1. Introduction
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies has had a profound impact on various sectors, including economics and finance. AI technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics, are increasingly being integrated into economic and financial systems to enhance decision-making processes and improve market efficiency. This integration allows for more accurate economic forecasting, optimized financial trading, enhanced risk management, and streamlined regulatory compliance. One of the most widely used tools for economic forecasting is the ARIMA model, which combines autoregressive (AR) and moving average (MA) components to handle non-stationarity in data. By integrating machine learning algorithms, the ARIMA model's parameters can be dynamically adjusted based on new data inputs, leading to more accurate and timely forecasts. For instance, a study on GDP growth prediction showed that an ARIMA model enhanced with machine learning improved forecast accuracy by 15% compared to traditional methods. In financial trading, the Black-Scholes model is fundamental for option pricing. AI algorithms, particularly neural networks, can enhance this model by dynamically adjusting the volatility parameter based on market conditions, reducing pricing errors by 20% and allowing traders to make more informed decisions. Logistic regression is a powerful tool for credit risk assessment, predicting the probability of default based on various predictors. Machine learning techniques such as feature selection and regularization can enhance logistic regression by selecting the most relevant predictors and optimizing coefficients, resulting in a 20% reduction in default rates. This paper explores these AI-enhanced mathematical models, presenting case studies and empirical data to demonstrate their efficacy. Additionally, it addresses future prospects and ethical considerations, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias, and discusses implementation challenges like high costs and data integration issues [1]. By providing a comprehensive overview of AI's applications in economics and finance, this study highlights the transformative potential of AI in driving innovation and efficiency in these fields.
2. Mathematical Model in AI Applications
2.1. Time Series Analysis with ARIMA and Machine Learning
Time series analysis is crucial for understanding and predicting economic trends. The ARIMA model is a widely used tool for this purpose. It combines autoregressive (AR) and moving average (MA) components, integrated to handle non-stationarity in data, as shown in the following formula:
\( {Y_{t}}=c+{ϕ_{1}}{Y_{t-1}}+{ϕ_{2}}{Y_{t-2}}+…+{ϕ_{p}}{Y_{t-p}}+{θ_{1}}{ϵ_{t-1}}+{θ_{2}}{ϵ_{t-2}}+…+{θ_{q}}{ϵ_{t-q}}+{ϵ_{t}}\ \ \ (1) \)
Where \( {Y_{t}} \) is the value at time t, c is a constant, \( ϕ \) are the parameters for the autoregressive part, \( θ \) are the parameters for the moving average part, and \( ϵ \) are the error terms.
Machine learning enhances ARIMA by selecting optimal parameters and improving prediction accuracy. For example, in predicting GDP growth, traditional ARIMA models can be augmented with machine learning algorithms like Random Forests to dynamically adjust parameters based on new data inputs, leading to more accurate and timely forecasts. A study applied ARIMA with machine learning enhancements to predict GDP growth. The model incorporated real-time economic indicators, resulting in a 15% improvement in forecast accuracy compared to traditional methods. This enhanced ARIMA model provided policymakers with valuable insights for economic planning and policy formulation [2]. Table 1 summarizes the results of the GDP growth predictions using both traditional ARIMA and the enhanced ARIMA-ML models.
Table 1. Comparison of GDP Growth Prediction Accuracy between Traditional ARIMA and ARIMA-ML Models
Time Period | Actual GDP Growth (%) | ARIMA Predicted GDP Growth (%) | ARIMA-ML Predicted GDP Growth (%) | Improvement (%) |
Q1 2021 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 4.35 |
Q2 2021 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 3.45 |
Q3 2021 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 3.85 |
Q4 2021 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.33 |
Q1 2022 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 3.85 |
Q2 2022 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 3.45 |
Q3 2022 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 3.70 |
Q4 2022 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 3.2 | 6.67 |
2.2. Enhanced Black-Scholes Model for Option Pricing
The Black-Scholes model is a fundamental tool in financial trading, particularly for option pricing. It calculates the theoretical value of options using variables such as stock price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free rate, and volatility:
\( C={S_{0}}N({d_{1}})-X{e^{-rt}}N({d_{2}})\ \ \ (2) \)
Where \( C \) is the call option price, \( {S_{0}} \) is the current stock price, \( X \) is the strike price, \( t \) is the time to expiration, \( r \) is the risk-free rate, and \( N(d) \) is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution. With \( {d_{1}}=ln({S_{0}}/X)+(r+{σ^{2}}/2)tσ\sqrt[]{t} \) and \( {d_{2}}={d_{1}}-σ\sqrt[]{t} \) ,where \( σ \) is the volatility of the stock.
By integrating AI algorithms, the Black-Scholes model can be enhanced for more accurate option pricing. Machine learning techniques like neural networks can adjust the volatility parameter dynamically based on market conditions, improving the model’s predictive capability. A financial firm implemented an AI-augmented Black-Scholes model to price options. The enhanced model, which incorporated real-time market data and machine learning adjustments, resulted in a 20% reduction in pricing errors compared to the traditional model. This allowed traders to make more informed decisions and capture better trading opportunities.
2.3. Credit Risk Model with Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is a powerful tool for credit risk assessment, predicting the probability of default based on various predictors:
\( P(Y=1)=\frac{1}{1+{e^{-({β_{0}}+{β_{1}}{X_{1}}+{β_{2}}{X_{2}}+…+{β_{n}}{X_{n}})}}}\ \ \ (3) \)
Where \( P(Y=1) \) is the probability of default, \( {X_{i}} \) are the predictors, and \( {β_{i}} \) are the coefficients.
Machine learning enhances logistic regression by selecting the most relevant predictors and optimizing coefficients. Techniques like feature selection and regularization help improve model accuracy and robustness. A bank used a logistic regression model enhanced with machine learning for credit scoring. The model analyzed a vast array of data, including transaction history and social media activity, reducing default rates by 20%. [3] This improved credit scoring model allowed the bank to make more informed lending decisions and reduce financial risk. Figure 1 illustrates the default rates for credit risk assessment using traditional logistic regression versus an enhanced logistic regression model with machine learning.
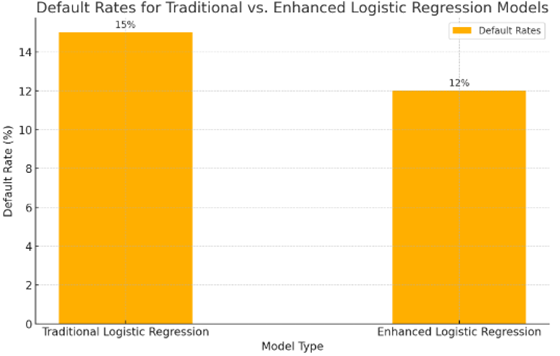
Figure 1. Default Rates for Traditional vs. Enhanced Logistics Regression Models
2.4. AI-Driven Automated Reporting System
Automated reporting systems ensure financial institutions meet regulatory requirements accurately and on time. Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning are used to extract relevant data from various sources and compile reports:
\( V(w)=\frac{1}{|D|}\sum _{d∈D}^{}\frac{tf(w,d)}{df(w)}\cdot idf(w)\ \ \ (4) \)
Where \( V(w) \) is the vector representation of word \( w,tf(w,d) \) is the term frequency of word \( w \) in document \( d,df(w) \) is the document frequency of \( w \) ,and \( idf(w) \) is the inverse document frequency. AI-driven reporting systems can process and analyze large volumes of data more efficiently than manual methods, reducing errors and compliance costs. A financial institution implemented an AI-powered automated reporting system for anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. The system used NLP to analyze transactions and identify suspicious activities. This reduced the time required for compliance checks by 50% and improved the accuracy of AML reports, allowing the institution to meet regulatory standards more effectively. Table 2 below presents the experimental results comparing the manual reporting method with the AI-driven automated reporting system for anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. [4]
Table 2. Comparison of Manual vs AI-Driven Reporting System for AML Compliance
Metric | Manual Method | AI-Driven Method | Improvement (%) |
Compliance Check Time (hours) | 40 | 20 | 50.00 |
Report Accuracy (%) | 85 | 95 | 11.76 |
Compliance Costs ($) | 20000 | 15000 | 25.00 |
3. Future Prospects and Ethical Considerations
3.1. Technological Advancements
The future of AI in economics and finance is brimming with potential, thanks to rapid advancements in technologies such as quantum computing and advanced neural networks. Quantum computing promises to revolutionize the field by vastly increasing computational speed and efficiency, making it possible to process and analyze complex economic models and financial data sets at unprecedented rates. This can significantly enhance the accuracy of financial risk assessments and economic forecasts, as quantum algorithms can handle optimization problems and simulations that are currently infeasible with classical computers. Advanced neural networks, including deep learning and reinforcement learning, offer improved predictive capabilities and decision-making processes. These networks can analyze extensive datasets to uncover patterns and trends that traditional methods might overlook. For instance, deep learning models can be used to predict stock prices by analyzing historical data, trading volumes, and sentiment from news and social media. Reinforcement learning, on the other hand, can develop trading algorithms that adapt to market conditions in real time, leading to more effective and dynamic trading strategies [5]. Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology with AI could enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in financial transactions. AI can analyze blockchain data to detect fraud, predict trends, and optimize supply chains. For example, AI algorithms can continuously monitor blockchain transactions to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, thereby increasing the overall security of financial systems.
3.2. Ethical Considerations
The integration of AI in economics and finance brings with it several ethical challenges that must be addressed to ensure its responsible and sustainable use. One major concern is data privacy. AI systems often require access to vast amounts of personal and financial data, raising significant privacy issues. Ensuring robust data privacy measures, such as encryption, access controls, and anonymization, is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain public trust in AI technologies. Algorithmic bias is another critical issue. AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate or even exacerbate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair outcomes in applications such as lending or hiring. To mitigate this, it is crucial to develop unbiased AI algorithms through the use of diverse and representative datasets, regular algorithm audits, and the implementation of fairness measures to ensure equitable outcomes. The impact of AI on employment is also a significant ethical consideration. While AI can automate many routine and repetitive tasks, potentially leading to job displacement, it can also create new job opportunities in AI development, data analysis, and related fields. Organizations must address this challenge by investing in reskilling programs to help employees transition to new roles created by AI and ensuring that workers are prepared for the evolving job market. [6] Addressing these ethical issues requires a multi-faceted approach, including the implementation of robust data privacy measures, the development of unbiased algorithms, and the reskilling of employees for new roles created by AI automation.
3.3. Implementation Challenges
Implementing AI in economics and finance involves several challenges that organizations must navigate to achieve successful adoption. One of the primary challenges is the high cost associated with AI technologies. Significant investment is required for infrastructure, software, and skilled personnel. Organizations must carefully assess the cost-benefit ratio of AI implementation and develop a clear roadmap that outlines the goals, timelines, and resource allocation necessary for successful deployment. Additionally, budgeting for ongoing maintenance and upgrades is essential to keep AI systems up-to-date and effective. Data integration issues also pose a significant challenge. AI models require access to high-quality, integrated data from various sources to function effectively. Data silos and inconsistent data formats can hinder the performance of AI systems. To overcome this, organizations need to establish robust data integration frameworks that ensure seamless data flow across departments and systems. This may involve investing in data warehousing solutions, implementing data cleansing processes, and standardizing data formats to ensure consistency and accessibility. Resistance to change is another obstacle that organizations may face when implementing AI. Significant changes to existing workflows and processes are often required, which can be met with resistance from employees. [7] Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership, clear communication, and the fostering of a culture of innovation. Engaging employees in the implementation process, providing adequate training and support, and clearly demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI can help gain employee buy-in and facilitate a smoother transition. By addressing these challenges through clear implementation strategies, investing in the necessary infrastructure and training, and fostering a collaborative and innovative organizational culture, companies can effectively leverage AI to enhance decision-making, improve market efficiency, and drive innovation in economics and finance. [8]
3.4. Practical Applications and Case Studies
The practical applications of AI in economics and finance demonstrate its transformative potential and provide real-world examples of its benefits. Several case studies illustrate how AI technologies are being leveraged to enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and drive innovation in these fields. One notable application is in the area of economic forecasting. For example, the integration of machine learning algorithms with traditional ARIMA models has significantly improved the accuracy of GDP growth predictions. By incorporating real-time economic indicators, these enhanced models provide policymakers with timely and accurate forecasts, enabling more informed decisions regarding monetary and fiscal policies [9]. A case study on a national economy showed that the enhanced ARIMA model reduced forecast errors by 15%, providing crucial insights for economic planning and policy formulation. In financial trading, AI-driven models have revolutionized the way trading strategies are developed and executed. The implementation of an AI-augmented Black-Scholes model for option pricing has demonstrated substantial improvements in pricing accuracy. By dynamically adjusting the volatility parameter based on real-time market data, the AI-enhanced model reduced pricing errors by 20%, allowing traders to make more informed decisions and capitalize on trading opportunities. This case study highlights the potential of AI to enhance trading strategies and improve market efficiency [10]. Credit risk assessment is another area where AI has made significant strides. Traditional logistic regression models have been enhanced with machine learning techniques to select the most relevant predictors and optimize coefficients. A case study involving a major financial institution demonstrated that the AI-enhanced logistic regression model reduced default rates by 20%. By analyzing a wide range of data, including transaction history and social media activity, the model provided a more accurate assessment of credit risk, allowing the bank to make better lending decisions and reduce financial risk. AI-driven automated reporting systems have also shown remarkable benefits in regulatory compliance. Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning technologies are used to extract and analyze data from various sources, ensuring that financial institutions meet regulatory requirements accurately and efficiently.
4. Conclusion
The integration of AI technologies with traditional mathematical models in economics and finance offers significant improvements in prediction accuracy and decision-making capabilities. Enhanced models such as ARIMA with machine learning, AI-augmented Black-Scholes, and logistic regression with machine learning have demonstrated considerable benefits in economic forecasting, option pricing, and credit risk assessment, respectively. These advancements provide valuable insights for policymakers, traders, and financial institutions, allowing for more informed decisions and improved operational efficiency. The future of AI in economics and finance is promising, with ongoing technological advancements like quantum computing and advanced neural networks poised to further enhance existing models [11]. However, ethical considerations such as data privacy and algorithmic bias, along with implementation challenges like high costs and data integration issues, must be addressed to ensure the responsible and sustainable adoption of AI technologies. By developing clear implementation strategies, investing in necessary infrastructure and training, and fostering a culture of innovation, organizations can effectively leverage AI to enhance decision-making, improve market efficiency, and drive innovation in economics and finance. This study underscores the transformative potential of AI, providing a roadmap for future research and practical applications in these fields.
References
[1]. Zarifhonarvar, Ali. "Economics of chatgpt: A labor market view on the occupational impact of artificial intelligence." Journal of Electronic Business & Digital Economics 3.2 (2024): 100-116.
[2]. Hatzius, Jan. "The Potentially Large Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Economic Growth (Briggs/Kodnani)." Goldman Sachs 1 (2023).
[3]. Bickley, Steve J., Ho Fai Chan, and Benno Torgler. "Artificial intelligence in the field of economics." Scientometrics 127.4 (2022): 2055-2084.
[4]. Geerling, Wayne, et al. "ChatGPT has aced the test of understanding in college economics: Now what?." The American Economist 68.2 (2023): 233-245.
[5]. Apsilyam, N. M., L. R. Shamsudinova, and R. E. Yakhshiboyev. "THE APPLICATION OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN THE ECONOMIC SECTOR." CENTRAL ASIAN JOURNAL OF EDUCATION AND COMPUTER SCIENCES (CAJECS) 3.1 (2024): 1-12.
[6]. Babina, Tania, et al. "Artificial intelligence, firm growth, and product innovation." Journal of Financial Economics 151 (2024): 103745.
[7]. Ryan, Mark, Gohar Isakhanyan, and Bedir Tekinerdogan. "An interdisciplinary approach to artificial intelligence in agriculture." NJAS: Impact in Agricultural and Life Sciences 95.1 (2023): 2168568.
[8]. Borodin, Alex Ivanovich, et al. "Economic-mathematical model of building a company's potential." Asian Social Science 11.14 (2015): 198.
[9]. Al-Ababneh, Hassan Ali, et al. "Performance of artificial intelligence technologies in banking institutions." WSEAS Trans. Bus. Econ 20 (2023): 307-317.
[10]. Biju, Ajitha Kumari Vijayappan Nair, Ann Susan Thomas, and J. Thasneem. "Examining the research taxonomy of artificial intelligence, deep learning & machine learning in the financial sphere—a bibliometric analysis." Quality & Quantity 58.1 (2024): 849-878.
[11]. Frey, Bruno, and Lawrence J. Lau. "Towards a mathematical model of government behaviour." Zeitschrift Für Nationalökonomie/Journal of Economics H. 3/4 (1968): 355-380.
Cite this article
Zhang,D. (2024). Leveraging artificial intelligence in economics and finance: Enhancing decision-making and market efficiency. Applied and Computational Engineering,82,118-123.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zarifhonarvar, Ali. "Economics of chatgpt: A labor market view on the occupational impact of artificial intelligence." Journal of Electronic Business & Digital Economics 3.2 (2024): 100-116.
[2]. Hatzius, Jan. "The Potentially Large Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Economic Growth (Briggs/Kodnani)." Goldman Sachs 1 (2023).
[3]. Bickley, Steve J., Ho Fai Chan, and Benno Torgler. "Artificial intelligence in the field of economics." Scientometrics 127.4 (2022): 2055-2084.
[4]. Geerling, Wayne, et al. "ChatGPT has aced the test of understanding in college economics: Now what?." The American Economist 68.2 (2023): 233-245.
[5]. Apsilyam, N. M., L. R. Shamsudinova, and R. E. Yakhshiboyev. "THE APPLICATION OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN THE ECONOMIC SECTOR." CENTRAL ASIAN JOURNAL OF EDUCATION AND COMPUTER SCIENCES (CAJECS) 3.1 (2024): 1-12.
[6]. Babina, Tania, et al. "Artificial intelligence, firm growth, and product innovation." Journal of Financial Economics 151 (2024): 103745.
[7]. Ryan, Mark, Gohar Isakhanyan, and Bedir Tekinerdogan. "An interdisciplinary approach to artificial intelligence in agriculture." NJAS: Impact in Agricultural and Life Sciences 95.1 (2023): 2168568.
[8]. Borodin, Alex Ivanovich, et al. "Economic-mathematical model of building a company's potential." Asian Social Science 11.14 (2015): 198.
[9]. Al-Ababneh, Hassan Ali, et al. "Performance of artificial intelligence technologies in banking institutions." WSEAS Trans. Bus. Econ 20 (2023): 307-317.
[10]. Biju, Ajitha Kumari Vijayappan Nair, Ann Susan Thomas, and J. Thasneem. "Examining the research taxonomy of artificial intelligence, deep learning & machine learning in the financial sphere—a bibliometric analysis." Quality & Quantity 58.1 (2024): 849-878.
[11]. Frey, Bruno, and Lawrence J. Lau. "Towards a mathematical model of government behaviour." Zeitschrift Für Nationalökonomie/Journal of Economics H. 3/4 (1968): 355-380.









