1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Motivation
Blockchain technology a system without centralized control, employing a distributed record of transactions to enable all participants to collectively maintain a single reliable database. Regarding cross-border payments, traditional methods often suffer from prolonged processing times, high costs, and reliance on multiple intermediaries for fund circulation, resulting in security vulnerabilities. However, thanks to the underlying technology of blockchain's data structure and encrypted transaction information, the security of cross-border payments is significantly bolstered. Leveraging blockchain for cross-border payments enhances transparency and ensures immutability, facilitating open and secure cross-border fund circulation. Furthermore, blockchain technology has given rise to digital currencies, addressing a market gap and providing innovative solutions for financial transactions.
As blockchain technology advances, its application aids in achieving integrated financial supervision platforms for enterprises, streamlining financial information flow, reducing financial costs, and mitigating financial risks. The transparency of blockchain-based financial information enables public disclosure of financial work, thereby avoiding risks associated with relevant personnel.
This research explores the advantages of blockchain technology in the areas of Cross-Border Payments, Digital Currencies, and Financial Risks as well as how can people use blockchain technology as well as addressing the risks associated with payments made across borders, digital currencies, and financial transactions using blockchain-based technology.
1.2. Literature Review
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force in the financial sector, providing novel solutions to traditional challenges in cross-border payments, financial risk management and digital currencies. This review evaluates the current status of blockchain research, points out the shortcomings of existing literature, and proposes avenues for future investigation. Blockchain technology has had a significant impact on cross-border payments, with the potential to improve efficiency, security, and reduce costs.
The latest studies on cross-border transactions have primarily concentrated on the implementation of blockchain-based technologies in payments across borders and investigating the risks associated with cross-border e-commerce payments utilizing blockchain technologies. For example, Li and Shahzadi discussed the hierarchical structure and functional modules of a blockchain-based cross-border e-commerce payment platform in a payment application framework [1,2]; Ding mainly analyzed blockchain's risk mitigation capabilities in cross-border e-commerce payments [3]. Recent research has mainly focused on the impact of blockchain technology on cross-border e-commerce payments, with little attention paid to the impact of blockchain technology on financial institutions in cross-border payments. This article will investigate how the blockchain applications in cross-border payments by financial institutions reduces the risks of cross-border payments, and what benefits it brings to cross-border payments by financial institutions.
Research on blockchain's role in digital currency development has been extensive. Zhang and Huang and Liu et al. analyzed the influence of blockchain technology on the development of central bank digital currencies and explored the functional and non-functional requirements of these currencies [4,5]. Faturahman et al. explored the utilization of blockchain technology in cryptocurrencies [6]. According to Bhaskar et al., Six of the eight reviews that were available were mainly technical in nature and dealt with financial technology, blockchain, and digital currencies [7]. As a supplement to the research on digital currencies using blockchain technology, the main goal of the article is to examine how blockchain technology has affected the evolution of Bitcoin.
The utilization of blockchain technology for the purpose of mitigating financial risks has always been a topic of increasing concern. Sun et al. analyzed the mechanism by which blockchain technology can reduce financing risks in supply chain finance [8]. However, their analysis only uses evolutionary game methods and focuses on accounts receivable factoring business, lacking an analysis of the entire financial risk management. To overcome these gaps, this article tends to analyze the "blockchain + financial management" model to further verify how blockchain technology reduces financial risks and what benefits enterprises can gain from the "blockchain + financial management" model.
1.3. Research Content
In terms of cross-border payments, this article focuses on studying how blockchain technology can shift from traditional centralized banking systems to decentralized, transparent, and secure networks, thereby redefining the infrastructure of cross-border payments. This study will explore the transition from relying on intermediary financial institutions to a decentralized blockchain architecture, emphasizing reducing transaction costs, minimizing fraud, improving transaction speed and transparency. In terms of digital currencies, this paper concentrates on the role of the blockchain technology in the emergence and popularization of digital currencies. Specifically, it examines how blockchain technology has aided in the creation, issuance, and acceptance of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. This section will delve into how the inherent characteristics of blockchain—decentralization, immutability, and transparency—make digital currencies an important trend that challenges traditional financial and monetary systems. In terms of risk management, this article will analyze how to integrate blockchain technology into financial management processes to reduce various financial risks, including investment risks, operational risks, and capital management risks. The focus of the research is on the potential of blockchain in enhancing transparency, improving financial reporting accuracy, simplifying compliance and risk management processes, thereby providing a safer and more efficient framework for financial businesses.
Comparative analysis between traditional payment systems and blockchain payment systems: Conduct a comparative analysis to highlight the differences in efficiency, security, and cost between traditional payment systems and blockchain-based alternative systems. This includes discussing the limitations of the current system and how blockchain can address these issues. Assessment of the implications of digital currency on traditional financial systems: Using relevant data to evaluate the influence of the technology of blockchain on digital currencies, especially Bitcoin, with a focus on the development trends of Bitcoin in the past decade and predicting the potential for its further development. Model analysis of blockchain in financial risk management: By analyzing the financial risk management model of blockchain technology, we demonstrate the effectiveness of blockchain in reducing specific financial risks within enterprises. This includes delicacies in the financial industry and studies on the implementation of blockchain technology to enhance financial services.
2. Blockchain Technology Ensures Security for Cross-Border Payments
In the past, cross-border payments were primarily facilitated by banks utilizing centralized counterparties operating on specific internet platforms. Centralized payment is used for conventional cross-border payments. Intermediaries require information from customers, including account details; intermediaries use this information to process withdrawals and remittances [9]. However, assessing the reliability of intermediary institutions and the potential risk of customer information leakage to these intermediaries proved challenging. Consequently, to mitigate these risks effectively, banks were compelled to establish sophisticated payment systems for counterpart banks involved in transactions. Additionally, it became necessary to create independent reserve accounts for all payment systems. Please refer to Figure 1 for a detailed illustration of traditional payment methods.
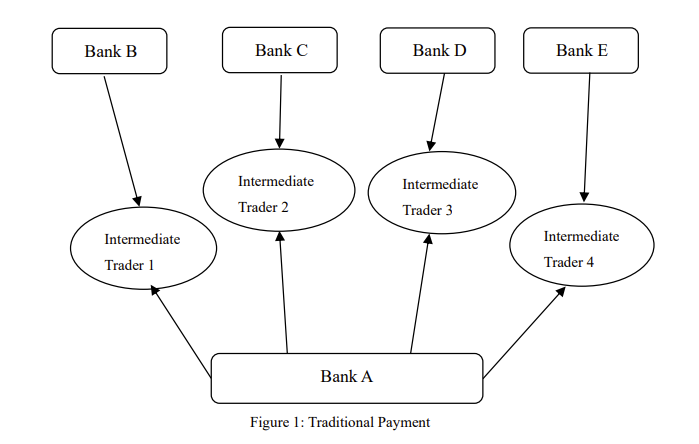
Figure 1: Tradition payment
In traditional online payment systems, the security of third-party financial institutions' server databases, crucial for managing the general ledger, is predominantly maintained through manual oversight. However, if vulnerabilities in server database management are exploited by hackers or if server database failures occur due to physical reasons, the financial security of the entire payment system may be compromised, posing significant risks to user transactions and data integrity.
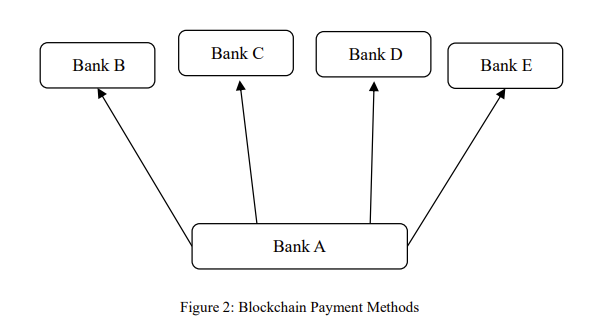
Figure 2: Blockchain Payment Methods
Figure 2 illustrates the blockchain payment methods. In the blockchain payment system, banks primarily operate on private blockchains, allowing for efficient currency transactions without the need for third-party banks. Consequently, this approach eliminates the requirement to store capital funds with central counterparties, enabling banks to allocate more resources to internal projects. Within blockchain-based payment platforms, each bank only requires one reserve account to establish a network-wide payment structure. This payment method bypasses the intermediary bank process, leading not only to reduced overall costs but also to enhanced transaction speed and efficiency.
As a result of the distributed ledger management facilitated by blockchain technology, each node maintains a complete ledger set. This decentralized architecture ensures that the failure of any single replica does not jeopardize the security of transactions between other nodes in the system. Consequently, this robust infrastructure markedly elevates system security in the context of cross-border payment scenarios.
Using blockchain technology for cross-border transactions offers numerous benefits. Decentralized systems, tamper-proofing, tracking, and reliability are features of the blockchain [10]. The decentralized nature of blockchain processing eliminates the need for third-party institutions, enabling more efficient transaction completion between involved parties and subsequently reducing overall transaction costs. Furthermore, transaction information recorded on the blockchain is immutable and irreversible. This characteristic ensures the consistency of transaction content with reality, and all participants have access to the details of previous transactions, thereby diminishing information asymmetry between the parties involved. As all participants can access the complete transaction history, any information asymmetry between trading parties is ultimately diminished, enhancing trust and transparency in cross-border transactions.
3. Blockchain Technology Facilitates the Swift Advancement of Digital Currencies
Due to the evolution of blockchain technology, digital currencies have emerged as a significant trend. Digital currency, being a form of cryptocurrency, relies on blockchain technology. The emergence of Bitcoin marks a pivotal milestone in the technological advancement of cryptocurrencies.
Due to its foundation on blockchain technology, the issuance of digital currencies circumvents the traditional binary banking system consisting of central bank-commercial bank base currency-deposit currency. Consequently, a portion of existing digital currencies, such as Bitcoin and Libra, are classified as private digital currencies.
Since the birth of Bitcoin in January 2009, this encrypted digital currency revolution has undergone decades of development, experiencing an explosive growth effect. Figures 3 and 4, based on data from the global cryptocurrency trading platform Coinmarketcap (www.coinmarketcap.com) as of February 2024, illustrate the global Bitcoin market prices and market capitalization:
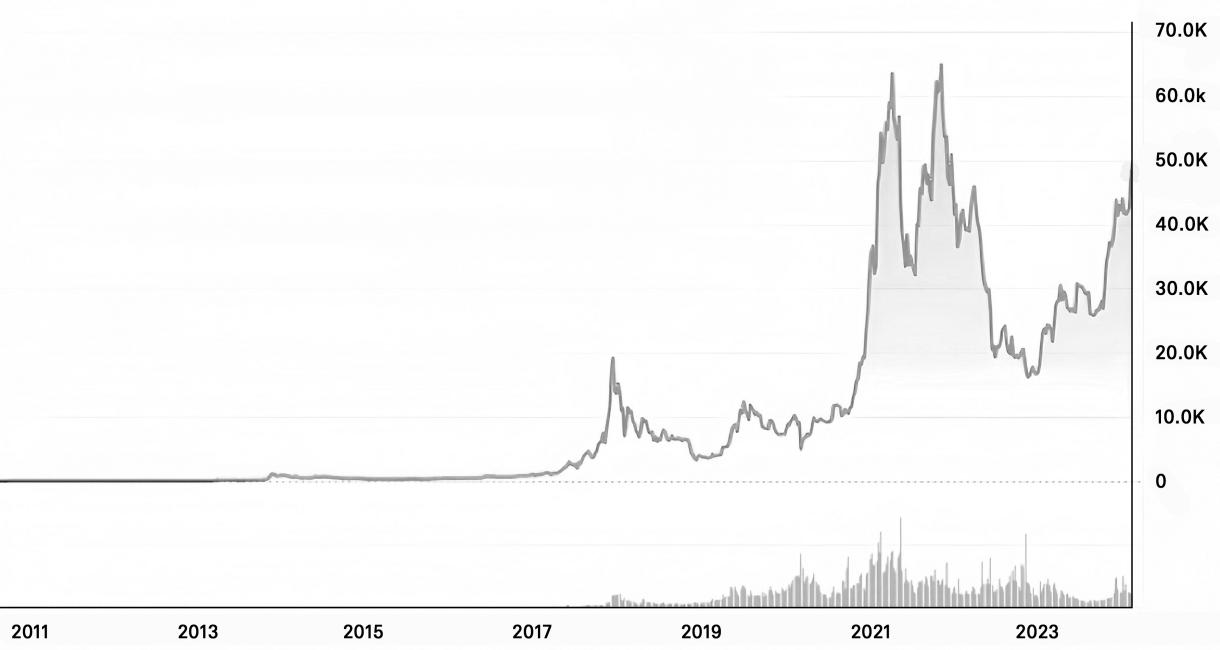
Figure 3: Global Bitcoin Market Prices
Data Source: Coinmarketcap (www.coinmarketcap.com).
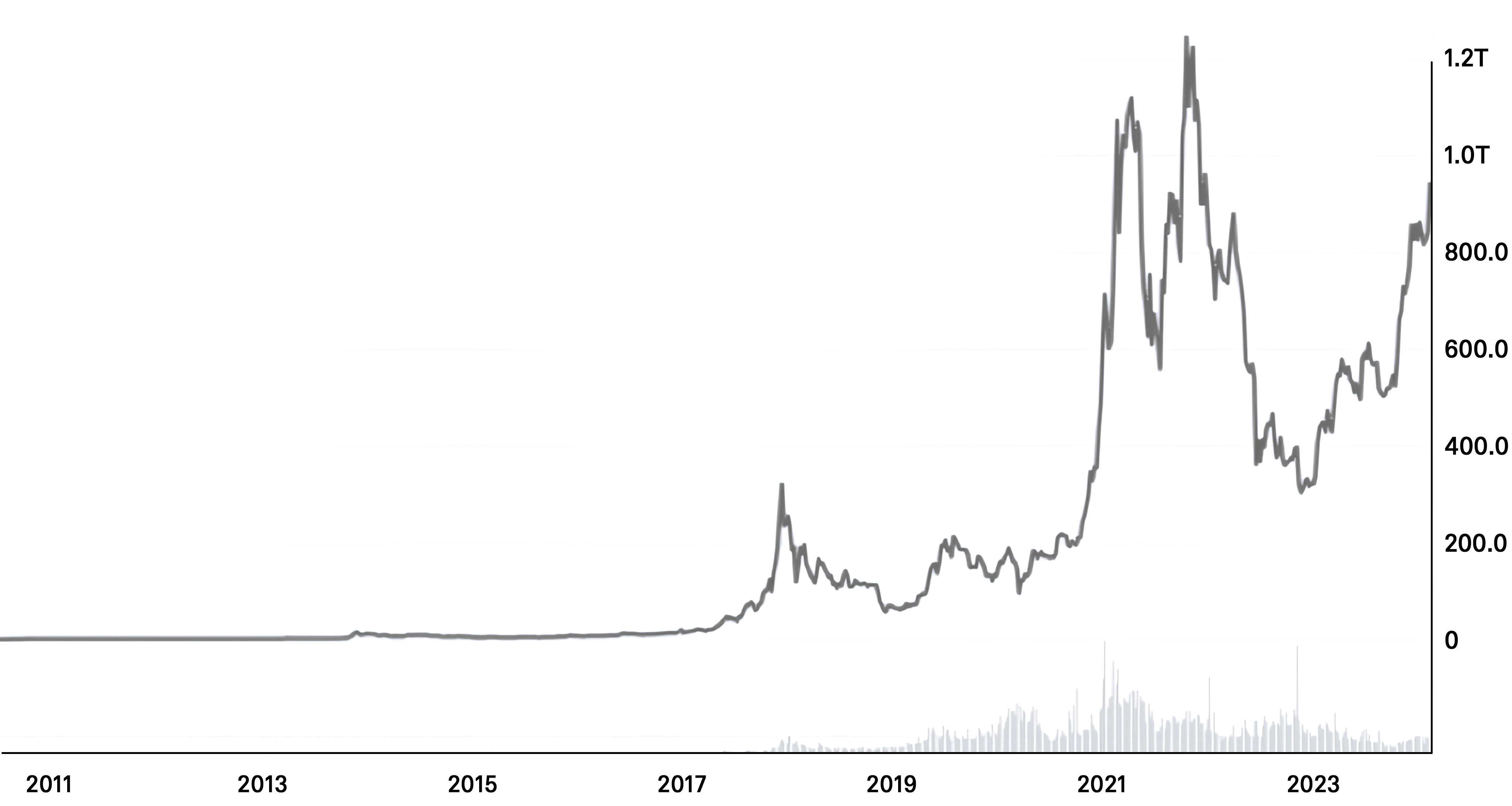
Figure 4: Global Bitcoin Market Value
Data Source: Coinmarketcap (www.coinmarketcap.com).
From Figure 3, it is evident that Bitcoin's market value experienced several significant increases between 2017 and 2024. In the initial years, the market value remained relatively subdued, but there were sharp spikes in late 2017 and early 2021, reaching peak levels. This surge is commonly attributed to heightened public interest, extensive media coverage, and growing acknowledgment among investors regarding the potential value of cryptocurrencies. Subsequently, fluctuations in market value may reflect reactions to various economic events, such as regulatory shifts, technological advancements, and broader macroeconomic influences. Figure 4 provides an overview of Bitcoin's market capitalization, which is calculated by multiplying the total number of Bitcoins in circulation by the prevailing market price per Bitcoin. Considering both figures, the trends in Bitcoin's market price and market value exhibit a close correlation.
Blockchain technology has sparked a monetary revolution, fueling the robust growth of digital currencies. While existing monetary payment and clearing systems, encompassing traditional banking and third-party payment systems, have indeed made notable strides in enhancing currency circulation speed, the advancement of digital currencies serves to further amplify the efficiency of currency circulation. Evidently, blockchain technology not only has the potential to foster the advancement of digital currency but also holds the promise of significantly boosting the circulation speed of currency across markets.
4. Blockchain Technology Enables the Mitigation of Financial Risks.
Financial risk issues commonly encountered in business operations include investment risk, investment operation risk, capital operation risk, among others. These risks exacerbate the financial management challenges for enterprises. Budget management within enterprises is fraught with risks, including the presence of financial personnel during planning operations, inaccurate planning results, lack of corresponding rationality in planning objects, and the potential unwarranted sacrifice of corporate funds. Underestimating the risks involved in preparing financial statements can lead to errors by senior decision-makers within the company, increasing the likelihood of negative impacts on the company's operating activities. Additionally, incomplete understanding of risks by internal management can exacerbate financial risks, hindering the healthy development of the enterprise. Financial risk issues are prevalent in business operations, encompassing various aspects such as investment, investment operation, and capital operation risks.
These challenges pose significant hurdles to effective financial management within enterprises. Budget management, in particular, presents numerous risks, including the involvement of financial personnel in planning processes, inaccuracies in planning outcomes, lack of rationale in planning objectives, and the potential misallocation of corporate funds. Failure to acknowledge the risks associated with financial statement preparation may result in misjudgments by senior executives, heightening the probability of adverse consequences on operational activities. Moreover, inadequate awareness of risks among internal management can exacerbate financial vulnerabilities, impeding the enterprise's sustainable growth trajectory.
The aforementioned financial risk issues can effectively be addressed through the integration of blockchain technology with financial management, thereby mitigating financial management risks. Risk management lowers an organization's expenses, which directly raises the enterprise's financial gains [10]. The amalgamation of blockchain technology with enterprise financial activities represents one of the core technological innovations of the modern era. By harnessing the advantages of blockchain technology and strengthening control over enterprise financial fund project information, the efficiency of company fund utilization can be significantly improved. Comprehensive records of all fund project information enable a more detailed depiction of the current state of fund information, facilitating effective control over the utilization of company funds and ultimately reducing the risk associated with financial fund management. This integration of blockchain technology offers immutable and transparent record-keeping, ensuring trust and accuracy in financial transactions and reducing the possibility of fraud or errors. Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining processes and reducing costs in financial management. Thus, blockchain technology presents a transformative solution to enhance financial risk management in enterprises, offering increased transparency, efficiency, and security in financial operations.
The distributed ledger technology of blockchain offers transparency and traceability [11]. In terms of project risk management, the traceability provided by blockchain technology enables comprehensive tracking of all budget information during budget control implementation. Additionally, during budget control execution, there can be comprehensive collection of all budget information and fine-grained management of budgets based on similar plans. This allows for enhanced budget preparation. The immutability of blockchain technology information facilitates the efficient realization of budget control information, thereby improving project control accuracy, reducing economic losses for enterprises, and enhancing budget execution. Ultimately, this approach leads to increased project control accuracy, decreased economic losses for enterprises, and improved precision in budget execution.
Figure 5 illustrates a graphical representation of the financial risk management model facilitated by blockchain technology.
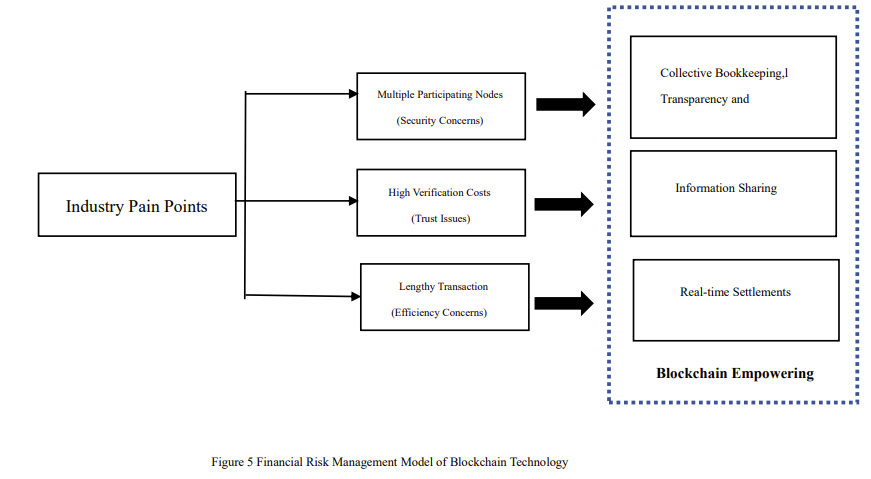
Figure 5: Financial Risk Management Model of Blockchain Technology
5. Suggestions
5.1. Suggestions for Cross-border Payments
Governments and international regulatory agencies should collaborate to create a unified regulatory framework to support blockchain technology in cross-border payments. This will involve standardization of regulations to reduce compliance costs and complexity, thus fostering broader adoption.
Globally, there is a need to develop and implement interoperable standards among different blockchain platforms. This will ensure seamless transactions between different networks, enhancing the effectiveness and scalability of cross-border payments. Governments around the world encourage traditional banking institutions to establish partnerships with blockchain startups. This collaboration can leverage the advantages of two worlds - the innovative potential of blockchain and the existing networks of traditional banks - to improve cross-border payment systems.
5.2. Suggestions for Digital Currency
Governments of various countries should support the creation and adoption of stable coins linked to stable assets such as fiat currency. Stable coins offer the benefits of digital currencies without the high volatility of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, making them more suitable for daily transactions. The government increases public and institutional understanding of digital currency through education programs. Increased awareness of blockchain and digital currencies among the public can foster trust among users and regulatory agencies, thereby promoting the application of digital currency.
5.3. Suggestions on Financial Risks
The government or enterprises can develop a framework to integrate blockchain technology into existing financial systems. These frameworks should address technical challenges, such as scalability and privacy, as well as regulatory issues, facilitating smoother adoption of blockchain technology by financial institutions. Create standardized smart contract templates for financial services to reduce entry barriers for enterprises using blockchain for risk management.
These templates help ensure the compliance and consistency of various transactions. The government should encourage the development of blockchain-based collaborative platforms, enabling financial institutions to securely share risk related information. Such platforms can enhance the collective ability to identify, evaluate, and minimize financial risks.
6. Conclusion
The core argument of this study is that blockchain technology greatly improves the effectiveness, security, and transparency of payments made across borders, promotes the explosive development of digital currencies, and effectively reduces financial risks for enterprises. By transitioning from traditional centralized financial systems to decentralized blockchain platforms, financial institutions stand to benefit from reduced transaction costs, heightened security against fraud, and accelerated transaction processing speeds. In the field of digital currency, blockchain technology facilitates the creation, issuance and acceptance of cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin, challenging the traditional financial system and promoting financial inclusion. In addition, integrating blockchain into financial management processes can provide powerful solutions for reducing various financial risks, improving the accuracy of financial transactions, and ensuring the integrity of financial transactions.
The study's scope is confined to theoretical and potential advantages of blockchain technology, without comprehensively studying the implementation challenges in the real world. These challenges include scalability issues, regulatory uncertainty and gaps in technology adoption across regions and industries. Future research can benefit from empirical data and case studies to better understand the practical challenges and solutions of implementing blockchain technology in these fields. In essence, this study offers a comprehensive analysis of how blockchain technology affects cross-border payments and digital currencies, and financial risk management, making contributions to the academic field. It emphasizes the necessity of understanding blockchain technology to advance the growth of digital currency, providing direction for upcoming studies on the connection between digital currency and blockchain technology. In addition, this study also calls for attention to the importance of integrating blockchain technology into existing financial systems to improve their efficiency and security. Subsequent research can explore practical issues in blockchain implementation based on this study, address identified limitations, and further investigate the transformative potential of blockchain technology in the financial field.
References
[1]. Li, X. H. (2021). Blockchainbased Crossborder Ebusiness Payment Model. 2021 2nd International Conference on ECommerce and Internet Technology (ECIT), 67–73.
[2]. Komal Shahzadi. (2023). Secure and Versatile Decentralized Ledger System Based on Blockchain for P2P Communication. International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications. 14:26-32.
[3]. Ding, Z. (2024). CrossBorder eCommerce Payment Risk Based on Blockchain Underlying Technology. In J. C. Hung, N. Yen, & J. Chang (Eds.), Frontier Computing on Industrial Applications. 2: 38–45.
[4]. Zhang, T., & Huang, Z. (2021). Blockchain and central bank digital currency. ICT Express, 8(2).
[5]. Liu, Z., Hou, W., Liu, Z., & Hou, W. (2023). Central Bank Digital Currency. In Digital Finance: How Innovation Reshapes the Capital Markets (pp. 83–98). Springer Nature Singapore.
[6]. Faturahman, A., Agarwal, V., & Lukita, C. (2021). Blockchain Technology - The Use of Cryptocurrencies In Digital Revolution. IAIC Transactions on Sustainable Digital Innovation (ITSDI), 3(1), 53–59.
[7]. Bhaskar, R., Hunjra, A. I., Bansal, S., & Pandey, D. K. (2022). Central Bank Digital Currencies: Agendas for future research. Research in International Business and Finance, 62, 101737.
[8]. Sun, R., He, D., & Su, H. (2021). Evolutionary Game Analysis of Blockchain Technology Preventing Supply Chain Financial Risks. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(7), 2824–2842.
[9]. Deng, Q. (2020). Application Analysis on Blockchain Technology in Cross-border Payment. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development (ICFIED 2020), 126.
[10]. Su, W. (2022). Blockchain Empowers Chain Enterprises in the Digital Economy to Strengthen Risk Management Research. Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2022, 1–12.
[11]. F. D'Amore, N. Sunny, D. Iruretagoyena, F. Bezzo, and N. Shah. (2019). European supply chains for carbon capture, transport and sequestration, with uncertainties in geological storage capacity: Insights from economic optimization. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 129, 106521.
Cite this article
Jiao,Y. (2024). The Impact of Blockchain Technology: Cross-Border Payments, Digital Currencies, and Financial Risks. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,85,8-17.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li, X. H. (2021). Blockchainbased Crossborder Ebusiness Payment Model. 2021 2nd International Conference on ECommerce and Internet Technology (ECIT), 67–73.
[2]. Komal Shahzadi. (2023). Secure and Versatile Decentralized Ledger System Based on Blockchain for P2P Communication. International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications. 14:26-32.
[3]. Ding, Z. (2024). CrossBorder eCommerce Payment Risk Based on Blockchain Underlying Technology. In J. C. Hung, N. Yen, & J. Chang (Eds.), Frontier Computing on Industrial Applications. 2: 38–45.
[4]. Zhang, T., & Huang, Z. (2021). Blockchain and central bank digital currency. ICT Express, 8(2).
[5]. Liu, Z., Hou, W., Liu, Z., & Hou, W. (2023). Central Bank Digital Currency. In Digital Finance: How Innovation Reshapes the Capital Markets (pp. 83–98). Springer Nature Singapore.
[6]. Faturahman, A., Agarwal, V., & Lukita, C. (2021). Blockchain Technology - The Use of Cryptocurrencies In Digital Revolution. IAIC Transactions on Sustainable Digital Innovation (ITSDI), 3(1), 53–59.
[7]. Bhaskar, R., Hunjra, A. I., Bansal, S., & Pandey, D. K. (2022). Central Bank Digital Currencies: Agendas for future research. Research in International Business and Finance, 62, 101737.
[8]. Sun, R., He, D., & Su, H. (2021). Evolutionary Game Analysis of Blockchain Technology Preventing Supply Chain Financial Risks. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(7), 2824–2842.
[9]. Deng, Q. (2020). Application Analysis on Blockchain Technology in Cross-border Payment. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development (ICFIED 2020), 126.
[10]. Su, W. (2022). Blockchain Empowers Chain Enterprises in the Digital Economy to Strengthen Risk Management Research. Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2022, 1–12.
[11]. F. D'Amore, N. Sunny, D. Iruretagoyena, F. Bezzo, and N. Shah. (2019). European supply chains for carbon capture, transport and sequestration, with uncertainties in geological storage capacity: Insights from economic optimization. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 129, 106521.









