1. Introduction
The area of biomedicine is entering a new era of research and discovery thanks to the widespread use of data science. The complexity and variability of this data frequently proves to be too much for traditional data management and analysis techniques to handle. A large amount of drug and disease research knowledge is scattered in unstructured literature data, although relevant research results can be retrieved through literature databases such as PubMed, these results are often scattered in a single literature, and it needs a great deal of time to obtain the required knowledge. PubMed is the most mainstream engine in biomedical literature field, containing more than 37 million articles as of Augest, 8, 2023 [1]. A typical PubMed query can retrieve hundreds to thousands of articles, but less than 20% of the top 20 articles are reviewed in detail.
Take drug research and development as an example. Drug research and development is a process with high investment, long time and low success rate [2]. A new drug's development typically costs around $2.6 billion, and drug discovery takes an average of three to six years. Once drug development fails, the huge human and financial resources invested will suffer serious losses, and this systemic difficulty greatly affects the progress of the medical field. Big data growth has brought new opportunities as well as obstacles for conventional drug research and development.
In this situation, the application of Biomedical Knowledge Graphs (KG) has emerged as an effective method for combining, organizing, and evaluating various types of biomedical data. Knowledge Graph arranges knowledge from the real world into organized data. The entity and entity connected by relation, the entity and the related attribute-value pairs are its fundamental building blocks, gradually forming the network [3]. The biological information represented by this integrated method aids in the discovery of new ideas, the identification of hidden links, and the acceleration of scientific progress.
Although there has been some progress in the research of knowledge graph, due to the complexity of the biomedical research field, the close correlation between biomedical knowledge and the multi-dimensional complex relationship (such as the complex pharmacological and biological relationship between drugs, diseases and side effects), the research of biomedical knowledge graph is not comprehensive enough and the number is relatively limited. Recent developments in Natural Language Processing (NLP) have considerably improved biological knowledge graph capabilities. Techniques such as Biomedical Named Entity Recognition (BNER) and Biomedical Relationship Extraction (BRE) make it possible to automatically extract entities and their relationships from large amounts of biomedical literature. In particular, pre-trained language models such as BioBERT [4] significantly improve the accuracy of these tasks, making building and updating knowledge graphs more scalable and efficient. There are also new explorations, such as DeepDR [5], for drug retargeting based on deep learning, Zhang et al. [6] proposed new methods for disease prediction using knowledge graphs.
This paper aims to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the process of creating a biomedical knowledge graph, including several often-used models and tools. This structure of Knowledge Graph will be organized as follows: Data collection, information extraction, knowledge representation, knowledge fusion, knowledge storage, and knowledge reasoning. The Information extraction part will be developed, because this step is largely related to the information quality of the final knowledge graph.
2. Method
2.1. Introduction of biological knowledge of graph
The Knowledge Graph arranges and collects knowledge from the real world into organized data. In order to progressively create a network structure, entities are marked with properties and connected through relationships. It can be broken down into multiple steps, as the Figure 1. shows. Among them, information extraction is the most important, which largely determines the quality of results and the speed of generation. This is a general framework for constructing knowledge graphs.
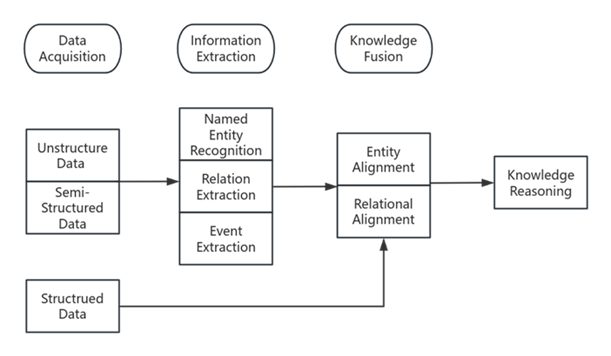
Figure 1. The steps of building knowledge graph (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
2.2. Construction of biomedical knowledge graph
2.2.1. Data acquisition
Literature data is an important source for obtaining first-hand and up-to-date data. Within the biomedical field, PubMed is the most well-known information retrieval system. Based on MEDLINE as the data source, this engine uses Information Retrieval (IR) technology to respond to queries from users and return the query results to users. The retrieval function of PubMed is very important for biomedical researchers. There are several other structured databases, such as Ensembl: that provide genomic data, including gene, transcript and protein sequence information. And DrugBank: contains detailed drug and drug target information, including pharmacology, chemical structure, and drug-target interactions [7].
2.2.2. Information Extraction (IE)
Common tools are Stanford Parser, SpaCy, NLTK. In general, some processing of the acquired data is done first, often symbolization and annotation, and syntactic analysis is used to construct a syntactic dependency map. Through these steps, the grammatical structure and logical relationship of the sentence are understood, which provides an important basis for the subsequent knowledge graph task extraction. In natural language processing (BioNLP) for biomedicine, information extraction has evolved from isolated Biological Named Entity Recognition (BNER) to Relationship Extraction (RE) to linked event extraction.
2.2.2.1. Biomedical Named Entity Recognition (BNER)
Biomedical named entity recognition focuses on the automatic identification of key terms and concepts within biomedical texts. To do this, models must be trained to identify and extract various entities, including medications, genes, and illnesses. Compared with named entity recognition in the general field, BNER is faced with more challenges: First, the ambiguity of the word is higher than that of common words [8], which increases the difficulty of entity recognition; Second, the problem of polysemy; Third, abbreviations, acronyms, aliases.
Initially, it was driven in rules-based and dictionary-based [9]. Rule-based and dictionary-based methods rely too much on expert rules and dictionary quality and are difficult to extend. As a result, approaches based on machine learning and deep learning have become mainstream. In the field of deep learning, there are general methods such as CNN, RNN that work well for related tasks, and transformer models (e.g. BERT, BioBERT).
It's important to note that BioBERT [4], a deep learning language model that has been pre-trained using BERT, does well on a range of biomedical natural language processing tasks. However, pre-training on a sizable biomedical corpus is necessary which means the inference speed is slow and the model is huge.
Many of the early results with better results used HMM+CRF model.In addition, the most popular method is the combination of several methods, such as LSTM+CRF[10], BioBERT+ (LSTM) +CRF[4].
2.2.2.2. Biological Relation Extraction (BRE)
Relational extraction is the identification and extraction of relationships between entities in context. In the biomedical field, Entities that need to be identified can be manually set, such as "gene-disease association" and "drug-disease treatment."
Common tools include OpenNRE[11], DNorm, SciSpacy and REBEL. Similar to named entity recognition, currently biomedical relationship extraction mainly includes rule-based (pattern matching), Deep learning and machine learning techniques. Many early biomedical entity relationship extraction systems were developed based on patterns and rules, with a high accuracy rate, but it was hard to build connections outside the established rule set, and the generalization ability was weak. The method based on statistical learning has the benefit of not requiring predefined patterns or rules, and because of its solid statistical theory and machine learning theory foundation, it has greater research potential and application prospects in the study of relationship extraction in the biomedical field. The mainstream methods and models for biomedical relationship extraction are similar to those for named entity recognition.
2.2.2.3. Biological Event Extraction
Biomedical Event Extraction refers to the method of automatically identifying intricate relationships between biomolecules in the vast medical research literature, such as gene expression, protein interactions, drug reactions, etc. Its purpose is to extract structured information about pre-defined event types from unstructured text [12]. Biomedical events usually consist of a Trigger word with action characteristics and an Argument of several actors. Trigger is a word that clearly describes what happens; An Argument refers to one or more participants in the event.
In 2009, the BioNLP'09 Share Task initiated by Tsujii et al. was the first international evaluation task for biomolecular event extraction [13]. In this evaluation task, the concept of biomedical event extraction is explicitly proposed for the first time, and nine biomolecular e.g. Gene expression and transcription are selected to establish the GENIA evaluation corpus.
Compared with simple relation extraction, event extraction usually involves multiple entities and complex semantic relationships, which is a more complex task. This task goes beyond NER and RE by capturing dynamic interactions and processes described in the literature. Tools like DyGIE++[12] have been developed to address multiple information extraction tasks simultaneously, showing promising results across various biomedical datasets
2.2.3. Knowledge representation
Entities and their relationships are represented as triples such as entity 1-relationship-entity 2 as well as entities and attribute-value pairs that correspond with them and constructed in the form of graphs [14]. These triples will form the basic structure of the knowledge graph. BioNER's results provide nodes, or entities, for the knowledge graph, and RE's results provide edges, or relationships, for the knowledge graph.
Entity: A specific object, such as a gene, disease, drug, etc.
Relation: The relation between entities, such as "treatment", "cause", "inhibit", etc.
Attribute: Express the characteristics of an entity, such as the name of a gene, the symptoms of a disease, and so on.
A data layer and a schema layer are often present in a comprehensive knowledge graph. One of the fundamental components of the knowledge graph is the schema layer. The data's semantic structure is provided by the schema layer, which makes it possible for the knowledge graph to allow advanced query and inference. The schema layer can be built in a variety of ways.
The construction process of knowledge graph data model from unstructured data adopts bottom-up modes. Top-down is to determine the conceptual classes and hierarchical relationships of drug repositioning knowledge graph according to the structure and hierarchy of existing ontology, while bottom-up is to determine the hierarchical structure of classes and relationships after induction, reasoning and summary of obtained biomedical entities and relationships.
Ontology [15] provides a formal knowledge representation method, usually uses the schema layer that manages the knowledge graph uses the ability of the ontology library to accommodate axioms, regulations, and limitations to control the interactions between objects, including entities, relationships, and the kinds and characteristics of entities
In the biomedical field, there are many standardized Ontology libraries that can be used directly, such as Gene Ontology (GO), Disease Ontology (DO), DrugBank, etc. Ontology libraries can also be customized according to specific requirements, and ontology editing tools such as Protege can be used.
Another commonly used approach is data-driven, such as in biomedical text mining, where pre-trained language models such as BioBERT[4] are used to extract entities and relationships from databases such as PubMed. Studies on the relationship between genes and diseases and medication discovery have benefited a lot from these methods.
2.2.4. Knowledge fusion
There are many techniques in the field of knowledge fusion, one of which is entity alignment: The term "Entity Alignment" describes the matching and merging of identical entities across several knowledge sets. Relational alignment: Relational alignment matches and merges entries representing the same relationship from different data sources. And entity disambiguation [16] : distinguish entities with the same name and different meanings, and determine which object is specifically referred to by the entity mentioned in the text through the context and knowledge base. Entity unification: Links entities in text to specific entities in the knowledge base. This step usually takes place after entity disambiguation. Reference resolution: Identifying and connecting different expressions in text that refer to the same entity.
2.2.5. Knowledge storage and knowledge reasoning
Biomedical knowledge storage is a key part of knowledge graph management. Due to the large amount of biomedical knowledge and data, it involves how to store and manage large-scale knowledge efficiently and reliably. There are many methods for knowledge storage, such as data graph database: Neo4j[17], JanusGraph; RDF databases, such as Apache Jena[18] and Virtuoso, are used to store RDF triples.
Compared with the general field, the research progress of biomedical knowledge inference is slow, mainly because the biomedical field data sets rely heavily on expensive, labor-intensive experts to carry out tasks by hand, the number of biomedical data sets is very limited, and the biomedical field involves a large number of technical terms, complex biological mechanisms and clinical knowledge. This specific domain knowledge places high demands on the general NLP model. Taking the field of drug repositioning [19] as an example, there are various methods applicable, such as the identification of molecular targets of drugs and gene expression analysis, to discover the potential of new drugs and the possibility of disease cure. For example, antidepressants can be used to treat pain and inflammation by affecting the same neurotransmitter pathways [20].
3. Discussion
Now, the biomedical knowledge graph is still in development, and there are still many shortcomings, Take the question of interpretability. On the one hand many methods used to construct and update knowledge graphs, such as deep learning algorithms, can be black boxes. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to interpret how certain connections or predictions are made that errors are almost inevitable. On the other hand, at this stage of model testing and training, the specificity of biomedical terminology and concepts requires a high level of expertise to interpret and validate the knowledge represented in the graph accurately. This makes model testing and training slow.
There are also data set quality and accuracy issues. The construction of biomedical knowledge graphs involves constant expansion and updating, Data extracted from unstructured sources, such as scientific literature, may contain errors or irrelevant information that can a negative impact on quality of the knowledge graph. Consequently, it is very critical to establish appropriate methods to evaluate the quality and content of literature.
It may also be a viable idea to combine the biomedical knowledge graph with the Apache Spark [21] architecture. Creating a knowledge graph is concerned with challenges with big data, real-time processing, and data storage. The data can be stored in HDFS, and then multiple RDD can be generated to process the data in memory, and multiple machines in the cluster can be used by parallel algorithms. Text mining can be carried out in the Apache Spark environment. Then, the second step is to import the entity relationship triples after relationship extraction and trigger, arguments (multiple groups) after event extraction into the Apache Spark environment for knowledge graph construction. Use spark streaming to update the data set in real time, and rely on spark platform for information retrieval. The speed of data processing is improved, and the storage capacity and security issues are greatly optimized. At the same time, the problem of data extensibility and timeliness is solved.
The biomedical field is extremely broad, and the existing models have weak generalization ability when dealing with previously unseen data and new fields, which is difficult to adapt to the rapidly changing biomedical research and application needs. The application of transfer learning [22] in biomedical knowledge graphing has great potential to help solve problems such as insufficient data, domain differences, and model generalization ability. Models can be pre-trained on large-scale generic knowledge graphs and then migrated to biomedical knowledge graphs by fine-tuning to a specific task in the biomedical field, or models trained in one subfield (e.g. Genomics) can be migrated to another related subfield (e.g. Proteomics). Cross-domain transfer of knowledge is achieved by sharing common biomedical characteristics and knowledge.
4. Conclusion
In this paper, the necessity and method of constructing biomedical knowledge graph are summarized and expounded. In addition, it describes limitations and research difficulties of current biomedical knowledge graph and puts forward two ideas to solve relevant problems. The application of biomedical knowledge graph has a broad picture, and it is expected to have greater applications in drug repositioning, clinical trial optimization and medical education and research.
References
[1]. National Library of Medicine. 2024. Preview Upcoming Improvements to PubMed Central (PMC). NLM Technical Bulletin, Mar-Apr, vol 457.
[2]. DiMasi JA, Grabowski HG & Hansen RW. 2016. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. Journal of Health Economics, vol 47, pp 20-33.
[3]. Hogan A, Blomqvist E, Cochez M, d'Amato C, de Melo G, Gutiérrez C, et al. 2021. Knowledge graphs. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol 54 (4), pp 1-37.
[4]. Lee J, Yoon W, Kim S, Kim D, Kim S, So CH, Kang J. 2020. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics, vol 36 (4), pp 1234-1240.
[5]. Zeng X, Zhu S, Liu X, Zhou Y, Nussinov R, Cheng F. 2019. DeepDR: A network-based deep learning approach to in silico drug repositioning. Nature Communications, vol 11 (1), p 1-13.
[6]. Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu F. 2018. Predicting drug-disease associations by using similarity constrained matrix factorization. BMC Bioinformatics, vol 19 (1), p 1-11. doi:10.1186/s12859-018-2290-9.
[7]. Lu Z. 2011. PubMed and beyond: a survey of web tools for searching biomedical literature. Database, vol 2011, baq036.
[8]. Chen L, Liu H, Friedman C. 2005. Gene name ambiguity of eukaryotic nomenclatures. Bioinformatics, Volume 21, Issue 2, January 2005, Pages 248–256.
[9]. Soomro PD, Kumar S, Banbhrani, Shaikh AA, Raj HR. 2017. Bio-NER: Biomedical Named Entity Recognition using Rule-Based and Statistical Learners. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 8(12). http://dx.doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2017.081220.
[10]. Huang Z, Xu W, Yu K. 2015. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.01991.
[11]. Han X, Gao T, Yao Y, Ye D, Liu Z, Sun M. 2019. OpenNRE: An Open and Extensible Toolkit for Neural Relation Extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp 169-174. doi:10.18653/v1/D19-3029.
[12]. Wadden D, Wennberg U, Luan Y, Hajishirzi H. 2019. Entity, Relation, and Event Extraction with Contextualized Span Representations. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 5784-5789.
[13]. Kim JD, Ohta T, Pyysalo S, Kano Y, Tsujii J. 2009. Overview of BioNLP’09 Shared Task on Event Extraction. In: Proceedings of the BioNLP 2009 Workshop Companion Volume for Shared Task, Boulder, Colorado, pp 1-9. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[14]. Moon C, Jin C, Dong X, Abrar S, Zheng W, Chirkova RY, Tropsha A. 2021. Learning Drug-Disease-Target Embedding (DDTE) from knowledge graphs to inform drug repositioning hypotheses. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, Jul;119:103838. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103838. Epub 2021 Jun 11. PMID: 34119691.
[15]. Hoehndorf R, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV. 2015. The role of ontologies in biological and biomedical research: a functional perspective. Brief Bioinform, Nov;16(6):1069-80. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv011. Epub 2015 Apr 10. PMID: 25863278; PMCID: PMC4652617.
[16]. Yamada I, Washio K, Shindo H, Matsumoto Y. 2022. Global Entity Disambiguation with BERT. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 3264–3271, Seattle, United States. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[17]. Guia J, Soares VG, Bernardino J. 2017. Graph Databases: Neo4j Analysis. In ICEIS (1), pp. 351-356.
[18]. Siemer S. 2019. Exploring the Apache Jena framework. George August University: Göttingen, Germany.
[19]. Jourdan JP, Bureau R, Rochais C, Dallemagne P. 2020. Drug repositioning: a brief overview. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 72(9), pp. 1145-1151.
[20]. Obata H. 2017. Analgesic mechanisms of antidepressants for neuropathic pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2483.
[21]. Guo R, Zhao Y, Zou Q, Fang X, Peng S. 2018. Bioinformatics applications on Apache Spark. GigaScience, Volume 7, Issue 8, August 2018, giy098.
[22]. Agarwal N, Sondhi A, Chopra K, Singh G. 2021. Transfer learning: Survey and classification. Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences: Proceedings of ICSICCS 2020, pp. 145-155.
Cite this article
Zhan,B. (2024). Application and investigation of knowledge graph in biomedical field. Applied and Computational Engineering,88,81-87.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. National Library of Medicine. 2024. Preview Upcoming Improvements to PubMed Central (PMC). NLM Technical Bulletin, Mar-Apr, vol 457.
[2]. DiMasi JA, Grabowski HG & Hansen RW. 2016. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. Journal of Health Economics, vol 47, pp 20-33.
[3]. Hogan A, Blomqvist E, Cochez M, d'Amato C, de Melo G, Gutiérrez C, et al. 2021. Knowledge graphs. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol 54 (4), pp 1-37.
[4]. Lee J, Yoon W, Kim S, Kim D, Kim S, So CH, Kang J. 2020. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics, vol 36 (4), pp 1234-1240.
[5]. Zeng X, Zhu S, Liu X, Zhou Y, Nussinov R, Cheng F. 2019. DeepDR: A network-based deep learning approach to in silico drug repositioning. Nature Communications, vol 11 (1), p 1-13.
[6]. Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu F. 2018. Predicting drug-disease associations by using similarity constrained matrix factorization. BMC Bioinformatics, vol 19 (1), p 1-11. doi:10.1186/s12859-018-2290-9.
[7]. Lu Z. 2011. PubMed and beyond: a survey of web tools for searching biomedical literature. Database, vol 2011, baq036.
[8]. Chen L, Liu H, Friedman C. 2005. Gene name ambiguity of eukaryotic nomenclatures. Bioinformatics, Volume 21, Issue 2, January 2005, Pages 248–256.
[9]. Soomro PD, Kumar S, Banbhrani, Shaikh AA, Raj HR. 2017. Bio-NER: Biomedical Named Entity Recognition using Rule-Based and Statistical Learners. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 8(12). http://dx.doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2017.081220.
[10]. Huang Z, Xu W, Yu K. 2015. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.01991.
[11]. Han X, Gao T, Yao Y, Ye D, Liu Z, Sun M. 2019. OpenNRE: An Open and Extensible Toolkit for Neural Relation Extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pp 169-174. doi:10.18653/v1/D19-3029.
[12]. Wadden D, Wennberg U, Luan Y, Hajishirzi H. 2019. Entity, Relation, and Event Extraction with Contextualized Span Representations. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 5784-5789.
[13]. Kim JD, Ohta T, Pyysalo S, Kano Y, Tsujii J. 2009. Overview of BioNLP’09 Shared Task on Event Extraction. In: Proceedings of the BioNLP 2009 Workshop Companion Volume for Shared Task, Boulder, Colorado, pp 1-9. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[14]. Moon C, Jin C, Dong X, Abrar S, Zheng W, Chirkova RY, Tropsha A. 2021. Learning Drug-Disease-Target Embedding (DDTE) from knowledge graphs to inform drug repositioning hypotheses. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, Jul;119:103838. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103838. Epub 2021 Jun 11. PMID: 34119691.
[15]. Hoehndorf R, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV. 2015. The role of ontologies in biological and biomedical research: a functional perspective. Brief Bioinform, Nov;16(6):1069-80. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv011. Epub 2015 Apr 10. PMID: 25863278; PMCID: PMC4652617.
[16]. Yamada I, Washio K, Shindo H, Matsumoto Y. 2022. Global Entity Disambiguation with BERT. In: Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 3264–3271, Seattle, United States. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[17]. Guia J, Soares VG, Bernardino J. 2017. Graph Databases: Neo4j Analysis. In ICEIS (1), pp. 351-356.
[18]. Siemer S. 2019. Exploring the Apache Jena framework. George August University: Göttingen, Germany.
[19]. Jourdan JP, Bureau R, Rochais C, Dallemagne P. 2020. Drug repositioning: a brief overview. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 72(9), pp. 1145-1151.
[20]. Obata H. 2017. Analgesic mechanisms of antidepressants for neuropathic pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2483.
[21]. Guo R, Zhao Y, Zou Q, Fang X, Peng S. 2018. Bioinformatics applications on Apache Spark. GigaScience, Volume 7, Issue 8, August 2018, giy098.
[22]. Agarwal N, Sondhi A, Chopra K, Singh G. 2021. Transfer learning: Survey and classification. Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences: Proceedings of ICSICCS 2020, pp. 145-155.









