1. Introduction
As global energy demand continues to grow, efficient, environmentally friendly and sustainable energy solutions have become a top goal for the research community. Among alternative energy technologies, battery technology has attracted much attention because of its characteristics of portability, high efficiency and environmental protection. In the current market, lithium batteries still dominate [1]. Among them, zinc battery, as an important form of battery technology, has gradually become an ideal energy storage device because of its rich raw material sources, excellent electrochemical performance, environmental protection and other characteristics. Quantum dots, as a new nanomaterial, have been widely used in zinc batteries in recent years. The application of quantum dots in zinc batteries is reviewed and discussed in this paper.
With its rich raw material resources, excellent electrochemical performance, environmental protection and high safety, zinc batteries have gradually become an important candidate for the next generation of efficient energy storage devices [2]. However, zinc batteries still have problems such as irreversible zinc expansion and battery overcharge and discharge performance, which limit the performance and application of zinc batteries to a certain extent [3]. At the same time, quantum dots, as a new type of nanomaterials, have unique photoelectric properties, adjustable energy levels and size effects, providing a new way for zinc batteries to solve problems [4]. Especially in the field of photoelectric conversion and energy storage, the application of quantum dots has achieved remarkable results. However, how to combine quantum dots with zinc batteries more effectively, how to optimize and improve the application effect of quantum dots in zinc batteries, is still an important challenge in the current research.
This study will start with quantum dots. Quantum dots (QDS), as a unique nanostructure, show great application potential in the fields of biomarkers, photovoltaics, diodes (leds) and photocatalysis due to their special physicochemical properties [5]. In the field of energy storage, quantum dots show unique advantages due to their excellent photoelectric properties, adjustable energy levels and size effects, especially in improving battery performance. Quantum dots are applied to zinc batteries primarily to improve the energy storage efficiency and cycle stability of the battery by optimizing the electrochemical performance of the battery, thereby expanding the zinc batteries' application range. Next, this research will delve into three specific applications of quantum dots in zinc batteries, i.e., their role in enhancing energy storage and increasing charge/discharge rates. For each application, this paper will discuss the principles involved, describe experimental results from past studies, and present relevant pictures to help understand. In addition, this study will also explore the challenges and prospects of the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries. Although quantum dots have many excellent properties, they still face many challenges in practical applications such as stability, consistency and cost. On the other hand, with the continuous development of nanotechnology and materials science, and the in-depth understanding of the characteristics of quantum dots, people are full of expectations for the prospect of using quantum dots to improve the performance of zinc batteries. This paper will also investigate the challenges and potential of quantum dots in zinc batteries. Even though quantum dots have many of the excellent properties scholars have reviewed, they still face many obstacles in practical applications, including stability, consistency, and cost issues. However, with the continuous development of nanotechnology and materials science, as well as the in-depth understanding of the characteristics of quantum dots, quantum dots will play an increasingly large role in zinc batteries, and people are optimistic about it. In conclusion, this study will look forward to the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries and future research directions. For example, researchers may look for new quantum dot materials and synthesis techniques to further improve the performance of zinc batteries. In addition, with the expansion of research on the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries, it is looking forward to discovering new applications for zinc battery design and preparation in the future, and to better cope with the increasing energy problems.
2. Descriptions of quantum dots
Quantum dots are nanoscale semiconductor particles, typically in the 1-10 nanometres range in size. Due to their tiny size, the electrons of quantum dots are limited in all three spatial dimensions, so their energy levels exhibit a discrete state, which is significantly different from traditional three-dimensional solid materials [6]. In addition, because its size is at the quantum scale, the movement of electrons is dominated by the laws of quantum mechanics, so quantum dots show a special size effect, that is, their physical and chemical properties (such as optical properties, electronic properties, magnetic properties) will change with the change of size. For example, the fluorescence emission colour of a quantum dot can be adjusted by changing its size, because the band gap of a quantum dot (a property that determines how much energy a quantum dot absorbs and emits) changes with its size. Specifically, the length of the wavelength emitted by a quantum dot is proportional to the size of its individual body [7]. This property makes it a good luminescent material.
There are many ways to prepare quantum dots, and one of the most common methods is chemical. This method mainly includes organic synthesis and hydrothermal/solvothermal synthesis. In organic synthesis methods, organometals and sulphur or selenium sources are dissolved in organic solvents, respectively, and then react to form quantum dots under certain reaction conditions [8]. This method can prepare quantum dots with excellent optical properties, but its disadvantage is that the organic solvents and precursors used are toxic. In hydrothermal/solvothermal synthesis methods, inorganic salts and sources of sulphur or selenium are dissolved in water or other environmentally friendly solvents and then react under high temperature and pressure conditions to form quantum dots. This method has the advantage of being environmentally friendly and low-cost, but the optical properties of the prepared quantum dots are usually inferior to those of organic synthesis [9]. No matter which method is used, controlling the reaction conditions (reaction time, temperature, type of coordination agent, etc.) is the key, which directly determines the size, shape and surface properties of the final prepared quantum dots.
Quantum dots (QDS) have wide application prospects in many fields because of their size-adjustable photoelectric properties and high surface activity. In the field of optoelectronics, quantum dots can be used in light-emitting diodes (LEDS), quantum dot solar cells and quantum dot lasers. Among them, quantum dot LED (QLED) has begun to gain a certain share in the display market due to its advantages of high purity, colour saturation and high brightness. In the biomedical field, quantum dots can be used as biomarkers for imaging and detection, and as drug carriers for drug delivery. In addition, due to their high surface activity and tuneable electrochemical properties, quantum dots are also used for environmental monitoring and governance, such as for the detection of heavy metal ions and the degradation of organic pollutants.
3. Applications in energy storage capacity of zinc batteries
Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) is a unique material that has attracted much attention from scientists due to its unique photoelectric properties, high surface area and excellent electrical conductivity. In battery technology, especially in the field of zinc batteries, GQDs has shown great potential in improving energy storage efficiency. Here are some more about it. Quantum particles of graphene can be used as a modified material for zinc battery electrodes, which can effectively increase their conductivity. Since the practical application of zinc metal anodes with high volume capacity is hampered by dendrite growth and corresponding interfacial parasitic reactions, Zhang et al. attempted to use carbon quantum dots as a consistently functional artificial interfacial layer to optimize large-scale electrolytes [6]. This practical and effective method for preparing functional CDs layers paves the way for stable metal anodes devoid of dendrites. This improves the battery's specific capacity, charge and discharge efficiencies, and cycle stability. In addition, GQDs can also improve the battery's energy storage capacity by providing more active sites. For example, Tian Ge et al. used nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots as electrode materials for zinc batteries in their study. They found that nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots were able to provide more active sites, thereby improving the battery's energy storage capacity [10]. This makes the battery have high performance, but also makes the battery energy efficiency has been improved. In general, graphene quantum dots are a new type of material with great application potential. In the field of zinc batteries, GQDs has shown its unique advantages, whether in improving the charging and discharging performance of batteries, or in enhancing the energy storage capacity of batteries. Therefore, one has reason to believe that graphene quantum dots will play an increasingly important role in the research and application of zinc batteries.
4. Enhancing charging and discharging efficiency of Zinc-Ion
Using graphene quantum dots as modification materials for zinc battery electrodes can also improve their charge-discharge performance. This modification can significantly improve the conductivity of the electrode, thus enhancing the charge and discharge ability of the battery. In the study, Han et al., found that the conductivity of the electrode was greatly improved by adding graphene quantum dots to the electrode material [10]. High stability static Zinc-iodide REDOX batteries were prepared by introducing graphene quantum dots into graphite felt. This means that the efficiency of the battery in the charge and discharge process has been significantly improved, especially at high charge and discharge rates, the performance of the battery is more excellent.
In addition, the high surface activity of graphene quantum dots also brings great potential for improving the charge-discharge performance of zinc batteries. Wang et al. found that the rich defects of the as-prepared N-GH-GQD-1000 were obtained through adding GQD into the composite and subsequently activating it with melamine (seen from Figure 1) [11]. Due to the abundant defects in N-GH-GQD-1000, it demonstrates superior ORR catalytic activity over Pt/C, making it an attractive alternative to noble-metal-based catalysts for use in zinc-air batteries. In this way, not only the working efficiency of the battery is improved, but also the life of the battery is improved, and the reliability of the battery is enhanced. The results are summarized in Figure 2.
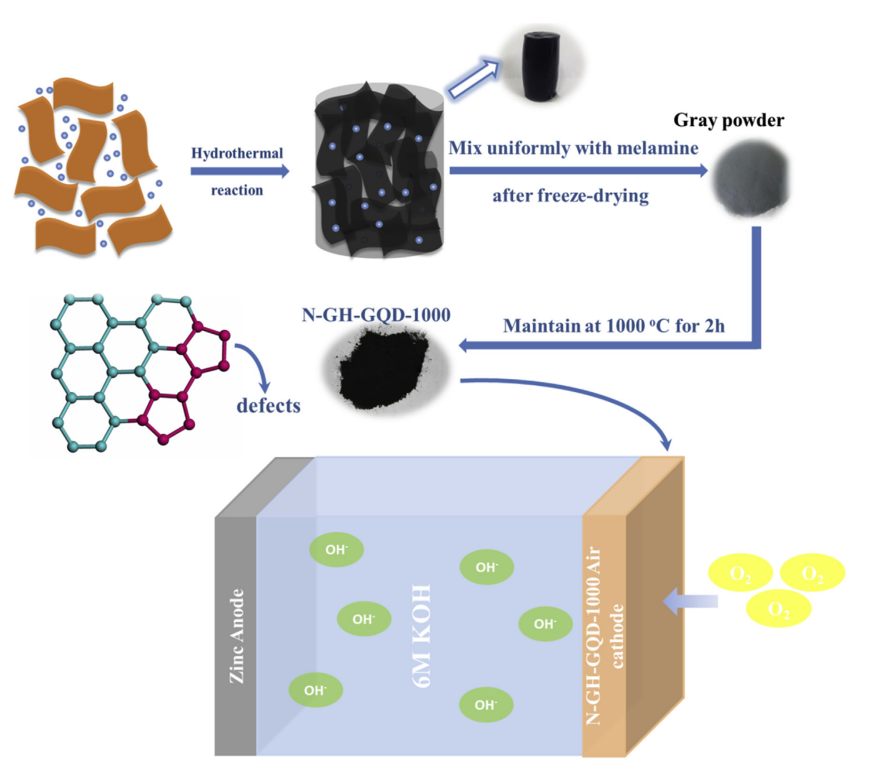
Figure 1. The sketch of the structure.
Figure 2. The discharge voltage profiles of N-GH-GQD-1000 (a) and Ptsingle bondC and the discharge curves of N-GH-GQD-1000 and Pt/C at 50 mA cm2 current density (b).
Overall, graphene quantum dots show great potential in improving the charge-discharge performance of zinc batteries. Whether as a modification material for the electrode to improve the conductivity of the electrode, or to provide additional active sites to improve the active region of the electrochemical reaction, graphene quantum dots have become a powerful tool to improve the charge and discharge performance of zinc batteries. Therefore, one has reason to expect that as the research and application of graphene quantum dots continue to deepen, it will play a greater role in the design and manufacture of zinc batteries in the future [12].
5. Limitations and prospects
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are a new type of material that has shown potential in scientific research to improve the performance of zinc-ion batteries. However, while this nanoscale material has shown great possibilities in battery technology, our understanding of this material is still limited. The complexity and versatility of GQDs presents research and application challenges, including how to efficiently synthesize this material, how to change its physical and chemical properties to meet the needs of specific applications, and how to scale up production to meet commercial needs. Although GQDs has been shown to largely improve the performance of zinc-ion batteries at laboratory scale, scaling this technology to larger scales remains a challenge. Manufacturing high-quality GQDs requires precise control, including particle size, shape, and chemical composition, which can become difficult in mass production. In zinc-ion battery applications, GQDs may have stability issues. During the charging and discharging process of the battery, these quantum dots may accumulate, thus affecting the long-term stability and performance of the battery. Therefore, this is an issue that needs further study. Although GQDs is widely regarded as a powerful tool for improving battery performance, the environmental impact that can be brought about by its production and use cannot be ignored. In the process of large-scale production and disposal of GQDs, harmful chemical byproducts may be created, which can adversely affect the environment [13-15].
In the future, it is expected to see more research focused on developing advanced GQDs synthesis techniques to better control the properties of this material. This may include developing new chemical and physical methods to precisely control the size, shape, and chemistry of GQDs to meet specific application needs. Another interesting future research direction is to explore the potential synergies of GQDs with other materials. Combining GQDs with other conductive or semiconductor materials, for example, could yield new or better properties, which would open up new possibilities for improving the performance of zinc-ion batteries. To fully exploit the potential of GQDs to improve the performance of zinc-ion batteries, one needs to gain a deeper understanding of the interaction between GQDs and zinc ions. Further research is needed to uncover the underlying principles and mechanisms of these processes. After solving the scalability and stability problems, the commercial application of GQDs in zinc-ion batteries becomes possible. Their excellent properties, such as high energy storage and efficient charge and discharge, make GQDS-based zinc-ion batteries expected to play an important role in the future of electricity storage. As part of responsible technology development, one needs to conduct a comprehensive life cycle analysis and environmental impact assessment of the application of GQDs in zinc-ion batteries. This will help to understand the full impact of this technology, including environmental impacts at the production, use and disposal stages. This will help to develop effective policies and strategies to ensure that this promising technology develops in a way that is both environmentally and socially sustainable.
6. Conclusion
To sum up, the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries is reviewed, and its future development trend is discussed in depth. Because of its rich raw material resources, excellent electrochemical performance, environmental protection and high safety characteristics, zinc batteries have gradually become an important candidate for the next generation of efficient energy storage devices. However, zinc batteries still have some challenges, such as irreversible zinc expansion and battery overcharge and over discharge performance issues. Quantum dots, as a new type of nanomaterial, provide a new way to solve the problem of zinc batteries with their unique photoelectric properties, adjustable energy levels and size effects. This study explores in depth three specific applications of quantum dots in improving energy storage and increasing charge and discharge rates of zinc batteries. However, how to combine quantum dots with zinc batteries more effectively, and how to optimize and improve the application effect of quantum dots in zinc batteries are still important challenges in current research. Image quantum dots also face a number of challenges, including stability, consistency, and cost issues. However, with the continuous development of nanotechnology and materials science, as well as the in-depth understanding of the properties of quantum dots, people are full of expectations for the prospect of using quantum dots to improve the performance of zinc batteries. In general, although the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries still faces some challenges, with the continuous progress of scientific research technology and our further understanding of these issues, researchers have reason to believe that quantum dots will play an increasing role in the design and preparation of zinc batteries in the future. In the future, researchers may look for new quantum dot materials and synthesis techniques to further improve the performance of zinc batteries. In addition, with the expansion of research on the application of quantum dots in zinc batteries, it is expected to find more new applications in the design and preparation of zinc batteries in the future to better cope with the growing energy problems.
References
[1]. Alivisatos A P 1996 Science vol 271(5251) pp 933–937.
[2]. Basov D, Averitt R D and Hsieh D 2017 Nature Materials vol 16(11) pp 1077–1088.
[3]. Bera D, Qian L, Tseng T and Holloway P H 2010 Materials vol 3(4) pp 2260–2345.
[4]. Gao X, Wu H, Su C et al. 2023 Energy and Environmental Science vol 16(4) pp 1364–1383.
[5]. Han C, Yan M, Mai L et al. 2013 Nano Energy vol 2(5) pp 916–922.
[6]. Zhang H, Li S, Xu L et al. 2022 Advanced Energy Materials vol 12(26) p 2200665.
[7]. Kathirgamanathan P, Bushby L M, Kumaraverl M, Ravichandran S and Surendrakumar S 2015 IEEE/OSA Journal of Display Technology vol 11(5) pp 480–493.
[8]. Mboukam J, Tchokonté M T, Bashir A et al. 2020 Journal of Alloys and Compounds vol 814 p 152228.
[9]. Michalet X, Pinaud F, Bentolila L A, et al. 2005 Science vol 307(5709) pp 538–544.
[10]. Murray C D, Norris D G and Bawendi M G 1993 Journal of the American Chemical Society vol 115(19) pp 8706–8715.
[11]. Wang M, Fang J, Hu L, Lai Y and Liu Z 2017 International Journal of Hydrogen Energy vol 42(33) pp 21305–21310.
[12]. Wang M, Fang Z, Zhang K et al. 2016 Nanoscale vol 8(22) pp 11398–11402.
[13]. Wang N, Wan H, Duan J 2021 Materials Today Advances vol 11 p 100149.
[14]. Xie R, Rutherford M and Peng X 2009 Journal of the American Chemical Society vol 131(15) pp 5691–5697.
[15]. Xie X, Li J, Xing Z et al. 2022 National Science Review vol 10 p 3.
Cite this article
He,S. (2023). Principle and applications of quantum dots in zinc battery. Applied and Computational Engineering,26,50-55.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Alivisatos A P 1996 Science vol 271(5251) pp 933–937.
[2]. Basov D, Averitt R D and Hsieh D 2017 Nature Materials vol 16(11) pp 1077–1088.
[3]. Bera D, Qian L, Tseng T and Holloway P H 2010 Materials vol 3(4) pp 2260–2345.
[4]. Gao X, Wu H, Su C et al. 2023 Energy and Environmental Science vol 16(4) pp 1364–1383.
[5]. Han C, Yan M, Mai L et al. 2013 Nano Energy vol 2(5) pp 916–922.
[6]. Zhang H, Li S, Xu L et al. 2022 Advanced Energy Materials vol 12(26) p 2200665.
[7]. Kathirgamanathan P, Bushby L M, Kumaraverl M, Ravichandran S and Surendrakumar S 2015 IEEE/OSA Journal of Display Technology vol 11(5) pp 480–493.
[8]. Mboukam J, Tchokonté M T, Bashir A et al. 2020 Journal of Alloys and Compounds vol 814 p 152228.
[9]. Michalet X, Pinaud F, Bentolila L A, et al. 2005 Science vol 307(5709) pp 538–544.
[10]. Murray C D, Norris D G and Bawendi M G 1993 Journal of the American Chemical Society vol 115(19) pp 8706–8715.
[11]. Wang M, Fang J, Hu L, Lai Y and Liu Z 2017 International Journal of Hydrogen Energy vol 42(33) pp 21305–21310.
[12]. Wang M, Fang Z, Zhang K et al. 2016 Nanoscale vol 8(22) pp 11398–11402.
[13]. Wang N, Wan H, Duan J 2021 Materials Today Advances vol 11 p 100149.
[14]. Xie R, Rutherford M and Peng X 2009 Journal of the American Chemical Society vol 131(15) pp 5691–5697.
[15]. Xie X, Li J, Xing Z et al. 2022 National Science Review vol 10 p 3.









