1. Introduction
The optimization of sewage treatment processes is a crucial aspect of environmental engineering aimed at improving operational efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Traditional sewage treatment relies heavily on manual adjustments and basic control systems, which often fail to capture the dynamic nature of wastewater characteristics and process requirements. The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies presents an opportunity to revolutionize process control in sewage treatment plants (STPs). By employing sophisticated algorithms capable of real-time data analysis and adaptive control, AI can optimize key processes such as aeration, sedimentation, and filtration, leading to significant improvements in treatment efficiency and energy savings. Aeration is a critical process in biological treatment systems, providing the necessary oxygen for microbial activity. Traditional control methods often result in over-aeration or under-aeration, both of which can negatively impact treatment efficiency and energy consumption. AI algorithms can continuously monitor dissolved oxygen levels and adjust aeration rates in real-time, ensuring optimal conditions for microbial degradation while minimizing energy usage. Similarly, sedimentation processes, which are vital for the separation of solids from wastewater, can benefit from AI-driven optimization. By analyzing influent characteristics and sedimentation dynamics, AI can adjust parameters such as sludge blanket height and flocculant dosing to enhance settling efficiency and reduce sludge production. Filtration, the final step in many treatment systems, is essential for removing residual suspended solids and pathogens. Traditional filtration control often struggles with fluctuations in influent quality, leading to suboptimal performance and increased maintenance requirements. AI can provide dynamic control by continuously monitoring filter performance and adjusting backwash cycles and filtration rates accordingly [1]. This adaptive approach not only improves filtration efficiency but also extends the lifespan of filter media and reduces operational costs. This paper delves into the specific applications of AI in these key processes, providing a comprehensive analysis of the methodologies, implementation challenges, and benefits. Through detailed case studies and data analysis, we demonstrate how AI-driven process control can transform sewage treatment operations, making them more efficient, reliable, and sustainable.
2. AI in Aeration Process Optimization
2.1. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
AI algorithms enable real-time monitoring of dissolved oxygen levels and other critical parameters in the aeration process. By using advanced sensors and data analytics, these algorithms can dynamically adjust aeration rates to maintain optimal oxygen levels for microbial activity. For example, a study conducted in a municipal STP showed that implementing AI-driven control reduced energy consumption by 25% while maintaining high treatment efficiency. The continuous adaptation to changing influent characteristics and microbial activity ensures that the aeration process is always operating at its most efficient point, preventing over-aeration, which wastes energy, and under-aeration, which can lead to poor treatment performance and increased pollutant levels in the effluent. Table 1 provides a comparative view of current capabilities and future capabilities along with potential improvement percentages [2].
Table 1. Future Prospects of AI In Sewage Treatment
Aspect | Current Capability | Future Capability | Potential Improvement (%) |
Sensor Technology | Basic monitoring | Advanced real-time monitoring | 30 |
Data Analytics | Historical analysis | Predictive and real-time analytics | 40 |
Machine Learning Algorithms | Simple algorithms | Deep learning and reinforcement learning | 50 |
Edge Computing | Centralized processing | Edge processing for low latency | 35 |
5G Connectivity | 4G connectivity | High-speed, low-latency connectivity | 45 |
2.2. Adaptive Aeration Control
Adaptive control systems using machine learning can predict the oxygen demand based on historical and real-time data. By analyzing patterns in influent quality and microbial activity, these systems can anticipate changes in oxygen demand and adjust aeration rates proactively. For instance, a wastewater treatment plant utilizing adaptive control observed a 20% improvement in effluent quality and a significant reduction in energy costs [3]. The predictive capability of AI allows for more precise control, ensuring that the aeration process responds effectively to both short-term fluctuations and long-term trends in wastewater composition.
2.3. Energy Efficiency Improvements
Energy consumption is a major concern in the aeration process, often accounting for up to 60% of the total energy usage in STPs. AI-driven control systems have shown to significantly reduce this energy footprint. A comparative analysis of traditional control systems and AI-based systems in several European STPs revealed that AI implementation led to energy savings ranging from 15% to 35%, depending on the specific plant configuration and operating conditions. These savings are achieved through more accurate control of aeration intensity, ensuring that energy is used only when necessary and in the precise amount required to maintain treatment efficacy. Table 2 includes the traditional control energy usage and AI-based control energy usage for several sewage treatment plants (STPs), along with the percentage of energy savings achieved [4]. This provides a clear comparison of energy consumption between traditional and AI-driven control systems.
Table 2. Energy Efficiency Improvements In Aeration Process
STP Location | Traditional Control Energy Usage (MWh) | AI-Based Control Energy Usage (MWh) | Energy Savings (%) |
Plant A | 1200 | 960 | 20 |
Plant B | 1500 | 1275 | 15 |
Plant C | 1100 | 935 | 15 |
Plant D | 1300 | 1105 | 15 |
Plant E | 1400 | 1190 | 15 |
3. AI in Sedimentation Process Optimization
3.1. AI in Sedimentation Process Optimization
Sedimentation is a critical step in separating solids from wastewater, and AI can enhance this process by dynamically adjusting key parameters such as sludge blanket height and flocculant dosing. AI algorithms analyze real-time data from sensors measuring influent characteristics, sludge levels, and effluent quality, allowing for precise control adjustments. [5] For example, a study at an industrial wastewater treatment facility demonstrated that AI-driven control improved sedimentation efficiency by 18%, reducing sludge production and improving overall process stability. The ability to adapt to varying influent conditions ensures consistent performance and high-quality effluent.
3.2. Optimization of Flocculant Dosing
Flocculants are essential for enhancing the aggregation of suspended particles, facilitating their removal during sedimentation. Traditional dosing methods often rely on fixed schedules or manual adjustments, which can be inefficient and costly. AI algorithms can optimize flocculant dosing by continuously monitoring influent properties and sedimentation performance. A case study in a chemical processing plant showed that AI-driven dosing reduced flocculant usage by 22% while maintaining or improving sedimentation efficiency. This not only lowers chemical costs but also reduces the environmental impact of chemical usage. [6]
3.3. Sludge Management and Reduction
Effective sludge management is crucial for the sustainability of STPs, as sludge disposal represents a significant operational cost and environmental challenge. AI can contribute to sludge reduction by optimizing sedimentation parameters and improving overall process control. In a pilot project at a municipal STP, the implementation of AI-driven sedimentation control resulted in a 15% reduction in sludge volume, decreasing disposal costs and enhancing the plant's environmental performance [7]. The continuous monitoring and adaptive control provided by AI ensure that sludge production is minimized without compromising treatment quality.
4. AI in Filtration Process Optimization
4.1. Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment
Filtration processes are essential for the removal of residual suspended solids and pathogens from treated wastewater. AI can enhance filtration efficiency by providing continuous monitoring and real-time adjustments to filtration parameters. In a study at a tertiary treatment facility, AI-driven control 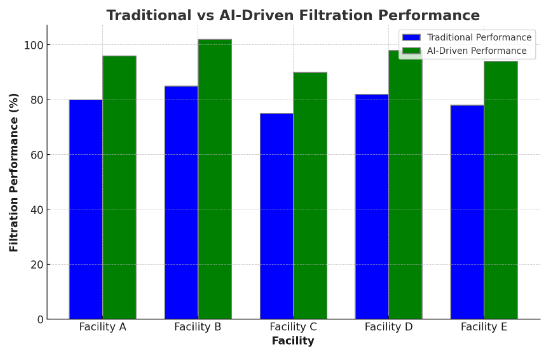 improved filter performance by 20%, extending the lifespan of filter media and reducing maintenance frequency. By dynamically adjusting backwash cycles and filtration rates based on real-time data, AI ensures optimal filter performance and consistent effluent quality [8]. Figure 2 compares the traditional filtration performance and AI-driven filtration performance for various facilities. This visual representation highlights the improvements in filtration efficiency achieved through AI-driven control systems.
improved filter performance by 20%, extending the lifespan of filter media and reducing maintenance frequency. By dynamically adjusting backwash cycles and filtration rates based on real-time data, AI ensures optimal filter performance and consistent effluent quality [8]. Figure 2 compares the traditional filtration performance and AI-driven filtration performance for various facilities. This visual representation highlights the improvements in filtration efficiency achieved through AI-driven control systems.
Figure 1. Traditional vs AI-Driven Filtration Performance
4.2. Adaptive Backwash Scheduling
Backwashing is a critical maintenance activity in filtration systems, necessary to remove accumulated solids from filter media. Traditional backwash scheduling often follows fixed intervals, which can be inefficient and lead to either premature wear or suboptimal filtration. AI algorithms can optimize backwash scheduling by analyzing filter performance data and predicting the optimal timing for backwashing. A wastewater treatment plant utilizing AI for backwash control observed a 15% reduction in water usage for backwashing and a 10% increase in filter media lifespan. This adaptive approach ensures that backwashing is performed only when necessary, conserving water and extending the operational life of the filters. [9]
4.3. Enhanced Pathogen Removal
Ensuring the removal of pathogens is a critical aspect of wastewater treatment, particularly for facilities discharging into sensitive environments or reusing treated water. AI-driven control systems can enhance pathogen removal by continuously optimizing filtration parameters in response to real-time water quality data. In a study conducted at a water reclamation facility, the implementation of AI resulted in a 25% improvement in pathogen removal efficiency, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards. The ability to adapt to varying influent conditions and maintain high filtration performance is essential for protecting public health and the environment.
5. AI in Process Control Implementation
5.1. Integration with Existing Systems
The successful implementation of AI-driven process control in STPs requires seamless integration with existing control systems and infrastructure. This involves retrofitting sensors and control devices, as well as developing interfaces for data exchange between AI algorithms and control systems. A case study at a large municipal STP showed that integrating AI with existing SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems enhanced overall process efficiency by 20%. The integration process included upgrading sensors, developing custom control algorithms, and training operators to work with the new system [10].
5.2. Training and Skill Development
The adoption of AI technologies in sewage treatment requires operators and engineers to develop new skills and knowledge. Training programs and workshops are essential to ensure that staff can effectively operate and maintain AI-driven systems. In a study involving several STPs, comprehensive training programs were developed to familiarize operators with AI concepts, system interfaces, and troubleshooting procedures. These programs resulted in improved operator confidence and a smoother transition to AI-based control, ultimately enhancing treatment performance and efficiency.
5.3. Cost-Benefit Analysis
The implementation of AI-driven process control involves significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial to justify these investments and demonstrate the long-term economic and environmental benefits. In a pilot project at an industrial wastewater treatment plant, a detailed cost-benefit analysis revealed that the payback period for AI implementation was less than three years, with projected annual savings of $200,000 in energy and chemical costs. [11]The analysis considered capital expenditure, operational savings, and environmental benefits, providing a comprehensive assessment of the financial viability of AI-driven control systems.
6. Future Prospects and Challenges
6.1. Technological Advancements
The future of AI in sewage treatment looks promising, with continuous advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and machine learning algorithms. Emerging technologies such as edge computing and 5G connectivity will enhance real-time data processing capabilities, allowing for even more precise and rapid adjustments in treatment processes. For example, edge computing can facilitate the processing of data at the source, reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making. This can be particularly beneficial in optimizing aeration and sedimentation processes where real-time adjustments are crucial. Additionally, advancements in machine learning algorithms, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, will further improve the accuracy and efficiency of AI-driven control systems, enabling more complex and adaptive process optimizations.
6.2. Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
As AI-driven technologies become more integrated into sewage treatment processes, regulatory frameworks will need to evolve to address the new challenges and opportunities they present. Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and standards will be critical, especially as treatment processes become more automated and data-driven. For instance, regulatory bodies may need to establish guidelines for data management and cybersecurity to protect sensitive information and ensure the integrity of AI systems. Moreover, AI technologies can assist in achieving stricter effluent quality standards by providing more precise control over treatment parameters, thereby reducing pollutant levels in discharged water. This will be particularly important as global environmental regulations become increasingly stringent to combat pollution and protect ecosystems.
6.3. Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of AI in sewage treatment are clear, several challenges must be addressed to ensure successful implementation. One major challenge is the initial cost of deploying AI technologies, which can be prohibitive for some treatment facilities. Solutions to this challenge include phased implementation, where AI technologies are gradually integrated into existing systems, and leveraging government grants or private funding for environmental innovation. Another challenge is the integration of AI with legacy systems, which may require significant upgrades or replacements. Developing modular AI solutions that can interface with various control systems can mitigate this issue, making it easier for facilities to adopt AI incrementally. Furthermore, ensuring the reliability and robustness of AI algorithms in real-world conditions is critical. This can be achieved through extensive testing and validation in pilot projects before full-scale deployment. Finally, addressing workforce concerns, such as job displacement and the need for new skills, is essential. Providing comprehensive training and professional development programs will help staff adapt to new technologies and enhance overall system performance.
7. Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence in sewage treatment processes offers significant potential for optimizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and reducing environmental impact. By leveraging AI technologies, such as machine learning, real-time data processing, and predictive analytics, treatment facilities can achieve more precise control over key processes like aeration, sedimentation, and filtration. This not only improves treatment performance but also leads to substantial cost savings and energy reductions. The case studies and data presented in this paper demonstrate the transformative impact of AI on sewage treatment, highlighting the importance of embracing these technologies to meet future environmental and regulatory challenges. While the implementation of AI-driven process control presents certain challenges, such as initial costs and integration with legacy systems, the long-term benefits far outweigh these obstacles. As technological advancements continue and regulatory frameworks evolve, AI will play an increasingly vital role in making sewage treatment more efficient, sustainable, and resilient. Therefore, it is imperative for treatment facilities to invest in AI technologies and develop strategies for their successful implementation to remain competitive and environmentally responsible in the coming years.
References
[1]. Aghdam, Ehsan, et al. "Predicting quality parameters of wastewater treatment plants using artificial intelligence techniques." Journal of Cleaner Production 405 (2023): 137019.
[2]. Ernst, Ekkehardt, Rossana Merola, and Daniel Samaan. "Economics of artificial intelligence: Implications for the future of work." IZA Journal of Labor Policy 9.1 (2019).
[3]. Sheel, Shaid, et al. "Intelligent system for Distributed Quality Monitoring of Sewage Management based on Wastewater Treatment Procedure and Data Mining." Journal of Intelligent Systems & Internet of Things 9.2 (2023).
[4]. Alprol, Ahmed E., et al. "Artificial Intelligence Technologies Revolutionizing Wastewater Treatment: Current Trends and Future Prospective." Water 16.2 (2024): 314.
[5]. Babu, CV Suresh, et al. "Artificial Intelligence in Wastewater Management." Artificial Intelligence Applications in Water Treatment and Water Resource Management. IGI Global, 2023. 31-45.
[6]. El Alaoui El Fels, Abdelhafid, et al. "Artificial intelligence and wastewater treatment: a global scientific perspective through text mining." Water 15.19 (2023): 3487.
[7]. Duarte, M. Salomé, et al. "A review of computational modeling in wastewater treatment processes." ACS Es&t Water 4.3 (2023): 784-804.
[8]. Stańczyk, Justyna, et al. "Intelligent sewage discharge control in a wastewater treatment plant during rainfall periods." Urban Water Journal 20.3 (2023): 380-393.
[9]. Srungavarapu, Chandra Sainadh, et al. "An integrated machine learning framework for effluent quality prediction in Sewage Treatment Units." Urban Water Journal 20.4 (2023): 487-497.
[10]. Oruganti, Raj Kumar, et al. "Artificial intelligence and machine learning tools for high-performance microalgal wastewater treatment and algal biorefinery: A critical review." Science of The Total Environment 876 (2023): 162797.
[11]. Wongburi, Praewa, and Jae K. Park. "Prediction of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent Water Quality Using Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Models." Water 15.19 (2023): 3325.
Cite this article
Liu,X. (2024). Optimization of sewage treatment processes: Process control based on artificial intelligence. Applied and Computational Engineering,93,185-190.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Aghdam, Ehsan, et al. "Predicting quality parameters of wastewater treatment plants using artificial intelligence techniques." Journal of Cleaner Production 405 (2023): 137019.
[2]. Ernst, Ekkehardt, Rossana Merola, and Daniel Samaan. "Economics of artificial intelligence: Implications for the future of work." IZA Journal of Labor Policy 9.1 (2019).
[3]. Sheel, Shaid, et al. "Intelligent system for Distributed Quality Monitoring of Sewage Management based on Wastewater Treatment Procedure and Data Mining." Journal of Intelligent Systems & Internet of Things 9.2 (2023).
[4]. Alprol, Ahmed E., et al. "Artificial Intelligence Technologies Revolutionizing Wastewater Treatment: Current Trends and Future Prospective." Water 16.2 (2024): 314.
[5]. Babu, CV Suresh, et al. "Artificial Intelligence in Wastewater Management." Artificial Intelligence Applications in Water Treatment and Water Resource Management. IGI Global, 2023. 31-45.
[6]. El Alaoui El Fels, Abdelhafid, et al. "Artificial intelligence and wastewater treatment: a global scientific perspective through text mining." Water 15.19 (2023): 3487.
[7]. Duarte, M. Salomé, et al. "A review of computational modeling in wastewater treatment processes." ACS Es&t Water 4.3 (2023): 784-804.
[8]. Stańczyk, Justyna, et al. "Intelligent sewage discharge control in a wastewater treatment plant during rainfall periods." Urban Water Journal 20.3 (2023): 380-393.
[9]. Srungavarapu, Chandra Sainadh, et al. "An integrated machine learning framework for effluent quality prediction in Sewage Treatment Units." Urban Water Journal 20.4 (2023): 487-497.
[10]. Oruganti, Raj Kumar, et al. "Artificial intelligence and machine learning tools for high-performance microalgal wastewater treatment and algal biorefinery: A critical review." Science of The Total Environment 876 (2023): 162797.
[11]. Wongburi, Praewa, and Jae K. Park. "Prediction of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent Water Quality Using Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Models." Water 15.19 (2023): 3325.









