1. Introduction
The Fast-track project, financed by the European Regional Development Fund program, aims to create a new slab-track framework for bullet-trains that is financially and environmentally sound. A constant real-time monitoring system is crucial for the success of the project. Three primary demonstrators have been used to validate the framework: a real slab-track research center demonstrator, a real slab-track demonstrator in Valencia (Spain) to study a ballast slab-track transition zone, and a trial of the data muling communication architecture. The first trial was conducted at the CEDEX research center in Madrid. The second trial was conducted on a section of railroad in Valencia that has a transition zone between slab-tracks and a ballast track. The third test was completed on a straight road in Malaga. To the author's knowledge, there are no projects for slab-tracks that include wireless sensor networks (WSNs) as part of the infrastructure [1]. The focus of this paper is on railway infrastructure, as India is now working on high-speed trains, Bullet trains, and due to their high-speed, there should be monitoring of rail-tracks as India has a large number of passengers on a daily basis. In India, initiatives have been taken by the government, such as Digital India, and with the help of WSNs, it is called smart infrastructure. Nowadays, slab-tracks are being replaced from traditionally used ballasted track for railways due to their qualities over ballasted such as low whole-life cost, long-life design, very-low maintenance required, high-speed operation, and vibrational performance. With the help of WSNs, it is installed with or along with slab-track which will reduce the installation process and will provide us with real-time data with accuracy. With the help of this data, after analysis, we can detect faults and prevent any failures. A slab-track demonstrator in CEDEX is shown in Figure 1. The architecture that is being discussed in this study primarily focuses on railroad infrastructure that uses slab track.
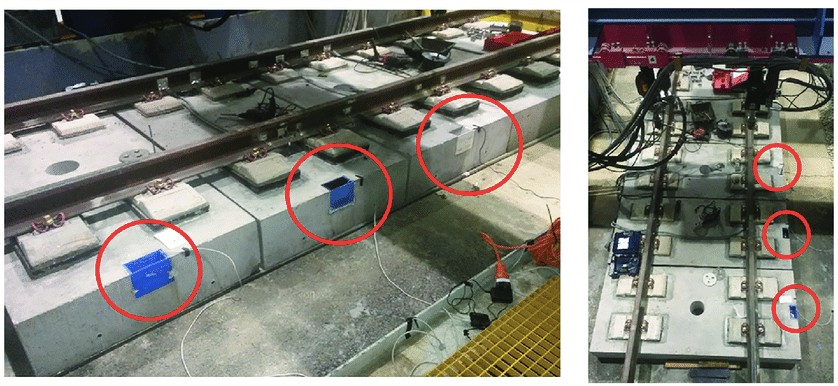
Figure 1. Slab track demonstrator in CEDEX.
2. Related work
This paper mainly aims at the superior ideology of using wireless sensor networks to reduce the cost of monitoring rail-tracks [2]. Wired devices are highly reliable but too costly as compared to wireless systems. By using a tree-type structure or hierarchical system, the efficiency and reliability of the system will be increased to its maximum level. The use of wireless sensors to remove duplicate paths from the route sensor deployed on the rail-tracks is also proposed. The data collected by the nodes will be transferred using GPRS (General Pocket Radio Service) or WIMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) to the control center [3]. Data collection is a critical task in communication and the wireless sensor, or routing feature, will be used to transmit the acquired data to the base station. This paper also includes mobile communication technologies used to convey the data to the control center. The system can detect track damage, such as gaps or cracks in the track, when ultrasonic sensors are combined with an accelerometer. Image detection and other potentially dangerous items on the rail-track are also included in this system. There is also another method for detecting rail-track structure as an integrated portion of wireless sensor networks, known as SENSORIAL [4], which includes many types of sensors and presents the data without using high-level programming. Wireless sensor networks can also be used for early detection of earthquakes and security controls. The zone in a highly seismic zone is quite challenging for railways to predict any kind of early earthquake situation but with the help of WSNs it will alert the authority and prevent major accidents. The limitation of the system is the nodes, if any nodes are compromised by a hacker or any hardware failure, it will lead to sending incorrect data. To prevent this scenario, the system will detect compromised nodes, known as Bad nodes [5].
2.1. Communication technology
This paper describes that trains will be used as data mules and are responsible for collecting the data generated by nodes placed on the slab track. Therefore, it is important to study the different possibilities to communicate with the WSNs on the slab track using trains as data mules. The authors have studied two major technologies, Radio transmitter and RFID, and a third available option is GPRS for remote areas where data mules will not be easily accessible. The architecture must meet the requirements of easy installation, low cost, energy efficiency, scalability, and fault tolerance. These three technologies are widely used and are cost-effective. The reliability of the system depends on two factors:
(i) The acceleration of the train, as the speed of the train increases, fewer data will be transferred for communication.
(ii) Range: a longer-range result in higher communication bandwidth.
2.0.1. Zigbee 868 MHz radio module using groups. Zigbee and radio modules are the WSNs system surveillance which is used two transmit the data. The more users in the roll-track are at a particular distance super- vised by a system. The working of these technologies depends upon their radiation/ emission of the wave lower the separation between the nodes stronger the network. Zigbee 868 both have their unique quality for transmitting the data [6]. The Zigbee used 2.4GHz bandwidth which will transmit the data at a high speed while the radio mod- ule has a higher range as compared to Zigbee. Zigbee made a connection via nodes that are monitored by a coordinate. The architecture of Zigbee is shown in Figure 2.
2.0.2. Radio modules 868MHz with groups. This technology is also used for transmitting the data to the data mules. In groups system, the design is like that data is passed via groups by groups or node to node, which is monitored by a coordinator, but it may possible that there can be superimposed of a wave can occur if there is a greater number of groups enrolled for transmission, to avoid this superimposed position the other 868 groups should be a turnoff. So that data can be transferred easily with-out any hindrance [7].
2.0.3. 868MHz without using groups. This is another way of transmitting the data this method is the same as the above method but in this method, there are no groups, each node has to manage itself and have to transfer data into visuals. As there are no coordinators to monitored other nodes also there is no superimposed condition in this method. In this method, direct communication takes place that is why this method is preferable above method [8].
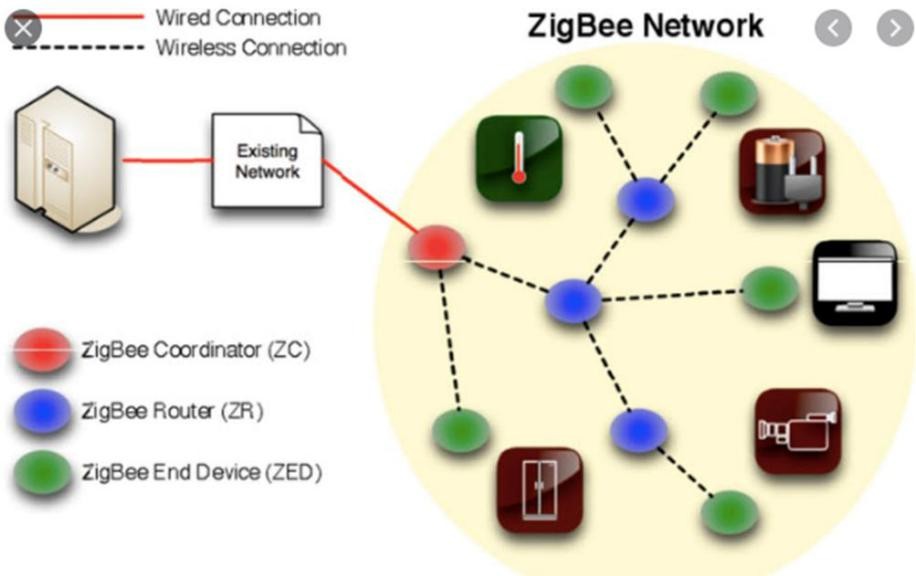
Figure 2. Zigbee system architecture.
2.0.4. RFID based. RFID is also a communication-based method in which radio frequency is used. This method is a short-range method. It spilled in two ways one has to store the data and transmitting using radio waves while the other has a function to read using WSNs transducer. This method is a short-range method this is the reason is consuming your power and have a low cost and maintained method. This system has a low range and cannot send continuously a large amount of data. To improve this quality there is another method integrated along with this but after integration, the cost of the complete system becomes more and due to over budget, this method is being blocked by the system [9].
2.0.5. GPRS communication. This is a cellular network-based method or communication. The GPRS used in the mobile telecommunication system. This is a packet directed mobile communication. In this method, the Arduino will work directly, not dependent on the train to collect the data but with the help of the GPRS device it will directly transmit the data to the internet. But require cellular connection as well as power consumption ratio is also high so, in a remote area it will not work. So, it is not attracted by the designer [10].
2.1. Security of WSNs
The security related problem in WSN is discussed in Table 1.
Table 1. Security related problem in WSN.
3. Result and discussion
Based on research study and of our knowledge, this paper has proposed a view to monitor the health structure of rail-tracks. From the proposed architectures based on radio transmitter has some advantages i.e., 868 MHz radio modules they do not require any association that is why they are more suitable for node to train communication. 2.4 GHz communication system is more reliable in short range communications and consumed less energy as well as cost effective, so it is also prefer- able for node-to-node communication. Once the data has been received on the train it will be sent to a database for storing and analysing the data. Collecting the data on the train and sending to the database is performed by Bee which is a class library of high-level python language.
4. Conclusion and future work
In this paper, we introduced a wireless sensor network using RFID as well as several methods for transmission of data and using the train as a data mule the transfer of the data. The WSNs can be used as several critical infrastructures to prevent them from degradation as well as to prevent it from any miss-happening. In this paper we pro- posed many methods for transmission of data. Our focus on railway structure as wireless devices will reduce the cost of the overall system and be used as Digital India initiatives. When we expand this project at a level where the WSNs generates large amount of data. This will create challenges to store and analyse the large amount of data and for storing large amount of data if we use traditional methods and techniques then it will be costly to store. Therefore, for storing large amount of data we should move to the new technologies such as cloud computing. It will provide us a cheap way to store our data and easy to access from any point.
References
[1]. Cañete, E., Chen, J., Díaz, M., Llopis, L., & Rubio, B. (2019). Wireless sensor networks and structural health monitoring: Experiences with slab track infrastructures. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 15(3), 1550147719826002.
[2]. Clements, R. L. (2006). A social and environmental impact assessment that examines the impacts that have resulted from the construction and operation of the Channel Tunnel.
[3]. Arafat, O., Gregory, M. A., & Khan, M. M. A. (2014, December). Interworking architecture between 3GPP IMS, Mobile IP and WiMAX in OPNET. In 2014 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and System Engineering (ICEESE) (pp. 48-53). IEEE.
[4]. Mistry, Y., & Rana, A. (2018). A Survey on Data Aggregation cluster based technique in wireless sensor network for modern railway track monitoring.
[5]. Yessembayev, A., Sarkar, D., & Sikder, F. (2018). Detection of good and bad sensor nodes in the presence of malicious attacks and its application to data aggregation. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 4(3), 549-563.
[6]. Cañete, E., Chen, J., Díaz, M., Llopis, L., Reyna, A., & Rubio, B. (2015). Using wireless sensor networks and trains as data mules to monitor slab track infrastructures. Sensors, 15(7), 15101-15126.
[7]. Cwalina, K. K., Ambroziak, S. J., Rajchowski, P., & Correia, L. M. (2017, August). Radio channel measurements in 868 MHz off-body communications in a ferry environment. In 2017 XXXIInd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
[8]. Babu, J. C., Kumar, M. S., Jayagopal, P., Sathishkumar, V. E., Rajendran, S., Kumar, S., ... & Mahseena, A. M. (2022). IoT-based intelligent system for internal crack detection in building blocks. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2022, 1-8.
[9]. Ramu, A. G., Kim, S., Jeon, H., Al-Mohaimeed, A. M., Al-onazi, W. A., Sathishkumar, V. E., & Choi, D. (2021). A study on the optimization of residual stress distribution in the polyethylene and polyketone double layer pipes. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 33(6), 101547.
[10]. Zhang, R., VE, S., & Jackson Samuel, R. D. (2020). Fuzzy efficient energy smart home management system for renewable energy resources. Sustainability, 12(8), 3115.
Cite this article
Singh,P.;Maurya,A.;Shankar,A.;E,S.V.;Diwakar,M. (2023). Wireless Sensor Network-based Monitoring System for Health Structure of Rail-tracks: An Efficient Design for Communication. Applied and Computational Engineering,8,42-47.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Cañete, E., Chen, J., Díaz, M., Llopis, L., & Rubio, B. (2019). Wireless sensor networks and structural health monitoring: Experiences with slab track infrastructures. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 15(3), 1550147719826002.
[2]. Clements, R. L. (2006). A social and environmental impact assessment that examines the impacts that have resulted from the construction and operation of the Channel Tunnel.
[3]. Arafat, O., Gregory, M. A., & Khan, M. M. A. (2014, December). Interworking architecture between 3GPP IMS, Mobile IP and WiMAX in OPNET. In 2014 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and System Engineering (ICEESE) (pp. 48-53). IEEE.
[4]. Mistry, Y., & Rana, A. (2018). A Survey on Data Aggregation cluster based technique in wireless sensor network for modern railway track monitoring.
[5]. Yessembayev, A., Sarkar, D., & Sikder, F. (2018). Detection of good and bad sensor nodes in the presence of malicious attacks and its application to data aggregation. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 4(3), 549-563.
[6]. Cañete, E., Chen, J., Díaz, M., Llopis, L., Reyna, A., & Rubio, B. (2015). Using wireless sensor networks and trains as data mules to monitor slab track infrastructures. Sensors, 15(7), 15101-15126.
[7]. Cwalina, K. K., Ambroziak, S. J., Rajchowski, P., & Correia, L. M. (2017, August). Radio channel measurements in 868 MHz off-body communications in a ferry environment. In 2017 XXXIInd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science (URSI GASS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
[8]. Babu, J. C., Kumar, M. S., Jayagopal, P., Sathishkumar, V. E., Rajendran, S., Kumar, S., ... & Mahseena, A. M. (2022). IoT-based intelligent system for internal crack detection in building blocks. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2022, 1-8.
[9]. Ramu, A. G., Kim, S., Jeon, H., Al-Mohaimeed, A. M., Al-onazi, W. A., Sathishkumar, V. E., & Choi, D. (2021). A study on the optimization of residual stress distribution in the polyethylene and polyketone double layer pipes. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 33(6), 101547.
[10]. Zhang, R., VE, S., & Jackson Samuel, R. D. (2020). Fuzzy efficient energy smart home management system for renewable energy resources. Sustainability, 12(8), 3115.









