1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has brought disruptive innovation to various industries, reshaping traditional workflows. Many companies are seeing improved convenience and increased revenue due to the application of AI. However, in the advertising industry, AI has not been genuinely involved in the workflow. Many advertising agencies are still searching for opportunities and strategies to look forward to the vast changes and benefits that AI will bring. There is a lot of research that combines AI technology and marketing methods, but there is less research from the perspective of advertising agencies. Advertising agencies cover a range of service processes, from customer service to media delivery and evaluation, and mere opinions on marketing methods cannot comprehensively address the industry's future development [1]. In order to analyze the impact of artificial intelligence on the workflow of advertising companies, this study reviews critical literature. It takes an in-depth look at advertising agency workflows and AI applications in light of current industry conditions. First, Mishra and Tripathi mentioned in their study that the rapid development of artificial intelligence today has transformed many industry workflows and business models [2]. However, Qin & Jiang conducted an extensive literature review with China as the background and found that the application of AI in the advertising agency process is still in the conceptual and explanatory stages [3]. Due to the gap between it and other mainstream industries, this study examines the workflow of the advertising industry. Second, current practice shows that AI can overcome some human limitations in computationally intensive intelligence and even creativity, thus opening up new areas of application for education and marketing, healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, with implications for productivity and performance [4]. Therefore, exploring the application and impact of AI in advertising agencies is a crucial topic. Lastly, integrating AI into advertising agencies' routine work necessitates comprehensive strategic planning to align the new approach with clients' long-term needs.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Workflow of Advertising Agency
Figure 2.1 shows a typical process for an advertising agency as proposed by Nicholson[5]. Starting from this series of steps, this study explores the application of artificial intelligence in the field of advertising and then analyzes which stages of work will be affected by the application of artificial intelligence. By listing the process of the advertising agency in Figure 2.1, the impact of AI applications can be more directly mapped to the various stages of work.
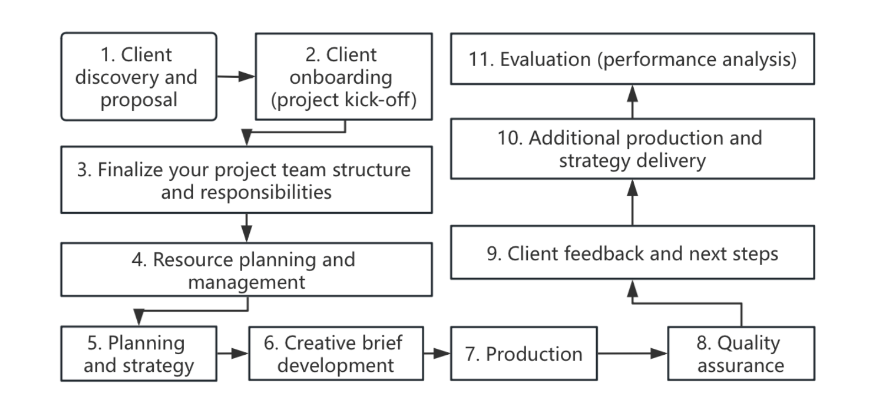
Figure 1: 11-Step advertising agency workflow process [5].
2.2. The Application Prospect of AI in Advertising Agencies
Putri et al. studied dance kreatif (an advertising agency in Indonesia), introduced AI to a range of the company's work, and measured the impact on the effectiveness of its advertising and financial returns [6]. The comprehensive evaluation shows that market research, creative, and production departments will become the leading application directions of AI technology for advertising companies. Firstly, AI for market research is an intelligent, extensive data taxonomy that can determine the appropriate marketing approach in different situations [7]. At the same time, their research also suggests the advantages of marketing automation in helping to understand potential customers. Secondly, Phay refers to advertising companies' AI integration. On the one hand, it has the ability to screen and analyze data points more quickly, primarily for the purpose of predicting the most influential creative points in advertising through big data [8]. On the other hand, the utilization of AI has the potential to produce innovative advertising. Thirdly, Gotab-Andrzejak mentions that artificial intelligence-generated advertising content has also been the subject of research [9]. He primarily focuses on generative AI-based tools and has developed a production model that involves conception, drafting, iteration, and testing. The study shows that the application of AI in advertising production has practical implications. Despite the lack of direct AI introduction by advertdvertising agencies, their production departments use AI-capable photo or video editing software, such as Canva. Haleem et al.'s study also mentions several applications, including predicting consumer trends, providing ideas, and generating marketing content [10]. However, it is worth noting that the study also points to AI support for programmatic advertising. This refers to the automated nature of ads, which constantly utilize machine learning to bid for space that is accessible to target audiences. Bir & Aksu pointed out that intelligent advertising is the next stage of programmatic advertising [11]. As a result, people may think that programmatic advertising is the trial operation stage of AI, but intelligent advertising is entirely dependent on AI.
2.3. The Impact of AI on Advertising Agencies
2.3.1. Market Research
The study by Brand et al. on the use of GPT in market research can give a specific perspective on the impact of AI on market research [12]. First, AI provides accurate market data, and the data in the experiment shows agreement with mainstream economic theory. Second, GPT can provide a forecast of future commodity demand, which can also assist advertising agencies with strategic planning and the choice of media. In addition, Brand et al. 's research also shows that AI other than GPT can bring additional benefits to market research. Paliwal and Chatradhi's research shows that understanding the way AI is reshaping the market research industry can promote the adoption of AI for customer insights, allowing market researchers to not only do their jobs faster but also improve accuracy [13].
2.3.2. Predict the Optimal Creative Attributes
Ameen et al. 's research shows that there are three possible ways for AI technology to create ideas [14]. Firstly, it can merge with some well-known concepts to form innovative combinations. Secondly, AI can expand the conceptual space. Third, AI can also create ideas that are currently impossible to achieve. Through the analysis of art data sets, Cetinic and She also put forward that AI technology has a particular potential for understanding and creating art, but there is no specific analysis for specific AI operations [15].
2.3.3. Produce Advertising Material
Anantrasirichai and Bull's research focuses on how current AI technology excels at image creation by automatically creating new digital images based on specific data sets [16]. Second, AI also assists with sound design, which is beneficial for digital media advertising. Applications of AI include searching large databases to identify the most suitable music or rhythm for the creation of specialized music formats. Finally, the text integration technology of natural language processing (NLP) is a standard copywriting tool, a widely used computing technology that can help advertising agencies write copywriting and other work. However, the authors note that current AI technology can indeed make work more efficient, but it also needs to work with humans.
2.3.4. Intelligent Advertising
Yang et al. presented the AiAds system, a Baidu-developed system that leverages machine learning technology for advertising automation and intelligence [17]. Specifically, it optimizes some advertising workflows by designing and implementing automated bidding strategies as well as targeting and creating models.
3. Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Advertising Agencies on Workflow
Firstly, this study posits that AI can significantly impact step eight of quality assurance due to its robust ability to read current market data and its remarkable accuracy in predicting future trends, surpassing human estimation. This finding is consistent with Pavl, D. [18]. Because of the accurate market analysis, the final advertising effect will be significantly improved. Secondly, artificial intelligence's prediction of creative attributes can improve the workflow of advertising agencies, especially in the fifth step of planning and strategy and the sixth step of creative needs development. This improvement stems from the need to organize strategies and plans based on creative attributes and propose creative needs development based on these identified attributes. Thirdly, the replacement of specific job responsibilities by AI will also impact the third step, which involves finalizing the structure and responsibilities of the project team. The production of text, music, and images can directly simplify step seven. However, this study argues that it is not feasible to reduce human resources significantly in the workflow. Ultimately, artificial intelligence-driven intelligent advertising development streamlines the advertising process into an automated one. AI alters the third step of the workflow to determine the structure and responsibilities of the project team, as AI tools can perform specific job duties. Additionally, AI-led projects will need to explicitly analyze whether this change has a positive or negative impact on the Step 11 assessment (performance analysis). Figure 2 shows that seven steps are the simplified workflow presented after AI technology enters the advertising agency process through analysis in this study. Note that this is only a scenario and is not a fixed workflow.
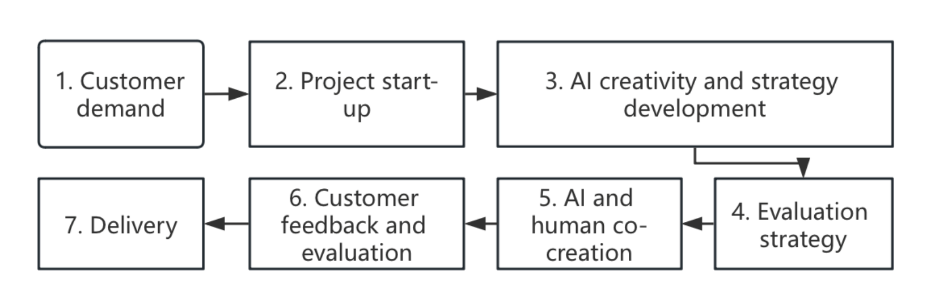
Figure 2: The workflow of advertising agencies after the introduction of AI.
3.2. Strategy for Advertising Agencies Using AI
The above considerations allow advertising agencies to introduce AI and its effect on workflow. This study proposes strategies for the current phase by assessing the changes brought about by this disruptive innovation and integrating the more immediate positive effects. The positive impact that AI can bring at this stage points to the introduction of AI in market research and creative attribute forecasting. This is because large amounts of data show that AI is able to integrate and update large amounts of information faster than humans. In addition, although many existing studies show that AI applications are promising in creative production and intelligent advertising, the current technology may require a significant investment, and the effect has yet to be measured. This study also takes into account that for the creative creation using AI and artificial co-creation mode, the ability of AI technology for artistic creation needs to be improved at this stage, and the specific mode makes it difficult to create personalized advertising products that meet the individual needs of customers.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, first of all, the workflow of advertising agencies and viable AI applications. Many studies in the field of advertising propose that the workflow of advertising agencies is roughly 11 steps, as shown in Figure 2.1. This series of processes typically include client output, agency planning based on market research, idea generation, and final evaluation. At present, many studies believe that artificial intelligence has application prospects in four aspects: market research, creative attribute exploration, creative production, and intelligent advertising. Second, the impact of artificial intelligence on the workflow of advertising companies. In general, the application of AI will change the resource allocation and personnel structure of projects. The workflow thus is greatly simplified and summed up in seven steps. From customer needs and project initiation to AI creative and strategic development, as well as evaluating strategies, AI and human co-creation, to final customer feedback and evaluation, and delivery. Third, the strategy of advertising agencies to use AI. Through a series of surveys, this study found that it is reasonable for advertising agencies to prioritize AI in market research and exploring creative attributes at this stage. In the production phase, we also need to supplement subjective creativity. Finally, this study provides general guidance and suggestions for the advertising agency industry. Its limitation is that it has not been studied for specific advertising agencies and may not apply to specific workflows of some companies, so additional market research and technical testing for the development and application of each company is required. In addition, as the current stage is the era of rapid development of digital marketing platforms and artificial intelligence and various electronic marketing platforms and new technical means are emerging in an endless stream, this study is time-sensitive, and future research may need to update the scientific and technological background and continuous research.
References
[1]. Horsky, S. (2006). The changing architecture of advertising agencies. Marketing Science, 25(4), 367-383.
[2]. Mishra, S., & Tripathi, A. R. (2021). AI business model: an integrative business approach. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 10(1), 18.
[3]. Qin, X., & Jiang, Z. (2019). The Impact of AI on the Advertising Process: The Chinese Experience. Journal of Advertising, 48(4), 338–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913367.2019.1652122
[4]. Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., ... & Williams, M. D. (2021). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International journal of information management, 57, 101994.
[5]. Nicholson, R. (2023). Advertising Agency workflows: 11 steps to building better processes. Work Life Balance Tips & Work Scheduling Blog. https://resourceguruapp.com/blog/agencies/advertising-agency-workflow
[6]. Putri, O. A., Ars, S., Wibisono, I. D., & Eng, M. (2024). Optimizing AI-integrated creative process in advertising industry through KBPMS approach. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 07(07), 4612–4625. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijcsrr/v7-i7-06
[7]. Mariani, M. M., Perez‐Vega, R., & Wirtz, J. (2022). AI in marketing, consumer research and psychology: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Psychology & Marketing, 39(4), 755-776.
[8]. Phay, H. (2019). Creative AI: a data-driven design approach for creative online ad optimisation using artificial intelligence and big data.
[9]. Gołąb-Andrzejak, E. (2023). The Impact of Generative AI and ChatGPT on Creating Digital Advertising Campaigns. Cybernetics and Systems, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969722.2023.2296253
[10]. Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., Singh, R. P., & Suman, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature-based study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3, 119-132.
[11]. Bir, G., & Aksu, S. (2024). An Examination of the Utilization of Artificial Intelligence Technologies by Advertising Agencies. Yeni Medya, (16), 19-37.
[12]. Brand, J., Israeli, A., & Ngwe, D. (2023). Using GPT for market research. Harvard Business School Marketing Unit Working Paper, (23-062).
[13]. Paliwal, M., & Chatradhi, N. (2024). AI in Market Research: Transformative Customer Insights-A Systematic Review. Exploring the Intersection of AI and Human Resources Management, 231-255.
[14]. Ameen, N., Sharma, G. D., Tarba, S., Rao, A., & Chopra, R. (2022). Toward advancing theory on creativity in marketing and artificial intelligence. Psychology & marketing, 39(9), 1802-1825.
[15]. Cetinic, E., & She, J. (2022). Understanding and creating art with AI: Review and outlook. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 18(2), 1-22.
[16]. Anantrasirichai, N., & Bull, D. (2022). Artificial intelligence in the creative industries: a review. Artificial intelligence review, 55(1), 589-656.
[17]. Yang, X., Sun, D., Zhu, R., Deng, T., Guo, Z., Ding, Z., ... & Zhu, Y. (2019, July). Aiads: Automated and intelligent advertising system for sponsored search. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining (pp. 1881-1890).
[18]. Pavlů, D. (2016). The Beginnings of Market Research and Measurement of Market Advertising Effectiveness. Communication Today, 7(1), 52-64.
Cite this article
Lin,S. (2024). Research on the Impact of Artificial Intelligence Applications on the Workflow of Advertising Agencies. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,117,106-110.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Horsky, S. (2006). The changing architecture of advertising agencies. Marketing Science, 25(4), 367-383.
[2]. Mishra, S., & Tripathi, A. R. (2021). AI business model: an integrative business approach. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 10(1), 18.
[3]. Qin, X., & Jiang, Z. (2019). The Impact of AI on the Advertising Process: The Chinese Experience. Journal of Advertising, 48(4), 338–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913367.2019.1652122
[4]. Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., ... & Williams, M. D. (2021). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International journal of information management, 57, 101994.
[5]. Nicholson, R. (2023). Advertising Agency workflows: 11 steps to building better processes. Work Life Balance Tips & Work Scheduling Blog. https://resourceguruapp.com/blog/agencies/advertising-agency-workflow
[6]. Putri, O. A., Ars, S., Wibisono, I. D., & Eng, M. (2024). Optimizing AI-integrated creative process in advertising industry through KBPMS approach. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 07(07), 4612–4625. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijcsrr/v7-i7-06
[7]. Mariani, M. M., Perez‐Vega, R., & Wirtz, J. (2022). AI in marketing, consumer research and psychology: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Psychology & Marketing, 39(4), 755-776.
[8]. Phay, H. (2019). Creative AI: a data-driven design approach for creative online ad optimisation using artificial intelligence and big data.
[9]. Gołąb-Andrzejak, E. (2023). The Impact of Generative AI and ChatGPT on Creating Digital Advertising Campaigns. Cybernetics and Systems, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/01969722.2023.2296253
[10]. Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., Singh, R. P., & Suman, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature-based study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3, 119-132.
[11]. Bir, G., & Aksu, S. (2024). An Examination of the Utilization of Artificial Intelligence Technologies by Advertising Agencies. Yeni Medya, (16), 19-37.
[12]. Brand, J., Israeli, A., & Ngwe, D. (2023). Using GPT for market research. Harvard Business School Marketing Unit Working Paper, (23-062).
[13]. Paliwal, M., & Chatradhi, N. (2024). AI in Market Research: Transformative Customer Insights-A Systematic Review. Exploring the Intersection of AI and Human Resources Management, 231-255.
[14]. Ameen, N., Sharma, G. D., Tarba, S., Rao, A., & Chopra, R. (2022). Toward advancing theory on creativity in marketing and artificial intelligence. Psychology & marketing, 39(9), 1802-1825.
[15]. Cetinic, E., & She, J. (2022). Understanding and creating art with AI: Review and outlook. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 18(2), 1-22.
[16]. Anantrasirichai, N., & Bull, D. (2022). Artificial intelligence in the creative industries: a review. Artificial intelligence review, 55(1), 589-656.
[17]. Yang, X., Sun, D., Zhu, R., Deng, T., Guo, Z., Ding, Z., ... & Zhu, Y. (2019, July). Aiads: Automated and intelligent advertising system for sponsored search. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining (pp. 1881-1890).
[18]. Pavlů, D. (2016). The Beginnings of Market Research and Measurement of Market Advertising Effectiveness. Communication Today, 7(1), 52-64.









