1. Introduction
Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, the country has committed to integrating ecological civilization into the overall layout of socialism with Chinese characteristics, establishing the significant role of green development in economic growth. The "14th Five-Year Plan and the 2035 Long Range Objectives Outline" explicitly states China's intention to actively pursue a green and low-carbon development model, reflecting the firm stance and determination of the Party Central Committee and the government to promote sustainable social development. As a comprehensive corporate governance system covering environmental, social, and governance dimensions, ESG is gradually gaining attention among Chinese enterprises. However, there are still some issues with ESG information disclosure among China's listed companies. Due to the voluntary disclosure model adopted in China, many companies choose not to disclose, or selectively disclose certain information, leading to a low rate and quality of ESG reporting in China [1]. Against this backdrop, studying the market reaction to ESG information disclosure can serve as a strong incentive for companies to improve their willingness to disclose ESG information and help promote the process of making ESG disclosure mandatory in China.
However, most scholars currently focus on the research of financial accounting information disclosure, with few comprehensive studies on market reactions, often discussed through empirical methodologies. The most recent study closely related to this research topic is by Liu Jiayuan [2]. Due to the development of China's real estate industry leading to investment overheating in the construction sector [3], it is difficult to eliminate the risky area phenomenon in China's real estate industry in a short time. Vanke Group, as a real estate giant, has its particularities in studies on market reactions. Midea Group, as a leading company in the home appliances industry, plays a significant role in its ESG report for all stakeholders. Researching the market reactions to Midea's ESG report can help enterprises comprehensively assess the positive and negative impacts of ESG reports on corporate development, thereby enhancing the motivation for companies to actively publish ESG reports. This study delves into the specific impact of ESG report disclosure on the stock returns of Midea Group.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on the Current Situation of ESG Disclosure
China's development of ESG started relatively late compared to the international context. However, with the increasing attention to environmental and social responsibility issues in China, ESG has become a research hotspot in both academia and industry. At the institutional level, China has adopted a mixed disclosure model, requiring some key enterprises to disclose ESG information while allowing others to choose not to disclose certain items but requiring an explanation for the decision. Additionally, voluntary disclosure by other enterprises is encouraged. Lou Qiuran [4], by comparing the information disclosure systems of China and the United States, thoroughly analyzed the existing problems and proposed that listed companies should be required to disclose ESG information to further improve China's ESG information disclosure system.
From the perspective of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information disclosure systems, Lou Qiuran conducted an in-depth study of the ESG information disclosure systems in China and the United States. By comparing the ESG information disclosure systems of both countries and delving into the definition of information "materiality," Lou Qiuran found that the existing disclosure frameworks based on economic materiality have significant flaws because their theoretical basis and legal grounds have not kept pace with the times. This leads to a lack of unified and clear standards for assessing the materiality of ESG information in practice, thereby affecting the effectiveness and reliability of information disclosure. After analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of mandatory and voluntary disclosure, Lou Qiuran believes that future ESG information disclosure systems need to strike a balance between ensuring the quality of information disclosure and considering the disclosure costs and autonomy of enterprises. This approach not only helps improve the transparency and comparability of corporate ESG information but also avoids imposing excessive burdens on enterprises.
2.2. Impact of ESG Disclosure on Corporate Value
Starting from the perspective of costs and benefits, Wang Rong [5] delves into the impact of ESG (environmental, social, and governance) information disclosure on corporate value and its underlying mechanisms. The empirical research results show a unique "U-shaped" correlation between ESG information disclosure and corporate value. In the short term, increased ESG information disclosure may lead to temporary declines in corporate value; however, from a long-term perspective, ESG information disclosure has a significant positive effect on corporate value by reducing the company's financing costs and increasing its market visibility.
Wang Linlin [6] and others conducted in-depth research on the relationship between corporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance and its economic value. Through empirical analysis, they found that companies with superior ESG performance often have higher market value. Good ESG practices can effectively alleviate corporate financing pressure, improve operational efficiency, and reduce financial risks. These positive factors collectively contribute to the enhancement of corporate value. Providing empirical support for the positive impact of ESG performance on corporate economic value, this research offers important theoretical references for enterprises and investors to consider ESG factors in the decision-making process, as well as for government departments in formulating and improving ESG incentive policies. Wang Bo [7] and others examined the mechanism of how ESG performance affects corporate value by analyzing company data from China's A-share market from 2015 to 2019. They found that high-quality ESG performance can enhance both the book value and market value of a company by reducing financing costs and increasing market attention. Bai Xiong [8] and others introduced investor shareholding data and, through panel regression models and other methods, found that corporate ESG practices can attract institutional investors to increase their holdings. They empirically demonstrated that institutional investors have a preference for ESG investments and are willing to tolerate short-term operational performance downturns in companies with good ESG performance.
Some scholars have studied the relationship between ESG information disclosure and stock prices to reflect market changes. Wang Wei and Jiang Gaofeng [9] found in early research that, after controlling for factors such as company size and financial risk, increasing the disclosure level of listed companies reduces the company's cost of equity capital. Similarly, Chen Guohui and Han Haiwen found that improving corporate information disclosure levels can effectively reduce capital costs, achieving a win-win situation for investors and listed companies in terms of disclosure strategies. In addition, [10] there is a positive correlation between market attention and the market response to social responsibility information disclosure. Companies that receive media attention are more likely to gain recognition from the capital market when transmitting signals through social responsibility disclosure, and initial disclosure of social responsibility reports is more likely to receive a positive attitude from the capital market.
By disclosing ESG information to attract external investors' favor and demonstrate their development potential, companies also receive feedback from external investors, which in turn supervises and encourages companies to release high-quality ESG information. Currently, scholars at home and abroad have conducted extensive research on the impact of ESG disclosure, but there is no consensus yet. However, after organizing and analyzing, we can find that most studies tend to believe that ESG information disclosure has a positive impact on companies, and these disclosures can be captured by the market and reflected in stock fluctuations, with higher disclosure leading to better market responses.
3. Analysis of Midea Group's ESG Content and Disclosure Status
Midea Group, established in 1968 and listed in Hong Kong in 2012, operates in the sectors of household appliances, intelligent manufacturing, and logistics services. It has evolved into a global technology group integrating intelligent home appliances, industrial technology, building technology, robotics and automation, and digital innovation. In 2020, the group released its Corporate Social Responsibility Report, highlighting philanthropy, employee rights protection, and sustainable development in the supply chain. Following the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Sustainable Development Reporting Standards, Midea Group released Sustainable Development Reports in 2021 and 2022, focusing on a green strategy and promoting energy conservation and emission reduction across the entire industry chain. The core contents include:
Green Strategy: Midea Group implements a green strategy around six pillars, committing to achieving internal carbon peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. The group issued $450 million in "green bonds" to promote strategy implementation and invested in cutting-edge technologies, with a cumulative R&D investment exceeding 50 billion yuan.
Supply Chain Management: Midea Group is committed to integrating sustainable development concepts into its procurement strategy and business processes, building a green procurement system. The group advocates for suppliers to practice green development, with two subsidiaries selected as "2022 National Green Supply Chain" units. Midea Group has established a supplier access and assessment mechanism and penalizes suppliers that violate regulations.
Occupational Health and Safety: Midea Group prioritizes employee health and safety, complies with relevant regulations, and improves working environments, aiming to create a zero-accident, risk-controllable EHS system. The group has a safety production committee that follows the "Safety Production Law of the People's Republic of China" and has invested 228 million yuan in EHS management. In 2022, the lost time injury rate decreased by 25.9% year-over-year, and there were no general production safety accidents throughout the year.
Additionally, Midea Group has received recognition from several international sustainable development indices, such as the Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI), FTSE4Good Index, and CSI. In 2022, the group achieved excellent ratings with China Chengxin Green Gold ESG Rating A+, China Securities Index ESG Rating AA, and Wind ESG Rating A. According to iFinD data from Tonghuashun, Table 1 selects the top twenty enterprises in the domestic home appliance industry by ESG ranking. Midea Group ranks second in the industry with an AA ESG composite rating and is the highest-valued company in the industry with an ESG industry rating of A, contributing significantly to environmental, social, and corporate governance while ensuring economic efficiency.
Table 1: Midea Group's Industry Performance.
Rank | Stock Code | Company Name | ESG Composite Rating | ESG Composite Score | Total Market Value (Billion Yuan) |
1 | 002242.SZ | Joyoung Co. | AA | 76.08 | 109.15 |
2 | 000333.SZ | Midea Group | AA | 75.94 | 3900.67 |
3 | 002508.SZ | Robam | A | 73.62 | 255.76 |
4 | 300160.SZ | Xiuqiang | A | 73.46 | 45.22 |
5 | 600890.SH | Haier Smart Home | A | 73.29 | 2,135.41 |
6 | 002032.SZ | Supor | A | 72.91 | 391.09 |
7 | 002035.SZ | Vatti | A | 72.53 | 50.6 |
8 | 688169.SH | Stone Tech | A | 72.23 | 388.33 |
9 | 000541.SZ | Foshan Lighting | A | 71.68 | 65 |
10 | 300625.SZ | 3D Aurora | A | 71.11 | 36.85 |
4. Analysis of Market Response to ESG Disclosure
This paper aims to evaluate market reactions to specific events using event study methodology, with Midea Group's release of the "2022 Midea Group ESG Report" as the research subject. The report was published on April 29, 2023. To ensure accuracy and completeness, this study selects a five-day window period before and after the report's publication date, i.e., t = [-5,5], while excluding non-trading days. Additionally, to calculate the expected normal returns during the event period, an appropriate estimation period needs to be chosen. Based on the research of most scholars, the estimation period is usually set between 100 and 300 days. Therefore, this study selects the time interval [-160,-5] as the estimation period.
4.1. Calculation of Expected Normal Returns
This paper adopts the single-factor market model to calculate the expected normal returns ER i during the event period as follows:
\( E{R_{i}} = {ɑ_{i}}+{β_{i}}E{R_{m}} \) (1)
Where R i represents the daily returns of Midea (SZ:000333); R m denotes the market returns; and Pi t indicates the closing price of Midea on day t. As Midea Group is a component of the SZSE Component Index, the SZSE Component Index is used to calculate the market returns.
In this paper, Shenzhen Stock index is selected to calculate the market return rate. The specific algorithm is as follows:
\( {R_{it}}= ({P_{it}}-{{P_{i}}_{(t-1)}})/{{P_{i}}_{(t-1)收}} \) (2)
\( R{m_{t}}= (Inde{x_{t}}- Inde{x_{(t-1)}})/Inde{x_{(t-1)m}} \) (3)
The fitting results are shown in Figure 1.
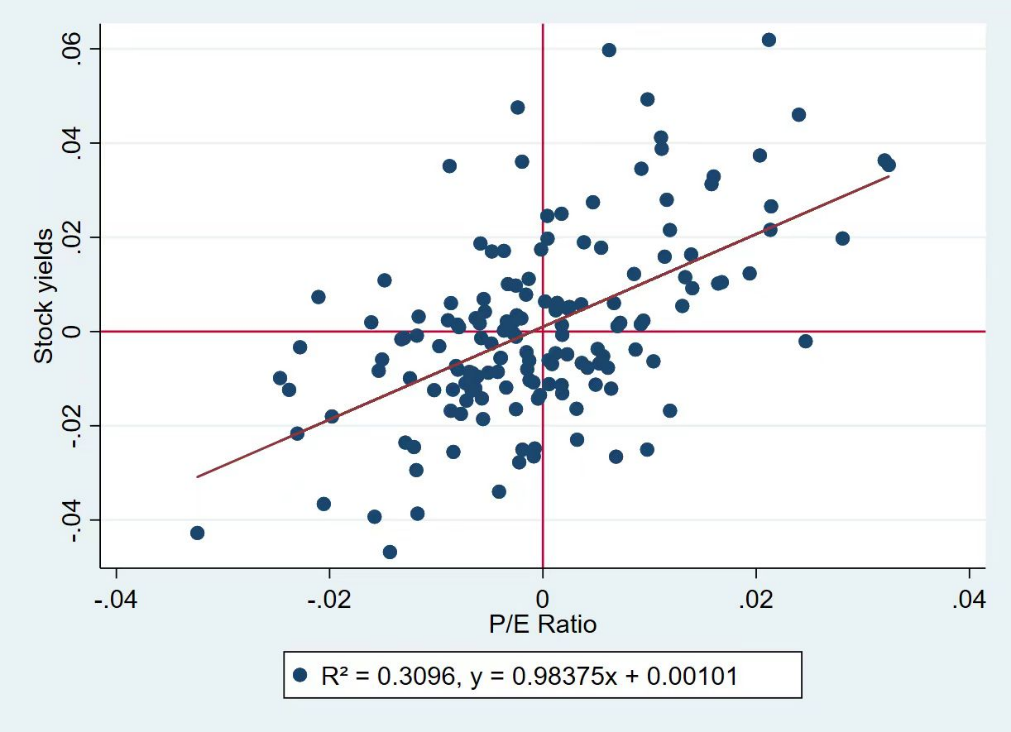
Figure 1: Event Period Fitting Graph.
The results were calculated by OLS regression: \( ɑ=0.00002 \) , \( β=0.62907 \) .
The regression equation is as follows: \( {R_{ i}} =0.00101i+0.98375{R_{m}} \)
4.2. Calculation of Excess Returns and Cumulative Returns
Based on the regression function obtained earlier, the daily normal returns during the event period [-5,5] are calculated, and subsequently, the daily excess returns and cumulative excess returns of Midea Group during the event period are calculated using the following formulae.
The expected normal returns are shown in Table 2.
\( A{R_{it}}={R_{it}}-{E_{Ri}} \) (4)
\( CA{R_{(t1,t2)}}= ∑_{t1}^{t2}A{R_{it}} \) (5)
Table 2: Changes in Key Indicators during Midea Group's Window Period.
Ri(%) | Rm(%) | ERi(%) | ARi | CARi | |
T=-3 | -1.65% | 0.33% | 0.42% | -2.07% | -2.07% |
T=-2 | 0.99% | 0.28% | 0.38% | 0.61% | -1.46% |
T=-1 | -0.84% | 1.08% | 1.17% | -2.01% | -3.47% |
T=0 | -0.35% | -0.57% | -0.46% | 0.11% | -3.36% |
T=1 | -2.21% | -0.82% | -0.71% | -1.50% | -4.86% |
T=2 | -0.58% | 0.40% | 0.50% | -1.07% | -5.93% |
T=3 | -0.38% | -0.90% | -0.78% | 0.40% | -5.53% |
T=4 | 1.09% | 0.14% | 0.24% | 0.86% | -4.67% |
T=5 | 0.09% | 0.02% | 0.12% | -0.03% | -4.70% |
T=6 | 0.67% | -1.23% | -1.11% | 1.77% | -2.93% |
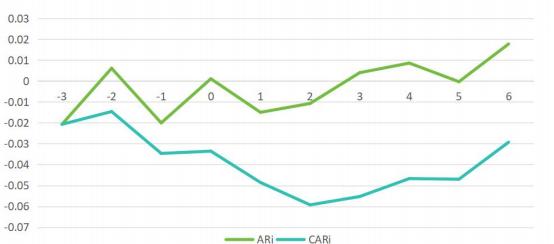
Figure 2: Trend Graph of Midea Group's AR and CAR.
4.3. Research Conclusion and Explanation
Through a detailed analysis of Figure 2, it is observed that Midea Group's excess returns show a significant positive trend after the specific event. Specifically, on the first trading day after the ESG report is published, the expected excess returns immediately manifest, and over the following six trading days, the cumulative excess returns show a continuous upward trend until reaching a peak on the sixth day after the event. Although there are slight declines on days T=1 and T=5, the overall fluctuation remains at a low level. Additionally, based on the data provided in Table 1, Midea Group's actual return performance during the event period is as follows: from T=-3 to T=0, the overall return rate is negative and fluctuates significantly; however, after T=0, although the return rate still fluctuates, the overall trend is positive.
When examining the increase in cumulative excess returns, it is observed that from three days before the report date to one day before, the increase is relatively small, and there is even negative growth in cumulative excess returns on day T=-1. However, from T=1 to T=3, Midea Group's cumulative excess returns increase significantly, until the fourth day after the report date, when the increase begins to decline.
In conclusion, Midea Group's publication of a sustainable development report and ESG disclosure has received positive market responses in the short term, positively impacting its stock price. This phenomenon indicates investors' positive attitude towards Midea Group's ESG disclosure. Furthermore, it further reflects the guiding role of ESG information in capital market investment and the emphasis of the capital market on corporate social responsibility and environmental protection responsibilities.
5. Insights and Recommendations
The research conclusions on Midea Group's ESG disclosure status and its market response in this paper can provide some suggestions for household appliance companies.
Enhance the ESG Framework: To establish a sound environmental, social, and governance (ESG) framework, it is necessary to systematically promote the improvement of the corporate ESG reporting system and establish an efficient reporting process. Given the current disclosure framework, it is essential for companies to refer to internationally representative ESG frameworks to enhance transparency across all dimensions. When preparing reports, companies should avoid overly general and vague content, instead adding informative guidance and data indicators. Corporate social responsibility reports are crucial avenues for stakeholders to access ESG information. Therefore, during crises, companies should effectively fulfill relevant regulations and functions, disclosing ESG information in more detail. Additionally, enhancing corporate management and internal control capabilities can help reduce operational risks, laying a solid foundation for high-quality corporate development.
Prioritize Corporate Environmental Governance: In the household appliance industry, environmental protection is a crucial issue. The production and use of household appliances consume significant resources and energy and generate a large amount of waste and emissions, which have a certain impact on the environment. Therefore, household appliance companies need to actively take environmental protection measures to reduce their negative impact on the environment and enhance their sustainable development capabilities. Companies should actively promote energy conservation, environmental protection, and sustainable development concepts, showcasing environmental initiatives in product design, production processes, and material selection through ESG reports. Emphasizing energy conservation, emissions reduction, and carbon footprint management, companies should promote the research and application of energy-saving and emissions reduction technologies, managing carbon footprints to reduce environmental impact. Prioritizing environmental protection in the household appliance industry is not only a manifestation of corporate social responsibility but also crucial for corporate sustainable development.
Actively Prevent "Greenwashing" Phenomenon: Enhancing the transparency of ESG reports of listed companies is a top priority, as it concerns the authenticity and reliability of information, forming the basis for maintaining fairness and transparency in the capital market. It is recommended that independent third-party organizations conduct due diligence, comprehensively collect, record, and analyze relevant data, and issue legally effective independent verification reports to ensure investors and the public access accurate and comprehensive information. To curb "greenwashing" behavior, penalties for illegal actions should be increased, strict punitive standards should be established, and events involving "greenwashing" should be handled openly and transparently to uphold market fairness and justice.
6. Conclusion
This paper analyzes the response of the capital market to Midea Group's ESG report, using Midea Group as the research subject and employing the single-factor market model method for analysis. The following conclusions are drawn: Midea Group receives positive responses from the capital market shortly after disclosing ESG-related information. This indicates that through detailed disclosure of ESG information, companies can clearly convey to investors their outstanding performance in social responsibility and internal governance. This practice not only helps companies to obtain more development opportunities and potential benefits in the future but also promotes their achievement of robust and sustainable growth. By showcasing a positive and proactive corporate image to investors, companies can instill confidence in investors, attract more potential investors, and inject new vitality into their long-term development.
Looking ahead, ESG information disclosure is of significant importance for the sustainable development and long-term growth of companies. By actively practicing ESG principles and enhancing disclosure efforts, companies can not only convey positive signals to investors, enhancing their trust and confidence but also achieve stable and sustainable development, attracting more potential investors. This will inject new vitality into the long-term development of companies and create greater value and influence.
References
[1]. Min, Z. H., & Xiao, R. K. (2024). Current situation and improvement of ESG information disclosure in China. Financial Management Research, (02), 109-114.
[2]. Liu, J. Y. (2023). Research on market reaction to ESG information disclosure: A case study of Vanke Group. Modern Marketing (Bi-monthly), 2023, (06), 109-111.
[3]. Di, S. N. (2017). Evolutionary path of the impact of China's real estate bubble on the macro economy. Science and Technology Market, 2017(07), 84-85.
[4]. Lou, Q. R. (2023). ESG information disclosure: Legal reflection and institutional construction. Securities Market Herald, (03), 24-34.
[5]. Wang, R. (2022). Research on the relationship between ESG information disclosure and corporate value from the perspective of cost-benefit. Journal of Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, 29(04), 74-86. https://doi.org/10.16060/j.cnki.issn2095-8072.2022.04.005.
[6]. Wang, L. L., Lian, Y. H., & Dong, J. (2022). Study on the impact mechanism of ESG performance on corporate value. Securities Market Herald, (05), 23-34.
[7]. Wang, B., & Yang, M. J. (2022). Research on the impact mechanism of ESG performance on corporate value: Empirical evidence from listed companies in China's A-share market. Soft Science, 36(06), 78-84. https://doi.org/10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2022.06.11.
[8]. Bai, X., Zhu, Y. F., & Han, J. M. (2022). ESG performance, institutional investor preference, and corporate value. Statistical Research Forum, 37(10), 117-128.
[9]. Wang, W., & Jiang, G. F. (2004). Information disclosure, transparency, and capital cost. Economic Research, 2004(07), 107-114.
[10]. Qi, Y., Liao, K. Z., & Wang, Z. H. (2020). Market attention, governance effectiveness, and market response to social responsibility information disclosure. Journal of Management Sciences, 17(10), 1523-1534.
Cite this article
Yang,Y.;Li,X. (2024). Market Reaction to ESG Information Disclosure — A Case Study of Midea Group. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,122,6-13.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Min, Z. H., & Xiao, R. K. (2024). Current situation and improvement of ESG information disclosure in China. Financial Management Research, (02), 109-114.
[2]. Liu, J. Y. (2023). Research on market reaction to ESG information disclosure: A case study of Vanke Group. Modern Marketing (Bi-monthly), 2023, (06), 109-111.
[3]. Di, S. N. (2017). Evolutionary path of the impact of China's real estate bubble on the macro economy. Science and Technology Market, 2017(07), 84-85.
[4]. Lou, Q. R. (2023). ESG information disclosure: Legal reflection and institutional construction. Securities Market Herald, (03), 24-34.
[5]. Wang, R. (2022). Research on the relationship between ESG information disclosure and corporate value from the perspective of cost-benefit. Journal of Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, 29(04), 74-86. https://doi.org/10.16060/j.cnki.issn2095-8072.2022.04.005.
[6]. Wang, L. L., Lian, Y. H., & Dong, J. (2022). Study on the impact mechanism of ESG performance on corporate value. Securities Market Herald, (05), 23-34.
[7]. Wang, B., & Yang, M. J. (2022). Research on the impact mechanism of ESG performance on corporate value: Empirical evidence from listed companies in China's A-share market. Soft Science, 36(06), 78-84. https://doi.org/10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2022.06.11.
[8]. Bai, X., Zhu, Y. F., & Han, J. M. (2022). ESG performance, institutional investor preference, and corporate value. Statistical Research Forum, 37(10), 117-128.
[9]. Wang, W., & Jiang, G. F. (2004). Information disclosure, transparency, and capital cost. Economic Research, 2004(07), 107-114.
[10]. Qi, Y., Liao, K. Z., & Wang, Z. H. (2020). Market attention, governance effectiveness, and market response to social responsibility information disclosure. Journal of Management Sciences, 17(10), 1523-1534.









