1. Introduction
The coffee industry in China was once inconspicuous but has rapidly developed in recent years. Over the past decade, Chinese coffee consumption has grown at an average rate of 15%, which is much higher than the global growth rate of 2% [1]. However, Chinese enterprises are facing increasing demand uncertainty due to global economic uncertainty. Management decisions on cost structure directly affect future operational risks and profitability [2]. Luckin Coffee has emerged as a significant player in the Chinese coffee industry. After experiencing financial fraud and delisting events, Luckin Coffee can still turn the tide and achieve the first overall transformation from losses to profits in 2022 [3]. The optimization of cost structure has played a key role in the upstream development of Luckin Coffee.
The cost structure of a company refers to the proportion of variable costs to fixed costs in production. It reflects the cost decisions made by the enterprise management. The academic community commonly uses “cost elasticity” to gauge an enterprise's cost structure based on the ratio of variable costs [4]. When variable costs make up a larger proportion of total costs, the speed at which costs change with income is faster, while a higher proportion of fixed costs leads to a slower speed of cost change with income [3]. According to Eldenburg and Kallapur's research [3,4], public hospitals in the United States have chosen a more elastic cost structure to cope with higher income uncertainty caused by changes in pricing rules. So, they believed that increasing demand uncertainty will increase cost structure elasticity. However, Banker et al. conducted empirical research on manufacturing companies in the US and found that managers choose a more rigid cost structure with greater demand uncertainty. They concluded that increasing demand uncertainty reduces cost structure elasticity [3, 4].
When demand uncertainty increases, different industries may have different cost structures, making it difficult to generalize elastic changes in cost structure strategies. And there has been little research on the cost structure and cost elasticity of emerging coffee industry enterprises in China. This article will fill the gap in cost structure analysis in the coffee industry. Aiming to find out the cost elasticity of Luckin Coffee, we investigate the cost composition and proportion of each cost component of Luckin Coffee. Then compare its cost structure horizontally with the cost structure of enterprises in the same industry, inferring the advantages of Luckin Coffee's cost structure. Finally, we use historical data for vertical comparison, study how the cost structure of Luckin coffee changes over time.
Based on the above analysis, we conclude that when demand uncertainty increases, Luckin Coffee will reduce fixed costs, such as store operating costs, to increase its profitability and stability. Luckin Coffee use a high-cost elastic cost structure to adapt to the unpredictable demand environment, which is conducive to better addressing the uncertainty of market demand, and in the end, we also get a better understanding of the high-cost elasticity of cost structure on the development of the entire coffee industry.
2. The Cost Structure of Luckin Coffee
2.1. Components of Cost Structure
The cost structure is a crucial business model component, playing a significant role in enterprise transformation and innovation. According to cost behavior classification, costs can be split into two categories: fixed costs and variable costs. Fixed costs are expenses that are not related to production or sales volume, such as rent or salaries. On the other hand, variable costs are expenses that are directly proportional to production or sales volume, such as raw materials or direct labor.
The cost structure of Luckin Coffee mainly includes material costs, depreciation, store rental and other operating costs, sales and marketing expense, general and management expenses, as well as store preopening and other expenses [5]. Variable costs include material costs, depreciation, sales and marketing expenses, delivery expenses. Fixed costs include store rental and other operating costs, general and management expenses, store preopening and other expenses. As explained in the "Introduction" section, the greater the proportion of variable costs in the total cost, the higher the cost elasticity, whereas the smaller the proportion of fixed costs in the total cost, the lower the cost elasticity. Therefore, to ascertain Luckin Coffee's cost elasticity, a analysis of the proportion of all costs is necessary.
2.2. Proportion of Each Cost Component of Luckin Coffee
Luckin Coffee experienced financial fraud and other turmoil in its first five years, resulting in an overall unfavorable profit for the company since its founding in October 2017. When people generally believe that Luckin Coffee can not be operated for a long time and believe that every cup of Luckin Coffee they drink may be the last one, Luckin Coffee turned a profit in 2022, earning tens of billions in revenue after five years of losses. The key to turning losses into profits is optimizing the proportion of costs, which Luckin Coffee did in 2022. The following is the data and proportion of the main costs of Luckin Coffee in 2022 [6].
As of December 31, 2022, the cost of material in Luckin Coffee was $750.879million, store rental and other operating costs, depreciation, delivery expenses, sales and marketing expenses, general and administrative expenses, store preopening and other expenses are $410.31million, $56.825million, $199.098million, $82.660million, $211.615million, $5.221million, respectively. Accounting for 43.7%, 24.0%, 3.3%, 11.6%, 4.8%, 12.9% and 0.3% of the total cost, respectively.
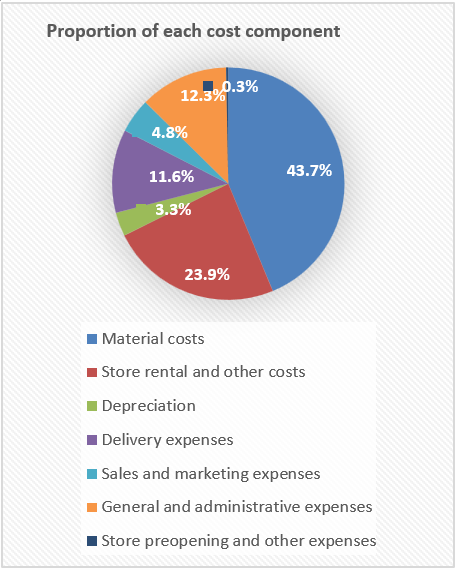
Figure 1: The proportion of each cost component of Luckin Coffee
From Figure 1, it can be seen that in the cost structure of Luckin Coffee in 2022, the proportion of variable costs (material costs, depreciation, sales and marketing expenses, delivery expenses) is about 64%, and the proportion of fixed costs (store rental and other operating costs, general and management expenses, store preopening and other expenses) is about 36%. According to the definition of cost structure, the larger the proportion of variable costs, the greater the cost elasticity. We can infer that Luckin Coffee adopts a cost structure with high-cost elasticity in today's unstable demand environment.
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Cost Structure
2.3.1. Horizontal Analysis: Comparison with Starbucks Coffee
Starbucks Coffee and Luckin Coffee are two major players in China's rapidly growing coffee industry, competing fiercely with each other. This section will compare the main cost indicators of Starbucks Coffee and Lucky Coffee, analyze their cost structure strategies, and infer how they differ in response to unstable demand.
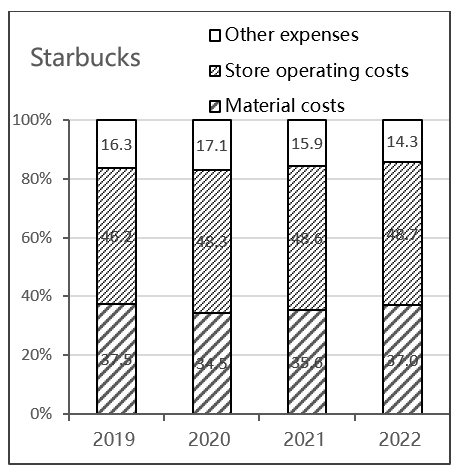
Figure 2: The proportion of main variable costs and main fixed costs of Starbucks coffee
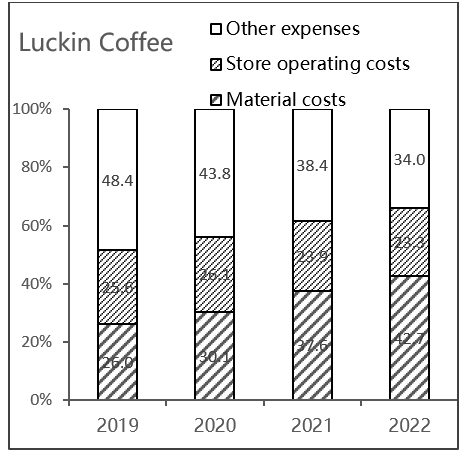
Figure 3: The proportion of main variable costs and main fixed costs of Luckin Coffee
Firstly, based on Figure 2 and Figure 3, it is evident that Starbucks Coffee consistently incurs a significant percentage of store operating expenses, whereas Luckin Coffee has been experiencing a decline in these costs. This disparity in in-store operating costs can be attributed to the distinct positioning of Luckin and Starbucks stores, which is evident in the varying costs of single-store decoration and equipment. The Starbucks stores in China are around 200 square meters in size and are decorated with different themes. The decor is quite elegant, and the average cost of decorating a single store in 2018 was $1.1697 million USD. Luckin Coffee stores are designed for self-pickup, with smaller store areas compared to Starbucks. This eliminates the need for elaborate designs to create a third space. The cost of decorating a single floor is lower, and standardized designs can be replicated quickly.
Secondly, we can also observe that Starbucks Coffee has a higher fixed-cost ratio compared to Luckin Coffee. This suggests that Starbucks Coffee follows a cost structure strategy with low-cost elasticity, particularly when the demand is unstable. On the other hand, Luckin Coffee is cutting down on its store operating expenses, but the percentage of material costs is slowly rising.
Moreover, Luckin Coffee has low operating costs for several reasons, such as utilizing small stores and automated coffee machines, resulting in lower rental and decoration expenses compared to Starbucks' larger stores. Additionally, automated coffee machines also decrease labor costs. Luckin Coffee prioritizes mobile payment and online sales to minimize manual checkout and order processing expenses. By utilizing their mobile apps and online ordering platforms, customers can conveniently book and pay, effectively cutting down on wait times and labor costs.
To sum up, this suggests that during times of uncertain demand, Luckin Coffee is more likely to prioritize increasing cost flexibility and decreasing fixed expenses. On the contrary, Starbucks coffee increases fixed costs and reduces cost elasticity.
2.3.2. Vertical Analysis: Comparison of Historical Data of Luckin Coffee.
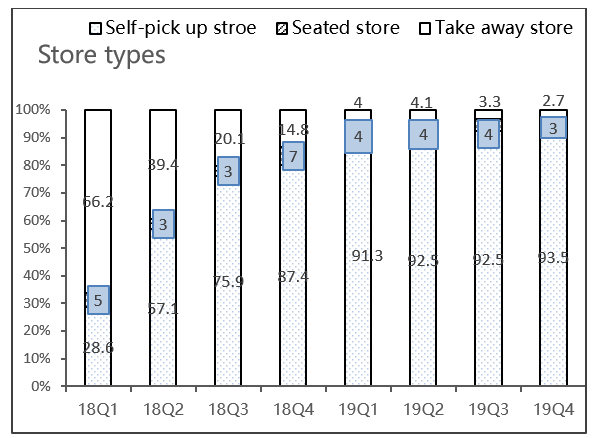
Figure 4: Store types of Luckin Coffee
From Figure 4, it can be seen that Luckin Coffee's physical stores have been consistently categorized as high-performing, comprising over 90% of their stores since Q1 2019. These stores have shown steady growth, increasing from 2163 in Q1 2019 to 3433 in Q3 2019.
In contrast, the number of delivery stores has been steadily decreasing since Q3 2018. However, there was a slight increase in Q3 2019, with the number of delivery stores rising from 99 to 109. Self-pick-up stores are mainly located in office buildings, university campuses, and commercial areas.
Luckin Coffee has been able to expand quickly and efficiently by strategically placing its take away stores in locations that are convenient for its target customers. This approach allows them to save money on rent and decoration costs. They first select locations that are suitable for delivery, quickly establish a delivery store at a low cost, and collect feedback on transaction data. Once they have enough data, they open self-pickup stores in areas with high customer traffic. As the self-pickup stores continue to expand, the delivery stores will eventually be closed.
As delivery stores have closed down and more self-pickup stores have opened up, the number of self-pickup stores has increased. This has resulted in a higher density of stores, which helps ensure that self-pickup stores are conveniently located near customers. Additionally, A pick-up store reduces employee costs and increases cost elasticity.
To sum up, Luckin Coffee has shifted from a delivery-focused store management model to a self-pickup store management model. This transition has led to a consistent decrease in the store's fixed costs, such as in-store leasing and decoration expenses. Meanwhile, variable costs have increased as Luckin Coffee utilizes methods to increase cost elasticity and reduce fixed costs during times of unstable demand.
3. Suggestions for the Coffee Industry with High-cost Elastic Cost Structure
When examining the cost structure of Luckin Coffee in comparison to Starbucks Coffee, it becomes clear that their distinct value propositions and brand positioning result in Luckin Coffee having a significant advantage in terms of labor costs and store operating costs (such as rent and labor expenses). This allows Luckin Coffee to have a more compressed cost structure, giving them a competitive edge. Reducing fixed costs is also one of the necessary conditions for the stable development of the coffee industry. Therefore, the coffee industry can increase cost structure elasticity to cope with uncertain demand.
3.1. Saving Energy and Resources
Coffee industry enterprises can implement measures to conserve energy and resources. One potential way to cut costs is by decreasing the amount of floor space in the store or limiting spending on decorative elements. It can also be achieved by using energy-efficient equipment and lighting systems, optimizing production processes to minimize waste, and encouraging sustainable farming and planting methods to reduce resource consumption and environmental impact.
3.2. Implement Automation and Digital Technology
The implementation of automation and digitization technologies can enhance production efficiency and lower labor costs. An instance of this is utilizing automatic coffee machines and automated production lines, which can lower manual operations and boost production efficiency. Moreover, digital management systems can provide real-time data and analysis to enable enterprises to monitor costs effectively and make necessary adjustments.
Managing human resources effectively can help coffee industry enterprises reduce labor costs. By implementing training and development plans, employee skills and efficiency can be improved, reducing personnel turnover and recruitment expenses. Additionally, flexible scheduling and reasonable labor planning can better accommodate changes in demand and prevent over or under-staffing.
3.3. Creating a Sensible Pricing Strategy
Creating a sensible pricing strategy is essential for coffee businesses to optimize resource usage and attain maximum profitability. It involves conducting market research and competitive analysis to comprehend customers' perception of product value, devising competitive prices, and being adaptable to market demand fluctuations.
4. Conclusions
The expansion of the coffee industry in China demands a critical evaluation of cost structures to minimize operational risks and enhance profitability. Luckin Coffee is one of the leaders in the Chinese coffee industry. By analyzing the cost structure of Lucky Coffee, we can better understand the development of the Chinese coffee industry in the face of unstable demand.
This article first studies the cost structure composition of Luckin Coffee, and then analyzes the proportions of different compositions. Thirdly, compare the cost structure of Luckin Coffee and Starbucks Coffee. Finally, by reviewing the historical data of Luckin Coffee, it can be concluded that the cost structure of Luckin Coffee can adapt to today's unpredictable needs, and get a better understanding of the high-cost elasticity of cost structure on the development of the entire coffee industry.
The study indicates that Luckin Coffee has implemented a cost structure that is highly elastic to adapt to the unpredictable demand environment. In general, Luckin Coffee's cost structure reveals that raw material costs have become the primary expenses over time, while depreciation and opening costs have decreased. Additionally, the percentage of these expenses in relation to the total cost structure has shown a positive trend. This cost structure highlights Luckin Coffee's competitive advantage and showcases the innovation within its business model.
The significance of studying the cost structure of Luckin Coffee is to help us understand the company's business model and profitability. This is very important for both the coffee industry and industry insiders, as it can help them make more accurate investment decisions and business strategies, as well as identify potential cost savings and efficiency improvement opportunities, thereby improving profitability and competitiveness.
References
[1]. W. Hou, “The Coffee Industry Shows Attractive Prospects in the Chinese Market,” [J]. Business Observation, p.10-12, 2022.
[2]. Y. Yao, and L. Wei, “Decision Research on Enterprise Cost Structure under the Condition of Increasing Demand Uncertainty,” [J]. China Management Accounting, p.37-45, 2020.
[3]. M. Wei, “Luckin Coffee: First Turning Over, Later Breaking Through,” [J]. Economic Management and Science, p.50-54, 2023.
[4]. L. Wei, and Y. Yao, “Does monetary policy affect the cost structure of enterprises?” [J] Scientific Decision Making, p.65-89, 2021.
[5]. L. Shu, “Innovation and Cost Structure Analysis of Luckin Coffee Business Model,” [D]. Xiamen University, 2023.
[6]. B. Zhu, and H. Xiong, “Economic Policy Uncertainty and Enterprise Cost Structure Decision,” [J]. Soft Science, 2022.
Cite this article
Chen,S. (2024). Analysis of the Cost Structure of Luckin Coffee. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,101,124-130.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. W. Hou, “The Coffee Industry Shows Attractive Prospects in the Chinese Market,” [J]. Business Observation, p.10-12, 2022.
[2]. Y. Yao, and L. Wei, “Decision Research on Enterprise Cost Structure under the Condition of Increasing Demand Uncertainty,” [J]. China Management Accounting, p.37-45, 2020.
[3]. M. Wei, “Luckin Coffee: First Turning Over, Later Breaking Through,” [J]. Economic Management and Science, p.50-54, 2023.
[4]. L. Wei, and Y. Yao, “Does monetary policy affect the cost structure of enterprises?” [J] Scientific Decision Making, p.65-89, 2021.
[5]. L. Shu, “Innovation and Cost Structure Analysis of Luckin Coffee Business Model,” [D]. Xiamen University, 2023.
[6]. B. Zhu, and H. Xiong, “Economic Policy Uncertainty and Enterprise Cost Structure Decision,” [J]. Soft Science, 2022.









