1. Introduction
In recent times, the issue of infringement pertaining to digital copyright has gained significant attention. To strengthen digital copyright protection from fake crises, many industries including BFSI, Government, Education, Healthcare, and the military, use digital signatures to ensure their digital files are not changed by third parties. Currently, the ongoing advancement of blockchain technology and other new technologies have opened up novel avenues for the protection of digital files. The combinations of digital signatures and blockchain, named data network, and quantum computer technology, are tried in many scenes which improves the protection ability of digital signatures.
Abhishek Roy [1] has overviewed the mainly digital signature algorithms in detail and illustrated the application of digital signature in E-Government in 2012. Within the development of digital signatures, digital signatures combined with new technology and applied in more industries and different scenarios trend to use different kinds of digital signatures. Therefore, this paper gives a view of present situations between fields and digital signature algorithms and illustrates the blockchain and digital signature. Furthermore, this paper includes a comparison between the mainly used digital signature algorithms with the key generation time, signing time, and verification time.
The paper is structured in the following manner. Section 2 indicates the digital signature definition and gives a view of blockchain, also presents the two digital signature algorithms. While in Section 3, this paper research the different signature algorithm used in the main fields which are using digital signature mainly, comparing their presents in the whole digital signature area. Furthermore, section 3 gives a performance comparison of the three mainly using algorithms.
2. Preliminary
2.1. Signature definition
The Digital Signature (DS) is a cryptographic implementation of an asymmetric mathematical technique to ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital data to its users. Similar to conventional signatures, digital signature provides evidence of the origin and unaltered state of the document, therefore the receiver possesses a justified basis to have confidence that the communicated message originated from the designated sender and was not altered during the course of transmission. Users can obtain a public key of the downloaded file from the Certificate Authority (CA) to verify its authenticity. Digital signatures technology is widely employed to ensure authentication, non-repudiation and data integrity, making use of three sub-phases in its algorithmic implementation, that include Key Generation, Signature Generation, and Signature Verification.
Key Generation: The process of Key Generation is based on the key generation algorithms, with two outputs Secret Key \( SK \) (private key) and Verify Key \( VK \) (public key). The common key generation algorithms are random number generators.
Signature Generation: Signature Generation is the second step in Digital Signature Process. In this step, the \( M \) (message) and secret key \( SK \) play the roles of input and the signature generation function will output a signature \( σ \) .
Input \( SK \) and message \( M \) to Sign Function get signature \( σ \) of \( M \) . At the end of a signature generation, send Message \( M \) and signature \( σ \) to receiver.
Signature Verification: The receiver generates a summary from the received message \( {M^{ \prime }} \) with the same algorithm in process 1. Then input Verify Key \( VK \) and Summary \( {S^{ \prime }} \) to get a new signature \( {σ^{ \prime }} \) . Compare \( σ,{σ^{ \prime }} \) , if same, proof that message is safe without attacker changed.
2.2. Common digital signature algorithms
This part illustrates three classes of mainly used digital signature algorithms, RSA, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), and Lamport digital signature.
2.2.1. RSA introduction. The Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) algorithm, named after its inventors, represents a milestone in cryptographic science as it firstly serves both for data encryption and digital signatures. The security strength of RSA algorithm stems from the complexity of decomposing large numbers, which serves as the bedrock of its security assurance. The algorithm uses two prime numbers in large size to generate public key and private key. Notably, it is estimated that the difficulty of deciphering the plaintext from the signal key and the cipher text depends on the decomposition of the product of two large prime numbers. The three processes of Key Generation (Algorithm 1.1), Signature Generation (Algorithm 1.2), and Signature Verification (Algorithm 1.3) are followed [2] [3].
Algorithm 1.1 Key Pair Generation in RSA |
Input: Security parameter \( l \) . Output: RSA \( VK \) \( (n,e) \) and \( SK \) \( d \) . Select two primes \( p \) and \( q \) of the same bitlength \( l/2 \) in random number generator. Compute \( n=pq \) and \( ϕ=(p-1)*(q-1) \) . Select an arbitrary integer with \( 1 \lt e \lt ϕ \) and \( gcd(e,ϕ)=1 \) Compute the integer d satisfying \( 1 \lt d \lt ϕ \) and \( ed≡1 mod ϕ \) . Returns \( (n,e,d) \) . |
Algorithm 1.2 Basic RSA Signature Generation |
Input: Both of \( VK \) \( (n,e) \) and \( SK \) \( d \) in RSA, message \( m \) . Output: Signature \( s \) of message \( m \) . Compute \( h=H(m) \) , \( H \) is a selected hash function to get message summary. Compute \( s=h\text{^}d mod n \) . Return \( s(s) \) . |
Algorithm 1.3 Basic Signature Verification Process in RSA |
Input: The group of \( VK \) \( (n.e) \) , received message \( m \) , signature \( s \) . Output: A Boolean value stands the validity of the signature. Compute \( h=H(m) \) . Compute \( h \prime ={s^{e}}mod n \) . If \( h=h \prime \) then return \( s(“Accept the signature”); \) else return \( s(“Reject the signature”) \) . |
2.2.2. ECC-based signature introduction. Elliptic Curve (EC) systems rely on the mathematical construct of the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem and have the advantage of a shorter key size for the same security level as RSA [3].
Algorithm 2.1 Elliptic Curve Key Pair Generation |
Input: Elliptic curve domain parameters \( (p,E,P,n) \) . Output: \( VK \) \( Q \) and \( SK \) \( d \) . Select \( d{∈_{R}}[1,n-1] \) Compute \( Q=dP \) . Return \( s(Q,d) \) . |
Algorithm 2.2 Basic ElGamal Elliptic Curve Encryption |
Input: Elliptic curve domain parameters \( (p,E,P,n) \) , \( VK \) \( Q \) , plaintext \( m \) . Output: Ciphertext \( ({C_{1}},{C_{2}}) \) . Represent the message m as a point M in \( E({F_{P}}) \) Select \( k{∈_{R}}[1,n-1] \) . Compute \( {C_{1}}=kP \) . Compute \( {C_{2}}=M+kQ \) . Return \( s({C_{1}},{C_{2}}) \) . |
Algorithm 2.3 Basic ElGamal Elliptic Curve Decryption |
Input: Domain parameters \( (p.E.P.n) \) , \( VK \) d, ciphertext \( ({C_{1}},{C_{2}}) \) . Output: Plaintext \( m \) . Compute \( M={C_{2}}-d{C_{1}} \) , and extract \( m \) from \( M \) . Return \( s(m) \) . |
The ECDSA is a cryptographic protocol that utilizes elliptic curve cryptography to provide digital signature functionality. This algorithm can be considered as the elliptic curve implement of the DSA algorithm. This section describes the procedures for generating and verifying signatures using the ECDSA [4].
The Edwards curve family, which belongs to the group of elliptic curves, has attracted considerable attention from security researchers due to its straightforwardness and remarkable resistance to side-channel attacks (SCAs). Elliptic curve point multiplication (ECPM) on Edwards curves is faster and more secure than that on the Weierstrass form of elliptic curves and the application EdDSA is widely using in the IoT field [4].
The SM2 algorithm is a standard established by China that is based on elliptic curve cryptography and serves to ensure the protection of sensitive internal information and data that does not pertain to state secrets. Compared to RSA, the advantages of SM2 algorithm is in the shorter key length and higher sign and verify performance [5].
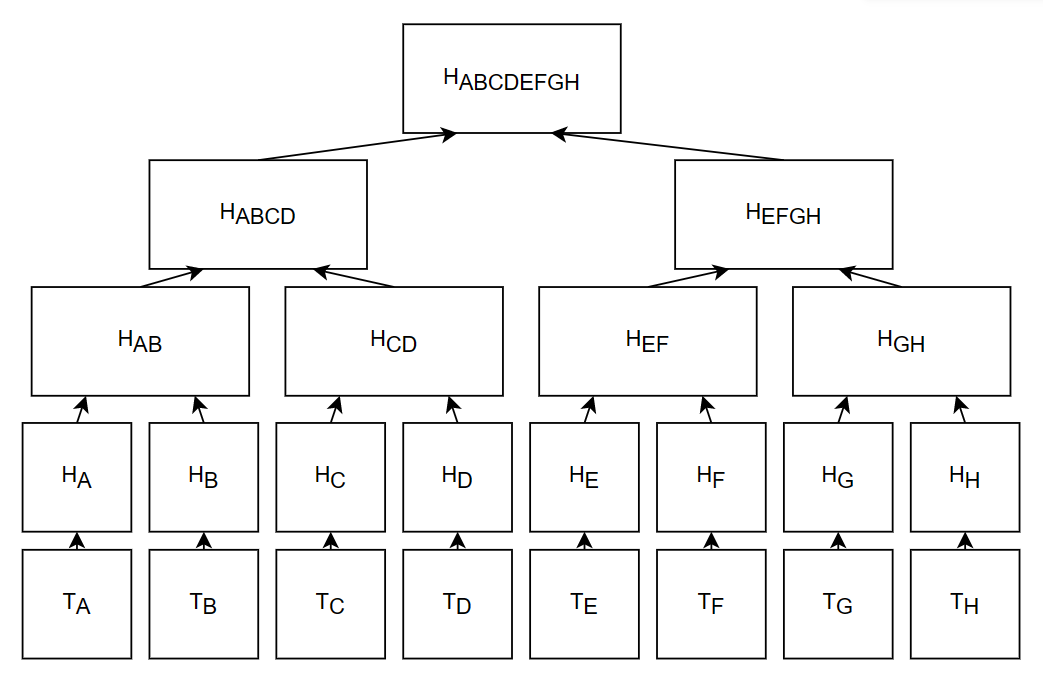
2.2.3. Lamport signature scheme. Lamport Signature Scheme is a one-time pad DS algorithm, that generates a same-size key pair with the summary. And Merkle signature scheme (MSS) is the Lamport Hash building in Markle Tree (Structure in Figure 1.), so that affords a powerful performance in the Blockchain Environment and flexible hash value.
|
Figure 1. Markel Tree Structure [6]. |
2.3. Blockchain definition
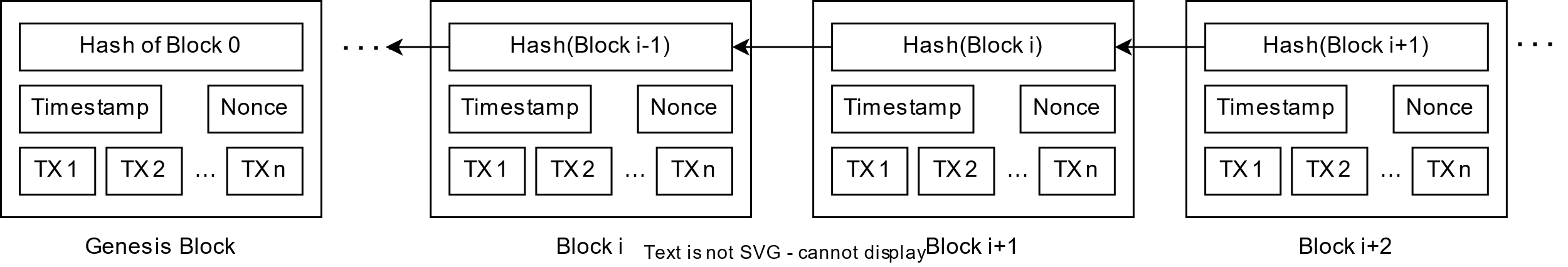
Blockchain is a disruptive abstraction that illustrates a trusty environment through its special data structure. Figure 2 presented a typical structure of blockchain. The data structure of blockchain is a link list containing numbers of the block, which contains multiple transactions, each block holds a total transactions message ( \( TX(1-n) \) in Figure 2.).
|
Figure 2. Blockchain Structure [7]. |
Moreover, aside from the transaction data, there exists an antecedent hash value, also known as the parent hash value, a timestamp, and a random number nonce which support verification of the hash. The aforementioned design provides assurance regarding the consistency and completeness of the complete blockchain, extending up to its initial section commonly referred to as the Genesis block. The uniqueness of the hash values ensures effective prevention of fraud, as any modifications made to any block would immediately alter the corresponding hash value. Once a consensus has been reached among a majority of nodes in the network regarding the validity of the transactions within a block and the block as a whole, it can be appended to the chain. With the aid of cryptography, individuals dispersed worldwide can partake in peer-to-peer transactions of various assets over the internet, with a degree of trustworthiness [7].
It is also because the blockchain has a trusted feature that cannot be tampered with, we can combine digital signatures with the blockchain and put the public key of the digital signature into the blockchain to replace the traditional CA-dependent model.
3. Detailed analysis
3.1. Applications of digital signature
Digital signatures are the most advanced and secure measure for electronic security, authenticity, and verification. With the reason of digital signatures can support the high levels of guarantee in the identification of signers and the authenticity of the signed documents, it is simple and convenient for people to meet the requirements of legal regulations through digital signature use.
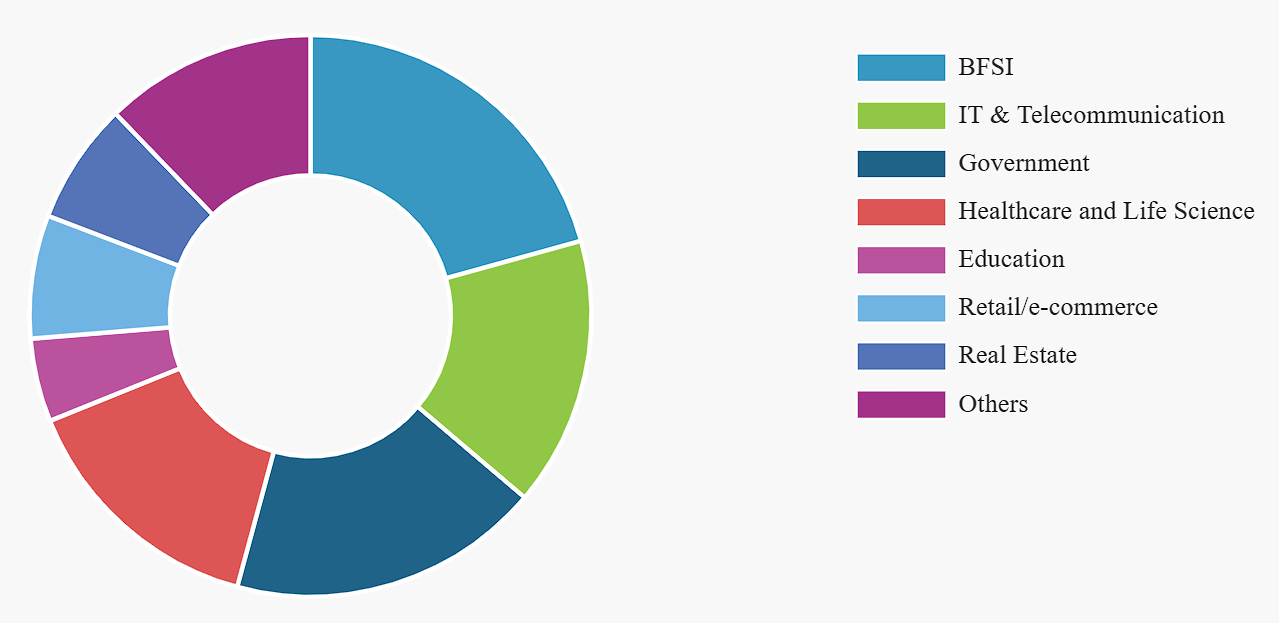
The classification methods of the digital signatures market are effect by many factors, like deployment approach, production, client industry, also countries and areas. For deploying, the digital signature can be segmented by cloud and local server. While in the way of production, the digital signature can implement by software, hardware, or even a service. And the end-user scenarios of digital signature are covered overall most every area that needs digital communication, including BFSI, E-government, healthcare, energy, military, logistics and transportation, research, education, and other industries (manufacturing, legal, real estate, and telecom) (See Figure 3.)[8]. The digital signature is widely used all over the world in the process of humans changing messages and information.
|
Figure 3. Global digital signature market share, By End User, 2021 [8]. |
This paper research those digital signature technologies in the main industries, the following table (Table 1.) illustrates the source paper and the main algorithm they use for signature while giving a description of the measures.
Table 1. Digital signature algorithms used in different industries. | ||
Industry | Main Idea | Strategy |
BFSI [9] | ECDSA with Blockchain | ECDSA can occupy less memory and is suitable for use in the blockchain environment. The combination of them is used in the BFSI area. |
Government [10] | RSA Algorithm | RSA is a common digital signature algorithm with the features of stabilization and efficiency in encryption and decryption. And RSA has the feature of a short time in verification and is suitable for those digital documents that need to wildly spread. |
HealthCare [11] | Lamport Signature Scheme with MSS | The approach of Lamport with MSS deployed in the blockchain network could take a high performance for Lamport DS. Dividing the key in Markel Tree has overcome the drawback of a one-time-pad signature with a large key size. |
Oil and Gas [5] | SM2 Algorithm | The energy industry is an important part of a country. And in [5] choose the Chinese standard, and designed a system for coping with digital copyright problems. |
IoT [12] | EdDSA Algorithm | EdDSA is an improved version of ECDSA, which choose to use the Edwards curves to take the higher performance in each process of digital signature. |
Education [13] | RSA Algorithm | RSA is a ripe technology that is easy to implement and import into the programs, which can conveniently apply in the education scenario. |
3.2. Performance analysis
For the digital signature algorithms used in the above several application scenarios, this paper established performance testing experiments of several major digital signature algorithms. Some main factors influence the performance of digital signatures. The most significant influence is token by the choice of algorithms, including RSA, ECDSA, and Lamport algorithms. In addition, the size of the file summary which is generated by the hash function, and the length of the key for encryption and decryption, are also the majority elements reflected in performance. Longer keys and larger messages can increase the security level while paying a cost of a low speed in signature generation and verification. Furthermore, the detailed implementations of the same digital signature algorithm bring a small difference in performance.
This paper offers eight groups of digital signature algorithms (Table 2.) and different influence factor, which contains the choice of the hash function, key size, backend, source code, and different ECC curves used in EdDSA and ECDSA. The test cases mainly focus on four types of signature algorithms, EdDSA, ECDSA, Lamport, RSA, and DSA. All the test code mainly depends on the python libraries: libsodium, python-devel, and gmp-devel. Program source code borrowed from [14].
Table 2. Test algorithm groups and characters[14]. | ||||||||
Alias | A-1 | A-2 | A-3 | A-4 | A-5 | A-6 | A-7 | A-8 |
Program Name | eddsa_libnacl.py | eddsa_pynacl.py | eddsa_25519.py | ecdsa_pyca.py | ecdsa_fast.py | Lamport.py | rsa_pyca.py | dsa_pyca.py |
Hash | SHA512 | SHA512 | SHA512 | SHA256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | SHA256 | SHA256 |
ECC Curve | Ed25519 | Ed25519 | Ed25519 | SECP256K1 | SECP256K1 | - | - | - |
Key Size | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2048 | 1024 |
Public Exponent(e) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 65537 | - |
Padding | - | - | - | - | - | - | PSS | - |
Backend | NaCL/libsodium | NaCL/libsodium | SUPERCOP | OpenSSL | C Implement | Python hashlib | OpenSSL | OpenSSL |
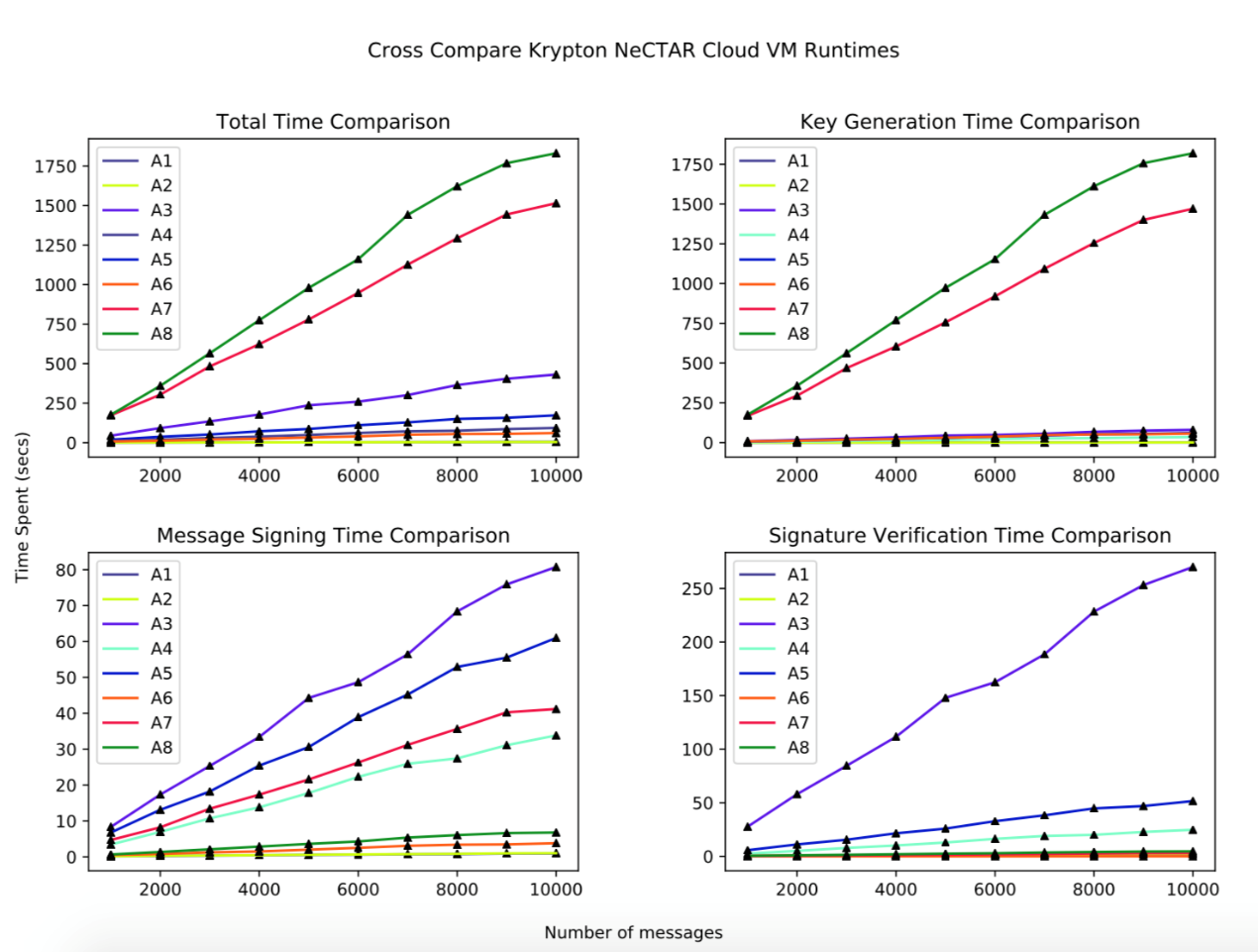
Run the different message sizes for the result, then receive the following line graph (Figure 4.) for speeding time in three processes of digital signature work, with the total time cost comparison.
|
Figure 4. Performance Comparison Line Graph [14] |
For the above line graph, those lines closer to the x-axis have a high performance, while they illustrate a lower start value with the smaller increasing rate of time for the large size message.
In the line graph, group A-8 (Lamport Algorithm) spent the longest time in total time at each number of messages but reach a good grade in message signing and signature verification. The reason why most of the time is spent in the process of key generation is that the Lamport algorithm is a one-time-pad scheme and needs to generate a same-size key with the message. The RSA algorithm used in group A-7 cost the second time in total time and has the feature of high speed of verification but slow in key generation and message signing.
The highest performance groups are A-1 and A-2 both use EdDSA algorithms and are very fast in each step of digital signature, costing less than 125ms for 900 messages of key generation, signing, and verification.
The following table (Table 3.) summarizes the results of the performance of RSA, ECDSA, EdDSA, and Lamport algorithms.
Table 3. Summarize of RSA, ECDSA, EdDSA, Lamport Algorithm. | ||||
RSA | ECDSA | EdDSA | Lamport | |
Computational Overhead | Padding | Signing and Verification Process | Hash Function, Scalar Multiplication | Many Hash Calculations |
NIST Security Strength(128-bit) | Yes(k=3072-bit) | Yes(NIST P-256) | Yes(Ed25519) | Yes (SHA-256) |
Key Size | Medium | Small | Very Small | Large |
Signature Size(bytes) | Medium | Small | Small | Large |
Key Generation Time | Very Slow | Fast | Very Fast | Slow |
Signing Time | Slow | Slow | Very Fast | Fast |
Verification Time | Fast | Slow | Fast | Very Fast |
Application Domain | Client-Server Deployment | Blockchain, Bitcoin | Software Release | IoT, Wearable Devices |
Quantum Computing Resistant [15] | No | No | No | Yes |
4. Conclusion
To sum up, different industries tend to use different digital signatures. ECDSA is combined with the blockchain structure used in BFSI, while its derivative version like SM2 is working in the energy industry, and the improved algorithm EdDSA has been applied to the new field of IoT in a short time. Lamport algorithm is active in the devices in healthcare. The E-education and E-government area is more preferred on stable algorithms like RSA, which takes short time to the verification and are friendly to disseminate.
With the widely using of digital signatures, the technology is also improving ever since. Facing the challenge of the quantum computer, most digital signature algorithms are losing their security containing RSA, DSA, and algorithms based on ECC. Lamport is a quantum-security algorithm but does not have the drawback of slow key generation and the large size of the key. In the future, those quantum security digital signature algorithms will replace the algorithms applied now and take a safer online environment for humans to protect the safety of files.
References
[1]. Roy A and Karforma S 2012 J Journal of Computer and Information Technology A Survey on digital signatures and its applications vol 3 pp 45-69
[2]. Zhou X and Tang X 2011 C Proceedings of 2011 6th international forum on strategic technology IEEE Research and implementation of RSA algorithm for encryption and decryption vol 2 pp 1118-1121
[3]. Hankerson D, Menezes A J and Vanstone S 2006 Springer Science & Business Media Guide to elliptic curve cryptography
[4]. Islam M M, Hossain M S, Hasan M K and et al 2020 Sensors Design and implementation of high-performance ECC processor with unified point addition on twisted edwards curve vol 20 p 5148
[5]. Feng T, Yang R and Gong R 2021 International Journal of Network Security Digital Copyright Protection System for Oil and Gas Knowledge Achievements Based on Blockchain vol 23 pp 631-641
[6]. Kaur J 2020 J New Paradigm in Business & Education BLOCK CHAIN: FROM BLOCK TO CHAINS p 60.
[7]. Nofer M, Gomber P, Hinz O and et al 2017 Business & Information Systems Engineering Blockchain vol 59 pp 183-187
[8]. Mordor Intelligence 2021 Digital Signature Market Share, Growth | Research Report p 2029
[9]. Sun H, Mao H, Bai X and et al 2017 18th International conference on parallel and distributed computing, applications and technologies (PDCAT), IEEE Multi-blockchain model for central bank digital currency pp 360-367
[10]. Pancholi V R, Bhadresh P and Hiran D 2018 A study on importance of digital signature for e-governance schemes vol 4 pp 7-10
[11]. Mehbodniya A, Webber J L, Neware R and et al 2022 Expert Systems Modified Lamport Merkle Digital Signature blockchain framework for authentication of internet of things healthcare data vol 39 p 12978
[12]. Guruprakash J and Koppu S 2022 Informatica An Empirical Study to Demonstrate that EdDSA can be used as a Performance Improvement Alternative to ECDSA in Blockchain and IoT p 46
[13]. Rahardja U, Sudaryono S, Santoso N P L and et al 2020 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research Covid-19: Digital Signature Impact on Higher Education Motivation Performance vol 4 pp 65-74
[14]. CorrineTan 2019 CorrineTan/Digital-Signature-Schemes-Evaluation: Analysing 3 digital signature algorithms – RSA, ECC and Lamport signature – to evaluate and compare them.
[15]. Kirsch Z, Chow M 2015 Quantum computing The risk to existing encryption methods
Cite this article
Fang,Y. (2023). A research on different digital signature schemes. Applied and Computational Engineering,16,27-35.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Roy A and Karforma S 2012 J Journal of Computer and Information Technology A Survey on digital signatures and its applications vol 3 pp 45-69
[2]. Zhou X and Tang X 2011 C Proceedings of 2011 6th international forum on strategic technology IEEE Research and implementation of RSA algorithm for encryption and decryption vol 2 pp 1118-1121
[3]. Hankerson D, Menezes A J and Vanstone S 2006 Springer Science & Business Media Guide to elliptic curve cryptography
[4]. Islam M M, Hossain M S, Hasan M K and et al 2020 Sensors Design and implementation of high-performance ECC processor with unified point addition on twisted edwards curve vol 20 p 5148
[5]. Feng T, Yang R and Gong R 2021 International Journal of Network Security Digital Copyright Protection System for Oil and Gas Knowledge Achievements Based on Blockchain vol 23 pp 631-641
[6]. Kaur J 2020 J New Paradigm in Business & Education BLOCK CHAIN: FROM BLOCK TO CHAINS p 60.
[7]. Nofer M, Gomber P, Hinz O and et al 2017 Business & Information Systems Engineering Blockchain vol 59 pp 183-187
[8]. Mordor Intelligence 2021 Digital Signature Market Share, Growth | Research Report p 2029
[9]. Sun H, Mao H, Bai X and et al 2017 18th International conference on parallel and distributed computing, applications and technologies (PDCAT), IEEE Multi-blockchain model for central bank digital currency pp 360-367
[10]. Pancholi V R, Bhadresh P and Hiran D 2018 A study on importance of digital signature for e-governance schemes vol 4 pp 7-10
[11]. Mehbodniya A, Webber J L, Neware R and et al 2022 Expert Systems Modified Lamport Merkle Digital Signature blockchain framework for authentication of internet of things healthcare data vol 39 p 12978
[12]. Guruprakash J and Koppu S 2022 Informatica An Empirical Study to Demonstrate that EdDSA can be used as a Performance Improvement Alternative to ECDSA in Blockchain and IoT p 46
[13]. Rahardja U, Sudaryono S, Santoso N P L and et al 2020 International Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research Covid-19: Digital Signature Impact on Higher Education Motivation Performance vol 4 pp 65-74
[14]. CorrineTan 2019 CorrineTan/Digital-Signature-Schemes-Evaluation: Analysing 3 digital signature algorithms – RSA, ECC and Lamport signature – to evaluate and compare them.
[15]. Kirsch Z, Chow M 2015 Quantum computing The risk to existing encryption methods