

Volume 191
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: The 4th International Conference on Applied Economics and Policy Studies
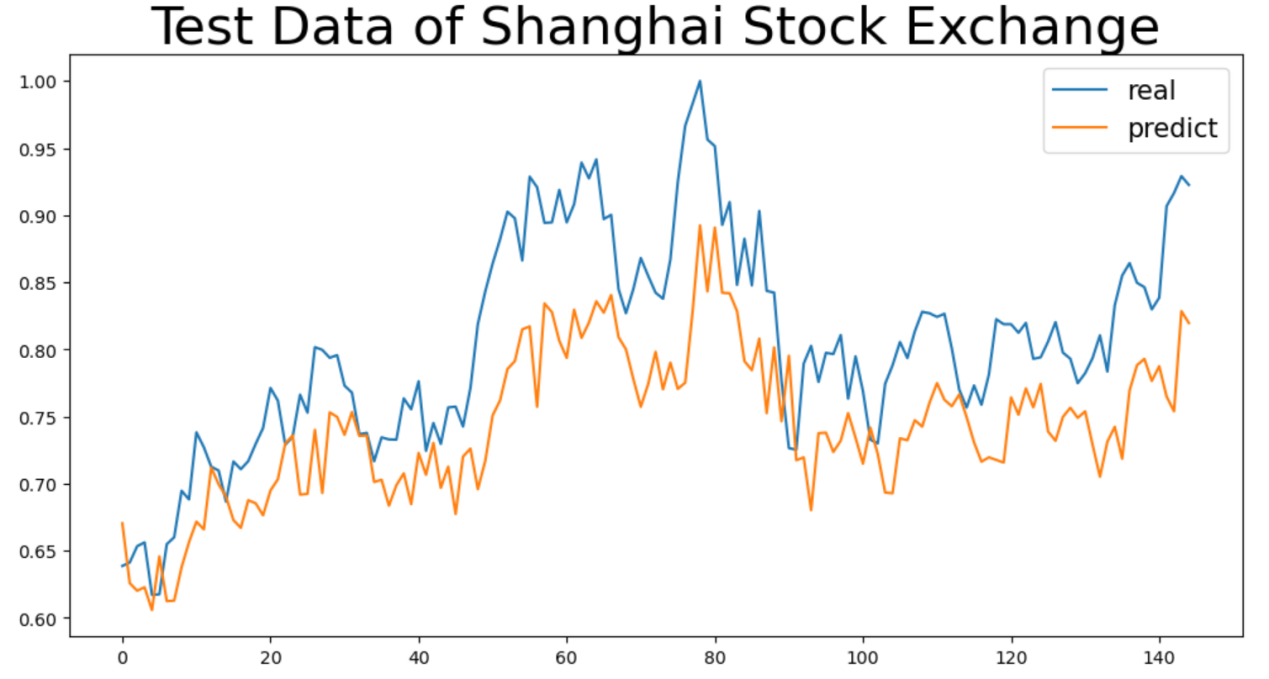
Stock price prediction faces significant challenges due to the high complexity and non-linear characteristics of financial markets. Traditional models often struggle to effectively capture their dynamic patterns. This paper, based on the Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN), constructs a multivariate time series forecasting model to explore the non-linear mapping relationship between historical trading data, such as opening price, closing price, lowest price, and highest price, and the next day’s closing price. To demonstrate the practical applicability of the model and the impact of data time span, two comparative experiments were designed, using two years and three years of historical data, respectively, to analyze stock price predictions for 13 major global securities markets. Empirical results show that BPNN exhibits strong forecasting ability in stable markets. Extending the time span can improve the prediction accuracy for some markets by covering a more complete market cycle. However, the effect is constrained by market volatility and external environmental factors. The research findings provide a theoretical basis for cross-market model adaptation and data governance strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines China’s 2021 “Double Reduction” policy through the lens of institutional economics and incentive theory, analyzing its implications for educational equity, efficiency, and resource allocation, The study identifies how institutional misalignments, particularly between policy goals and the exam. oriented evaluation system-undermine implementation. While the policy has achieved partial success in redistributing resources and shifting household educational expenditures, its long-term effectiveness remains constrained by structural rigidities, uneven governance capacity, and behavioral adaptations. The paper argues that improving institutional coherence, optimizing micro-level incentives, and reforming the education evaluation system are essential for achieving sustainable outcomes. These findings contribute to the growing literature on the economics of education and institutional policy design in transitional economies.

 View pdf
View pdf


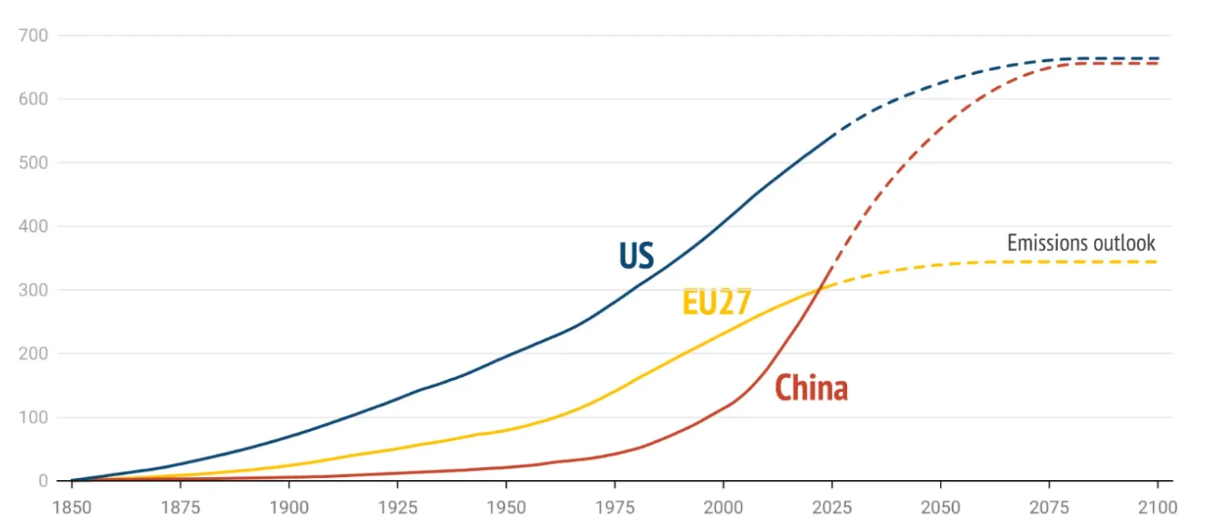
Climate change represents a critical global challenge, exacerbating both ecological and economic inequalities. This article examines how global economic disparities influence carbon emission reduction policies, particularly in the United States and China. The study highlights the historical responsibility of developed countries in emissions and their greater capacity to mitigate climate impacts, contrasted with the development pressures faced by emerging economies. Through case studies of U.S. and Chinese policies, the article explores how current climate governance frameworks reflect these imbalances and the institutional challenges of implementing effective, equitable carbon policies. The findings suggest that while developed nations have greater resources to address climate change, developing nations face significant barriers in balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility. However, the study has limitations, particularly in its geographical focus on just the U.S. and China, overlooking experiences from other countries, especially developing ones. Future research should expand the scope to include a wider range of nations, particularly low-income countries, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of global climate governance and the disparities within it.

 View pdf
View pdf


As a critical policy tool for mitigating agricultural risks and stabilizing farmers’ incomes, agricultural insurance has been the subject of extensive scholarly investigation. However, there is still no consensus regarding the relationship between agricultural insurance and farmers' income, and the mechanism by which agricultural insurance affects farmers' disposable income requires further empirical examination. In this study, farmers’ disposable income is taken as the dependent variable, and agricultural insurance development is measured across three dimensions: coverage density, coverage depth, and compensation efficiency. The entropy method is applied to integrate these indicators into a composite index used as the independent variable. Control variables include urbanization rate, per capita crop-sown area, the proportion of the primary industry, and fiscal support for agriculture. Using panel data from 30 provincial-level administrative regions in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Tibet) for the period 2014–2024, a two-way fixed effects model is constructed. The empirical results reveal that a one-unit increase in agricultural insurance development leads to a statistically significant 1.098-unit increase in farmers’ disposable income (p < 0.01), though the effect is partially diluted by control variables. Urbanization (β = 4.349) exhibits a structural substitution effect through non-agricultural employment, while fiscal support for agriculture (β = 0.001) synergistically boosts income through infrastructure improvements. In contrast, per capita sown area (β = -0.048) negatively moderates insurance efficiency due to its reliance on natural resources. A regional heterogeneity analysis reveals that the income-enhancing effect of insurance is significant in the eastern (β = 2.027) and central (β = 2.155) regions (p < 0.01), but only marginally significant in the western region (β = 0.323, p < 0.1), reflecting the moderating role of economic development and agricultural modernization. The model passes tests for endogeneity using lagged terms and for robustness using 1% winsorization. Based on these findings, this study recommends enhancing insurance density and depth, optimizing product design and claims efficiency, and improving fiscal subsidies and agricultural modernization to effectively boost farmers’ disposable income.

 View pdf
View pdf


Moore's Law has long driven the semiconductor industry's pursuit of miniaturization, yet firms continue investing in mature nodes (e.g., 28nm/200mm fabs) due to the powerful sunk cost fallacy. This phenomenon distorts rational decision-making, trapping companies in outdated technologies despite the availability of more advanced alternatives. This paper develops a framework that integrates technical rigidity, behavioural commitment, and institutional lock-in to explain this paradox, challenging conventional market-demand narratives. By introducing the Sunk Cost Escalation Multiplier (SCEM), this research identifies critical thresholds where continued investment transitions from strategic to irrational. The analysis highlights how industry structure and cognitive biases interact to sustain technological lock-in, presenting significant policy implications for capital reallocation and technology transition roadmaps. It further illustrates how sunk costs create self-reinforcing cycles: specialized equipment with long lifespans, such as 200mm fabs, becomes economically obsolete yet remains physically operational. Additionally, policy incentives like subsidies often inadvertently perpetuate these inefficiencies, hindering innovation and progress.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid rise of financial technology(fintech) is changing the traditional financial landscape and bringing new challenges while leading to financial innovation. Financial regulation faces the contradiction between tradition and innovation and needs to find a balance between development and risk. This paper combs through the core technology of fintech and analyzes its impact on traditional finance. Secondly, it explores the dilemma of the current regulatory framework, examines innovative models such as sandbox regulation, and summarizes the global experience of differentiated regulation. Next, this paper explores the mutual dual impact between fintech and financial regulation. Finally, this paper puts forward the future direction of regulation, emphasizing preventive regulation and technology-enabled regulation. This paper hopes that by deeply analyzing the dynamic relationship between fintech and regulation, exploring to understand the regulatory model that adapts to the development of fintech, providing ideas for building an agile and robust regulatory ecology and promoting the healthy development of the financial industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid development of artificial intelligence is reshaping the global financial competition pattern. Studying the impact of AI on China's stock market is of great theoretical and practical significance for improving market efficiency and optimizing regulatory mechanisms. However, China's stock market is facing the limitations and efficiency bottlenecks of traditional analytical methods, so there is an urgent need to explore new ways with the help of AI. Studying the impact of AI on China's stock market is of great theoretical and practical significance for improving market efficiency and optimizing regulatory mechanisms. Through empirical analysis, case comparison and international empirical studies, this paper systematically explores the application of AI in the fields of high-frequency trading, quantitative modeling and regulatory technology, and analyzes its comprehensive impact on China's stock market efficiency, structural anomalies and regulatory model. The paper concludes that AI significantly improves market information processing speed and trading efficiency, but exacerbates the deterioration of small-order liquidity and the risk of algorithmic convergence and that China's regulatory framework centered on "technologically controllable" is more adaptable than that of the U.S. and Europe, but needs to guard against algorithmic failures in extreme markets. This paper lays a theoretical foundation for the construction of a "technologically controllable regulation" system with Chinese characteristics, and provides policy guidance for balancing AI technology innovation with risk prevention and control.

 View pdf
View pdf


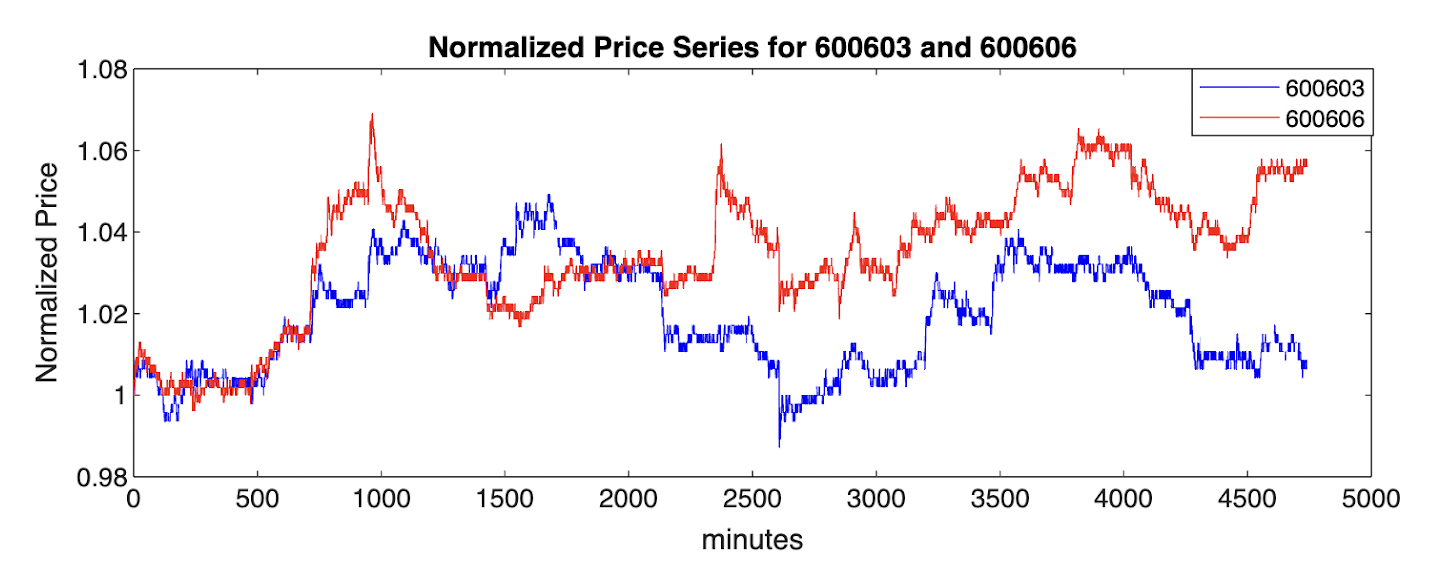
This study outlines some integrated approaches for pairs trading and portfolio analysis, focusing on the performance in generating consistent returns under varying market conditions over one year. The relationships between returns and some relevant factors are also explored. Steps for pairs trading involve selecting securities with strong historical associations or return correlations, normalizing their price series, calculating related price statistics, and employing a strategy based on Z-score to identify trading opportunities. Regression analysis of performance metrics across thousands of pairs highlights the significant relationship between the standard deviation of spread and profitability, whereas the return correlation is insignificant. The chosen portfolio exhibits low volatility, a high Sharpe ratio, and minimal drawdowns. Incorporating trading costs reveals a break-even point where the overall profit is zero. This confirms the strategy's robustness and real-world feasibility. In this paper, our result is against the weak form of the market efficiency theory, showing that strategies based on past information can generate consistent returns.

 View pdf
View pdf


A notable feature of the Chinese economy over the past decade has been the continuous decline in nominal interest rates. As of May 2025, the one-year loan prime rate (LPR) had gradually declined from 5.3% to 3.1% (data from the People's Bank of China (PBoC). Although conventional wisdom suggests that a low interest rate environment can stimulate economic activity, many studies in recent years have shown that a persistently low interest rate environment can exacerbate capital misallocation in the credit market, leading to economic contraction. This paper studies the impact of the current low interest rate environment on the credit market under China's economic system by constructing an Agent-Based Model. The study found that a sustained low interest rate environment will exacerbate the capital mismatch between state-owned enterprises and private enterprises in the credit market, which in turn will lead to a decline in the average return on investment. Structural reforms can eliminate the adverse effects of this phenomenon, but there are still difficulties in practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, as Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) reports have evolved from marginal texts to strategic tools, investors have gradually recognized the limitations of traditional financial indicators. This study focuses on how accounting information in CSR reports penetrates the superficial layer of "responsibility narratives" and actually influences investment decisions. Through literature analysis, case studies, and theoretical reasoning, it answers two core questions: Which accounting data truly trigger investors' nerves? How do these data convey the sustainable development potential of enterprises? The study finds that accounting indicators, such as environmental governance costs and employee welfare expenditures, constitute the anchor points of "responsibility credibility", and the quality of their disclosure directly affects the risk pricing in the capital market. It suggests that enterprises adopt "industry-customized" disclosure strategies, while investors need to establish a "financial-responsibility" dual-dimension analysis framework. The study reveals a new path for the capitalization of non-financial information, providing a new perspective for value assessment in the era of responsibility.

 View pdf
View pdf




