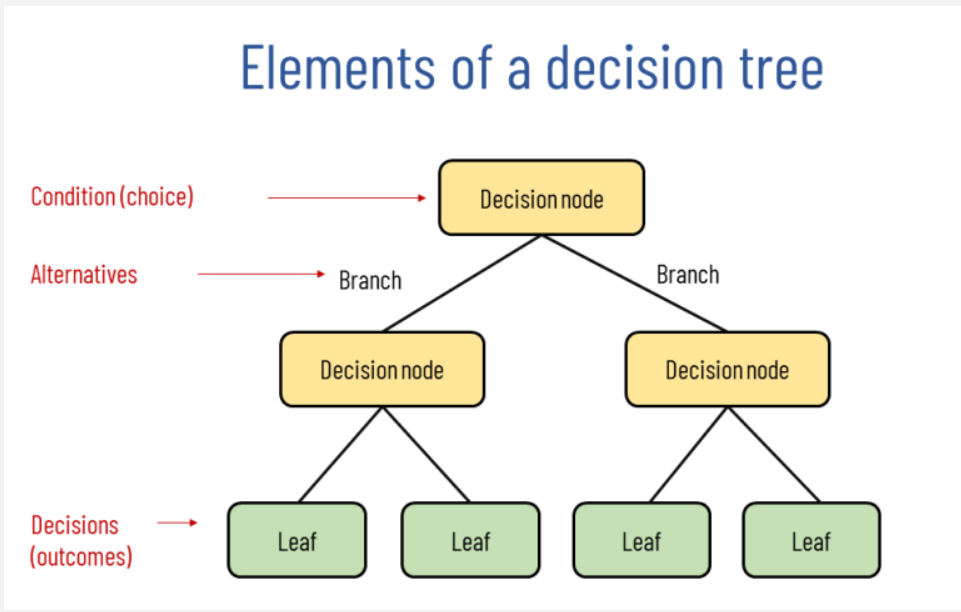
Figure 4. The structure of Decision Tree [8]
In the research of decision trees, major breakthroughs have been made in handling large amounts of features and data, enabling efficient classification and prediction. For example, decision trees can analyze various transaction attributes such as transaction amount, location, time, and user behavior. By training models on these attributes, decision trees can identify which combinations of features are more likely to indicate fraudulent activity. In practical applications, many financial institutions and payment platforms have begun using decision tree technology for fraud detection. For instance, e-commerce platforms like Amazon employ decision tree technology to protect both buyers and sellers. By analyzing users' browsing and purchase history, payment methods, and return behaviors, decision tree models can effectively identify potential fraudulent orders and take appropriate actions, such as temporarily freezing the transaction or conducting a manual review.
Similarly, credit card companies like Visa and MasterCard utilize decision tree technology to prevent fraudulent activities. These companies analyze historical transaction data to train decision tree models that can identify unusual transactions. Like Figure 5, if the system detects that a user's transaction location suddenly changes from one country to another and the transaction amount is substantial, the decision tree model may classify this transaction as high risk and promptly send a verification request to the user.
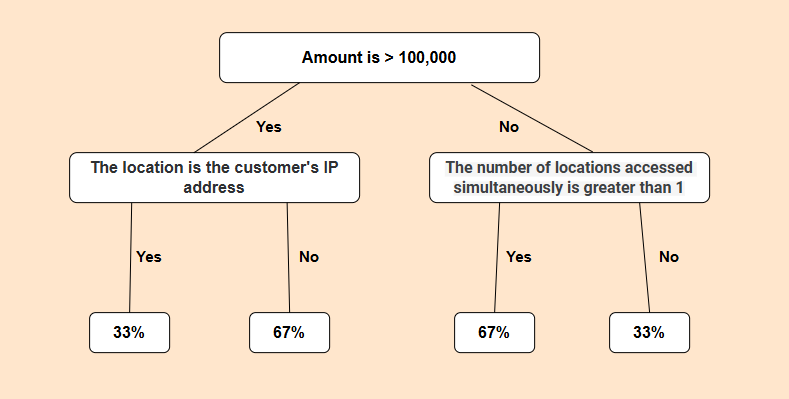
Figure 5. E-commerce Fraud Detection Decision Tree(Photo/Picture credit : Original)
3.1.2. Random Forest. During training, numerous decision trees are built using the random forest ensemble learning method, which then outputs the mean prediction (regression) or the mode of the classes (classification) for each individual tree [9]. It seeks to lower the chance of overfitting while enhancing forecast stability and accuracy. In order to ensure variety among the trees and strong overall performance, each tree in the forest takes into account a random selection of attributes and data points. Significant advancements have been made in the application of random forests, particularly in handling high-dimensional data and improving prediction accuracy. Random forests excel at managing large datasets with many features, as each tree in the forest is trained on a random subset of the data, which helps in capturing a wide range of patterns and relationships. This ensemble method is particularly effective in reducing variance and increasing model reliability.
In practical applications, JPMorgan Chase utilizes random forest algorithms to analyze its vast transaction data to identify potential fraudulent activities. The bank's system collects various features for each transaction, including transaction amount, frequency, location, time, and user's historical behavior patterns. The random forest model is trained on these features to identify abnormal patterns. For instance, if a user's transaction behavior suddenly changes from low-frequency, small-amount transactions to high-frequency, large-amount transactions, especially occurring in locations where the user does not usually appear, the model may flag these transactions as high risk. The bank then conducts further manual reviews on these high-risk transactions or directly contacts the user for confirmation. This approach enables JPMorgan Chase to promptly detect and prevent potential fraud, thereby protecting customers' assets.
3.2. Deep Learning for Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading refers to the method of using computer algorithms to automatically buy and sell securities or other financial assets based on predetermined strategies and market conditions. It relies on high-speed computing and complex mathematical models to analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades at the optimal times. The flowchart in Figure 6 clearly shows the basic working principle of algorithmic trading. Algorithmic trading uses software created by programmers to automate trading strategies. The software analyzes market conditions in real-time and executes trades quickly, reducing the workload for traders and allowing them to focus on strategy. This automation enhances efficiency and helps capture fast-moving market opportunities, making it a crucial tool in modern financial markets. Algorithmic trading can be applied to various financial markets, including stocks, futures, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
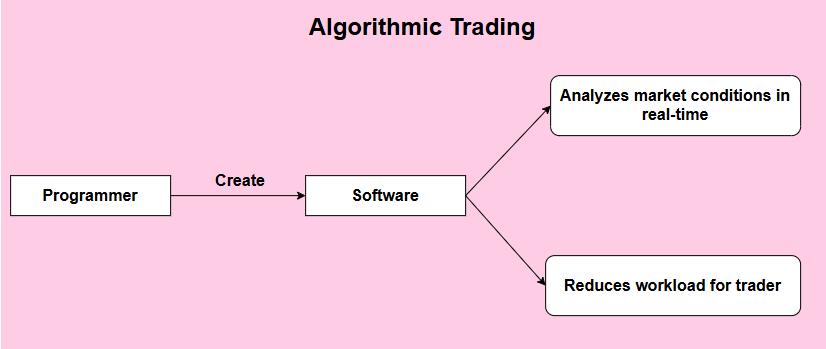
Figure 6. The process of Algorithmic Trading (Photo/Picture credit : Original)
In the context of algorithmic trading, deep learning techniques can analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time market data to predict future price movements and make trading decisions. Deep learning models, such as CNNs and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), have proven particularly effective in this domain. In the following text, I will focus on CNN models to illustrate how deep learning specifically impacts algorithmic trading.
3.2.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). CNNs, initially designed for image and spatial data analysis [10], have been successfully adapted for time-series data and financial chart analysis. CNNs capture spatial hierarchies in data through their unique convolutional layers, which contain filters—small matrices that move across the input data. Every filter is made to identify particular characteristics. A mathematical process known as convolution is carried out by the filters as they move across the data, creating a feature map that indicates the locations of features that have been identified. These layers apply filters to detect and learn complex patterns, such as trends and cycles in stock prices.
For instance, in trading applications, CNNs can be used to analyze candlestick charts or other visual representations of stock prices. Candlestick charts are widely used in stock trading to display the open, high, low, and close prices over a specific period. CNNs can identify shapes and patterns in stock price charts that often foreshadow significant price movements. For example, a trading algorithm can be trained to identify a "head and shoulders" pattern, which often indicates a reversal of an uptrend. When the algorithm identifies this pattern in real-time trading data, it can trigger a sell order to take advantage of an expected price drop. Similarly, the detection of a "double bottom" pattern can foreshadow an upcoming price increase, prompting the algorithm to place a buy order.
A practical application of CNNs in trading can be seen in quantitative hedge funds such as Renaissance Technologies and Two Sigma, which use machine learning models, including CNNs, to analyze large amounts of market data and identify trading opportunities. These funds use deep learning models like ResNet and Inception to detect complex patterns in price movements, allowing them to execute trades with greater accuracy and speed than traditional methods. Additionally, individual traders can use platforms such as MetaTrader or TradingView, which incorporate CNN-based indicators to help identify trading patterns. For example, traders using TradingView can use a ResNet-based plugin that automatically highlights potential "flag" patterns, which often indicate a continuation of a current trend, enabling traders to make informed decisions about entering or exiting a position.
By leveraging CNNs' ability to detect and learn complex patterns in stock prices, algorithmic trading systems can identify trading opportunities with higher precision and execute trades more effectively. This leads to more accurate and profitable trading strategies, enhancing efficiency and profitability in financial markets.
3.3. Computer Vision for Document Verification
With the advancement of artificial intelligence, computer vision applications in document verification have emerged as a significant research focus. Each year, numerous document verification tasks experience inefficiencies and frequent errors due to the constraints of manual processing. These constraints include human fatigue, negligence, inconsistency in subjective judgment, and slow processing speeds, leading to prolonged verification processes and a high likelihood of errors [11]. The introduction of computer vision technology can markedly improve the speed and accuracy of document verification. Computer vision employs automated processing and precise algorithms to rapidly analyze and verify large volumes of documents, thereby reducing human errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
The application of computer vision technology in document verification can be divided into two main parts: image processing and image analysis. Advanced image processing algorithms are used for pre-processing document images, including denoising and enhancement, which optimize image clarity and contrast for further analysis. In image analysis, optical character recognition (OCR) technology efficiently extracts text information from document images (Figure 7). Additionally, feature extraction and matching algorithms identify and verify key features in documents, such as signatures, seals, and security watermarks. These technologies significantly improve the accuracy and speed of document verification. The image below effectively demonstrates how an AI model, such as LeNet-5, processes and recognizes handwritten digits, showcasing the practical application of computer vision in understanding and verifying document content.
Figure 7. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) [12]
In practical applications, banks and financial institutions employ computer vision technology to automate the processing of vast amounts of customer documents, thereby reducing the workload and error rate associated with manual reviews. For example, Citibank and Bank of America utilize computer vision systems to manage account opening applications, loan documents, and customer identification documents. These systems swiftly scan and analyze documents, extract key information, and verify authenticity, enhancing processing efficiency and minimizing errors.
Moreover, government agencies leverage this technology to verify identity documents, ensuring the security and accuracy of the identity verification process. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) uses computer vision technology to detect watermarks and security features in passports, ensuring the authenticity of passports and visas. Similarly, India's Aadhaar project employs computer vision technology to verify identity documents by scanning and matching biometric data on personal ID cards, guaranteeing the uniqueness and accuracy of each identity.
The advantages in government applications include enhanced security and reduced fraud risk. By automating the verification process, computer vision systems can detect sophisticated forgery attempts that might be missed by human inspectors. This technology also improves the efficiency of the verification process, allowing agencies to handle a higher volume of documents without compromising accuracy.
On the downside, these systems can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks where malicious actors attempt to deceive the algorithm with specially crafted images. Additionally, the reliance on biometric data raises privacy concerns, as the collection and storage of such data must be handled with strict security measures to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Overall, computer vision technology not only enhances the accuracy and efficiency of document verification but also reduces reliance on manual labor, thereby lowering operational costs. Furthermore, it improves system security by reducing the risk of errors caused by human factors.
4. Issues in the Application of AI
4.1. Technical Issues
In the financial sector, AI technology is widely utilized for stock prediction, risk management, trading strategy optimization, and customer service. Despite the significant efficiency improvements and cost reductions brought by AI, its implementation still faces various technical challenges, limiting its full potential. Currently, data quality and acquisition issues are particularly prominent. For instance, in the stock market, trading data may contain noise and missing values, directly impacting the accuracy of model predictions. Moreover, due to privacy protection and regulatory restrictions, obtaining personal credit data is challenging, further hindering the training and application of credit scoring models and diminishing the value of AI in finance.
Data processing and feature engineering also present significant challenges. Financial data is usually high-dimensional, including numerous features such as market prices, trading volumes, and economic indicators. For example, in quantitative trading, analysts need to extract useful features from vast amounts of historical trading data to construct trading strategies. Processing this high-dimensional data and conducting effective feature selection and dimensionality reduction are crucial for enhancing model performance. However, finding relevant and useful features is often very complex, requiring the integration of domain expertise in finance, which complicates automation. The complexity of feature engineering not only affects the efficiency and effectiveness of model development but also imposes higher demands on the model's adaptability to different market environments.
The complexity and interpretability of models are also significant issues. The intricate and dynamic nature of financial markets necessitates models with high complexity and flexibility, yet overly complex models may lead to overfitting, reducing their ability to generalize to new data. For example, deep learning models used in hedge funds, while performing well on historical data, may not perform well under new market conditions, thus increasing investment risk. Furthermore, the decision-making processes of complex models are often hard to interpret, which not only affects user trust but also fails to meet regulatory requirements. Although complex models like deep learning offer performance advantages, their lack of transparency creates numerous obstacles in practical applications.
Finally, real-time capability and computational resources are critical issues for AI in the financial sector. Financial markets change rapidly, requiring models to have real-time analysis and decision-making capabilities. For instance, high-frequency trading systems demand data analysis and trading decisions within milliseconds, placing extremely high demands on computational resources. Additionally, training and running complex AI models require substantial computational and storage resources, posing a significant challenge for small to medium-sized financial institutions. The demand for high computational resources not only increases costs but also limits the broader application of AI technology. Data security and privacy protection are equally important; the sensitivity of financial data necessitates ensuring data security during storage, transmission, and processing to prevent leaks and tampering. For example, banks using AI for anti-money laundering detection must ensure the absolute security of customer data to prevent breaches and legal risks. Addressing these issues requires multi-faceted technical support and innovation to fully unleash the potential of AI in the financial sector.
4.2. Ethical and Legal Issues
In the financial sector, AI technology offers transformative potential but also raises significant ethical and legal issues. Despite the efficiency and innovation AI brings, its implementation must be carefully managed to address these concerns. Currently, issues related to bias and fairness are particularly prominent. For instance, AI models used in credit scoring may inadvertently perpetuate existing biases present in historical data, leading to discriminatory lending practices [13]. If the historical data shows a trend where certain demographics, such as minority groups, have been systematically denied loans or given higher interest rates, the AI model trained on this data might learn to replicate these patterns. As a result, even if two applicants have similar financial profiles, the AI system might unfairly favor applicants from non-minority backgrounds while disadvantaging those from minority groups, perpetuating a cycle of inequality and making it harder for affected individuals to access fair credit. Furthermore, the opacity of AI decision-making processes complicates the identification and correction of such biases, undermining fairness and potentially violating anti-discrimination laws.
There are additional difficulties with accountability and transparency. AI systems in finance frequently function as "black boxes," with opaque decision-making procedures. Insufficient transparency may result in a deficiency of responsibility, as it becomes challenging to assign blame for incorrect or detrimental judgments made by AI [14]. For example, it might be difficult to determine who is responsible and what options are available to impacted parties when an AI system wrongly rejects a loan application. In order to maintain responsibility and confidence, regulatory agencies are putting more and more pressure on AI systems to be open and to justify their decision-making procedures.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for AI in finance is still evolving, creating legal uncertainties. Financial institutions must navigate a complex and rapidly changing regulatory environment that varies by region and jurisdiction. For example, the introduction of new AI-specific regulations or amendments to existing financial regulations can impact how AI systems are developed and deployed. Ensuring compliance with these evolving regulations requires significant resources and ongoing monitoring. Moreover, the lack of standardized regulations can lead to inconsistencies in AI governance, further complicating legal compliance and risk management.
5. Countermeasures and Recommendations
5.1. Technological Improvements and Innovations
To address data quality and acquisition issues, implementing effective data cleaning and preprocessing strategies, such as noise removal and missing value imputation, will ensure high-quality input data, thereby improving the accuracy of model predictions. Additionally, using data augmentation and synthesis techniques, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), can generate more high-quality training data, especially when personal credit data is limited, thus enhancing model performance. By implementing these strategies, noise and missing values in trading data will be effectively addressed, significantly improving data integrity and reliability, and consequently, model prediction accuracy. For the privacy and regulatory constraints on personal credit data, data augmentation techniques will provide an effective solution, ensuring that the model still receives sufficient training data under privacy protection conditions.
In data processing and feature engineering, the use of automated feature engineering can simplify the feature selection and engineering process, improve efficiency, and save time and resources. Encouraging close collaboration between financial experts and data scientists to extract and construct meaningful features will significantly enhance the model's applicability and stability. By implementing these measures, handling high-dimensional financial data will become more efficient, reducing the complexity of feature engineering, and significantly improving the efficiency and adaptability of model development. Particularly in quantitative trading, effective feature engineering will greatly improve the speed and quality of constructing trading strategies, enhancing the model's adaptability to different market environments.
To address model complexity and interpretability issues, using model simplification and regularization techniques can prevent overfitting and improve the model's generalization ability on new data. For example, regularization techniques can reduce model complexity, thereby enhancing its stability and reliability. Adopting interpretable models such as decision trees and linear regression, or using model interpretation tools like LIME and SHAP, can increase model transparency and meet regulatory requirements. By implementing these strategies, overfitting issues will be mitigated, the model's generalization ability will improve, and the transparency and interpretability of the model will be enhanced, addressing user trust and compliance issues. In applications like hedge funds, this will effectively reduce investment risk and improve model performance under new market conditions.
To tackle real-time capability and computational resources issues, developing and adopting efficient algorithms and optimization techniques can improve model computational efficiency, meeting the needs for real-time analysis and decision-making. For example, in high-frequency trading systems, fast algorithms can significantly enhance the speed of trading decisions. Utilizing cloud computing and edge computing technologies can provide powerful computing and storage resources, reducing the cost burden for small to medium-sized financial institutions while ensuring data security. By implementing these measures, the challenges posed by rapid changes in financial markets will be effectively addressed, the real-time requirements of high-frequency trading systems will be met, the pressure on computational resources will be greatly reduced, and data security will be ensured. This will make the training and operation of complex AI models more feasible and support the broader application of AI technology in more financial institutions.
5.2. Formulation of Relevant Regulations and Ethical Standards
To address bias and fairness issues, conducting data audits and ensuring diversity in training data before model training is crucial to prevent the perpetuation of historical biases. Introducing fairness evaluation standards, such as Demographic Parity and Equal Opportunity, can help correct biases during the model training process, ensuring model fairness. Demographic Parity requires that the distribution of the model's predictions be similar across different groups, meaning that the probability of a specific prediction (such as loan approval) should be the same for different groups (e.g., gender, race). Equal Opportunity focuses on the fairness of the model on true positive cases, ensuring that, in cases where a positive prediction is truly warranted, the probability of receiving a positive prediction is the same across different groups. By implementing these evaluation standards, the fairness of the model can be quantified, biases can be identified and corrected, ensuring that AI systems in financial applications do not lead to discriminatory practices, thus enhancing their ethical deployment.
To tackle transparency and accountability issues, using interpretability tools like LIME and SHAP can enhance model transparency, ensuring that decision-making processes are understandable and auditable. LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) is a model-agnostic explanation method that perturbs the input data locally, generates multiple similar data points, and observes how these perturbations affect the prediction results. This helps in constructing a simple, interpretable model that approximates the behavior of the complex model locally. LIME helps users understand the reasons behind specific predictions and reveals which features the model is sensitive to. SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) is based on the Shapley value from cooperative game theory. It considers all possible combinations of features and their contributions to the prediction, calculating the marginal contribution of each feature. SHAP values provide a consistent measure of feature importance, explaining both global and local model behavior. By using these tools, the decision-making processes of AI models will become more transparent, increasing user trust and meeting regulatory requirements. This ensures that developers and users are accountable for model decisions and can provide effective remedies in case of errors or harm.
To address regulatory uncertainty issues, establishing a dedicated compliance team to continuously monitor and assess changes in relevant laws and regulations is vital to ensure that AI systems' development and deployment comply with the latest regulatory requirements. Additionally, participating in international and regional AI governance collaborations to promote the unification of AI regulations and standards will reduce compliance difficulties caused by regulatory discrepancies. By implementing these measures, financial institutions can navigate the complex and evolving regulatory landscape more effectively, ensuring that their AI systems remain compliant and reducing the risks associated with legal uncertainties.
6. Conclusion
This research has examined the application of AI in the financial sector, focusing on its current uses, existing challenges, and potential solutions. The findings highlight the significant benefits of AI in enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making processes within financial institutions. Through effective data cleaning, automated feature engineering, model simplification, and the use of interpretability tools like LIME and SHAP, we can significantly improve the performance and transparency of AI models. These improvements address critical issues such as data quality, model complexity, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The impact of this research extends beyond the immediate findings, offering valuable insights for improving AI applications across various sectors. For instance, the methods and solutions discussed can be adapted to enhance AI systems in healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing, where similar challenges of data quality and model interpretability exist. Additionally, the emphasis on ethical considerations and fairness evaluation standards provides a framework for addressing biases in AI models, ensuring more equitable and just applications of AI technology.
Looking to the future, this research underscores the importance of continuous innovation and collaboration in the development and deployment of AI. As AI technology evolves, it is crucial to stay ahead of emerging challenges through adaptive regulatory frameworks and robust ethical guidelines. Future studies should explore the integration of AI with other advanced technologies, such as blockchain and quantum computing, to further enhance its capabilities and applications. By fostering a multidisciplinary approach, we can ensure that AI technology continues to advance, driving innovation and positive change across all sectors of society.
References
[1]. Gordon, B. M. 2011. Artificial Intelligence: Approaches, Tools, and Applications. Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
[2]. Jordan, M. I., & Mitchell, T. M. 2015. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science, 349(6245), 255-260.
[3]. Ciaburro, G. 2017. MATLAB for machine learning. Packt Publishing Ltd.
[4]. LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. 2015. Deep learning. nature, 521(7553), 436-444.
[5]. Saha, S. 2018. A comprehensive guide to convolutional neural networks—the ELI5 way. Towards data science, 15, 15.
[6]. Weinstein, B. G. 2018. A computer vision for animal ecology. Journal of Animal Ecology, 87(3), 533-545.
[7]. De Ville, B. 2013. Decision trees. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 5(6), 448-455.
[8]. Image source: Yulia Kosarenko, 2021 How to Create Decision Trees for Business Rules Analysis," Why Change, November 13.
[9]. Rigatti, S. J. 2017. Random forest. Journal of Insurance Medicine, 47(1), 31-39.
[10]. O'shea, K., & Nash, R. 2015. An introduction to convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.08458.
[11]. Sharma, N., Gupta, S., Mehta, P., Cheng, X., Shankar, A., Singh, P., & Nayak, S. R. 2022. Offline signature verification using deep neural network with application to computer vision. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 31(4), 041210-041210.
[12]. LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., & Haffner, P. 1998. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11), 2278-2324.
[13]. Griffith, M. A. 2023. AI Lending and the ECOA: Avoiding Accidental Discrimination. NC Bank. Inst., 27, 349.
[14]. Uzougbo, N. S., Ikegwu, C. G., & Adewusi, A. O. 2024. Legal accountability and ethical considerations of AI in financial services. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 19(2), 130-142.
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2024). Applications and issues of artificial intelligence in the financial sector. Applied and Computational Engineering,87,54-65.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Gordon, B. M. 2011. Artificial Intelligence: Approaches, Tools, and Applications. Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
[2]. Jordan, M. I., & Mitchell, T. M. 2015. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science, 349(6245), 255-260.
[3]. Ciaburro, G. 2017. MATLAB for machine learning. Packt Publishing Ltd.
[4]. LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. 2015. Deep learning. nature, 521(7553), 436-444.
[5]. Saha, S. 2018. A comprehensive guide to convolutional neural networks—the ELI5 way. Towards data science, 15, 15.
[6]. Weinstein, B. G. 2018. A computer vision for animal ecology. Journal of Animal Ecology, 87(3), 533-545.
[7]. De Ville, B. 2013. Decision trees. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics, 5(6), 448-455.
[8]. Image source: Yulia Kosarenko, 2021 How to Create Decision Trees for Business Rules Analysis," Why Change, November 13.
[9]. Rigatti, S. J. 2017. Random forest. Journal of Insurance Medicine, 47(1), 31-39.
[10]. O'shea, K., & Nash, R. 2015. An introduction to convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.08458.
[11]. Sharma, N., Gupta, S., Mehta, P., Cheng, X., Shankar, A., Singh, P., & Nayak, S. R. 2022. Offline signature verification using deep neural network with application to computer vision. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 31(4), 041210-041210.
[12]. LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., & Haffner, P. 1998. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11), 2278-2324.
[13]. Griffith, M. A. 2023. AI Lending and the ECOA: Avoiding Accidental Discrimination. NC Bank. Inst., 27, 349.
[14]. Uzougbo, N. S., Ikegwu, C. G., & Adewusi, A. O. 2024. Legal accountability and ethical considerations of AI in financial services. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 19(2), 130-142.









