

Volume 174
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-CDS 2025 Symposium: Data Visualization Methods for Evaluation
The advent of multimedia technology has precipitated a paradigm shift in the realm of human-computer interaction and affective computing, thus rendering multimodal emotion recognition a pivotal domain. However, the issue of modal absence, resulting from equipment failure or environmental interference in practical applications, significantly impacts the accuracy of emotion recognition. The objective of this paper is to analyse multimodal emotion recognition methods oriented to modal absence. The focus is on comparing and analysing the advantages and disadvantages of techniques such as generative class and joint representation class. Experimental findings demonstrate the efficacy of these methods in surpassing the conventional baseline on diverse datasets, including IEMOCAP, CMU-MOSI, and others. Notably, CIF-MMIN enhances the mean accuracy by 0.92% in missing conditions while concurrently reducing the UniMF parameter by 30%, thus preserving the SOTA performance. Key challenges currently being faced by researchers in the field of multimodal emotion recognition for modal absence include cross-modal dependencies and semantic consistency, model generalisation ability, and dynamic scene adaptation. These challenges may be addressed in the future through the development of a lightweight solution that does not require full-modal pre-training, and by combining comparative learning with generative modelling to enhance semantic fidelity. The present paper provides both theoretical support and practical guidance for the development of a highly robust and efficient emotion recognition system.

 View pdf
View pdf


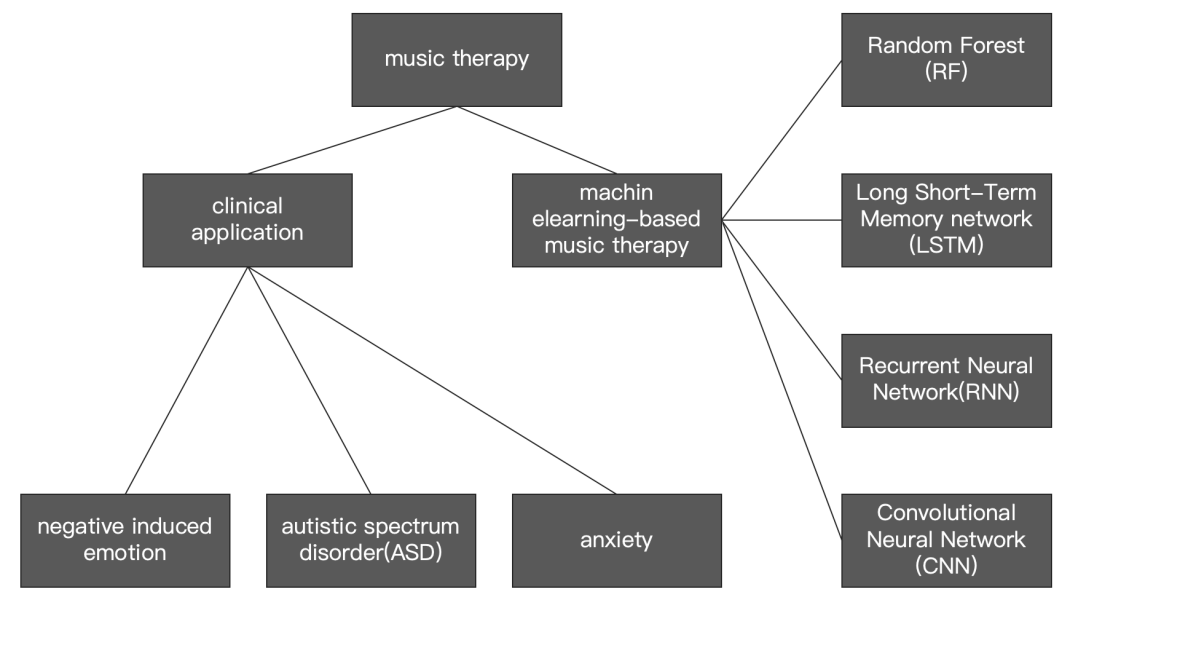
Due to its non-pharmacological nature and low cost, music therapy has gained increasing attention in the fields of medicine and mental health and has been applied in the treatment of various diseases. However, traditional music therapy is limited by the lack of standardized treatment duration and frequency, as well as its inability to meet individual patient needs, hindering further development and broader application. This paper reviews relevant studies, highlighting the therapeutic effects of current music therapy methods on various diseases, and explores the application and efficacy of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies such as Random Forest (RF), Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTM), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) in supporting music therapy. The results show that music therapy can help improve patients’ negative emotions and alleviate symptoms, while AI technologies can enhance and optimize traditional music therapy in areas such as music selection and treatment plan formulation, leading to more personalized and effective outcomes. In conclusion, music therapy demonstrates potential in clinical applications, and integrating AI technologies may offer more individualized and effective treatment plans. Future research and practice in this area should be further strengthened.

 View pdf
View pdf


Social media algorithms, as the invisible architects of user decision-making in the digital age, construct a new paradigm of human-computer interaction through behavior prediction and content curation. Using a combination of computational behavioral analysis and psychological experiments, this study systematically reveals the dual effects of algorithmic recommendation systems between enhancing user engagement and eroding mental health. Data analysis showed that the engagement prioritization mechanism of platforms such as Instagram increased the exposure of negative emotional content by 23%, leading to a significant decrease in self-esteem levels of adolescent users (β = -0.41, p < 0.05); and the personalized recommendation of TikTok resulted in a strong correlation between adolescent anxiety symptoms and eating disorder behaviors (r = 0.57, p < 0.01). The study innovatively constructed a causal mapping model between neurocognitive indicators and algorithmic feature vectors, and found that the algorithmic black box induced 19% of users to have elevated cortisol levels through a dopamine feedback loop, resulting in a pattern of addiction-like behavior. The experiment proves that the introduction of dynamic transparency index and digital nutrition labeling can reduce anxiety symptoms by 17%, but it needs to be coupled with digital literacy education to achieve a sustainable improvement in the behavioral pattern. The conclusion is that the platform economy needs to establish a new balance between technological efficiency and ethical responsibility, and build a third-generation governance paradigm to safeguard the spiritual sovereignty of digital citizens through interpretable algorithmic architectures and preventive regulatory tools. The study provides empirical benchmarks and transformational paths for solving the “surveillance capitalism-humanism” dilemma.

 View pdf
View pdf


Emotion recognition technology has been widely used in human-computer interaction, medical health and other fields. However, in practical applications, emotion datasets often have class imbalance problems, which lead to the model being seriously biased towards the majority class, significantly reducing the recognition accuracy and reliability of minority emotion classes. This paper focuses on comparing and analyzing methods such as ESC-GAN generative data augmentation technology, DER-GCN dialogue and event relationship perception graph model, and MultiEMO multimodal fusion framework to solve the problem of imbalanced emotion recognition categories, and explores the innovations and limitations in multiple scenarios. These methods compensate for minority emotions from different angles: for example, MultiEMO significantly improves the ability to classify minority emotions through cross-modal attention mechanism and weighted contrast loss, which can not only be applied to detect the psychological emotions of patients in the medical health field, but also help to provide support for fine-grained emotion classification in security scenarios. Experimental results show that these solutions significantly improve the accuracy and F1 value of emotion recognition, especially in extremely unbalanced categories. This paper provides a systematic reference for the selection of technology for high-value scenarios such as medical monitoring and intelligent security, promotes the interdisciplinary collaborative development in the field of emotional computing, and accelerates the application transformation of this technology in practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


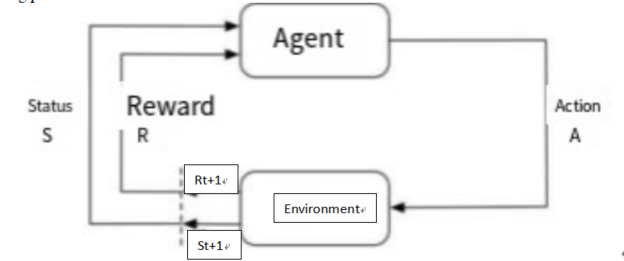
As a typical sequential decision-making and gaming problem, board games have the complexity of large state space and strong dynamic confrontation, however, traditional methods have many limitations in dealing with them, so they need to be based on reinforcement learning to achieve strategy optimization by virtue of data-driven. Reinforcement learning can promote the realization of AI decision-making ability from rule-dependent to data-driven leap, and show significant advantages in game AI. This paper systematically sorts out the core algorithms of reinforcement learning in board games, comparatively analyzes their technical characteristics, applicable scenarios, advantages and disadvantages, discusses the current technical bottlenecks and ethical challenges, and look forward to the future development direction. This paper concludes that reinforcement learning is effective in board games, which not only helps AIs such as AlphaGo and Libratus to surpass the human level in Go, Texas Hold'em and other scenarios, but also forms the transition from “model-dependent” to “data-driven”, From “model-dependent” to “data-driven”, and from “single-intelligence” to “multi-intelligence”, it has also formed a technological evolution vein. At the same time, reinforcement learning has been breaking through in processing high-dimensional states, complex reward functions, etc., and has shown the potential of generalization in the fields of education, healthcare, etc. [1]. This paper can provide theoretical references and practical guidance for subsequent AI research on board games, as well as a universal methodology for complex decision-making problems.

 View pdf
View pdf


As technology advances and living standards improve, people's awareness of vital signs monitoring is gradually increasing. Meanwhile, the potential of wireless sensing technology in this field has become increasingly evident. Wireless sensing technology can efficiently monitor the health status of individuals by analyzing changes in wireless signals. This article highlights four typical wireless sensing vital signs monitoring technologies. By employing methods such as Fresnel zone modeling, intelligent reflective surface (IRS) optimization, and a multi-module system framework, these technologies are applied practically. The article concludes that the RSSI model has high accuracy for single-person detection in fixed scenarios but is sensitive to the environment and location. The CSI combined with the IRS model enhances robustness through dynamic beamforming, and improves multi-user separation accuracy, but comes with higher hardware costs. The article aims to deepen the understanding of wireless sensing vital signs monitoring and to provide theoretical support and technical analysis for the advancement of wireless sensing in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


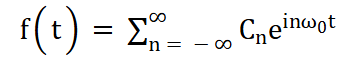
In this paper, we take a closer look at Stirling’s formula, a method used to estimate factorials, particularly when nnn is large. Starting with its historical background, we then give a derivation using the Gamma function and examine how the formula behaves asymptotically. While it's a classic result in mathematics, we also discuss where it shows up in real-world problems—like signal processing, rubber-based materials, and even brain imaging. The way it links with Fourier transforms of the Gamma function shows how useful it is for interpreting patterns like power-law decay and frequency changes in signals.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, deep learning has demonstrated revolutionary impacts in medical image analysis due to its powerful feature learning and pattern recognition capabilities. This paper systematically reviews advances in core tasks and methodologies for medical image segmentation and classification. For segmentation tasks, this paper discusses how Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN) laid the foundation for pixel-level prediction, while their variants, such as the DeepLab series, optimized lesion segmentation accuracy through atrous convolution and multi-scale feature fusion. This research also covers U-Net and its 3D extensions (3D U-Net, V-Net), which significantly improved boundary consistency in organ segmentation by integrating skip connections and residual learning. Furthermore, this review examines Generative Adversarial Networks (SegAN, SCAN) and how they effectively addressed data scarcity and class imbalance through adversarial training. For classification tasks, this paper highlights classical convolutional neural networks like AlexNet, VGGNet, and ResNet, which achieved a paradigm shift from manual feature engineering to end-to-end learning via hierarchical feature abstraction and residual connections. Combined with transfer learning and multi-scale pooling strategies, these models substantially enhanced disease diagnosis accuracy and generalization. This review concludes that these technological breakthroughs have driven the transition of medical image analysis from traditional manual interpretation to intelligent, precise solutions, providing efficient and reliable support for clinical decision-making.

 View pdf
View pdf


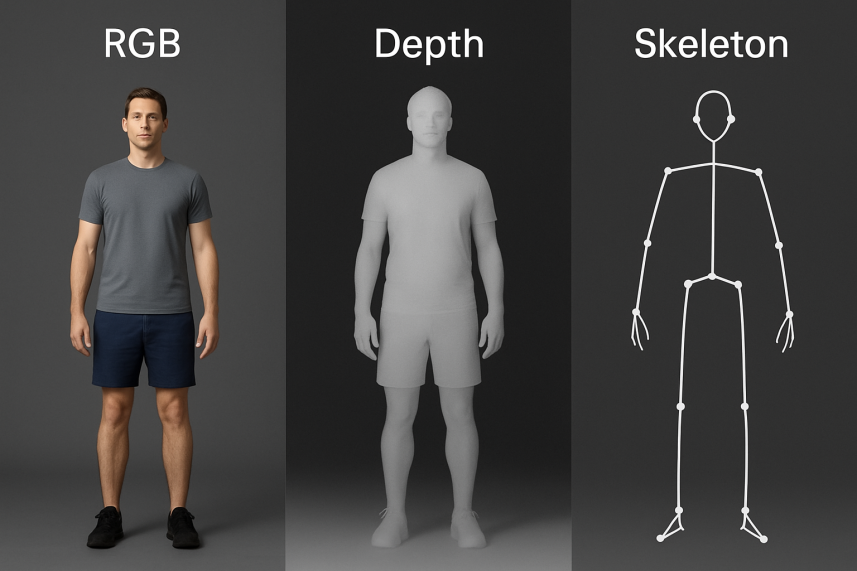
In complex real environments, traditional human behavior recognition methods are easily affected by factors such as lighting changes, occlusion, and background interference, resulting in incomplete perception information and insufficient robustness, making it difficult to meet the stable recognition requirements in scenarios such as intelligent security and medical monitoring. Multimodal perception mechanisms can achieve multidimensional modeling and feature complementarity of behavior information by fusing multi-source perception modalities such as RGB, depth, and skeleton, and have attracted significant research attention in recent years. This paper takes "perception modality" as the core of analysis, systematically sorts out the mainstream perception data types in multimodal behavior recognition, analyzes the advantages and limitations of RGB, Depth, and Skeleton modalities, and summarizes their complementary mechanisms and typical application methods in fusion combinations. This study provides theoretical support for the modality selection and fusion strategy design of behavior recognition systems from the perspective of perception modality and has important research and application value.

 View pdf
View pdf


Facial Expression Recognition (FER) holds extensive application value in fields such as human-computer interaction, intelligent security, and affective computing. However, it also faces challenges from complex conditions like illumination variations, occlusions, and head pose deviations, which cause significant performance degradation in traditional methods. This paper systematically analyzes recent advances in FER technologies addressing these issues and explores the application and innovation of deep learning methods in this domain. The analysis focuses on the following research directions: (1) Enhancement of recognition rate and robustness under illumination variations. Improved models incorporating transfer learning, activation function optimization, and anti-aliasing techniques have significantly boosted recognition accuracy. Approaches such as self-supervised learning and multi-feature aggregation demonstrate strong robustness and adaptability. (2) Feature compensation in occluded scenarios. Effective representation and facial feature-based methods are employed to restore occluded regions, improving recognition efficiency while fully leveraging the spatial structure of occlusions. This enables better representation and reconstruction of original samples. (3) Multi-pose facial expression recognition. By utilizing 3D deformable models for pose estimation and designing pose-invariant feature extraction networks, the challenges of expression recognition under large-angle head rotations are effectively addressed. This paper outlines the limitations of existing approaches and provides an outlook on potential future application scenarios and directions for technological breakthroughs.

 View pdf
View pdf




