

Volume 233
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Data-Driven Decision Making in Business and Economics
The current film and television industry is thriving, with movies being the most representative form that has always received attention. In the past, public relations in the film industry was limited to hosting premieres and issuing press releases. Nowadays, public relations in the film industry is no longer limited to basic administrative assistance, but has developed into a strategic field. It fundamentally shapes the audience's perception of the movie, promotes word-of-mouth dissemination, and enhances brand value in the long run. Not only that, public relations work starts from the script creation stage and continues even after the movie is released. The PR team not only creates topics. It will also help the production team gain a deeper understanding of the changing trends in audience values, such as focusing on sustainability, diversity, or corporate ethics issues. Then integrate these values into the public relations story. This continuous two-way interaction makes public relations a "dynamic feedback loop" between the film industry and the audience.

 View pdf
View pdf


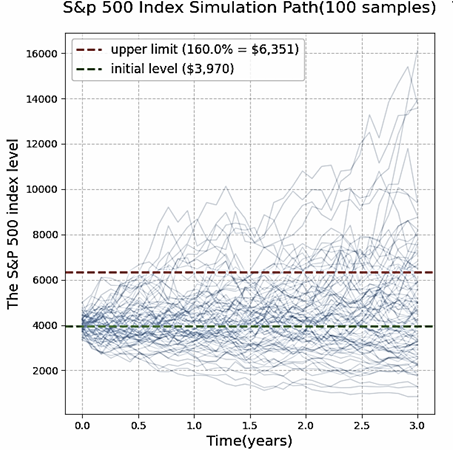
This article aims to address the issues of the guaranteed return realization path, derivative income quantification, and comprehensive risk assessment for the 100% guaranteed return structured notes in US dollars, as well as to fill the current research gap in the academic field regarding the pricing logic and risk-return characteristics of this specific type of product, and to improve the pricing theory system for structured products. The study uses the discounted cash flow (DCF) model to calculate the value of the fixed income hedging layer. It quantifies the return elasticity of the S&P 500-linked options through Monte Carlo simulation and completes the pricing calibration by combining sensitivity tests and comparisons with similar products in the market. The data used are the actual values of the three-year US Treasury bond yield in July 2025 at 3.824%, the annualized volatility of the S&P 500 over the past three years at 15.91%, and the dividend rate at 1.23%. The results show that for a principal of $1 million, $874,200 of low-risk assets are required to ensure the principal is protected. The value of the derivative layer options is $118,600. After deducting a 1% cost, the annualized expected return is 7.81% (in the best scenario, 23.86%), which is in line with the similar products of DBS Bank during the same period, thus verifying the fairness. This research can provide support for the decision-making of cross-border investors, the optimization of issuers' products, and the improvement of the market pricing system.

 View pdf
View pdf


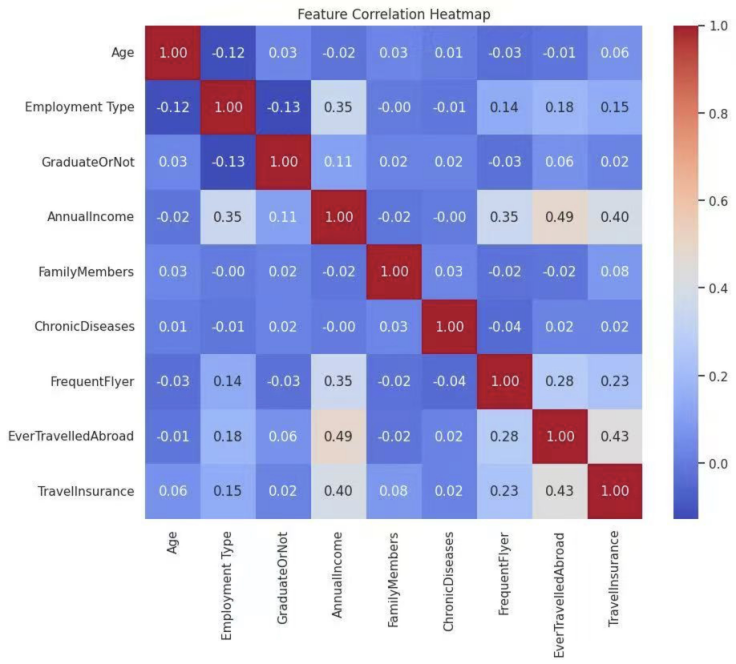
Understanding consumers' purchasing behavior in travel insurance is necessary to segment customers further and maximize targeted marketing for insurance companies. This research intends to develop a predictive classification model to classify those who would purchase travel insurance so that insurers can better utilize their resources and reduce customer acquisition costs. Using a real dataset downloaded from Kaggle, the research aims to apply machine learning models to identify purchasing intention. The research uses some of the classification techniques in the form of Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, and Random Forest, and subsequently with the Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique (SMOTE) and Grid Search for model improvement. The experiment result indicates that the model using Random Forest has the best predictive accuracy. Specifically, the four most influential features that impact the prediction of travel insurance buying are Annual Income, Family Members, Age, and EverTravelledAbroad, respectively. The findings provide valuable information regarding behavioral traits and demographic variables influencing travel insurance consumption behavior. Through the models, insurers can target high-probability customers better and hence make outreach more efficient and effective. The research highlights the advantages of evidence-based approaches towards enabling more strategic and fairer marketing processes in the travel insurance industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


Amidst the rapid development of the global digital economy and the advancement of rural revitalization strategies, this study examines the role of e-commerce livestreaming as an innovative model that integrates digital technology with the rural economy. Using literature review and case analysis methods and drawing on theories from agricultural economics, digital marketing, and rural sociology, the research reveals that in 2023, rural e-commerce livestreaming in China achieved a transaction volume of 586 billion yuan, a year-on-year growth of 65.3%, demonstrating significant advantages in reducing circulation costs, enhancing brand value, and creating employment opportunities. Three main models have emerged—farmer-led, enterprise-led, and government-supported—with practical cases such as Dongfang Zhenxuan and Danling citrus livestreaming validating their effectiveness. However, challenges remain, including insufficient product standardization, a shortage of professional talent (with a gap of 1.2 million people), difficulties in traffic acquisition for small and medium-scale farmers, underdeveloped cold chain logistics (coverage below 35%), inadequate regulation, and intense homogeneous competition. The study concludes by proposing a multi-stakeholder collaborative governance framework involving governments, enterprises, village-level organizations, farmers, and industry associations to promote sustainable development of rural economy and society.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the face of the growing complexity and vulnerability of the e-commerce supply chain, artificial intelligence (AI) is used to improve risk prediction and decision-making greatly. This paper explores how AI-driven solutions have improved demand forecasting, logistics scheduling, and supplier risk management, as well as created new challenges, such as algorithmic bias, overreliance, and data privacy issues. The study also delves into the analysis of benefits and potential risks, supported by recent literature and industry case studies. To tackle these issues, this study offers suggestions about making the best use of AI in this situation, like improving data management, using both people and AI to watch over things, making sure computer stuff is safe from bad people who might want to mess with it, and following rules for being a good friend to AI. As shown in the result, with transparency in data governance and the addition of good technical protection, AI could help with supply chain resiliency and efficiency. The findings show that for these e-commerce businesses to do more than operate well, but actually have sustainable, resilient supply chains, they need to strategically and ethically embrace AI.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of the dual-carbon policy and the rise of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investment, there is still a lack of research on the mechanism by which ESG ratings affect stock price fluctuations. This paper is based on 11,934 observations of A-share stocks from 2019 to 2023. It employs a panel fixed effects model, with the SynTao Green Finance ESG rating as the core explanatory variable and the adjusted stock price fluctuation (VARADJ) as the dependent variable. It controls for enterprise size, financial and governance variables, and conducts an empirical test to examine the relationship between the two. The research has found that ESG ratings are significantly negatively correlated with stock price volatility. In the Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression, the ESG coefficient was -0.134 (without control variables) and -0.051 (with control variables). In the two fixed effects model, it was -0.037 (with industry and year fixed) and -0.024 (with control variables added), all of which passed the significance test (at 1% to 10% levels), indicating that for every 1 unit increase in ESG rating, stock price volatility decreases by 2.4% to 13.4%. The conclusion confirms that ESG performance mitigates abnormal stock price fluctuations by alleviating information asymmetry and conveying signals of sustainable development. It is recommended that enterprises enhance environmental and governance information disclosure to reduce valuation discrepancies, and investors incorporate ESG into the risk assessment framework to optimize asset allocation.

 View pdf
View pdf


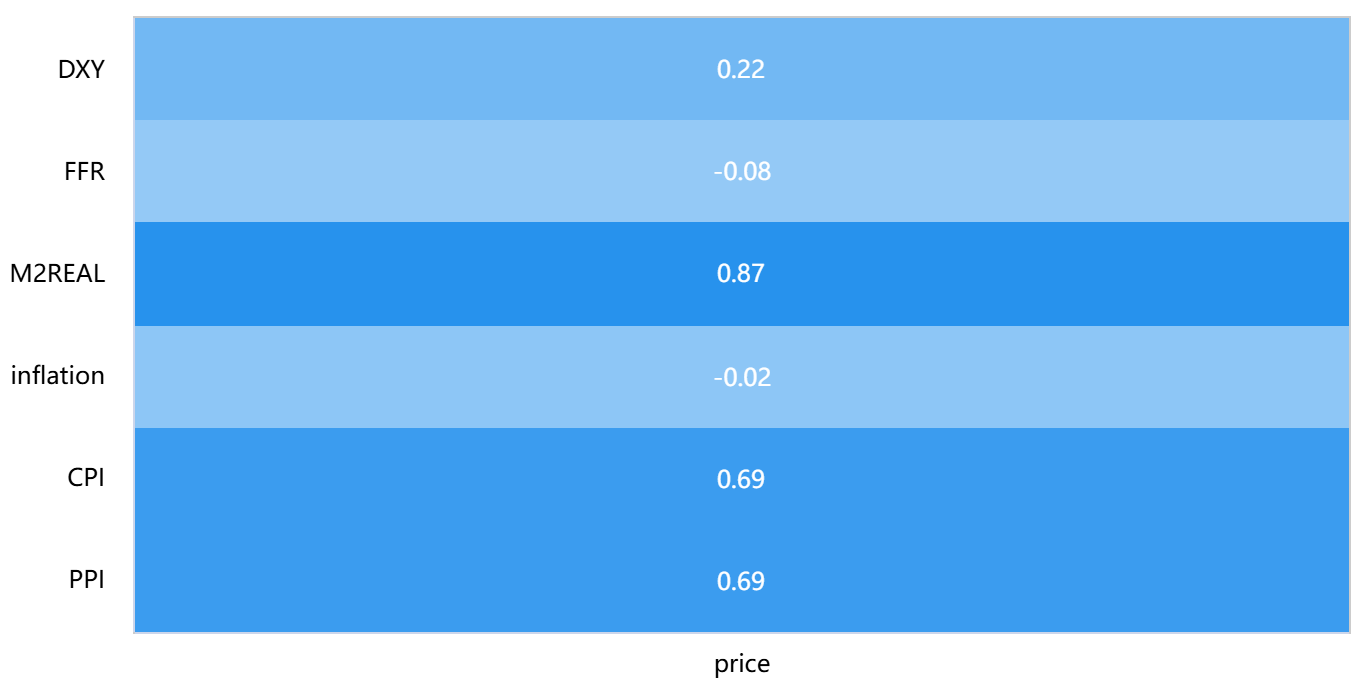
With the upgrading of blockchain technology, cryptocurrency has already become an important financial product. However, due to its unpredictable nature of price volatility, it rarely appears in asset allocation. This article uses the Pearson correlation coefficient and the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model to quantify monetary policy in macro factors, study its time-varying correlation with Bitcoin price fluctuations, and observe whether it can accurately predict cryptocurrency prices through macro variables. In the study, the Pearson correlation coefficient was used to find that M2 money supply, Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), and US dollar index are correlated with Bitcoin price, with a significant correlation with M2 money supply. The prediction performance of the ARIMA model is poor, and the research method still needs improvement. The purpose of this study is to quantify macro monetary policy, reflect the impact of cryptocurrency price fluctuations, and construct a more stable asset framework.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study, based on the theories of gender, the glass ceiling, and role conflict, systematically examines the multi-dimensional challenges faced by Chinese women in the workplace from the perspectives of society, organization, and individual. The research reveals that women not only encounter explicit and implicit gender discrimination in recruitment and promotion, persistent pay gaps, and the "glass ceiling" effect, but also endure the psychological and physical stress caused by the dual role conflict of work and family. These challenges are deeply rooted in the complex interaction of traditional gender cultural norms, structural flaws in enterprise systems, and insufficient policy implementation mechanisms. This paper further constructs a three-level collaborative countermeasure framework of "policy-organization-culture," proposing to break the cycle of gender segregation and discrimination through systematic paths such as improving gender equality legislation and evaluation mechanisms, promoting enterprises to establish transparent promotion and flexible working systems, and facilitating the reshaping of gender concepts in the media and education fields. This study provides an integrated analytical perspective for understanding the formation mechanism of women's workplace challenges and puts forward operational policy suggestions and practical directions for promoting substantive gender equality at the government, enterprise, and social levels.

 View pdf
View pdf


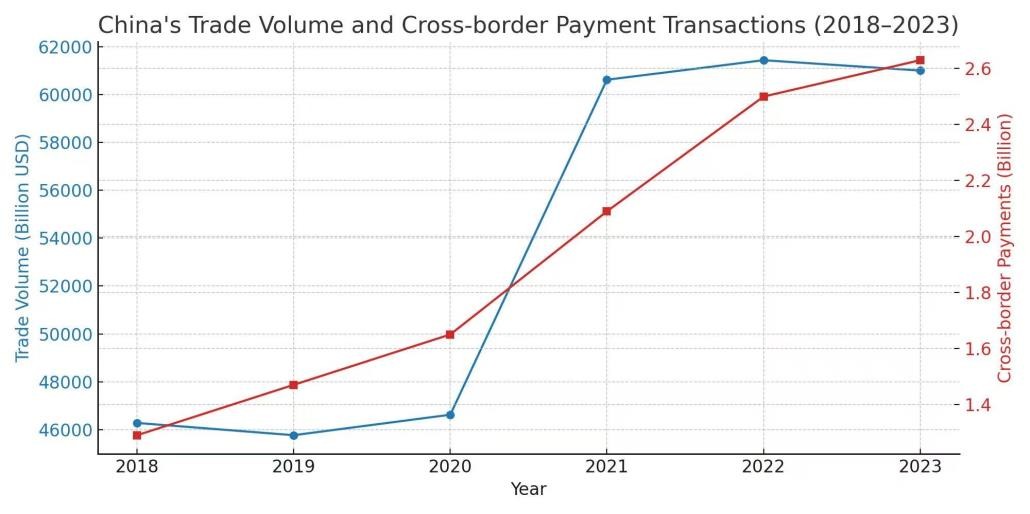
Cross-border digital payment systems have become increasingly pivotal in international trade, with China’s fintech expansion reshaping global commerce—particularly post-COVID-19, as contactless and digital transactions became standardized. This paper examines the role of such systems in China from 2018 to 2023, analyzing their impacts on trade efficiency and structural changes. It explores how fintech, big data, and logistics jointly shape trade dynamics, employing correlation analysis, ordinary least squares (OLS) regression, and structural tests to assess the interlinkages between payment growth, trade expansion, and logistics performance. Findings indicate that while total trade volume and digital payment transactions experienced significant growth, the average trade value per payment declined, reflecting a shift toward small-value, high-frequency transactions. Statistical results confirm that cross-border digital payments exert a significant positive effect on trade volume (correlation coefficient r=0.94, regression coefficient β1=0.82), yet fail to enhance per-transaction efficiency. Additionally, logistics performance exhibits a strong correlation with both digital payments and trade (r=0.88), underscoring its complementary role in trade facilitation. This structural transformation presents distinct challenges and opportunities for SMEs’ global engagement and policymakers’ formulation of financial infrastructure strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper compares three forecasting approaches-autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), multivariate linear regression (MLR), and long short-term memory networks (LSTM)-for daily stock prices of Starbucks (SBUX) and Luckin Coffee (LKNCY). Trading calendars are aligned across tickers, missing observations are forward-filled, and technical indicators are engineered (log returns and lags, SMA/EMA, RSI, and volume change). A chronological split (80% train, 20% test) prevents look-ahead bias. Performance is evaluated using RMSE, MAE, and MAPE; Diebold-Mariano (DM) tests assess pairwise differences in forecast errors. On LKNCY, MLR attains the lowest error (RMSE 0.891; MAPE 2.74%), outperforming a baseline ARIMA (RMSE 7.155) and a univariate LSTM trained on prices with min-max scaling (RMSE 6.849). Results on SBUX show the same ranking. Diebold-Mariano tests show no statistically significant difference between LSTM and ARIMA forecast errors (SBUX: p=0.52; LKNCY: p=0.70). Diagnostics further indicate that, during downtrends, the price-target LSTM drifts toward the lower bound of the training range, a pattern consistent with sensitivity to scaling and distributional shift. To mitigate this issue, a robustness variant is introduced that predicts next-period log-returns using z-score standardization with a multi-layer LSTM. Taken together, the results emphasize the short-horizon strength of simple linear baselines and the central role of target choice, scaling, and evaluation protocol in financial time-series forecasting.

 View pdf
View pdf




