1. Introduction
In the frontier fields of robotics, autonomous driving, UAV control and geographic information system, the importance of path planning as one of the core technologies is self-evident. With the increasing requirements of real-time, accuracy and dynamic adaptability in these fields, the research of path planning algorithms is also facing new challenges. AStar (A*), LPA* (Lifelong Planning A*) and DStarLite (Dynamic A*Lite) are classical and advanced algorithms in the field of path planning [1]. Their realization and optimization on the Matlab platform are of great significance for promoting the development of related technologies.
Through Matlab platform simulation experiments, the performance of the algorithm in different scenarios can be visually observed, and key indicators such as path planning efficiency, path quality and computing resource consumption can be evaluated. In addition, the comparative analysis of these three algorithms is helpful to reveal their respective advantages and disadvantages, and provide scientific basis for the selection and optimization of algorithms. Therefore, the research topic of this paper focuses on AStar, LPA* and DStarLite path planning algorithms based on Matlab, aiming to provide new perspectives and ideas for the research and application of relevant path planning algorithms through systematic review and analysis, and promote the continuous progress and development of relevant technologies [2].
In order to achieve the above research objectives, this paper will use the methods of literature induction, sorting, analysis and comparison, to conduct a comprehensive and systematic discussion of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite three path planning algorithms. This paper will combine the characteristics of Matlab platform, elaborate the implementation details of each algorithm and simulation process. Finally, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by simulation experiments, and the performance of different algorithms is compared. In addition, this paper will also discuss the potential challenges and future development direction of these algorithms in practical applications, so as to provide ideas and directions for future research and application.
2. Algorithm Overview
2.1. AStar algorithm
AStar algorithm is a widely used heuristic search algorithm. By combining the global search capability of Dijkstra algorithm with the heuristic information of best-first search, the efficiency of path search is effectively improved [3]. Its core lies in the design of the cost function f(n) = g(n) + h(n), where g(n) represents the actual cost from the starting point to the current node, and h(n) represents the estimated cost from the current node to the end point. AStar algorithm performs well in static environments and can quickly find the shortest path [4].
2.2. LPA* algorithm
LPA* algorithm is an extension of AStar algorithm in dynamic environment. By introducing mechanisms such as "key value" and "priority queue" into the algorithm [5], it realizes fast response to dynamic changes. When the environment changes, the LPA* algorithm can only re-plan the affected area, rather than the global re-plan, thus improving the efficiency of the algorithm [6]. This gives LPA* algorithms significant advantages in dynamic path-planning tasks.
2.3. DStarLite algorithm
It uses the DStarLite algorithm, a simplified version of the D* algorithm, which is also suitable for dynamic environments. The strategy of reverse search to the starting point realizes rapid response to dynamic changes by maintaining "Cost-to-Come" and "Cost-to-Go" information and a priority queue of "Key" values [7]. The DStarLite algorithm has high path planning efficiency in dynamic environments and can maintain the continuity and smoothness of paths [8].
3. Matlab simulation experiment and result analysis
3.1. Experimental design and simulation results
This paper evaluates the performance of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite algorithms by conducting simulation experiments on the Matlab platform. The simulation results are shown in figure 1, figure 2 and figure 3 respectively. The core of the experiment is to construct a preset two-dimensional grid map. The map depicts the distribution of static obstacles that act as fixed constraints in the environment, putting path planning algorithms to the test. At the same time, dynamic obstacle movements were simulated through programming to evaluate the algorithm's adaptability and response speed in intricate dynamic scenarios.
In order to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the algorithm, a meticulous selection and recording of numerous key parameters were undertaken to ensure a thorough analysis, the most core of which is the path planning time (that is, the time required by the algorithm from receiving the information of the starting point and the end point to output the complete path, which directly reflects the computational efficiency and response speed of the algorithm) and the path smoothness (an indicator to measure the degree of curvature of the path). It is of great significance to improve driving efficiency, reduce energy consumption and extend equipment life. In addition, attention is also given to the algorithm's performance in aspects such as path length, among others, to foster a comprehensive understanding of its overall efficacy.[9].
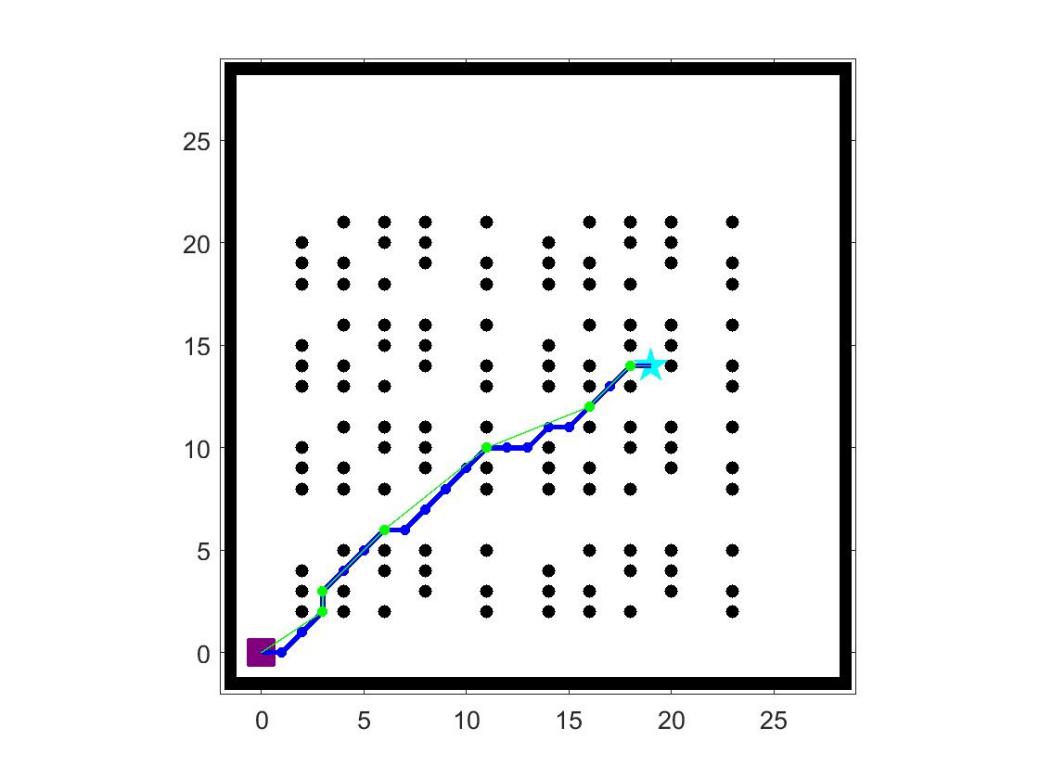
Figure 1. AStar algorithm map 1 simulation results
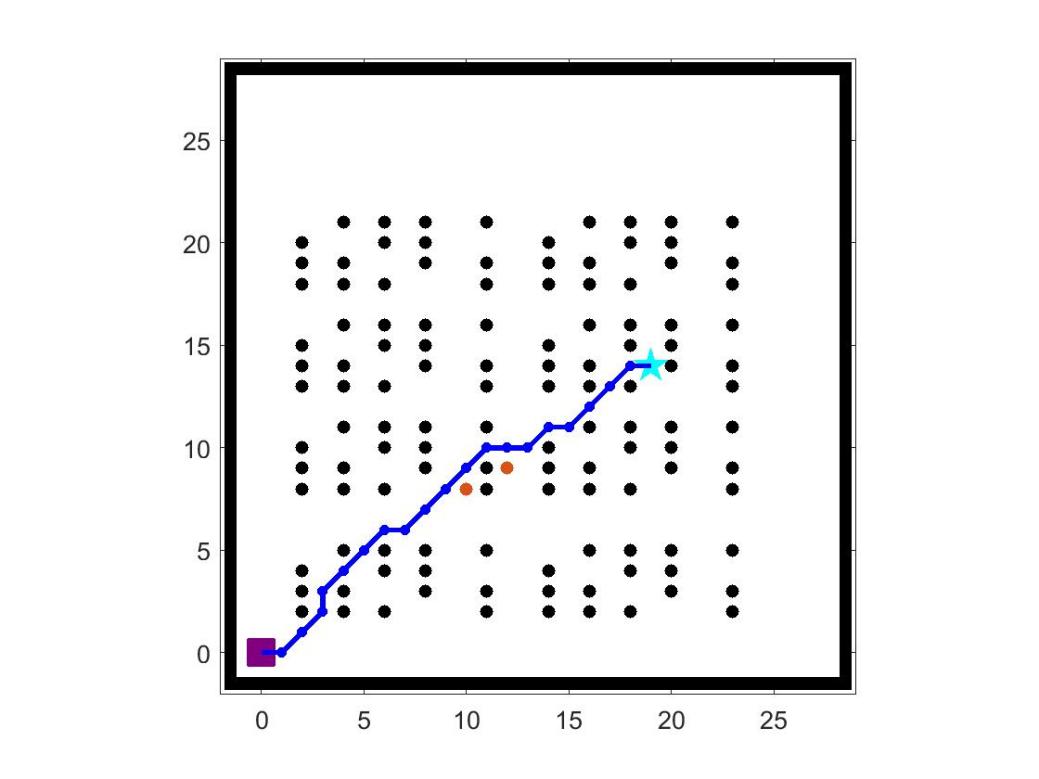
Figure 2. Simulation results of LPA* algorithm map 1
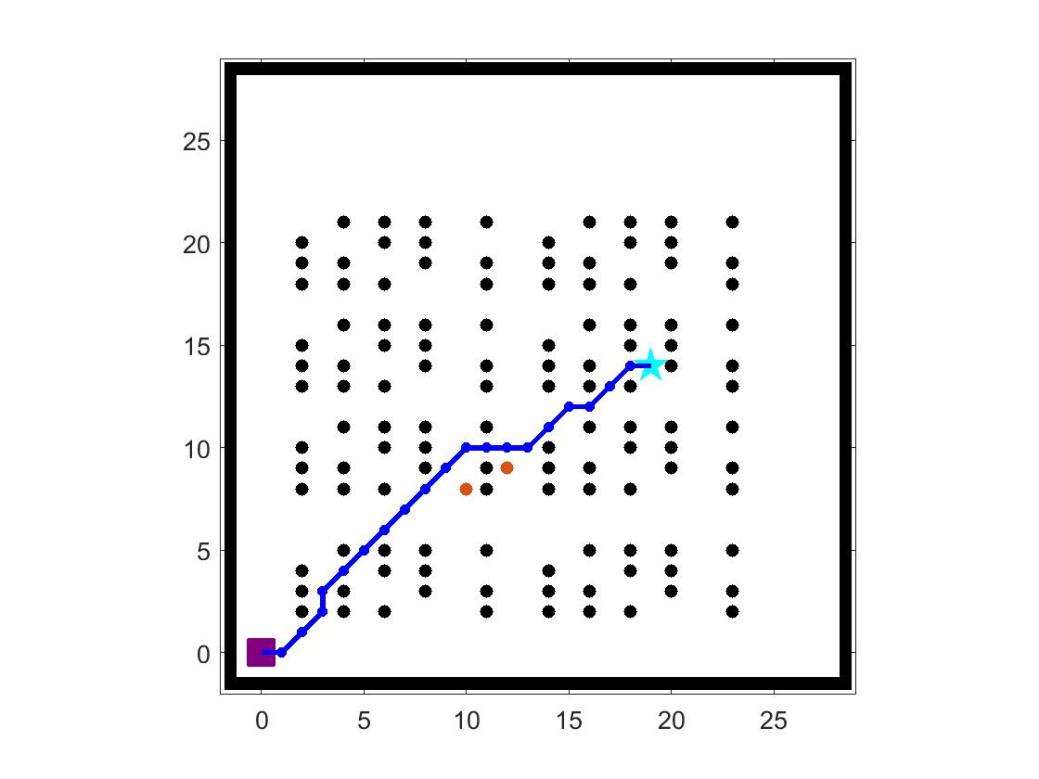
Figure 3. Simulation results of DStarLite algorithm map 1
3.2. Result analysis
In the simulation experiment of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite path planning algorithms based on Matlab, The algorithm's performance was evaluated across three distinct map environments. Table 1 records the key parameters of different algorithms on different maps. According to the data results, each algorithm has its own characteristics on different maps, but in general, it shows some common trends.
Table 1. Comparison of parameters of different algorithms under different maps
map | algorithm | smoothness | run time for path | cost |
map1 | AStar | 4.7124 | 0.23235 | 23.5563 |
LPA* | 7.8540 | 0.10741 | 24.1421 | |
DstarLite | 6.2832 | 0.09506 | 24.1421 | |
map2 | AStar | 3.9270 | 0.36327 | 23.7990 |
LPA* | 7.0686 | 0.28883 | 24.3848 | |
DstarLite | 7.0686 | 0.14481 | 24.3848 | |
map3 | AStar | 7.8540 | 0.32364 | 20.3137 |
LPA* | 7.8540 | 0.13205 | 20.3137 | |
DstarLite | 6.2832 | 0.11249 | 20.3137 |
3.2.1. Path smoothness. The comparison of the path smoothness of the three algorithms is shown in figure 4, where LPA* and DStarLite are superior to AStar in most cases. Especially in maps 1 and 3, the smoothness of LPA* is the highest, reaching 7.8540 and 7.8540 respectively, while DStarLite also performs well, its smoothness is 6.2832 in figure 1 and 6.2832 in figure 3, showing that the two algorithms can better consider the continuity and fluency of the path when generating the path. In contrast, although AStar algorithm can also find an effective path, it is slightly less smooth [10].
Figure 4. Comparison of path smoothness of different algorithms on different maps
3.2.2. Run time for path. The running time of the three algorithms is shown in figure 5, among which DStarLite algorithm shows the fastest computation speed in most cases. In particular, in figure 1 and figure 3, DStarLite has the shortest running time, 0.09506 seconds and 0.11249 seconds respectively, showing its high efficiency in handling path planning problems. The LPA* algorithm is close behind, with shorter running times in Map 1 and Map 3, at 0.10741 seconds and 0.13205 seconds, respectively. Although AStar algorithm can also complete path planning in a reasonable time, its running time is slightly longer than the other two algorithms [11].
Figure 5. Comparison of running time of algorithms on different maps
3.2.3. Route cost. The path cost of the three algorithms is shown in figure 6, and the three algorithms can find a path with similar cost in most cases. This shows that given the map and the starting point and the end point, the three algorithms are equally capable of optimizing the path cost. However, it is worth noting that in some cases, LPA* and DStarLite algorithms have a slightly higher path cost than AStar algorithm despite their shorter running time, which may be due to the trade-off they make in the optimization of path cost in the pursuit of path smoothness and computational efficiency [12].
Figure 6. Comparison of route costs of different algorithms on different maps2
4. Discussion
Through Matlab simulation experiments, the performance of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite path planning algorithms is evaluated. AStar, LPA* and DStarLite algorithms have their own advantages and disadvantages in path planning. AStar algorithm can find effective paths in various scenarios because of its simplicity and wide applicability, but its path smoothness and computational efficiency may not be as good as the other two algorithms. By introducing a dynamic cost update mechanism, the LPA* algorithm significantly improves the smoothness of the path while keeping the path cost close to the optimal, but it may sacrifice some computational efficiency in some cases. The DStarLite algorithm performs well in dynamic environments with its efficient incremental update strategy, which can quickly re-plan paths when the environment changes, while maintaining high path smoothness and low computational costs.
4.1. The guiding significance of this paper for practical application
AStar algorithm: Its broad applicability and simplicity of implementation make it ideal for many basic path planning tasks. In static or infrequent environments, AStar algorithms can quickly find efficient paths, facilitating beginners and rapid prototyping. For resource-constrained or computation-less application scenarios, such as indoor service robot navigation, AStar algorithm still has significant advantages.
LPA* algorithm: By introducing a dynamic cost update mechanism, LPA significantly improves the smoothness of the path while keeping the cost of the path close to the optimal, which is crucial for improving the efficiency of the robot or vehicle, reducing energy consumption, and extending the life of the equipment. In applications requiring high-precision path control, such as the navigation of autonomous vehicles in complex urban road conditions, the advantages of LPA algorithms are particularly obvious.
DStarLite algorithm: Its efficient incremental update strategy makes DStarLite perform well in highly dynamic environments, such as emergency rescue, military reconnaissance and other scenarios, which require the algorithm to quickly respond to environmental changes and re-plan paths. The introduction of DStarLite provides strong technical support for dealing with unpredictable environmental changes.
4.2. Deepening and improving direction of future research
Given the unique advantages of each algorithm, future research should focus on how to effectively combine the broad applicability of AStar, the path smoothness and dynamic cost optimization of LPA*, and the efficient incremental update capability of DStarLite to develop a comprehensive path planning algorithm. This fusion algorithm will be able to better adapt to the complex and changeable actual scenes, and improve the robustness and flexibility of the whole system.
With the continuous improvement of computing power and the continuous progress of algorithm optimization technology, future path planning algorithms should strive to find the best balance between computational efficiency and path quality. By introducing more advanced heuristic search strategies, parallel computing techniques, or machine learning algorithms, the execution speed and path planning quality of the algorithm can be further improved.
In view of highly dynamic environment, future research should pay more attention to the real-time response ability and dynamic adaptability of the algorithm. By optimizing incremental update mechanisms, introducing predictive models, or building more intelligent decision support systems, algorithms can be ensured to run stably and efficiently in complex and changing environments.
In practical applications, path planning often needs to consider multiple objectives and constraints, such as shortest path, optimal time, lowest energy consumption, avoiding obstacles, etc. Future research can explore how to incorporate multi-objective optimization theory in algorithm design to better meet the complex requirements in practical applications.
5. Conclusion
In this study, the performance of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite path planning algorithms is evaluated by Matlab simulation, and the advantages and disadvantages of each algorithm in path smoothness, computational efficiency and dynamic adaptability are revealed. The research results provide a theoretical basis for the selection of path planning algorithms, and point out future research directions such as algorithm fusion, computational efficiency and path quality optimization, dynamic adaptability improvement and multi-objective optimization. With the rapid development of robot navigation, automatic driving and other fields, the demand for path planning algorithms will become higher and higher. Future research can further explore how to combine the advantages of different algorithms to develop more efficient, flexible and robust path planning algorithms. In addition, as technology evolves, path planning algorithms will play a key role in a wider range of fields, driving the continued development of related technologies.
References
[1]. Zhou Wf Yang Xd Zhang Ch et al 2019 Research on path planning algorithm based on MATLAB J Autom Appl p 216218221
[2]. Ma Pc 2023 Intelligent mobile robot path planning algorithms PhD Thesis Changchun University of Technology
[3]. Yin C Tan C Wang C Shen F 2024 An Improved A Path Planning Algorithm Based on Mobile Robots in Medical Testing Laboratories Sensors p 1784
[4]. Ou Y Fan Y Zhang X Lin Y Yang W 2022 Improved A Path Planning Method Based on the Grid Map Sensors p 6198
[5]. Li S Li My Fangzhou et al 2022 Virtual Person Path Planning based on Improved LPA Algorithm Equip Manuf Technol p 82 84105
[6]. Liu Jq Liu Sh Ren Hr et al 2019 Research on Combined path planning Method of Guide roller Workshop AGV based on LPA and DWA algorithms Chin Papermaking p 175184
[7]. Fu L Liu F Liu S et al 2019 Twodimensional path continuous dynamic planning algorithm based on improved DLite Radio Commun Technol p 10421051
[8]. Liu C Xie S Sui X Huang Y Ma X Guo N Yang F 2023 PRM D Method for Mobile Robot Path Planning Sensors p 3512
[9]. Khanmirza E Haghbeigi M Nazarahari M Doostie S 2017 A Comparative Study of Deterministic and Probabilistic Mobile Robot Path Planning Algorithms Proc 5th RSI Int Conf on Robotics and Mechatronics ICRoM Tehran Iran pp 534539
[10]. Ali H Gong D Wang M Dai X 2020 Path Planning of Mobile Robot With Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and MDP to Produce Smooth Trajectory in GridBased Environment Front Neurorobot p 44
[11]. Muñoz P Bellutta P RMoreno MD 2023 Proposing new pathplanning metrics for operating rovers on Mars Sci Rep p 22256
[12]. Chen J Chen Y Nie R Liu L Liu J Qin Y 2024 Application of improved grey wolf model in collaborative trajectory optimization of unmanned aerial vehicle swarm Sci Rep p 17321
Cite this article
Huang,Z. (2024). A Comparative Study of AStar, LPA* and DStarLite Path Planning Algorithms Based on Matlab. Applied and Computational Engineering,80,35-42.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA Workshop: Mastering the Art of GANs: Unleashing Creativity with Generative Adversarial Networks
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhou Wf Yang Xd Zhang Ch et al 2019 Research on path planning algorithm based on MATLAB J Autom Appl p 216218221
[2]. Ma Pc 2023 Intelligent mobile robot path planning algorithms PhD Thesis Changchun University of Technology
[3]. Yin C Tan C Wang C Shen F 2024 An Improved A Path Planning Algorithm Based on Mobile Robots in Medical Testing Laboratories Sensors p 1784
[4]. Ou Y Fan Y Zhang X Lin Y Yang W 2022 Improved A Path Planning Method Based on the Grid Map Sensors p 6198
[5]. Li S Li My Fangzhou et al 2022 Virtual Person Path Planning based on Improved LPA Algorithm Equip Manuf Technol p 82 84105
[6]. Liu Jq Liu Sh Ren Hr et al 2019 Research on Combined path planning Method of Guide roller Workshop AGV based on LPA and DWA algorithms Chin Papermaking p 175184
[7]. Fu L Liu F Liu S et al 2019 Twodimensional path continuous dynamic planning algorithm based on improved DLite Radio Commun Technol p 10421051
[8]. Liu C Xie S Sui X Huang Y Ma X Guo N Yang F 2023 PRM D Method for Mobile Robot Path Planning Sensors p 3512
[9]. Khanmirza E Haghbeigi M Nazarahari M Doostie S 2017 A Comparative Study of Deterministic and Probabilistic Mobile Robot Path Planning Algorithms Proc 5th RSI Int Conf on Robotics and Mechatronics ICRoM Tehran Iran pp 534539
[10]. Ali H Gong D Wang M Dai X 2020 Path Planning of Mobile Robot With Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and MDP to Produce Smooth Trajectory in GridBased Environment Front Neurorobot p 44
[11]. Muñoz P Bellutta P RMoreno MD 2023 Proposing new pathplanning metrics for operating rovers on Mars Sci Rep p 22256
[12]. Chen J Chen Y Nie R Liu L Liu J Qin Y 2024 Application of improved grey wolf model in collaborative trajectory optimization of unmanned aerial vehicle swarm Sci Rep p 17321









