1. Introduction
At present, images are one of the most common and direct data representations. Whether companies or individuals, or various industries, are inseparable from digital images. One of the most common problems is that the amount of image data may be large. The progress of current image acquisition technology and various industry technologies make the resolution and quality of images increasingly high, which leads to the increase of image file size. Larger image files not only mean more difficult to store, but also the increase of time and bandwidth requirements for transmitting and uploading such images [1, 2].
Therefore, image compression has become a particularly important part of digital image processing [3]. In the past decades, people have developed a variety of coding technologies for image coding, including lossless and lossy coding technologies. Lossy coding has higher compression capacity, reaching 60:1 or higher, but it lacks the ability to accurately restore the original images; Although lossless coding has poor compression ability, the compressed images can be recovered [4]. Most of the latest developments have occurred in the field of image lossy coding technology, while lossless coding technology has developed slowly [4].
Huffman coding and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) coding are two common types of lossless image coding [4]. The compression efficiency of the image will affect the speed of transmission and upload of the compressed file, which is an important part of evaluating the coding technology. However, in current studies, most of them just use one of these methods or simply improve it [1-5]. It is still blank to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of various methods in different situations.
In this paper, the compression efficiency of Huffman coding and LZW coding for colour images or black and white images when the sizes of source image files are small was studied through comparison to find the most appropriate coding method for small images [6].
The rest of this paper is arranged as follows. The Huffman coding and LZW coding methods are reviewed in section Ⅱ. The compression efficiency of the two coding methods for image data in varied sizes image files is compared in section Ⅲ. Finally, the conclusion is given in section Ⅳ.
2. The descriptions of Huffman and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) algorithms
There are the descriptions of Huffman and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) algorithms, which were used in experiments.
2.1. Description of Huffman coding
|
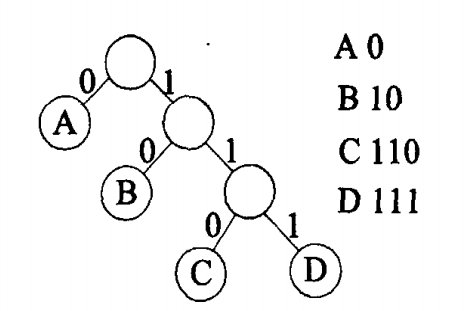
Figure 1. Huffman coding diagram [7]. |
Huffman coding is a highly efficient variable length lossless source coding method, which was proposed in 1952 and is a bottom-up coding method [6, 7]. Figure 1 shows the basic concept of Huffman coding. In the past two decades, image and video compression technology has made considerable progress. In order to improve coding efficiency, Huffman coding is widely used [8]. This coding method needs to first calculate the statistical data characteristics of the information source (the information to be encoded), and then code by the frequency of each source symbol. According to [7], taking binary Huffman coding as an example, the coding steps are as follows:
Start
• Count the number of occurrences of all source symbols and calculate their corresponding frequencies.
• Ignore the elements with zero frequency. Then in the order of high probability to low probability, arrange the source symbols. For convenience, recorded \( p({a_{1}})≥p({a_{2}})≥⋯≥p({a_{n}}) \) .
• Assign a code bit "0" and "1" to each of the two source symbols \( p({a_{n-1}}) \) and \( p({a_{n}}) \) with the lowest probability. Then combine the two source symbols to form a new symbol, and the sum of their probabilities is used as the probability of the new symbol. Next, a new source with n-1 source symbols is obtained, which is represented by \( {S_{1}} \) .
• Arrange \( {S_{1}} \) from large to small and repeat the third step. Obtain the source \( {S_{2}} \) containing only n-2 symbols.
• Repeat the above steps until there are two source symbols left, thus establishing a Huffman tree. Then, starting from the last level of the tree, the codeword corresponding to each symbol is obtained according to the path of Huffman tree (coding path).
End
It can be seen from the above encoding steps of Huffman encoding that this encoding method is faster when processing smaller image files, because the computation of statistical data characteristics of information sources is less. However, in the face of large image files, Huffman coding needs more time for data preprocessing because of the large amount of information contained in their information sources. This is the same as Shannon, Fano and other traditional encoding methods [6].
To analyze the ability of the algorithm to compress images and the quality of compressed images, some image parameters, such as Compression Ratio (CR), Mean Square Error (MSE), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Bits Per Pixel (BPP), can be considered.
Compression Ratio (CR) is an especially important parameter in analyzing image compression algorithm, which can be defined as the ratio between the size of uncompressed image and the size of compressed image. The higher the CR, the greater the information compression capacity of the algorithm [8, 9].
\( CR=\frac{uncompressed image size}{compressed image size} \) (1)
Mean Square Error (MSE) is also one of the parameters for evaluating image compression algorithms. When the value of MSE is small, it indicates that the quality of the compressed image is high, and vice versa [8]. The formula is as follows:
\( MSE=\frac{1}{MN}\sum _{X=1}^{M}\sum _{Y=1}^{N}[f(x,y)-{f^{ \prime }}(x,y){]^{2}} \) (2)
Where the length and width of the images are represented by M and N, and \( f(x,y) \) is the input image (uncompressed image), the compressed image is represented as \( {f^{ \prime }}(x,y) \) .
Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) is defined as the ratio between the size of uncompressed image and the Mean Square Error (MSE). Generally, a higher PSNR value means a higher compressed image quality, and vice versa [8, 9]. The typical value of PSNR for compression is in the range of 30 dB and 50 dB [10]. The equation is:
\( PSNR=10 lo{g_{10}}(\frac{M×N}{MS{E^{2}}}) \) (3)
Where M × N is the size of the input image (uncompressed image).
Bits Per Pixel (BPP) generally refers to pixel depth. Pixel depth is defined as the number of bits used to store each pixel. It is usually used to measure image resolution [8]. The higher the BPP, the image has higher resolution and higher clipping freedom. The formula is:
\( BPP=\frac{size of compressed image}{total no. of pixel in the image} \) (4)
The simulation results of image compression using Huffman algorithm are as follows in Figure 2:
|
Figure 2. Input image [8]. |
|
Figure 3. Compressed image using Huffman algorithm [8]. |
The images in Figure 3 illustrate the original image and the image compressed by Huffman algorithm. The image specification used here is 512 × 512. Here is the data to evaluate the image quality. The parameters of Huffman algorithm were summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Various parameters of Huffman algorithm [8]. | ||||
Algorithm | Huffman | |||
Parameters | CR | PSNR | MSE | BPP |
Apple | 31.69 | 24.52 | 15.20 | 1.51 |
Grass | 13.46 | 14.06 | 15.72 | 1.55 |
Lena | 27.94 | 26.13 | 2.85 | 1.28 |
Man | 43.91 | 28.83 | 2.09 | 1.23 |
Penguin | 29.21 | 22.30 | 19.62 | 0.95 |
On average, CR, PSNR and BPP are 29.24, 23.17 and 1.30, respectively.
To make the experiment more comparative, another experiment using Huffman algorithm is considered [11]. Its images are as following in Figure 4 and Figure 5:
|
Figure 4. The original images [11]. |
|
Figure 5. The output images [11]. |
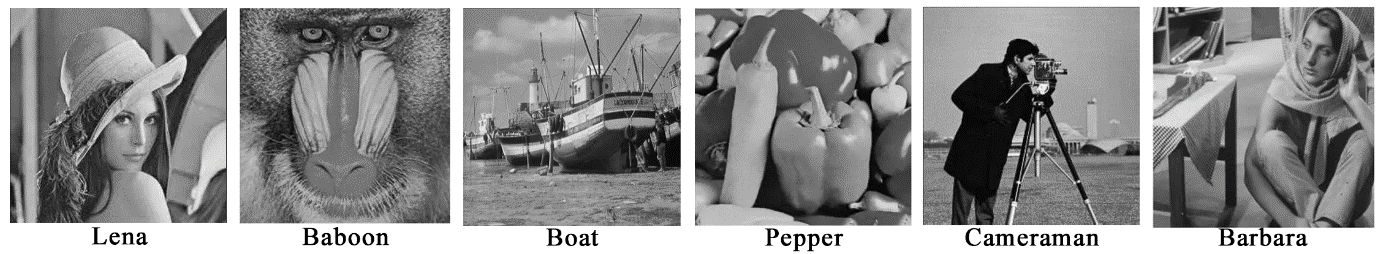
As shown in Figure 4, the original image are black and white images, which contains less information and is easier to encode. The images used in the experiment are all 512 × 512 in size. The calculated PSNR values under different CR conditions are illustrated in Table 2.
Table 2. The PSNR of Huffman algorithm in different CR [11]. | ||||
Algorithm | Huffman | |||
Parameters | PSNR | |||
CR | 20 | 40 | 60 | |
Lena | 40.67 | 36.11 | 33.91 | |
Baboon | 31.36 | 29.11 | 28.91 | |
Boat | 40.23 | 35.62 | 32.62 | |
Pepper | 41.03 | 36.68 | 33.88 | |
Cameraman | 37.82 | 30.23 | 28.73 | |
Barbara | 33.89 | 29.60 | 27.56 | |
It was found that when CR gradually increased, the average value of PSNR decreased steadily, and the value was basically stable above 30.
2.2. Description of Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) coding
Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) algorithm was created by Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv and Terry Welch in 1984. It is also a common lossless data compression algorithm [10]. LZW algorithm is a dynamic compression algorithm based on ASCII dictionary. The main idea is to read substrings of strings and assign encoded output. The LZW coding algorithm can skip the repeated characters (information) in the information source according to the dictionary references. Therefore, it has the function of information compression [1,12]. Especially for large files, they contain more information, and the information compression capability of LZW algorithm is more obvious. The steps of LZW coding algorithm are as follows:
• Based on the ASCII dictionary, initialize the dictionary needed for LZW coding, and use a file reader to read the uncompressed information stream.
• From the first character, judge whether P+C is in the dictionary. Where P is the character currently read, and C is the next character of the current character.
• If yes, P=P+C, repeat the previous step. If not, output the codeword corresponding to the current P, create a new character containing P and C, and add it to the dictionary, then make P=C, and repeat the previous step. Note that the new codewords are extended from the original dictionary according to the sequence of symbols.
• When the last character of the information flow is read, the encoding is completed, and the whole LZW encoding dictionary is completed.
The above coding steps represent the biggest difference between LZW coding and Huffman coding. LZW algorithm does not need to calculate the occurrence frequency of all source symbols, or even read a complete information source when sources are encoded. In other words, when compressing large image files, LZW encoding will be faster.
The quality of image files compressed by LZW coding can also be analyzed by Compression Ratio (CR), Mean Square Error (MSE), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Bits Per Pixel (BPP) [1], [9]. In addition, it can be predicted that when the image file size is small, the CR of LZW coding is not ideal, because the LZW codewords are based on ASCII code, that means, the codewords are eight bits or more. When the size of file is large, its CR will be more ideal.
Taking the image of "Lena" as an example, the simulation results of image compression using LZW algorithm are as following in Figure 6:
Figure 6. (a) The input image; (b) Compressed image [13]. |
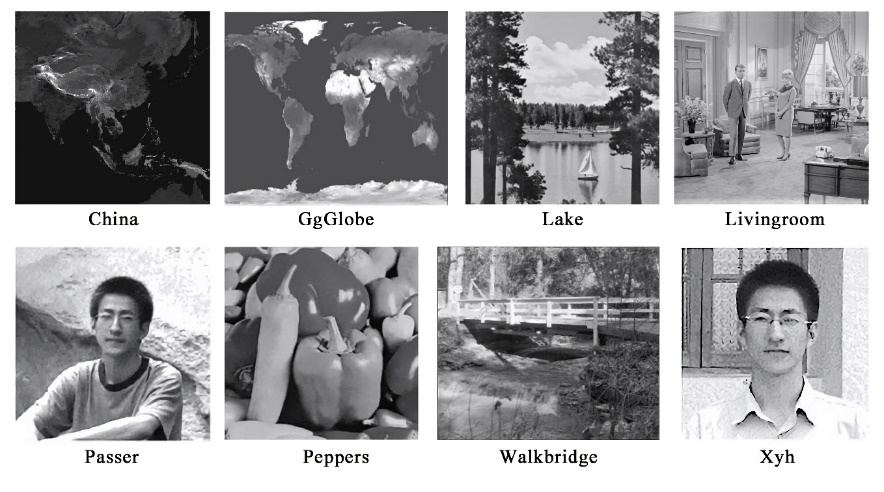
There are eight other images used in the experiment, as shown in Figure 7. All images are black and white.
|
Figure 7. Other uncompressed images [13]. |
The 9 pictures here are all 256 × 256 size image files. The PSNR of the above images is shown in the Table 3.
Table 3. The parameters of the nine images using LZW coding [13]. | ||
Algorithm | Lempel-Ziv-Welch | |
Parameters | BPP | PSNR |
Lena | 6.49 | 51.14 |
China | 6.71 | 51.13 |
GgGlobe | 5.76 | 51.16 |
Lake | 6.89 | 51.16 |
Livingroom | 7.10 | 51.16 |
Passer | 6.39 | 51.10 |
Peppers | 6.46 | 51.16 |
Walkbridge | 7.81 | 51.17 |
Xyh | 5.88 | 51.12 |
The calculated average BPP and PSNR values were 6.61 and 51.14, respectively.
In addition, considering the reliability of the results, the results of another experiment are referred to. The experimental images are as following in Figure 8 and 9:
Figure 8. The three experimental images [10]. |
Figure 9. Compressed images using LZW algorithm [10]. |
The three images are 197kb, 23kb and 67kb in size. The relevant data representing the compressed image quality are as follows in Table 4:
Table 4. Different parameters of LZW algorithm [10]. | |||
Algorithm | Lempel-Ziv-Welch | ||
Parameters | CR | PSNR | MSE |
Image 1 | 3.08 | 22.83 | 0.0052 |
Image 2 | 1.77 | 39.03 | 0.0041 |
Image 3 | 2.23 | 42.68 | 0.0017 |
The calculated average values of CR, PSNR and MSE are 2.36, 34.85 and 0.0037, respectively.
3. Comparison of Huffman coding and LZW coding
According to the experimental results of two different encoding methods, it is found that the CR of LZW algorithm is smaller; The PSNR of Huffman algorithm is lower, while that of LZW algorithm is higher but more stable; In addition, the value of MSE obtained by LZW algorithm is smaller, while the value of MSE obtained by Huffman algorithm is larger. Finally, the BPP value obtained by Huffman algorithm is smaller and more stable.
Firstly, as mentioned above, CR represents the information compression capacity of image compression algorithm. Although different uncompressed images are selected in the experiment, the file size difference is not large, and they are all small images. In other words, the experiment is aimed at compression of images with low resolution. In this case, the CR of LZW algorithm is about 1.77 to 3.08 and increases steadily with the increase of image size. The average of CR of the compressed image under Huffman algorithm reaches 29.24. Of course, the image calculated by LZW algorithm is smaller than that of Huffman algorithm experiment, with a difference of 80kb approximately. However, considering the CR experiment results of LZW algorithm, if the same 512 × 512 size image is used, its CR is still less than 29.24. Therefore, it is reasonably estimated that Huffman algorithm has stronger information compression capability under the condition of image compression with low resolution.
The second parameter is PSNR. The higher the value of this parameter, the higher the compressed image quality. It can be found that in the experiment of Huffman algorithm, the average value of PSNR is 23.17. In the second compression experiment for black and white pictures, the average value of PSNR is about 33.78; In the first experiment of LZW algorithm, the average value of its PSNR reached an ideal 51.14. In the second experiment, the average value of PSNR is 34.85. This parameter has no absolute relationship with the file size of the original images. Therefore, under the LZW algorithm, whether for black and white images or color images, the PSNR value is higher, which means that the compressed image quality is higher.
Similarly, under the Huffman algorithm, the MSE value of the compressed images is large, and the experimental results range from 2.09 to 19.62. However, the mean MSE of LZW algorithm is only 0.0037, which also indicates that the compressed image quality of LZW algorithm is higher.
Finally, BPP, which can represent the resolution of the compressed image. Since the BPP obtained from the two algorithms are based on different images (color images and black and white images), the comparison of BPP is not significant. However, it can be seen preliminarily that the image compressed by LZW algorithm has a larger BPP and higher resolution.
Therefore, in conclusion, when the image size is small, Huffman coding has stronger image compression capability, while the compressed image obtained by LZW coding has higher quality and higher resolution. Among them, it is predictable that Huffman coding has a stronger compression capability for smaller uncompressed images conditions. This is because Huffman algorithm encodes lone source symbols. When the image resolution is small or the overall size of the image is small, there are fewer single symbol sources. In this case, fewer source symbols need to be encoded, resulting in simpler codewords corresponding to each symbol after encoding and shorter codewords. Therefore, the compressed image is smaller, which makes CR larger. However, LZW algorithm will have more advantages when the size of the image files gradually increases. Under these circumstances, the average codeword length obtained by Huffman algorithm is getting longer and longer, while the average codeword length of LZW algorithm is fixed at 8 to 9 bits, resulting in smaller compressed image files and larger CR. In addition, because LZW coding is not based on lone source symbols, its coded codewords are more logical, which also leads to higher quality of compressed images obtained by LZW algorithm, and better PSNR, MSE and BPP.
According to the principle of the two algorithms, when the sizes of the uncompressed image files continue to increase, the CR obtained by LZW algorithm will gradually increase more than that of Huffman algorithm, and this intersection can be obtained through experiments. Therefore, when the sizes of the source image files are larger than the intersection point, theoretically, the image compression capability and the quality of the compressed image of LZW algorithm will be better than that of Huffman algorithm.
However, in addition to CR and the quality of compressed images, the time required for algorithm implementation should also be considered when evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of the algorithm. Huffman algorithm encodes based on the entire image files, while LZW algorithm needs to generate an extended ASCII dictionary in the process of reading the uncompressed image files. These will affect the time required for algorithm implementation. A new experiment is needed to be proposed to measure the time required for the implementation of the two algorithms in assorted sizes source image files.
4. Conclusion
In this paper, we compared two image compression technologies based on Huffman algorithm and LZW algorithm, respectively. Through these two methods, the compressed image results when the source image files are black and white images and color images are obtained respectively, and the CR, PSNR, MSE, BPP four performance parameters of the compressed images are calculated and compared. According to the comparison results, we found that when the sizes of the uncompressed image files are small (about 300kb or less), the image Compression Ratio (CR) of Huffman algorithm is better, and the compressed image quality of LZW algorithm is better. Therefore, the Huffman algorithm can be chosen when the CR is more important than the compressed image quality, otherwise choose LZW algorithm. In this paper, we also briefly introduced the lossy image compression technology and lossless image compression technology, as well as the principles of two available image compression algorithms. As a supplement to the research on image compression algorithms, this research aims to analyze how to choose the better method from the two commonly used image compression algorithms, Huffman algorithm and LZW algorithm, and analyze the advantages of the two algorithms when compressing small images. The results when the source images are larger, and the time required for the two algorithms to run are not considered in this study. In future work, the above two points can be considered for further research.
References
[1]. Birajdar A, Agarwal H, Bolia M and Gupte V, Image Compression Using Run Length Encoding and Lempel Ziev Welch Method, 2019 Global Conf. for Advancement in Technology (GCAT), 2019, pp 1-6
[2]. Khaitu S and Panday S, Canonical Huffman Coding for Image Compression, 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conf. on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), 2018, pp 184-190
[3]. Patel R, Kumar V, Tyagi V and Asthana V, A fast and improved Image Compression technique using Huffman coding, 2016 International Conf. on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), 2016, pp 2283-2286
[4]. Li X, Shen Y and Ma J, An Efficient Medical Image Compression Scheme, 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conf., 2005, pp 3437-3439
[5]. Sangeetha M, Betty P and Kumar G, A biometrie iris image compression using LZW and hybrid LZW coding algorithm, 2017 International Conf. on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS), 2017, pp 1-6
[6]. Chen Y, Zhou L, Chen X, Chen W, 2016, Information Theory and Coding, ed T P Han, Publishing House of Electronic Industry, Beijing, pp 40-44
[7]. Sun B, Wu K, Improvement of Huffman Algorithm and Its Application in Image Compression, Microcomputer Information, 2011, Vol 27, pp 264-266
[8]. Praisline Jasmi R, Perumal B and Pallikonda Rajasekaran M, Comparison of Image Compression Techniques Using Huffman Coding, DWT and Fractal Algorithm, 2015International Conf. on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), 2015, pp 1-5
[9]. Ahmed Z and George L, A Comparative Study Using LZW with Wavelet or DCT for Compressing Color Images, 2020 International Conf. on Advanced Science and Engineering (ICOASE), 2020, pp 53-58
[10]. Prudvi C, Muchahary D and Raghuvanshi A, Analysis of Image Compression Techniques for IoT Applications, 2022 2nd International Conf. on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), 2022, pp 1-5
[11]. Vaish A and Kumar M, A new Image compression technique using principal component analysis and Huffman coding, 2014 International Conf. on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing, 2014, pp 301-305
[12]. Sharma K and Gupta K, Lossless data compression techniques and their performance, 2017 International Conf. on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), 2017, pp 256-261
[13]. Sun M, Xie Y, Tang X and Sun M, Image Compression Based on Classification Row by Row and LZW Encoding, 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2008, pp 617- 621
Cite this article
Ma,S. (2023). Comparison of image compression techniques using Huffman and Lempel-Ziv-Welch algorithms. Applied and Computational Engineering,5,793-801.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Birajdar A, Agarwal H, Bolia M and Gupte V, Image Compression Using Run Length Encoding and Lempel Ziev Welch Method, 2019 Global Conf. for Advancement in Technology (GCAT), 2019, pp 1-6
[2]. Khaitu S and Panday S, Canonical Huffman Coding for Image Compression, 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conf. on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), 2018, pp 184-190
[3]. Patel R, Kumar V, Tyagi V and Asthana V, A fast and improved Image Compression technique using Huffman coding, 2016 International Conf. on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), 2016, pp 2283-2286
[4]. Li X, Shen Y and Ma J, An Efficient Medical Image Compression Scheme, 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conf., 2005, pp 3437-3439
[5]. Sangeetha M, Betty P and Kumar G, A biometrie iris image compression using LZW and hybrid LZW coding algorithm, 2017 International Conf. on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS), 2017, pp 1-6
[6]. Chen Y, Zhou L, Chen X, Chen W, 2016, Information Theory and Coding, ed T P Han, Publishing House of Electronic Industry, Beijing, pp 40-44
[7]. Sun B, Wu K, Improvement of Huffman Algorithm and Its Application in Image Compression, Microcomputer Information, 2011, Vol 27, pp 264-266
[8]. Praisline Jasmi R, Perumal B and Pallikonda Rajasekaran M, Comparison of Image Compression Techniques Using Huffman Coding, DWT and Fractal Algorithm, 2015International Conf. on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), 2015, pp 1-5
[9]. Ahmed Z and George L, A Comparative Study Using LZW with Wavelet or DCT for Compressing Color Images, 2020 International Conf. on Advanced Science and Engineering (ICOASE), 2020, pp 53-58
[10]. Prudvi C, Muchahary D and Raghuvanshi A, Analysis of Image Compression Techniques for IoT Applications, 2022 2nd International Conf. on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), 2022, pp 1-5
[11]. Vaish A and Kumar M, A new Image compression technique using principal component analysis and Huffman coding, 2014 International Conf. on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing, 2014, pp 301-305
[12]. Sharma K and Gupta K, Lossless data compression techniques and their performance, 2017 International Conf. on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), 2017, pp 256-261
[13]. Sun M, Xie Y, Tang X and Sun M, Image Compression Based on Classification Row by Row and LZW Encoding, 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2008, pp 617- 621