1. Introduction
With the intensification of global resource consumption and the deepening of environmental problems, waste recycling has become an important measure of sustainable development [1-4]. Among many waste products, the recycling and classification of footwear products still faces outstanding challenges: the current degree of automation is still insufficient, mainly relying on manual sorting, which not only costs manpower, but also makes it difficult to achieve efficient recycling. According to the research of Resources, Protection and Recycling, footwear contains multiple composite materials such as rubber, fabric and leather, and conventional technology is difficult to achieve accurate classification, which restricts the improvement of recycling value [5]. Therefore, improving the level of classification technology has become a key link to be broken through.
With the development of computer vision technology, it is applied to the industrial field and can reach 89% success rate, which opens up a new path for smart shoe sorting[6]. Deep learning models such as MobileNet, ResNet, and Vision Converter (ViT) demonstrate significant advantages in image recognition. Studies have shown that ViT has more advantages than traditional CNN in processing large-scale images and provides a new idea for automatic classification of complex items [7]. By integrating advanced vision algorithms and mechanical control systems, footwear sorting accuracy and efficiency can be effectively improved, reducing labor costs and promoting recycling efficiency.
In order to verify the feasibility of this technology, image data sets of cloth shoes, leather shoes, sandals and sports shoes were collected. Based on this, three deep learning frameworks, RegNet, Swin Transformer and ViT, are built to build intelligent footwear sorting model. The test data show that the classification accuracy of the model is stable at about 85%, which confirms the effectiveness of deep learning in this application scenario.
The structure of this paper is as follows: firstly, the current status of waste shoes and clothing recycling technology is described, then the technical principle of the adopted method is systematically discussed, and then the experimental design and result analysis are detailed. Finally, the research results are summarized and the technical optimization direction is prospected.
The purpose of this study is to promote the development of intelligent sorting system, apply vision technology to the field of shoe material recycling, and help the efficient use of resources and environmental pollution control. With the continuous optimization of deep learning technology, the intelligent recycling system will have higher operational efficiency in the future, providing a practical guarantee for sustainable development.
2. Manuscript Preparation
Currently, the main ways of recycling used clothing and footwear include donations, recycling bins/recycling stations, remanufacturing/reprocessing, and branded recycling programs.
Donation is the most common way, with many charitable organizations and thrift stores accepting used clothing to help low-income groups or others in need. Despite the social significance of the donation, some clothes may end up being discarded or resold due to issues such as the cognitive impairment of the donor, attitude disorders, and the mismatch of the needs of the recipient, making true resource recycling difficult to achieve [8].
Recycling bins and recycling stations provide a more convenient way to recycle, where consumers can drop off their unwanted clothing at designated locations and recycling organizations will sort and reuse them. However, the subsequent disposal process of this method is often opaque and has a low reuse rate, which affects the effective recycling of resources.
Remanufacturing and reprocessing is an important means of increasing the utilization of clothing, whereby used clothing can be transformed into new products, such as home textiles or industrial fibers. While the method can reduce waste, the process is more complex and the demand in the market is limited, making it difficult to achieve large-scale application.
In addition, some brands have launched recycling programs where consumers can collect used clothing in stores or designated locations and the brand is responsible for reuse or disposal. For example, H&M recycles jeans after consumption, to make new clothes and new products [9]. This approach helps improve recycling efficiency but is limited by coverage and participation thresholds, which makes it difficult to be widely promoted.
Overall, although these recycling methods have played a role in promoting resource recycling, they still face problems such as low efficiency and insufficient market demand, and policy support and technological innovation are urgently needed to improve the recycling system.
3. Method
3.1. Resnet
3.1.1. Residual Learning
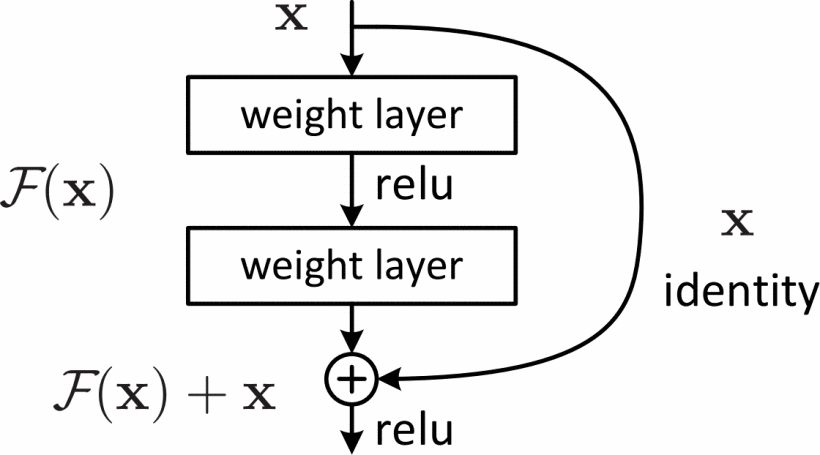
Deep neural networks are susceptible to gradient disappearance and gradient explosion during training, which makes it difficult for the model to converge effectively. To solve this problem, He et al proposed Residual Network, the core idea of which is to introduce residual learning through skip connection, so that the network can learn residual mapping instead of directly learning the complete mapping function [10].
Figure 1: Residual learning: A building block.
Note: source from He, K. , Zhang, X. , Ren, S. , & Sun, J. . (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE
Let the expected mapping function of the neural network be \( H(x) \) ,ResNet transforms through the Residual Block so that it converts to
\( H(x)=F(x)+x \) .
Among them: x is the input feature, F(x) is the residual mapping that needs to be learned, H(x) is the final output. This structure enables the network to pass input directly through identity mapping even if F(x)=0, effectively alleviating the gradient disappearance problem and promoting the optimization of deep networks.
3.1.2. Residual Block
The basic unit of ResNet is the residual block, and its structure is
\( y=F(x,W)+x \)
Here, W is the weight of the convolution layer, F(x, W) represents a series of convolution operations, and y is the output of the residual block.
In ResNet-50 and deeper network structures, a Bottleneck Block is used to reduce computational complexity. Its expression is as follows:
\( y={W_{3}}σ({W_{2}}σ({W_{1}}x)) \)
Here, \( {W_{1}},{W_{3}} \) are 1*1 convolution kernels, used to reduce and restore the number of channels, \( {W_{2}} \) is a 3*3 convolution kernel, \( σ \) is a ReLU nonlinear activation function.
When the input dimension and the output dimension do not match, a 1*1 convolution kernel is introduced for linear transformation to ensure that the dimensions are consistent.
3.1.3. Degradation Problem
In traditional deep networks, as the depth of the network increases, the training error does not necessarily decrease, and may even increase, that is, the so-called degradation problem. However, in the ResNet structure, assuming that the network can learn the identity mapping, then \( { H_{l}}(x)=x \) .
This means that even increasing the depth of the network does not result in greater errors than the shallow network, thus improving the optimization ability of the deep network.
3.1.4. Variants of ResNet
To further improve network performance, the researchers propose a variety of ResNet variants:
ResNet-18/34/50/101/152: Increase the number of layers to improve the feature expression capability. Networks with 50 layers or more adopt a Bottleneck Block to reduce computing costs.
ResNeXt: Based on the ResNet structure, grouped convolutions are introduced to improve parallel computing capabilities [11].
ResNet v2: Optimizes the location of Batch Normalization (BN) to improve model stability [12].
3.2. Vision Transformer
ViT was proposed by Dosovitskiy et al. [13]. Its core idea is to divide images into patches of fixed size and use Transformer for modeling to capture global features.
3.2.1. Patch Embedding
The input image is divided into patches of size P*P, and each patch is converted into D-dimensional feature vector by linear mapping:
\( {z_{i}}={W_{p}}*Flatten({X_{i}})+{b_{p}} \)
A learnable location code \( {E_{pos}} \) is added to retain spatial information.
3.2.2. Transformer Encoder
ViT uses multiple Transformer layers for feature learning. Each layer includes multi-head Self-attention (MHSA) and feedforward neural network (FFN), whose core calculations are as follows:
\( Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(\frac{Q{K^{T}}}{\sqrt[]{{d_{k}}}})V \)
3.2.3. Classification
Finally, take the CLS token or use global average Pooling (GAP) to get the final feature and complete the classification through the full connection layer:
\( y=Softmax({W_{cls}}*{Z_{cls}}) \)
3.3. MobileNet
MobileNet is an efficient convolutional neural network designed for mobile devices to provide better performance with limited computing resources [14]. The core idea is to reduce the amount of computation by using depth-separable convolution, thereby improving the computational efficiency.
3.3.1. Depthwise Separable Convolution
In traditional convolutional neural networks, each convolutional kernel is computed with all channels of the input, which is very computationally intensive. MobileNet uses Depthwise Separable Convolution to decompose standard convolution into two steps:
Deep convolution: Each input channel performs convolution computations independently and does not interact with other channels, reducing the amount of computation.
Point-by-point convolution: Use 1*1 convolution to check the results of the deep convolution for linear combinations between channels.
This decomposition method significantly reduces the amount of computation and the number of parameters, enabling MobileNet to maintain high accuracy while greatly improving computational efficiency [15].
3.3.2. Hyperparameters
MobileNet further optimizes the model with two hyperparameters:
Width Multiplier: Adjust the number of channels in the convolutional layer to control the complexity of the model and reduce the amount of computation.
Resolution Multiplier: Reduces the resolution of the input image, thereby reducing computation and memory footprint.
By adjusting these two factors, MobileNet can choose the right balance between accuracy and computational efficiency for the specific application scenario.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment setup
In this experiment, we used a dataset containing four types of footwear images from Baidu Image Library, 360 Image Library and Google Image Library. The four categories in the dataset were Cloth Shoes, Leather Shoes, Sandals, and Sneakers. As shown in figure 2, each category of images is divided into a training set and a test set for the training and evaluation of the model.
The specific category distribution is as follows:
Cloth Shoes: The training set contains 1610 images and the test set contains 216 images.
Leather Shoes: The training set contains 960 images and the test set contains 193 images.
Sandals: The training set consisted of 772 images and the test set consisted of 120 images.
Sneakers: The training set contains 953 images and the test set contains 123 images.
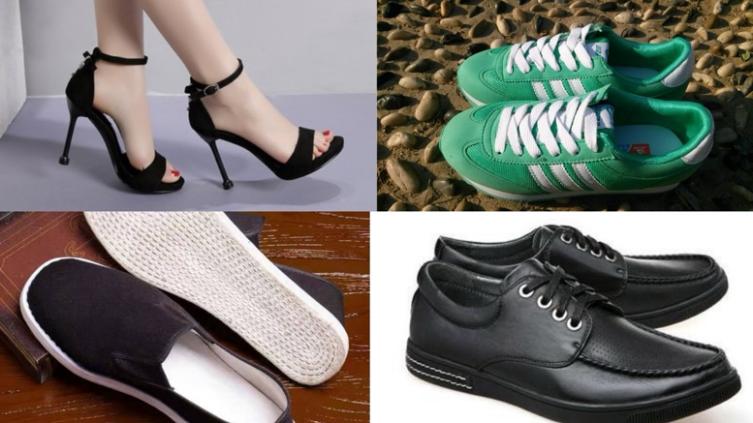

Figure 2: Training sets for different types of shoes
The image distribution of the data set ensures that the sample size of each category is sufficient to support the training and optimization of deep learning models. In addition, the division of the training set and the test set ensures the reliability of the experimental results, which can effectively evaluate the generalization ability of the model on different classes.
The data set has good application value in image classification, especially in the field of footwear recognition, and provides sufficient data support for the training and testing of the model.
4.2. Hyperparameters
Table 1: The hyperparameters in different models
Model | Batch size | Epochs | Learning Rate |
RegNet | 32 | 30 | 0.001 |
Resnet 50 | 0.002 | ||
Resnet 152 | 0.001 | ||
Swim transformer | 0.001 | ||
ViT | 0.0001 |
Note: The height and width of the picture are 224
The model categories included RegNet, Resnet 50, Resnet 152, Swim transformer, and ViT. In the training configuration, 32 samples were used for each training, and the whole data set was iteratively trained 30 times. In terms of learning rate, the models differ: the RegNet, Resnet 152 and Swim transformer are set to have a learning rate of 0.001, the Resnet 50 is set to have a learning rate of 0.002 and the ViT is set to have a learning rate of 0.0001.
4.3. Experiment result
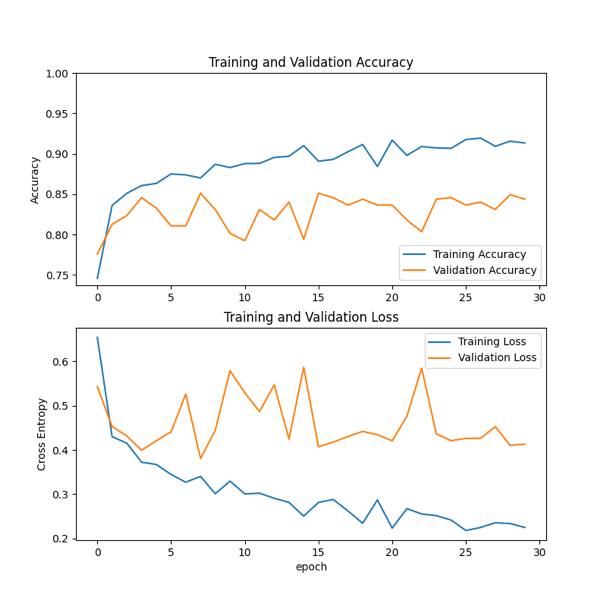
First, we use RegNet for shoe classification. The experimental results are shown in the figure 3. In this experiment, the chart above shows how the training accuracy (blue curve) and validation accuracy (orange curve) change with the training rounds (epoch). After the training began, both of them showed a rapid rising trend, and remained stable at about 0.9 in the later stage, which showed that the model had a high ability of correct recognition of shoe classification on the training set. However, validation accuracy levels off after rising to the range of about 0.85-0.87.
The chart below shows how training losses (blue curve) and validation losses (orange curve) change over the course of the training round, i.e. the convergence curve. The training loss decreased rapidly in the initial stage, gradually slowed down with the progress of training, and stabilized below 0.3 in the later stage, indicating that the model gradually reached a convergence state. Validation losses also showed a downward trend at first, then stabilized to about 0.4-0.45, and were always higher than training losses.
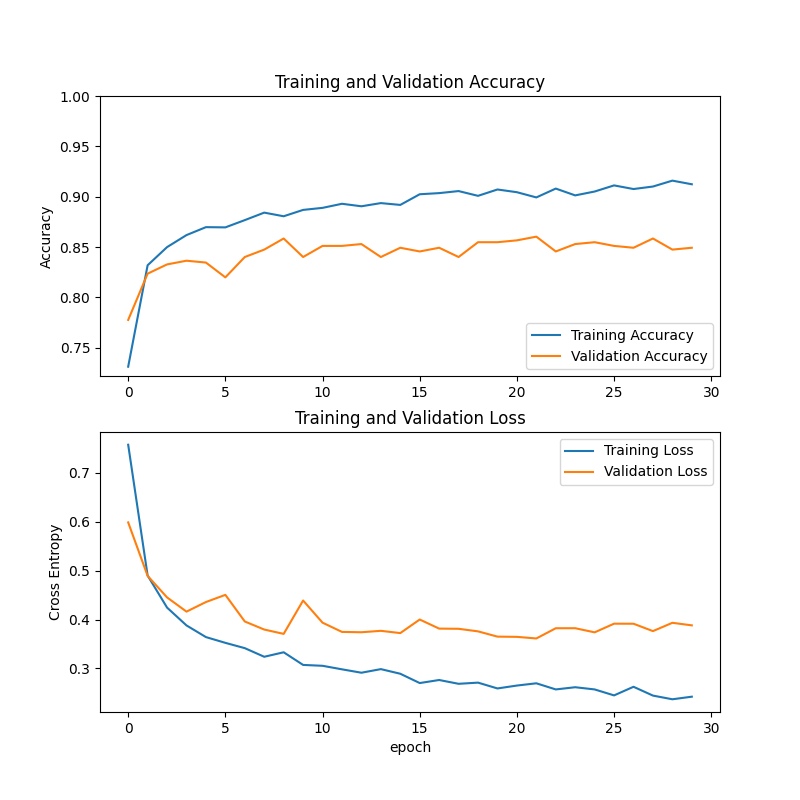
Figure 3: Training results using RegNet
Then, we used ResNet50 and ResNet152 respectively to conduct classification training on shoes. The results are described and compared in terms of accuracy and convergence as follows:
ResNet50 training results
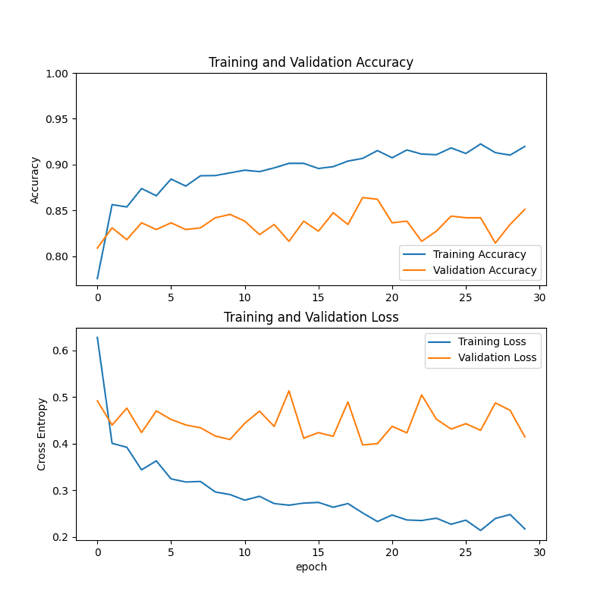
Accuracy: As shown in the figure 4, the training accuracy of ResNet50 was at a low level in the early stage of training, and showed a rapid rising trend with the gradual increase of training rounds, and remained stable within the range of 0.9-0.95 in the later stage. Validation accuracy also increased at the beginning of training and then fluctuated in the range of 0.8-0.85.
Convergence: Training losses decrease significantly at the beginning of training and stabilize in the range of 0.2-0.3 at the end. Verification loss drops to 0.4-0.5 and then levels off.
ResNet152 Training results
Accuracy: As shown in the figure 5, the training accuracy of ResNet152 improved significantly in the early training period, and stabilized at around 0.9-0.95 in the later period. Validation accuracy stabilizes around 0.8-0.85 after rising.
Convergence: Training loss drops rapidly at the beginning of training and stabilizes at 0.2-0.3 later; Verify that the loss drops to 0.4-0.5 and remains stable.
To sum up, the performance of ResNet50 and ResNet152 in the shoe classification task is similar, and both show good results on the training set.
Figure 4: Training results using ResNet50 |
Figure 5: Training results using ResNet152 |
Then, we use Swin-Transformer to carry out the shoe classification task, and the training results obtained are shown in figure 6.
In the initial stage of training, both the training accuracy and the verification accuracy showed a rapid rising trend. With the continuous progress of training, the training accuracy rate increased steadily and remained at about 0.95 in the later stage. The accuracy of verification tends to be stable after rising to about 0.9.
The training loss decreased rapidly at the beginning of training, then gradually slowed down, and stabilized below 0.15 in the later period, indicating that the model gradually converged during the training process. The verified loss drops to about 0.25-0.3 and then levels off.
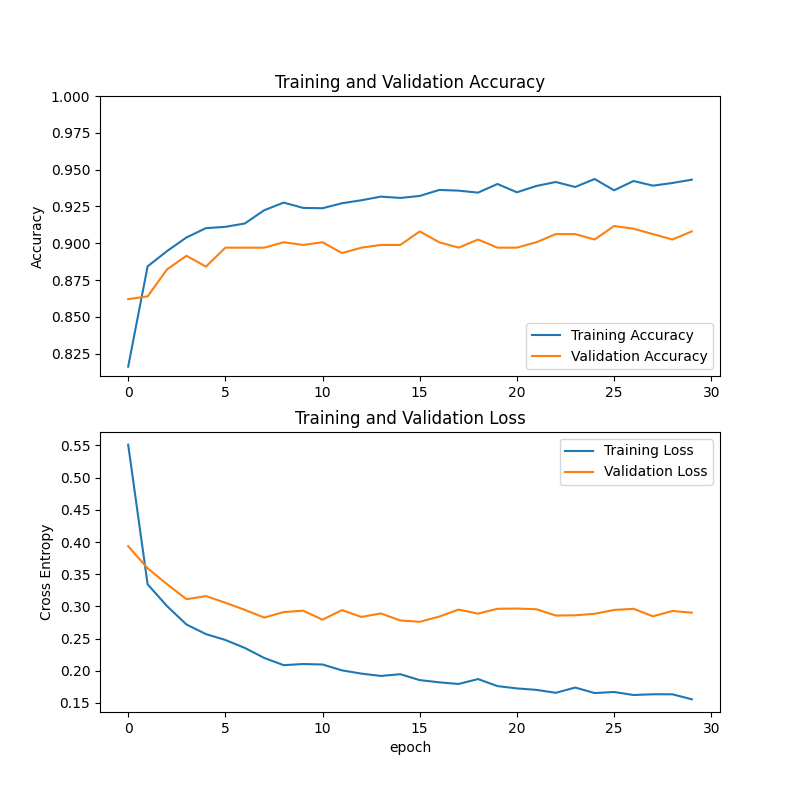
Figure 6: Training results using Swin-Transformer
Finally, we used Vision Transformer (ViT) for the task of sorting shoes.
As shown in Figure 7, in the initial stage of training, the training accuracy rate showed a rapid rising trend, gradually increasing from about 0.4 to about 0.9 in the later stage. Validation accuracy has also increased, but the increase is relatively small, from about 0.4 to about 0.6.
Training losses decrease rapidly at the beginning of training, from about 1.5 to about 0.25 in the later stages. The fluctuation of verification loss is relatively obvious, showing a downward trend as a whole, and fluctuating in the range of about 1-2 in the later period.
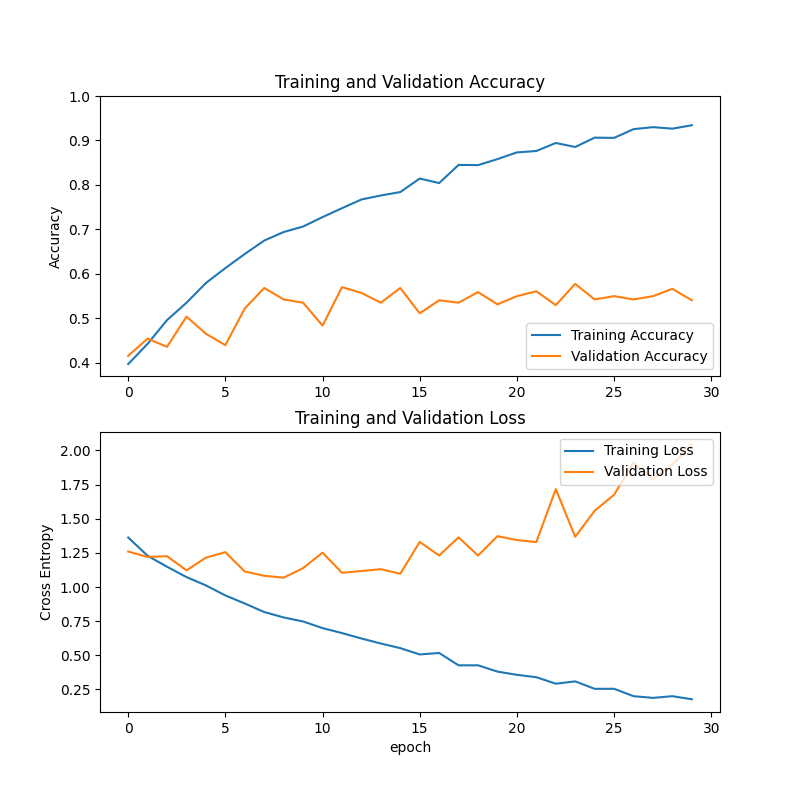
Figure 7: Training results using Vision Transformer
The verification accuracy results of these five models for shoe classification training show that Swim transformer and RegNet have excellent performance, with accuracy close to or above 0.85; The accuracy of Resnet 152 and Resnet 50 is the second, about 0.8; The accuracy of ViT is relatively low, about 0.6. In the task of footwear classification, the performance of different models is different. Similar to the results of this study, when testing multiple deep learning models for image classification, Song et al. finds that Swin Transformer and RegNet have high accuracy and obvious advantages in processing complex image classification tasks [16].
Figure 8: Training results using 5 different models
5. Conclusion
In the context of increasing global resource consumption and deepening environmental pollution, the recycling of waste materials has become a key measure to promote sustainable development. However, the recycling and classification of waste footwear is faced with many problems, its degree of automation is low, and it mainly relies on manual sorting, and the traditional classification method is difficult to accurately classify footwear composed of a variety of materials, which makes the recycling value greatly reduced.
Based on this, with the help of computer vision technology, this study uses deep learning models such as RegNet, Swin Transformer and ViT to build relevant networks and carry out training, and finally achieves an accuracy rate of about 85% in the task of footwear classification. This result preliminarily validates the effectiveness of deep learning methods in this field.
Nevertheless, there are some limitations to this study. On the one hand, the sample diversity of the dataset is poor, only covering common footwear images, and the adaptability is insufficient in the face of complex and changeable actual conditions. On the other hand, there is still room for improvement in model performance, some models have overfitting or underfitting phenomena, and the classification accuracy also has the potential to be further improved. In addition, the current research is only in the experimental stage, and has not fully considered complex factors such as lighting changes and differences in acquisition equipment in practical application scenarios, resulting in difficulties in the transformation of research results into practical applications.
Looking ahead, we plan to conduct in-depth research from various aspects. First, the data set is greatly expanded to collect images from a wide range of sources, and data enhancement techniques such as rotation, cropping, and adding noise are used to further improve the diversity of the data. Secondly, optimize the model structure and training strategy, fully combine the advantages of different models, and constantly improve the model performance by adjusting hyperparameters and adopting advanced optimization algorithms. Finally, real application scenarios are simulated for testing and optimization to enhance the robustness of the model in complex environments, so as to promote the research results from the laboratory to practical application and help the development process of intelligent recycling of waste shoes.
References
[1]. Abubakar, I. R., Maniruzzaman, K. M., Dano, U. L., AlShihri, F. S., AlShammari, M. S., Ahmed, S. M. S., Al-Gehlani, W. A. G., & Alrawaf, T. I. (2022). Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(19), 12717.
[2]. Ram M, Bracci E. Waste Management, Waste Indicators and the Relationship with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2024; 16(19):8486.
[3]. Waheeb, Rasha, Recycling Waste to Maintain Environmental Quality and Achieve Sustainable Development Goals (November 4, 2023). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4623519
[4]. Nandkishor Lodhi, Chadar SN*, Deshraj Singh Thakur and Ashish Raikwar. Recycling and Sustainable Development. Annals of Chemical Science Research Vol4, Issue5
[5]. Elsevier. Resources,Conservation and Recycling. Retrieved from https://www.journals.elsevier.com/resources-conservation-and-recycling
[6]. J. Yang, S. Jiang, K. Chen and L. Liu, "Yolov5-based rotating target pose grasping," 2022 2nd International Conference on Algorithms, High Performance Computing and Artificial Intelligence (AHPCAI), Guangzhou, China, 2022, pp. 367-373
[7]. K. Han et al., "A Survey on Vision Transformer," in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 87-110, 1 Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3152247.
[8]. Anthouli, A., Aravossis, K., Charitopoulou, R., Tot, B., & Vujic, G. (2013). Opportunities & barriers of recycling in Balkan countries: The cases of Greece and Serbia. HSWMA, SeSWA, and ISWA.
[9]. Lascity, M. E., & Cairns, M. R. (2020). Complicated green advertising: Understanding the promotion of clothing recycling efforts. Westminster Papers in Communication and Culture, 15(2).
[10]. He, K. , Zhang, X. , Ren, S. , & Sun, J. . (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE.
[11]. Xie, S. , Girshick, R. , Dollár, Piotr, Tu, Z. , & He, K. . (2016). Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. IEEE.
[12]. He, K. , Zhang, X. , Ren, S. , & Sun, J. . (2016). Identity mappings in deep residual networks. Springer, Cham.
[13]. Howard A G , Zhu M , Chen B ,et al.MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications[J]. 2017.DOI:10.48550/arXiv.1704.04861.
[14]. Dosovitskiy, A. , Beyer, L. , Kolesnikov, A. , Weissenborn, D. , & Houlsby, N. . (2020). An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale.
[15]. Howard, A. G. , Zhu, M. , Chen, B. , Kalenichenko, D. , Wang, W. , & Weyand, T. , et al. (2017). Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications.
[16]. Song B, KC DR, Yang RY, Li S, Zhang C, Liang R. Classification of Mobile-Based Oral Cancer Images Using the Vision Transformer and the Swin Transformer. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):987.
Cite this article
Chen,Y. (2025). Classification Method of Waste Shoes Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Applied and Computational Engineering,146,83-93.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of SEML 2025 Symposium: Machine Learning Theory and Applications
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Abubakar, I. R., Maniruzzaman, K. M., Dano, U. L., AlShihri, F. S., AlShammari, M. S., Ahmed, S. M. S., Al-Gehlani, W. A. G., & Alrawaf, T. I. (2022). Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(19), 12717.
[2]. Ram M, Bracci E. Waste Management, Waste Indicators and the Relationship with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability. 2024; 16(19):8486.
[3]. Waheeb, Rasha, Recycling Waste to Maintain Environmental Quality and Achieve Sustainable Development Goals (November 4, 2023). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4623519
[4]. Nandkishor Lodhi, Chadar SN*, Deshraj Singh Thakur and Ashish Raikwar. Recycling and Sustainable Development. Annals of Chemical Science Research Vol4, Issue5
[5]. Elsevier. Resources,Conservation and Recycling. Retrieved from https://www.journals.elsevier.com/resources-conservation-and-recycling
[6]. J. Yang, S. Jiang, K. Chen and L. Liu, "Yolov5-based rotating target pose grasping," 2022 2nd International Conference on Algorithms, High Performance Computing and Artificial Intelligence (AHPCAI), Guangzhou, China, 2022, pp. 367-373
[7]. K. Han et al., "A Survey on Vision Transformer," in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 87-110, 1 Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3152247.
[8]. Anthouli, A., Aravossis, K., Charitopoulou, R., Tot, B., & Vujic, G. (2013). Opportunities & barriers of recycling in Balkan countries: The cases of Greece and Serbia. HSWMA, SeSWA, and ISWA.
[9]. Lascity, M. E., & Cairns, M. R. (2020). Complicated green advertising: Understanding the promotion of clothing recycling efforts. Westminster Papers in Communication and Culture, 15(2).
[10]. He, K. , Zhang, X. , Ren, S. , & Sun, J. . (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE.
[11]. Xie, S. , Girshick, R. , Dollár, Piotr, Tu, Z. , & He, K. . (2016). Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. IEEE.
[12]. He, K. , Zhang, X. , Ren, S. , & Sun, J. . (2016). Identity mappings in deep residual networks. Springer, Cham.
[13]. Howard A G , Zhu M , Chen B ,et al.MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications[J]. 2017.DOI:10.48550/arXiv.1704.04861.
[14]. Dosovitskiy, A. , Beyer, L. , Kolesnikov, A. , Weissenborn, D. , & Houlsby, N. . (2020). An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale.
[15]. Howard, A. G. , Zhu, M. , Chen, B. , Kalenichenko, D. , Wang, W. , & Weyand, T. , et al. (2017). Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications.
[16]. Song B, KC DR, Yang RY, Li S, Zhang C, Liang R. Classification of Mobile-Based Oral Cancer Images Using the Vision Transformer and the Swin Transformer. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):987.