1. Introduction
As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation, Electric Vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular. However, one of the biggest challenges facing EV owners is the limited driving range of their vehicles due to battery capacity. To address this issue, battery swap stations has been proposed as an alternative to charging stations, allowing drivers to exchange their depleted batteries for fully charged ones in a matter of minutes [1].
Despite their convenience, battery swap stations face significant security and privacy challenges. The exchange process involves sensitive information, such as the location of the user's vehicle and personal and identity information. Moreover, the batteries themselves are valuable assets that require secure tracking and management.
To address these challenges, the paper proposes a privacy protection system for electric vehicle battery swap stations using blockchain technology. The blockchain technology can be used to create a semi-decentralized network of electric vehicles and charging stations that are able to share data (battery information and condition) based on continuous monitoring [2]. The blockchain can also be used as the network and data layer of the application [2].
The system in the paper includes two key roles: battery service providers and users. The blockchain is used to protect battery safety, traceability, user location, and privacy, including personal and identity information.
This paper presents the design and implementation of a secure battery swap system. The system aims to address the security and privacy issues faced by battery swap stations. The features, benefits, and potential applications of the system will be highlighted. The ultimate goal of this paper is to provide a comprehensive solution to the security and privacy issues faced by battery swap stations.
2. Related works
This section reviews the existing literature on privacy protection methods in electric vehicle systems, focusing on charging and communication systems, location privacy, and security protocols.
The charging infrastructure for electric vehicles has introduced new privacy and security challenges. One of the main concerns is the privacy of users' charging data, as it can reveal sensitive information about their driving habits, locations, and personal preferences. For instance, the work by Dustin Kern et al. [3] proposed a privacy-preserving architecture for the charging and billing of EVs that aims to protect the security of an EV user's payment credentials based on trusted computing methods and protect the privacy of users based on a concept for unlinkable charge authorizations.
Location privacy is another critical aspect of electric vehicles, as the continuous tracking of an EV's location can lead to privacy breaches. To address this issue, various methods have been proposed to enable anonymous and unlinkable communication between vehicles and infrastructure. For example, Mahmoud Nabil et al. [4] introduced a secure and privacy-preserving payment system based on Camenisch-Lysyanskaya (CL) signatures and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) technology, where CL signatures are used to protect the privacy of EV drivers when booking charging services. In addition, the system also supports anonymous identity authentication and priority scheduling, which can further protect the user's location privacy. Specifically, the system uses zero-knowledge proof technology to verify the user's identity and authorization information, and uses a priority-based scheduling algorithm to intelligently schedule the charging sequence of vehicles, thereby avoiding the leakage of user location information.
In addition to the privacy concerns, ensuring secure communication and data exchange in electric vehicle systems is also crucial. One of the primary security requirements is the authentication of users, vehicles, and infrastructure components. Jose P. Martins et al. [5] proposed an electric vehicle charging system based on Touchalytics system and blockchain technology, aiming to improve the security and privacy protection of the charging process. At the same time, the article also introduces some related technologies and protocols, such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) protocol to ensure the security of the communication process.
In conclusion, various privacy protection methods have been proposed in the literature for electric vehicle systems, addressing the challenges of charging and communication systems, location privacy, and security protocols. However, there is currently no literature that proposes a security protection scheme for electric vehicle swap stations. With the increase of electric vehicle swap stations and the introduction of more new brands, it is necessary to pay more attention to the privacy security of users and introduce a safe privacy protection solution.
3. Preliminaries
This section of the paper presents the privacy protection system for electric vehicle battery swap stations that utilizes blockchain technology. The system comprises two primary roles: battery service providers and users. Blockchain technology is employed to ensure the security of the battery, track its history, locate the user's vehicle, and safeguard their privacy. The section delves into the specifics of the cryptographic primitives and algorithms that underpin the system's functionality.
3.1. Elliptic curve cryptography
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a public-key cryptography method that uses the properties of elliptic curves over finite fields to provide secure communication over the internet. The security of ECC is based on the difficulty of solving the Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (ECDLP) [6].
The system utilizes ECC to generate public and private keys for the battery service providers and users. The public key is employed to authenticate the battery service providers and users, while the private key is utilized for signing and decryption purposes.
The elliptic curve equation used in the system is as in equation (1), where \( a \) and \( b \) are constants, and \( p \) is a prime number.
\( {y^{2}}={x^{3}}+ax+b (mod p) \) (1)
3.2. Schnorr signature scheme
The Schnorr signature scheme is a digital signature algorithm that provides strong security properties, including unforgeability, non-repudiation, and message integrity [7]. It is based on the hardness of the discrete logarithm problem [7].
To ensure the authenticity and integrity of the battery service providers and users' messages, the system employs the Schnorr signature scheme, which encompasses the following steps:
Key Generation. The battery service provider and user each generate a public-private key pair using ECC.
(1) They choose a large prime number \( p \) and a subgroup of order \( q \) , where \( q \) is a factor of \( p-1 \) .
(2) They find a generator \( g \) of the subgroup of order \( q \) .
(3) They randomly choose a private key \( x \) , where \( 1 \lt =x \lt =q-1 \) .
(4) They compute the public key \( y={g^{x}} (mod p) \) .
Signing. The battery service provider or user signs a message using their private key and generates a signature.
(1) They choose a random number k, where \( 1 \lt =k \lt =q-1 \) .
(2) They compute \( r=g\text{^}x (mod p) \) .
(3) They compute \( e=Hash(m || r) \) , where Hash is a cryptographic hash function.
(4) They compute \( s=k + ex (mod q) \) , where x is the private key.
Verification. The signature is verified using the public key of the battery service provider or user.
(1) They compute \( e=Hash(m || r) \) .
(2) They compute \( {v_{1}}= {g^{s}} {y^{-e}} (mod p) \) .
(3) They compute \( {v_{2}}={r^{e}} (mod p) \) .
(4) They verify the signature by checking if \( v1=v2 \) . If they are equal, the signature is valid; otherwise, the signature is invalid.
3.3. Ring signature
Ring signature is a type of digital signature that can be performed by any member of a group of users that each have a public key [8]. The security of ring signatures is based on the difficulty of determining the identity of the signer [9].
The signature process of Ring Signature is as follows:
(1) They choose a ring that includes the public key and multiple other public keys, where the public keys on the ring are called the pseudo-random numbers.
(2) They randomly choose a secret key \( k \) .
(3) They compute \( c=Hash(m||ring||k) \) , where Hash is a cryptographic hash function.
(4) They compute \( s=k+cx (mod q) \) .
It can be seen that the signature process of the Schnorr Signature Scheme requires the participation of the private key, while the signature process of Ring Signature does not require the participation of the private key [10]. Instead, it only needs to choose a ring of public keys to sign the message. This is one of the main differences between the two signature algorithms.
In addition, the security of the Schnorr Signature Scheme is based on the difficulty of solving the discrete logarithm problem, which means that the private key cannot be calculated from the known public key and signature [10]. The security of Ring Signature, on the other hand, is based on the difficulty of determining the identity of the signer, which means that the signer's identity cannot be determined from the known signature [11]. This is also one of the fundamental differences between the two signature algorithms.
3.4. Merkle tree
The Merkle tree is a data structure that allows efficient verification of the integrity and authenticity of large datasets [12]. The Merkle tree is utilized in the system to store the battery's history and to ensure that it remains untampered with.
The construction of Merkle Tree can be expressed using the formula (2).
\( {H_{i}}=f({H_{2i-1}}||{H_{2i}}) \) (2)
Here, \( {H_{i}} \) represents the hash value of the \( i \) level in Merkle Tree, \( f \) represents the hash function, and \( {H_{2i-1}} and {H_{2i}} \) represent the hash values of the child nodes in the \( i \) level.
Merkle Proof is a proof that proves the existence of a data block in Merkle Tree. Merkle Proof consists of a hash path from the leaf node to the root node and the hash value of the root node. The hash path can be calculated using the formula (3).
\( {P_{j}}=[{H_{{k_{1}}}},{H_{{k_{2}}}},…,{H_{{k_{m}}}}] \) (3)
Here, \( {P_{j}} \) represents the hash path of the data block \( {x_{j}} \) in Merkle Tree, and \( {H_{{k_{1}}}} \) to \( {H_{{k_{m}}}} \) represent the hash values of all non-leaf nodes from the leaf node where \( {x_{j}} \) is located to the root node.
The advantages of Merkle Tree include efficiency, security, verifiability, and scalability. The efficiency of Merkle Tree is reflected in the fast calculation of hash values and verification of Merkle Proof. The security of Merkle Tree can be guaranteed by the hash function to ensure the integrity and security of data blocks. The verifiability and scalability of Merkle Tree can be expressed using the formula (4).
\( Root={H_{1}} \) (4)
Here, \( Root \) represents the hash value of the root node of Merkle Tree, and \( {H_{1}} \) represents the hash value of the first level. By verifying the hash value of the root node, the integrity of the entire Merkle Tree can be verified. Merkle Tree can also quickly add and delete data blocks to achieve scalability.
4. Design of secure EV battery swap station system
The subsequent section provides an in-depth exposition of the design of the EV Battery Swap Station System, which is intended to facilitate the seamless swapping of electric vehicle batteries.
4.1. System framework diagram
System framework diagram in this system is to provide a clear understanding of the system's structure, functionality, architecture, and security measures. It serves as an important tool for planning and designing the system architecture and ensuring that the system meets the security and privacy requirements of the EV battery swap station.
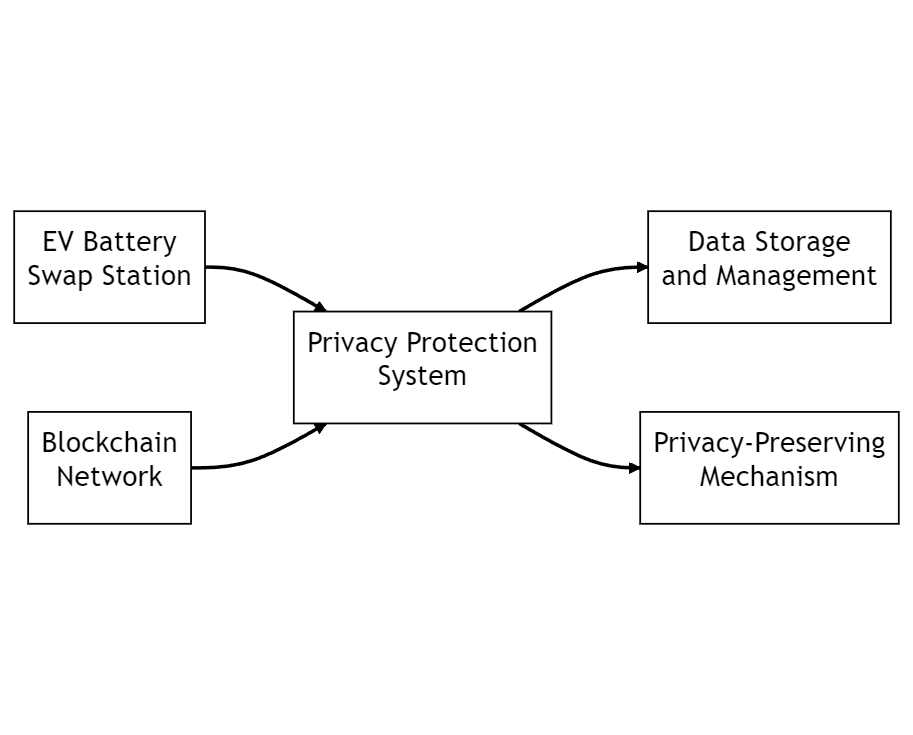
As shown in Figure 1, the following is a system framework diagram consists of three main components:
EV Battery Swap Station. This is a traditional electric vehicle battery swap station and the core component of the entire system. It interacts with the blockchain network through the privacy protection system to ensure data privacy and security.
Blockchain Network. This is a distributed, immutable, and secure database used to store and manage all data related to the EV battery swap station. The data in the blockchain network is encrypted and can only be accessed and modified by users with corresponding permissions.
Privacy Protection System. This is a system designed to protect the privacy of data in the EV battery swap station. It consists of two main parts - data storage and management, and privacy-preserving mechanisms. The data storage and management part stores and manages all data related to the EV battery swap station, while the privacy-preserving mechanisms part ensures data privacy and security.
|
Figure 1. System framework diagram. |
In the system framework diagram, the EV battery swap station is connected to the privacy protection system and the blockchain network. The EV battery swap station interacts with the blockchain network through the privacy protection system to ensure data privacy and security. The privacy protection system consists of data storage and management, and privacy-preserving mechanisms. The data storage and management part stores and manages all data related to the EV battery swap station, while the privacy-preserving mechanisms part ensures data privacy and security.
In summary, the system framework diagram depicts an EV battery swap station system based on blockchain and privacy protection mechanisms, aimed at protecting the data privacy and security of the EV battery swap station.
4.2. Roles and capabilities diagram
The user roles and capabilities diagram is crucial in this system because it helps designers understand user needs, evaluate the system's complexity and completeness, and facilitate communication and collaboration among team members. It is an essential tool in system design and implementation, leading to improved reliability and user experience.
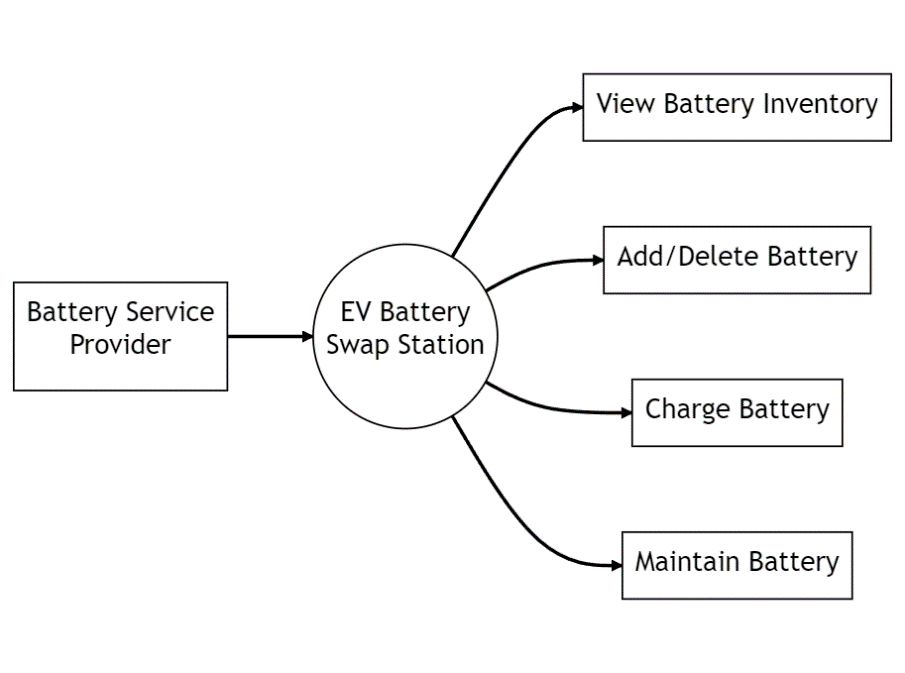
For the battery service provider, the Figure 2 shows the interaction and functions between it and the EV battery exchange station. The battery service provider provides battery exchange services to users through the EV battery exchange station. It can use the check battery inventory function to understand its inventory status and add or remove batteries when necessary. Additionally, it can charge and maintain batteries to ensure their reliability and performance. The EV battery exchange station provides the specific implementation of these functions.
|
Figure 2. Application range of battery provider. |
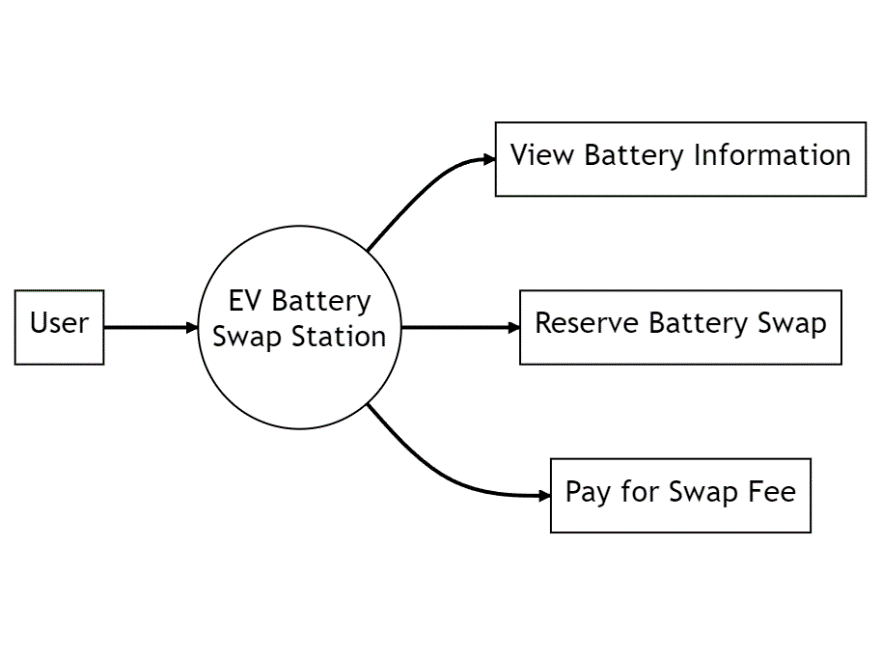
For the user, the Figure 3 shows the interaction and functions between it and the EV battery exchange station. Users can use the check battery information function to understand the availability of batteries and use the reserve battery exchange function to reserve the desired battery for exchange. After exchanging the battery, they also need to pay the exchange fee. The EV battery exchange station provides the specific implementation of these functions.
|
Figure 3. Application range of user. |
Overall, these two diagrams clearly show the interaction and functions between the battery service provider and the user, which helps to better understand and implement the system, improving the reliability and user experience of the electric vehicle charging and service system.
4.3. Flow chart
In this system, the flowchart is used to clearly illustrate the steps involved in the battery exchange process. It helps relevant personnel to understand the core steps of the service and facilitates coordination and communication. The flowchart can also prevent errors, improve efficiency, and provide valuable insights for service improvement.
4.3.1. New user registration and battery exchange request. The Figure 4 describes the business process of new user registration and battery exchange request in the privacy protection system for EV battery swap stations using blockchain.
|
Figure 4. New user registration and battery exchange request. |
In this process, the new user provides personal information, and the system generates an anonymous identity to protect the user's privacy. The system stores this anonymous identity on the blockchain to ensure its immutability and traceability. When the user needs to exchange the battery, the system locates the nearest available battery swap station and verifies the user's identity. After the battery exchange is completed, the system updates the blockchain record, including relevant information about the battery exchange. The flowchart demonstrates how blockchain technology is used to protect user privacy and ensure the security of transactions. By storing the user's anonymous identity and battery exchange record on the blockchain, the system can ensure the traceability and immutability of transactions, thereby enhancing the security and credibility of the system.
The flowchart shows that the proposed privacy protection system for electric vehicle battery swap stations using blockchain involves two roles: battery service provider and user. The use of the blockchain technology is limited to protecting the safety and traceability of batteries, the location of user cars (as navigation to the swap station is required), and user privacy (such as personal and identity information). By using the blockchain technology, the system can provide a secure and trustworthy platform for battery exchange by protecting the users' privacy and ensuring the traceability and immutability of transactions. The proposed system can potentially facilitate the adoption of electric vehicles by addressing privacy and security concerns associated with battery swap stations.
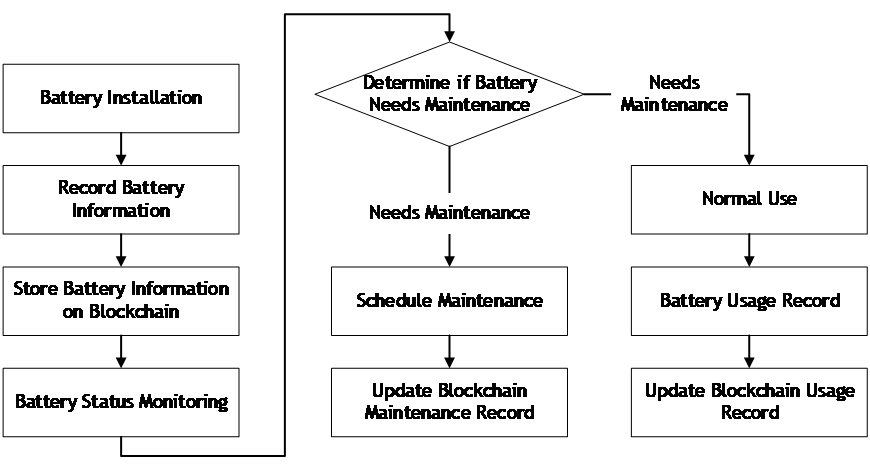
4.3.2. Battery status monitoring and traceability. As shown in Figure 5, the following flowchart describes a scenario in the privacy protection system for EV battery swap stations using blockchain, where the battery status is monitored and traced using blockchain technology.
|
Figure 5. Battery status monitoring and traceability. |
The process begins with the installation of the battery, where the system records the battery information and stores it on the blockchain for traceability. The system then monitors the battery status and determines whether the battery needs maintenance or not. If the battery requires maintenance, the system arranges for maintenance and updates the maintenance record on the blockchain. If the battery is in normal condition, the user can use it for normal operations, and the system updates the usage record on the blockchain.
The use of blockchain technology in monitoring and tracing battery status provides several benefits, such as ensuring the authenticity and immutability of battery information, enabling the identification of problematic batteries, and facilitating maintenance and replacement procedures. By recording battery information on the blockchain, the system can trace the entire history of the battery, including its installation, usage, and maintenance records. This information can be accessed by authorized parties, such as the battery service provider and users, to verify the battery's authenticity and ensure its safety. Additionally, the use of blockchain technology can also improve the efficiency of maintenance and replacement procedures by providing accurate and up-to-date information about the battery's condition. Overall, this flowchart demonstrates how the proposed privacy protection system for EV battery swap stations using blockchain can enhance the safety and reliability of the battery exchange process.
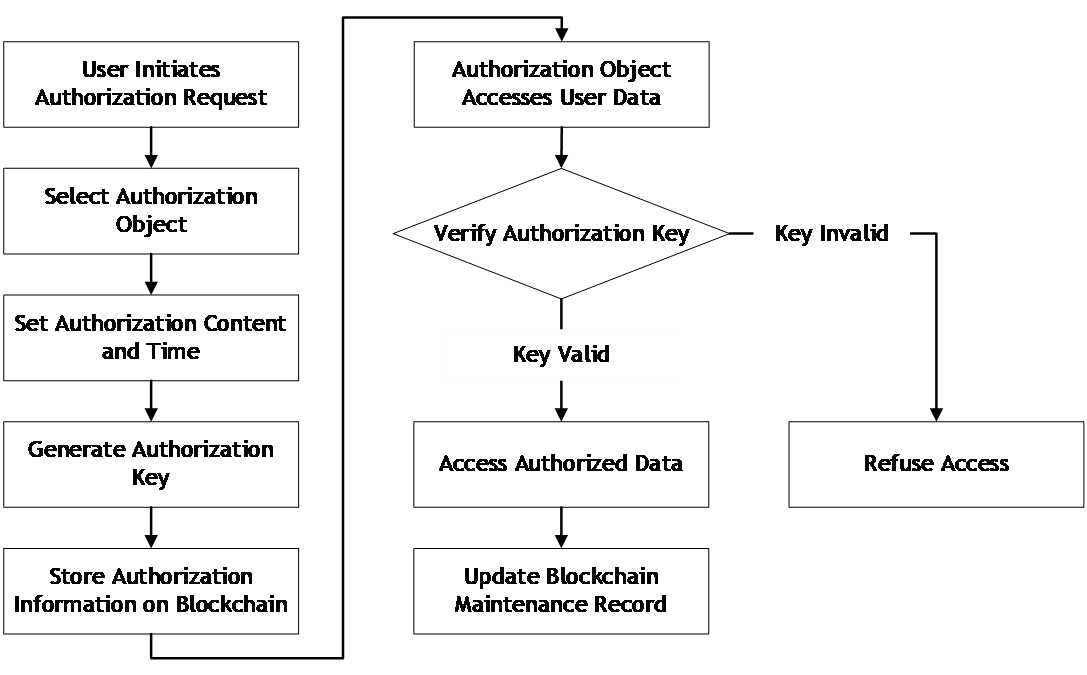
4.3.3. User privacy protection and authorization. As shown in Figure 6, the following flowchart describes a scenario in the privacy protection system for EV battery swap stations using blockchain, where user privacy is protected through a secure authorization process.
|
Figure 6. User privacy protection and authorization. |
The process begins with the user initiating an authorization request, selecting the authorized party, and setting the scope and duration of the authorization. The system then generates an authorization key and stores the authorization information on the blockchain, ensuring its immutability and traceability. Once the authorized party receives the authorization key, they can access the user's data within the authorized scope and duration. The system then verifies the authorization key's validity, and if it is valid, the authorized party can access the user's data. The system updates the blockchain authorization record after the authorized party accesses the data.
The use of blockchain technology in user privacy protection and authorization provides several benefits, such as ensuring the security of personal and identity information, enabling the user to control their data, and facilitating secure data sharing between authorized parties. By storing the authorization information on the blockchain, the system can ensure the authenticity and traceability of the authorization process, enhancing the credibility of the system. Additionally, the use of blockchain technology can also improve the efficiency of the authorization process by eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs. Overall, this flowchart demonstrates how the proposed privacy protection system for EV battery swap stations using blockchain can enhance the security and privacy of user data.
5. Implementation of secure EV battery swap station system
This section implements the EV Battery Swap Station System in detail, including diagrams and algorithms.
5.1. Unified modeling language (UML) diagram
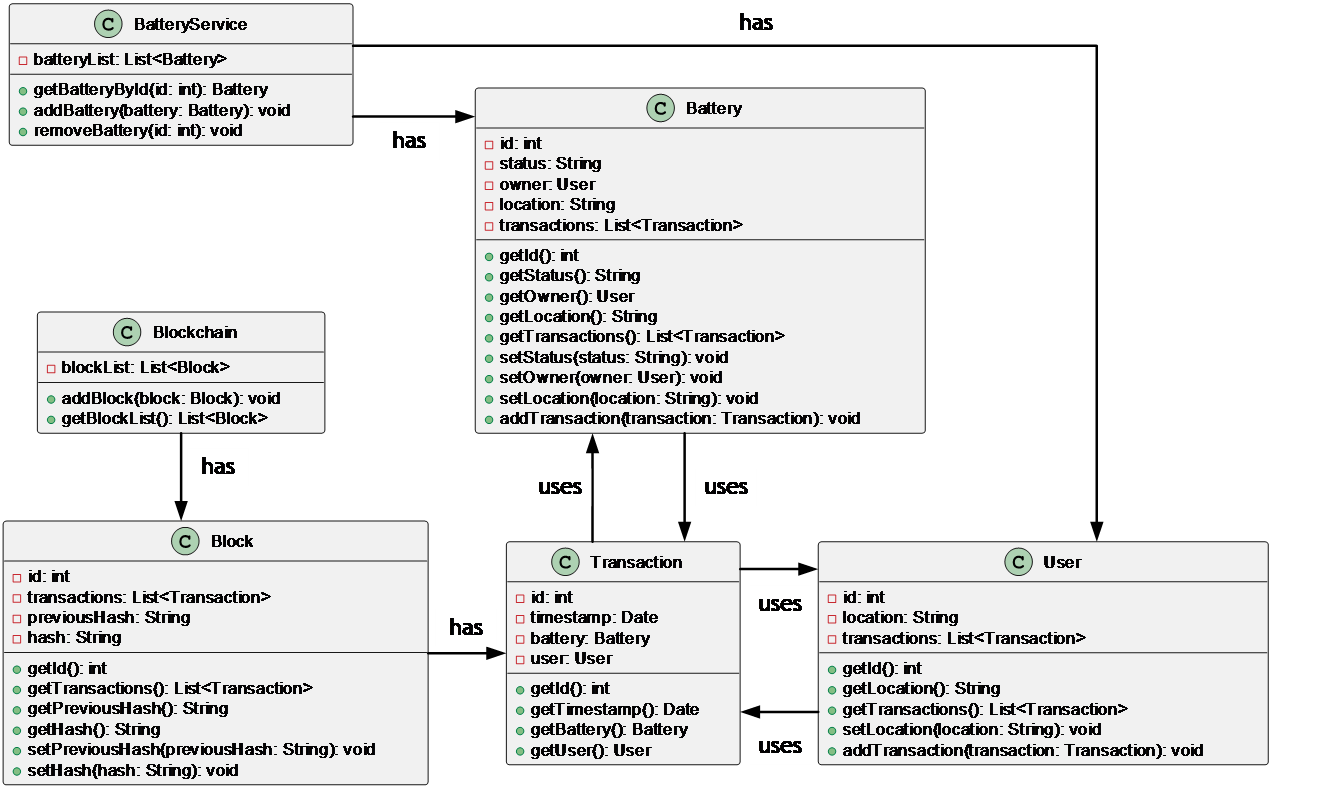
As shown in Figure 7, UML diagram can visualize the structure and relationships of the system, and better understand its various components.
|
Figure 7. UML diagram. |
Here is a detailed explanation of the UML diagram:
BatteryService class. This class represents the battery service, which includes a batteryList property that is a list of Battery objects used to manage the information of all batteries. In addition, the BatteryService class includes the getBatteryById(), addBattery(), and removeBattery() methods used to find, add, and remove batteries by ID.
Battery class. This class represents a battery, which includes properties such as id, status, owner, location, and transactions to represent the battery's unique identifier, status, user, location, and transaction history. The Battery class also includes a series of getter and setter methods used to obtain and set property values, as well as an addTransaction() method used to add transactions to the battery's transaction history.
User class. This class represents a user, which includes properties such as id, location, and transactions to represent the user's unique identifier, location, and transaction history. The User class also includes a series of getter and setter methods used to obtain and set property values, as well as an addTransaction() method used to add transactions to the user's transaction history.
Transaction class. This class represents a transaction between a battery and a user, including properties such as id, timestamp, battery, and user to represent the transaction's unique identifier, timestamp, battery, and user. The Transaction class also includes a series of getter methods used to obtain property values.
Blockchain class. This class represents a blockchain, including a blockList property that is a list of Block objects used to manage the information of the entire blockchain. The Blockchain class also includes the addBlock() and getBlockList() methods used to add blocks and obtain the block list.
Block class. This class represents a block, including properties such as id, transactions, previousHash, and hash to represent the block's unique identifier, transaction list, previous block's hash value, and its own hash value. The Block class also includes a series of getter and setter methods used to obtain and set property values.
In the UML diagram, the BatteryService class has instances of the Battery and User classes, while the Battery and User classes are also associated with the Transaction class. In addition, the Blockchain class has instances of the Block class while the Block class is also associated with the Transaction class.
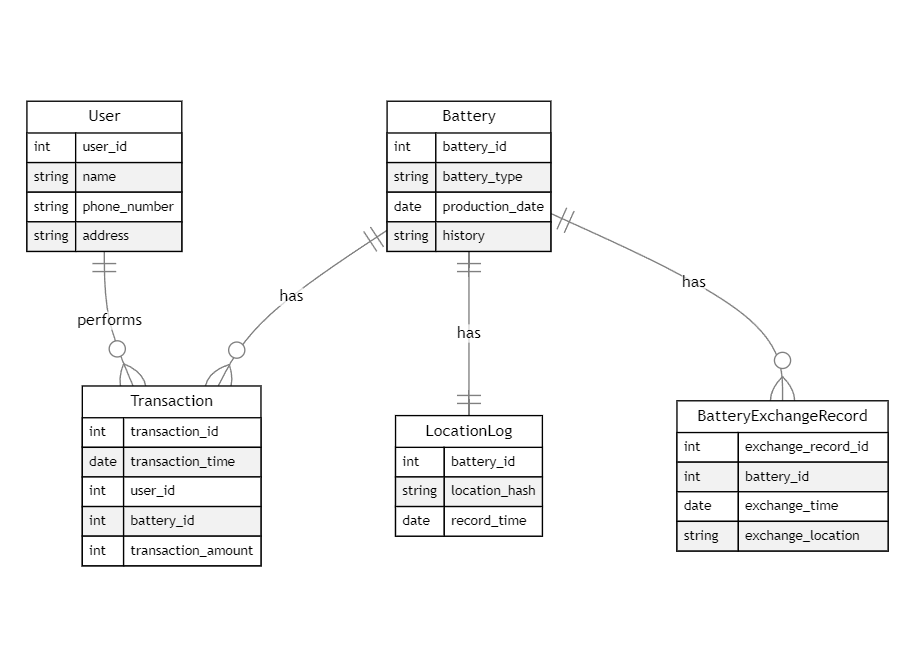
5.2. Entity-relationship (ER) diagram
The Figure 8 is the ER diagram and clarifies the relationships between entities, provides a foundation for database design, facilitates system extension and modification, and enhances system maintainability and scalability.
|
Figure 8. ER diagram. |
The entities in this ER diagram include Battery, User, Transaction, Location Log, and Battery Exchange Record, and they have different connections and relationships.
5.2.1. Battery entity. Represents the batteries in the system, including battery ID, battery type, production date, and historical records. It has the following connections and relationships with other entities:
The Battery entity has a one-to-many relationship with the Transaction entity, as a battery can be purchased and used by multiple users. Moreover, the Battery entity possesses a one-to-one relationship with the LocationLog entity, where each battery is associated with one location log record. Similarly, the Battery entity maintains a one-to-one relationship with the BatteryExchangeRecord entity, with each battery linked to one battery exchange record.
5.2.2. User entity. Represents the users in the system, including user ID, name, phone number, and address. It has the following connections and relationships with other entities:
The User entity exhibits a one-to-many relationship with the Transaction entity, as a user can conduct multiple transactions.
5.2.3. Transaction entity. Represents the transactions conducted by users in the system, including transaction ID, transaction time, user ID, battery ID, and transaction amount. It has the following connections and relationships with other entities:
The Transaction entity displays a one-to-many relationship with the User entity, as a user can conduct multiple transactions. Additionally, the Transaction entity demonstrates a one-to-many relationship with the Battery entity, where each transaction corresponds to one battery.
5.2.4. Location log entity. Represents the records of battery location in the system, including battery ID, location hash value, and record time. It has the following connections and relationships with other entities:
The LocationLog entity exhibits a one-to-one relationship with the Battery entity, where each battery corresponds to one location log record.
5.2.5. Battery exchange record entity. Represents the records of battery exchange in the system, including exchange record ID, battery ID, exchange time, and exchange location. It has the following connections and relationships with other entities:
The BatteryExchangeRecord entity maintains a one-to-one relationship with the Battery entity, where each battery corresponds to one battery exchange record.
In summary, this ER diagram designates the connections and relationships among the entities in the system, providing a foundation for the database design and system implementation.
5.3. Pseudocode
To accomplish the objectives of the proposed blockchain privacy protection system for electric vehicle battery swap stations, a set of pseudocode examples is presented to demonstrate how to securely track battery location and status, safeguard user privacy, and conduct battery swap transactions on the blockchain.
The aim of this section is to showcase the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed system by utilizing pseudocode as a tool to explicate the technical intricacies of its implementation. The pseudocode examples presented in this section offer a clear and succinct depiction of the essential functions and algorithms that serve as the foundation of the system's capability to securely manage battery service providers and users while maintaining the privacy and security of their personal and identification information.
This approach is intended to provide a practical and easily comprehensible method of comprehending the technical complexities of the proposed system. It is hoped that this will facilitate its adoption and implementation by stakeholders in the electric vehicle and battery swap station industries.
5.3.1. Battery tracking on blockchain. As shown in Algorithm 1, this algorithm aims to securely track the location and status of batteries by adding battery location and status events to the blockchain.
The algorithm commences by invoking the "trackBatteryLocationAndStatus" function, which adds battery location and status events to the blockchain.
Next, the "blockchainRules.applyBatteryTrackingRules" function is called to enforce the battery tracking rules and verify that the battery location and status are in accordance with the predefined standards. The algorithm concludes, thereby ensuring the secure tracking of battery location and status.
Algorithm 1: Battery Tracking on Blockchain |
Require: batteryID, location, status 1: function trackBatteryLocationAndStatus(batteryID, location, status) 2: // Add battery location and status event to blockchain 3: blockchain.addBatteryTrackingEvent(batteryID, location, status) 4: // Apply battery tracking rules 5: blockchainRules.applyBatteryTrackingRules(batteryID, location, status) 6: end function |
5.3.2. User privacy protection on the blockchain. As shown in Algorithm 2, this algorithm aims to protect user privacy by encrypting user privacy information and storing it on the blockchain.
The algorithm initiates by invoking the "protectUserPrivacyOnBlockchain" function, which encrypts the user's location, contact information, and identification information and stores the encrypted data on the blockchain.
Subsequently, the "blockchainRules.applyUserPrivacyRules" function is called to enforce user privacy rules and verify that the user's privacy is safeguarded. Ultimately, the algorithm concludes, thereby ensuring the security and protection of user privacy.
Algorithm 2: User Privacy Protection on the Blockchain |
Require: userID, location, contactInfo, identificationInfo 1: function protectUserPrivacyOnBlockchain (userID, location, contactInfo, identificationInfo) 2: // Encrypt user privacy information 3: encryptedLocation = encryptData (location) 4: encryptedContactInfo = encryptData (contactInfo) 5: encryptedIdentificationInfo = encryptData(identificationInfo) 6: // Store encrypted user privacy information on blockchain 7: blockchain.storeEncryptedPrivacyInformation(userID, encryptedLocation, encryptedContactInfo, encryptedIdentificationInfo) 8: // Apply user privacy rules 9: blockchainRules.applyUserPrivacyRules(userID, location, contactInfo, identificationInfo) 10: end function |
5.3.3. Battery swap transactions on the blockchain. As shown in Algorithm 3, this algorithm aims to securely execute and track battery swap transactions by adding battery swap transactions to the blockchain.
The algorithm commences by invoking the "performBatterySwapOnBlockchain" function, which adds battery swap transactions to the blockchain. Next, the "batteryDatabase.updateBatteryStatus" function is called to update the battery status as "in use".
Subsequently, the "blockchainRules.applyBatterySwapRules" function is called to enforce battery swap rules and verify that the battery swap adheres to the predefined standards. Ultimately, the algorithm concludes, thereby ensuring the secure execution and tracking of battery swap transactions.
Algorithm 3: Battery Swap Transactions on the Blockchain |
Require: batteryID, userID, swapTime, swapLocation 1: function performBatterySwapOnBlockchain(batteryID, userID, swapTime, swapLocation) 2: // Add battery swap transaction to blockchain 3: blockchain.addBatterySwapTransaction(batteryID, userID, swapTime, swapLocation) 4: // Update battery tracking 5: batteryDatabase.updateBatteryStatus(batteryID, "in use") 6: // Apply battery swap rules 7: blockchainRules.applyBatterySwapRules(batteryID, userID, swapTime, swapLocation) 8: end function |
6. Conclusion
This paper introduces a privacy protection system for electric vehicle battery swap stations that employs blockchain technology. The system aims to tackle the security and privacy challenges that battery swap stations face, such as safeguarding sensitive information and securely managing and tracking batteries.
The system comprises two primary roles: battery service providers and users. It leverages the transparency and immutability of blockchain technology to guarantee the safety, traceability, and privacy of batteries and users. This paper details the design and implementation of the system, emphasizing its features, advantages, and potential applications.
The performance and security of the system have been evaluated using various metrics and scenarios. The results indicate that the system provides a feasible solution to the security and privacy challenges confronting battery swap stations and can contribute to the advancement of sustainable transportation.
Looking ahead, it is believed that the system can be further refined and expanded to other transportation applications. By harnessing the potential of blockchain technology, a more secure, transparent, and sustainable future for transportation can be envisioned.
References
[1]. Ahmad F, Saad Alam M, Saad Alsaidan I and Shariff SM 2020 IET Smart Grid, Battery swapping station for electric vehicles: Opportunities and challenges vol 3 pp 280–286
[2]. Florea BC and Taralunga DD 2020 Sustainability, Blockchain IOT for Smart Electric Vehicles Battery Management vol 12 p 3984
[3]. Kern D 1970 Privacy-preserving architecture for EV charging and billing
[4]. Nabil M, Bima M, Alsharif A, Johnson W, Gunukula S, Mahmoud M and Abdallah M 2019 Smart Cities Cybersecurity and Privacy, Priority-based and privacy-preserving electric vehicle dynamic charging system with divisible e-payment pp 165–186
[5]. Martins JP, Ferreira JC, Monteiro V, Afonso JA and Afonso JL 2019 Energies, IOT and blockchain paradigms for EV Charging System vol 12 p 2987
[6]. Singh LD and Singh KM 2015 Procedia Computer Science, Implementation of text encryption using elliptic curve cryptography vol 54 pp 73–82
[7]. Lyubashevsky V 2021 National Science Review, Lattice-based digital signatures vol 8
[8]. Shim K-A 2015 Information Sciences, An efficient ring signature scheme from pairings vol 300 pp 63–69
[9]. Feng H, Liu J, Li D, Li Y-N and Wu Q 2021 Designs, Codes and Cryptography, Traceable ring signatures: General framework and post-quantum security vol 89 pp 1111–1145
[10]. Yuen TH, Esgin MF, Liu JK, Au MH and Ding Z 2021 Advances in Cryptology, Dualring: Generic construction of ring signatures with efficient instantiations pp 251–281
[11]. Fiore D, Garms L, Kolonelos D, Soriente C and Tucker I 2022 Computer Security, 2022 Ring signatures with user-controlled Linkability pp 405–426
[12]. Liu H, Luo X, Liu H and Xia X 2021 2021 International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science, Merkle tree: A fundamental component of blockchains pp 556-561
Cite this article
Qiu,K. (2023). A secure system for electric vehicle battery swap stations using blockchain. Applied and Computational Engineering,16,13-26.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Ahmad F, Saad Alam M, Saad Alsaidan I and Shariff SM 2020 IET Smart Grid, Battery swapping station for electric vehicles: Opportunities and challenges vol 3 pp 280–286
[2]. Florea BC and Taralunga DD 2020 Sustainability, Blockchain IOT for Smart Electric Vehicles Battery Management vol 12 p 3984
[3]. Kern D 1970 Privacy-preserving architecture for EV charging and billing
[4]. Nabil M, Bima M, Alsharif A, Johnson W, Gunukula S, Mahmoud M and Abdallah M 2019 Smart Cities Cybersecurity and Privacy, Priority-based and privacy-preserving electric vehicle dynamic charging system with divisible e-payment pp 165–186
[5]. Martins JP, Ferreira JC, Monteiro V, Afonso JA and Afonso JL 2019 Energies, IOT and blockchain paradigms for EV Charging System vol 12 p 2987
[6]. Singh LD and Singh KM 2015 Procedia Computer Science, Implementation of text encryption using elliptic curve cryptography vol 54 pp 73–82
[7]. Lyubashevsky V 2021 National Science Review, Lattice-based digital signatures vol 8
[8]. Shim K-A 2015 Information Sciences, An efficient ring signature scheme from pairings vol 300 pp 63–69
[9]. Feng H, Liu J, Li D, Li Y-N and Wu Q 2021 Designs, Codes and Cryptography, Traceable ring signatures: General framework and post-quantum security vol 89 pp 1111–1145
[10]. Yuen TH, Esgin MF, Liu JK, Au MH and Ding Z 2021 Advances in Cryptology, Dualring: Generic construction of ring signatures with efficient instantiations pp 251–281
[11]. Fiore D, Garms L, Kolonelos D, Soriente C and Tucker I 2022 Computer Security, 2022 Ring signatures with user-controlled Linkability pp 405–426
[12]. Liu H, Luo X, Liu H and Xia X 2021 2021 International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science, Merkle tree: A fundamental component of blockchains pp 556-561