1. Introduction
With the advance of globalization and digitalization and the in-depth promotion of sustainable development concept, the development of supply chain has been highly valued by enterprises. Globalization makes the supply chain more complex and diverse, and enterprises will face more global procurement, production and sales situations, which puts higher requirements on enterprises' transnational cooperation and supply chain coordination capabilities. The development of digital technology can become an effective tool to improve the operational efficiency of enterprise supply chain. At the same time, the development process of information technology of different enterprises will form differentiated market competitiveness. In addition, as the society attaches importance to sustainable development, the government will give more support to enterprises with social responsibility, and only enterprises that develop and operate in accordance with this concept can enjoy this special dividend. Huawei is committed to the green logistics system, optimize the transportation process and product design through information technology, by the end of 2020, the packaging of Mate series flagship models has reduced the paper use of about 550 tons per 10 million units, product packaging has used 100% environmentally friendly soybean graphite, and product suppliers have 100% established QC 080000 hazardous substances process management system. With the blessing of globalization and the concept of sustainable development, how to combine information technology tools to monitor and govern the entire supply chain, so that the sustainable performance of enterprises can be steadily developed and improved is an urgent problem for the senior management of contemporary Chinese enterprises.
Many scholars have studied the mechanism of influence of supply chain governance on performance through empirical methods such as structural equation model. For example, Hongtao Yang takes the automobile industry as the research object to study the impact of supply chain governance on corporate innovation performance. The research results show that relational governance can enhance the mutual trust between companies, make suppliers not easily terminate the cooperative relationship with existing partners, thus achieving a long-term and stable investment in enterprise operation and effectively improving the supply chain performance. The study of Van de Ven shows that clear and specific contracts are a strong guarantee for enterprises to conduct efficient transactions. Through the investment of special funds, the risk cost of supply chain transactions can be reduced, which is conducive to the formation of long-term cooperative relations and the reduction of partner search costs, so that enterprises can focus on their core obligations and improve the overall performance of the supply chain. The essence of supply chain governance is to conduct relationship governance among cooperative enterprises. Enterprises need to exert their collaborative ability, reduce information asymmetry through information and knowledge sharing, promote collaboration and communication, and formulate unified goals, so as to improve supply chain performance. It can be seen that Chinese and foreign scholars focus on the impact mechanism of supply chain governance on supply chain performance, but lack consideration of enterprise performance.
Therefore, this study integrates supply chain performance into the measurement of enterprise performance, and explores the relationship between supply chain governance and enterprise performance on the basis of previous studies. In addition, the impact of information sharing, trust and supply chain integration on enterprise performance has been verified. Then, can supply chain governance indirectly have a significant impact on enterprise performance through information sharing, supplier trust and supply chain integration? Can government support as an external variable provide impetus for supply chain governance? Based on the above analysis, this study takes information sharing, supplier trust and supply chain integration as intermediaries, government support as moderating factors, and enterprises in Sichuan Province as survey objects. 560 questionnaires are distributed in the form of questionnaires to empirically study the impact mechanism of supply chain governance on enterprise performance.
The innovation of this study lies in the following three points: Firstly, different from many researches on the impact of supply chain governance on supply chain performance, this paper only takes supply chain performance as a part of the overall performance of enterprises, and analyzes the impact of supply chain governance and enterprise performance in a more in-depth and comprehensive way, so as to provide more intuitive theoretical enlightenment for enterprises' practical operation. Secondly, government support, as an important part of enterprise management in contemporary Chinese market, has not been discussed much in the existing literature on supply chain governance. In this study, it is introduced as a moderating variable, so as to help enterprises have a deeper understanding of its importance. Thirdly, this study takes information sharing involving technical support, supplier trust involving interpersonal communication, and supply chain integration covering customer integration related to globalization and supplier integration related to sustainable development concept as intermediary variables, and fully considers the combination of times development factors and human and material resources.
The following parts of this paper are arranged as follows: The second part is literature review; The third part is the theoretical mechanism and research hypothesis; The fourth part is the research design; The fifth part is the discussion of the research results and management enlightenment; The sixth part is divided into research limitations and future prospects.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Supply Chain Governance
Supply chain governance refers to the core enterprise as the center, through the control of the key links of the supply chain, coordination and governance including suppliers, distributors, retailers, consumers and other members of the supply chain of the internal organization structure, so as to drive the smooth operation of the entire supply chain. According to the previous research results of Chinese and foreign scholars, supply chain governance can be studied and analyzed from three perspectives: structural perspective, behavioral perspective and institutional perspective. From the perspective of structure, Gereffi G. et. al argued that supply chain governance structure can be divided into five governance models, including market, restriction, module, level and relationship. Supply chain governance relies on transactions, gifts and other ways, and managers use contract governance and relationship governance to achieve balanced flow of resource benefits. Based on the behavioral perspective, scholar Hongtao Yang proposed that supply chain governance utilizes contract governance and relationship governance to coordinate conflicts among stakeholders, so as to promote the sustainable development of supply chain network. Based on the institutional perspective, Wathne divided supply chain governance into contract governance and relationship governance from the perspective of supply chain operation, and believed that supply chain governance is a formal and informal governance mechanism for coordinating nodal enterprise conflicts. Supply chain governance covers the relationship coordination among supply chain members and the use of contract signing to realize the behavior arrangement of supply chain stakeholders. This study agrees with Wathne's division of the dimensions of supply chain governance, that is, supply chain governance is divided into relational governance and contract governance. Contract governance mainly constrains the behavior of both parties through contracts and written provisions, while relationship governance focuses on the cultivation of interpersonal trust.
2.2. Information Sharing
Supply chain information sharing refers to the information exchange and transmission between different enterprises in a specific transaction process or cooperation process. In the process of information sharing, information dispersion, information inadequacy and information asymmetry are all hindering factors of supply chain coordination, which will result in bullwhip effect. A large number of studies have shown that information sharing is one of the important solutions to weaken bullwhip effect and help improve supply chain performance. At present, the classification of information shared in the supply chain is complex and the standards are different. Information sharing can be divided into three categories, namely transaction information, operational information and strategic information[1]. The information shared among supply chain members mainly includes: forecast information, order information, production status information and production plan information[2]. The information shared between manufacturers and suppliers in the computer industry can be divided into five types: inventory levels, sales data, order status tracking, sales forecasts, and production and delivery information[3]. Based on existing literature, this study classifies information sharing into the following five types: capacity information, production planning information, material or inventory level information, order processing information, and demand forecasting information.
2.3. Supplier Trust
Trust is a vital factor in the management of inter-enterprise relationship and plays an important role in the market transaction and cooperation. The definition of trust has different interpretations in different subject areas and is not unified at present. Trust between partners is based on the reliability and loyalty of both parties[4]. From the perspective of economics, trust, also known as situational trust, depends only on the environment, that is, the trust of both partners depends on whether the cooperative behavior with the other party is in line with their own interests. Under trading conditions, the trust formed based on the perception of the other party that the other party has credibility is quality trust. Many scholars have conducted in-depth research on quality trust. From the perspective of social psychology, Trust can be divided into emotional trust and cognitive trust[5]. The former is due to the close relationship and strong feelings between the two parties, while the latter is based on the trust generated by the cognition of the other party's behavior. Quality trust into three dimensions: competence, goodwill and loyalty[6]. In the field of management, reliability and goodwill can be used to measure trust when studying trust in supply-buying relationship[7,8]. In this study, supplier trust is divided into two dimensions: emotional trust and competence trust. The former emphasizes the close emotional connection and loyalty between the two parties, while the latter focuses on whether the skills of the trusted meet the expectations of the other party.
2.4. Supply Chain Integration
Supply chain integration is necessary to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve product quality and customer satisfaction. For the concept of supply chain integration, different scholars have different definitions. Supply chain integration means that supply chain partners and enterprises jointly manage internal and external processes, including products, services, information and funds, in order to provide maximum value to customers at low cost[9]. Supply chain integration is an efficient sharing behavior of logistics, information flow and capital flow[10]. Supply chain integration is the strategic collaboration between an enterprise and its supply chain partners to jointly manage internal and external processes in order to achieve an efficient "four-stream" model, and divided supply chain integration into three dimensions: supplier integration, internal integration and customer integration[11]. Internal integration refers to efficient management by adjusting internal strategy, business model and operation process. Customer integration and supplier integration respectively refer to the formation of strategic partnerships between enterprises and customers and suppliers, so that enterprises can control and cooperate in operation. This dimension has been widely recognized by scholars. This study will also adopt Flynn's definition of supply chain integration and measure it into supplier integration, customer integration and internal integration.
3. Theoretical mechanism and research hypothesis
3.1. The relationship between supply chain governance and information sharing
Supply chain governance can be divided into contract governance and relationship governance. Among them, contract governance is also known as formal governance and social control, and its remarkable characteristics are the formulation of documents and normative constraints. By clearly specifying the rights, obligations and responsibilities of all parties in the contract, such as order quantity and transaction period, the contract increases the willingness of cooperation between participants, thus facilitating information sharing and exchange between partners and promoting the stable development of production and operation. A stronger degree of joint information sharing is associated with greater use of contract governance[12]. Contract governance relies on both parties to clarify contract terms and update payment through negotiation, and ultimately form transaction information that is valuable to both companies[13]. Specifically, contract makers can share effective information by specifying entry and exit criteria, modifying quantities on contract terms to maintain flexible production, and promote positive interaction and long-term cooperation between partners.
Relational governance, also known as informal governance and social control, is based on trust. Relationship governance can significantly improve the level of information sharing and knowledge transfer, enabling information and knowledge to flow fully among partners. The higher the trust between enterprises in the supply chain node, the higher the level of information sharing, and the internal information system of the enterprise will update in real time according to the intensity and validity of information exchange. Based on the theory of social interaction, in the face of uncertain environment, the relationship governance with trust as the core is helpful to restrain the behavior of both sides of the transaction and reduce the incidence of opportunism. Both sides of the transaction will solve the problem jointly by sharing information and bear the loss jointly. The validity of relationship governance can be extreme due to the degree of trust. Therefore, it is particularly critical to maintain competence trust and emotional trust by improving technology and strengthening sincerity, so as to promote information sharing. It can be seen that the mandatory constraints of contract governance can provide institutional guarantee for the openness and transparency of the transaction process, thus promoting effective information sharing. Relationship governance is more humanized governance, and the degree of trust becomes an important measure of the level of information sharing. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H1: Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on information sharing
3.2. The relationship between supply chain governance and supplier trust
A perfect supply chain governance system can enhance the trust of enterprises in suppliers, and relationship governance is closely related to the emotional trust of suppliers. The closeness of the personal relationship can indirectly affect the knowledge transfer between dealers by promoting the development of interpersonal trust. The higher the corporate reputation of suppliers, the stronger the promotion of trust between suppliers and distributors. A good reputation of an enterprise represents the reliability of its supply chain governance, and distributors' trust in it will increase with the improvement of its reputation, thus enhancing cooperation confidence and reducing transaction costs of enterprise search. It can be seen that relationship governance, as an implicit consideration of priority cooperation between enterprises, plays a key role in building more stable supplier trust through company’s reputation impact, personal relationship density, and cooperation reputation accumulation. Good contract governance means the formulation of clear contract terms, which provides a basis for the establishment of trust, and also facilitates the supervision of the cooperation process between the two parties, thereby enhancing trust in the capabilities of suppliers. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H2: Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on supplier trust
3.3. The relationship between supply chain governance and supply chain integration
Different mechanisms of supply chain governance will affect the degree of supply chain integration. In the context of supply chain management, things such as information flow empowerment, mutual cooperation as a win-win concept, and creating value for customers as the core are conducive to improving the capital turnover efficiency of enterprises and solving low operational efficiency problem. At the same time, the effective implementation of integrated supply chain management can improve the rapid response ability of enterprises in market competition, and promote the reduction of operating costs and the enhancement of market competitiveness. In addition, when a good trust relationship and cooperation mechanism is established among supply chain members, that is, when relationship governance and contract governance are effectively implemented, a higher degree of supply chain integration is usually achieved.
Among the influence mechanism of supply chain governance on supply chain integration, there are few literature describing the direct impact of the two. Therefore, this study added the variable of government support for adjustment and observed the influence effect after adjustment. Government support, as an important representation of institutional environment, guides and promotes the healthy development of enterprises mainly through policy and technical capital support. The favorable policies issued by the government for the sustainable development of relevant enterprises can not only promote the effective integration of supply chain information, but also facilitate timely information sharing with suppliers and customers, which is beneficial to the information integration between enterprises and major suppliers and customers, forming participation in decision-making and joint problem solving. At the same time, by providing financial subsidies, technical support and service measures, the government can encourage enterprises to carry out efficient and orderly internal integration and improve the overall operational efficiency of the supply chain. According to signal theory, enterprises that receive government support will send out a more high-quality and credible signal, making it easier for enterprises to find partners to establish network relations and promote knowledge sharing. As a stakeholder of the external interests of enterprises, the support provided by the government can guarantee the supply chain governance in the uncertain market environment. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H3: Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on supply chain integration
H4: Government support plays a moderate role between supply chain governance and supply chain integration
3.4. The relationship between information sharing and firm performance
Information sharing is one of the important factors affecting enterprise performance. Effective information sharing can promote the communication and collaboration within the organization, promote the transfer and accumulation of knowledge, facilitate the innovation and improvement of the structure, and thus enhance the performance of the enterprise. Sharing order status information can shorten the payment cycle, improve the quality of customer service, and increase customer viscosity and order volume. On the technical level, the use of inter-organizational information systems is positively correlated with the operational performance of supply and demand parties. Sharing inventory information can avoid the extreme situation of excessive squeeze and excessive shortage to a certain extent, so as to improve inventory turnover and enterprise capital utilization efficiency. Both the degree and quality of information sharing have a positive impact on enterprise performance. The level of information sharing positively corresponds to the level of supply chain operation performance. Effective information sharing can help enterprises better understand the market demand and supply, timely adjust the production plan and inventory strategy, and achieve customized production and personalized service for customers, so as to improve the enterprise's anti-risk ability, market competitiveness and customer loyalty and satisfaction. Therefore, a more complete and efficient information sharing mechanism can propel the effective circulation of information, promote the progress of cooperation, and thus improve the cooperation performance of enterprises. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H5: Information sharing has a significant positive impact on enterprise performance
3.5. The relationship between supplier trust and firm performance
When a fine trust relationship is established between enterprises and suppliers, the transaction efficiency between them will be improved, so that the procurement cost of enterprises will be reduced and the profit rate will be improved. The stability and reliability of product quality will also be guaranteed, which is conducive to enhancing the reputation of the enterprise and customer satisfaction. At the same time, the degree of trust among supply chain partners has a significant positive impact on the operational performance of enterprises. In an uncertain market environment, trust is positively correlated with improved supply chain responsiveness. Benign trust relationship also helps enterprises and suppliers to carry out deeper cooperation and innovation, which can enhance the market competitiveness of enterprises, that is, trust between enterprises helps to improve cooperation performance. In addition, building trust can also help companies better manage supply chain risks and prevent potential supplier risks and supply chain instability. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H6: Supplier trust has a significant positive impact on enterprise performance
3.6. The relationship between supply chain integration and firm performance
Through supply chain integration, enterprises can reduce the cost of procurement, production, logistics and other links, can improve the efficiency of resource utilization, and thus enhancing the competitiveness and profitability of enterprises. Companies can also better manage supply chain risk and reduce uncertainty in the face of external shocks. Supply chain integration can help enterprises achieve the following financial indicators: reduce operating costs, improve return on assets and profit rate. Supplier integration optimizes enterprise production process through information sharing, and propels the reduction of industrial cost. Customer integration can facilitate positive interaction with customers and reduce risks caused by uncertain demand. In addition, supply chain integration helps to shorten the time of information and logistics circulation, so that enterprises can respond more quickly to changes in market demand. It is helpful to strengthen the control of product quality, enhance the brand value of enterprises, and consumers' trust and satisfaction with products. Therefore, effective supply chain integration is beneficial to optimizing enterprise production process, improving enterprise operation efficiency, reducing cost, enhancing competitiveness and brand trust, and thus driving steady growth of enterprise performance. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H7: Supply chain integration has a significant positive impact on enterprise performance
3.7. The relationship between supply chain governance and firm performance
Effective supply chain governance can not only optimize processes and resource utilization in the supply chain, in order to reduce costs and improve efficiency, but also helps to promote cooperative innovation of suppliers and rapid adjustment of supply chain, so that enterprises can adapt to market changes faster and better meet customer needs. Anin K E pointed out that relational governance has a positive impact on supply chain performance in both market and operation. Relationship governance can limit the limited rationality of managers of enterprises and reduce opportunistic behaviors to a certain extent, which can improve the performance of supply chain cooperation with long-term relationships. Formal contracts can provide detailed cooperation arrangements and renegotiation procedures brought about by uncertainty, so that the short-term performance of enterprises can be measured more accurately. The more detailed the contract terms are, the less opportunism is likely to occur in the transaction, and thus the overall supply chain performance is higher. Benign supply chain governance is beneficial to identify, evaluate and manage various risks in the supply chain, and to guarantee the stable operation of enterprises to a certain extent. It also make contributions to the common pursuit of sustainable development goals by all parties in the supply chain, and indirectly promote the long-term performance of enterprises. It can also improve customer satisfaction and enhance market competitiveness by controlling product quality, on-time delivery rate and other indicators. The improvement of supply chain performance has a great role in promoting the rise of enterprise performance. There is a close relationship between supply chain performance and enterprise performance. Supply chain affects enterprise operation efficiency, customer satisfaction and cost management to a large extent. Therefore, the effectiveness of supply chain governance has an important impact on the improvement of enterprise performance.
Supply chain governance can promote the formation of more open information sharing among enterprises through the mandatory constraint of contracts and the implicit governance of relationships, so as to facilitate the communication and cooperation of supply chain members, and the optimal implementation of schemes, thus improving the cooperation performance of enterprises. The increasing closeness of the relationship is in favour of the improvement of the supplier trust level, thus enhancing the supply chain response ability and the improvement of enterprise operation performance. In addition, from the perspective of integrated supply chain governance, supply chain integration helps to reduce operating costs and improve product quality, thus making contributions to the improvement of enterprise profit margins. In summary, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
H8: Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on enterprise performance
H9: Information sharing plays an intermediary role between supply chain governance and enterprise performance
H10: Supplier trust plays an intermediary role between supply chain governance and enterprise performance
H11: Supply chain integration plays an intermediary role between supply chain governance and enterprise performance
The theoretical framework of this study is as follows:
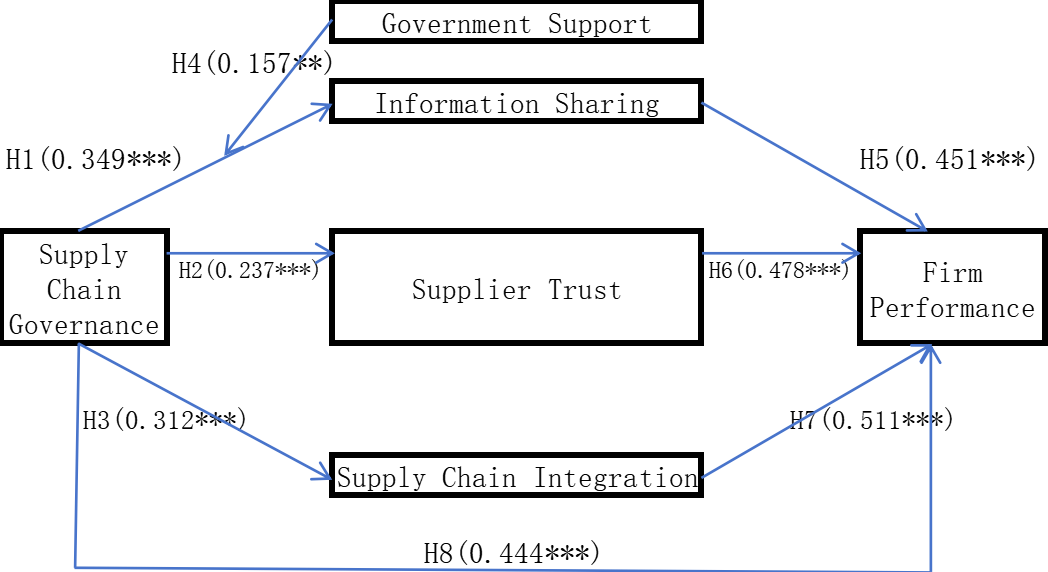
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework
4. Study Design
4.1. Questionnaire Design
The reliability and validity of the test scale in the questionnaire were guaranteed through literature collection and pretest. This study tried to adopt the mature scale that has been used at home and abroad, and made appropriate amendments according to the research purpose. Based on the literature, supply chain governance consists of 2 factors with 9 items; Information sharing includes 5 items; Supplier trust consists of 2 factors with 7 items; Supply chain integration consists of 3 factors with 15 items; Enterprise performance includes 6 items; Government support consists of four items. Likert 5-point scale is used to score the scale, and respondents made truthful evaluations according to the actual situation of the company from "1= strongly disagree" to "5= strongly agree".
4.2. Sample Data Collection
This paper selects a number of industrial cluster areas in Sichuan province to conduct formal questionnaire survey, the survey objects are mainly middle and senior management personnel in different parts of enterprises. The survey covers industries such as machinery manufacturing (23%), transportation (26%), wholesale and retail (39%), and biomedicine (21%). A total of 560 questionnaires were sent out. After deducting the incomplete questionnaires, 204 valid questionnaires were collected, and the effective questionnaire recovery rate was 36.43%.
4.3. Reliability, Validity Test and Correlation Analysis
In terms of reliability measurement, Cronbach's α coefficient was used in this study to detect the reliability of each variable. It is generally considered that α value greater than or equal to 0.7 is a high reliability value. The reliability of each variable in this study is shown in Table 1. Cronbach's α value of each variable is greater than 0.7, which indicates that the variables in this study have good reliability.
SPSSAU software was used for confirmative factor analysis. The factor load of each variable and item is above 0.5, as shown in Table 1, they all passed the T-test and the P-value reached a significant level, indicating that each variable had high convergence validity.
SPSS was further used to conduct correlation analysis on supply chain governance, information sharing, supplier trust, supply chain integration, enterprise performance and government support, and the results showed that there was a strong correlation among all variables.
Table 1: Reliability Test Table
Variable | Project | Standard Load Factor(Std. Estimate) | Cronbach's α |
Relational Governance | The two sides will mobilize resources to solve most problems and difficulties together(SCG1) | 0.78 | 0.835 |
Supply chain partners have never taken advantage of cooperation opportunities to profit at our company's expense(SCG2) | 0.68 | ||
Our company works with our partners to adapt our plans to the changing environment(SCG3) | 0.702 | ||
Our relationships with our partners are increasingly guided by informal rules and procedures(SCG4) | 0.705 | ||
The two sides enjoy close personnel exchanges and harmonious relations(SCG5) | 0.686 | ||
Contractual Governance | The contract spells out the rights and obligations of both parties(SCG6) | 0.714 | 0.784 |
Both parties sign a clear and standardized contract containing all details of business dealings(SCG7) | 0.647 | ||
A contract governs most aspects of our relationship and is the most powerful tool for binding both parties(SCG8) | 0.693 | ||
The contract clearly stipulates how to deal with accidents(SCG9) | 0.705 | ||
Information Sharing | We share production capacity information on relevant products with key supply chain partners(IS1) | 0.916 | 0.871 |
We share production planning information for related products with key supply chain partners(IS2) | 0.759 | ||
We share information on material or inventory levels for relevant products with key supply chain partners(IS3) | 0.728 | ||
We share order processing information for related products with key supply chain partners(IS4) | 0.693 | ||
We share demand forecast information for related products with key supply chain partners(IS5) | 0.719 | ||
Emotional Trust | Major suppliers take our interests into account when making major decisions(ST1) | 0.719 | 0.8 |
Even if the situation changes, we are confident that the major suppliers will be willing to help and support us(ST2) | 0.67 | ||
When we approached a major supplier with difficulties in meeting his requirements, we knew he would be understanding(ST3) | 0.721 | ||
In the future, major suppliers will take our expectations into account(ST4) | 0.719 | ||
Competence Trust | Major suppliers often keep their promises to our company(ST5) | 0.725 | 0.777 |
For the advice from our major suppliers, we believe that that is his best judgment(ST6) | 0.767 | ||
We can expect suppliers to be sincere(ST7) | 0.71 | ||
Suppliers Integration | Our company shares information with major suppliers(SCI1) | 0.768 | 0.824 |
Our company has established a rapid order system with major suppliers(SCI2) | 0.659 | ||
Key suppliers always share production plans with us(SCI3) | 0.697 | ||
Key suppliers always share stock levels with us(SCI4) | 0.72 | ||
Our company builds strategic partnerships with major suppliers(SCI5) | 0.639 | ||
Customer Integration | Our company gets a lot of market information from our clients and collaborates(SCI6) | 0.74 | 0.822 |
The degree to which our company communicates with its major customers(SCI7) | 0.676 | ||
Our company establishes rapid order system with major customers(SCI8) | 0.665 | ||
Key customers share sales timing information with us(SCI9) | 0.709 | ||
Our company tracks key customers to get feedback(SCI10) | 0.68 | ||
Internal Integration | Data and application integration across functional departments(SCI11) | 0.812 | 0.87 |
Implement integrated inventory management(SCI12) | 0.715 | ||
Take real-time logistics operation data monitoring query(SCI13) | 0.735 | ||
The company operates cross-functional teams on process transformation and new product development(SCI14) | 0.79 | ||
Departments coordinate planning to anticipate and solve problems(SCI15) | 0.736 | ||
Firm Performance | Our company maintains a high profit margin(EP1) | 0.891 | 0.885 |
Our company's supply chain performance remains at a high level(EP2) | 0.71 | ||
Our company's business processes are becoming more streamlined(EP3) | 0.717 | ||
The quality of our company's products is maintained at a high level(EP4) | 0.75 | ||
Our company maintains a high level of customer satisfaction(EP5) | 0.74 | ||
Our company is in a better competitive position than its peers(EP6) | 0.72 | ||
Government Support | The government provides policies and regulations in favor of the company(GS1) | 0.871 | 0.851 |
The government provides financial subsidies and tax breaks(GS2) | 0.682 | ||
The government provides necessary technical support and introduces technology and equipment(GS3) | 0.779 | ||
The government provides adequate service measures for the company(GS4) | 0.682 |
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Research Results
This study uses empirical methods to verify the relationships among supply chain governance, information sharing, supply chain integration, firm performance and government support in Chinese context. The empirical results show that supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on information sharing (p<0.001), that is, hypothesis H1 is supported. There is a significant positive relationship between supply chain governance and supplier trust (p<0.001), that is, assuming that H2 is supported. Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on supply chain integration (p<0.001), that is, assuming that H3 is supported. There is a significant positive relationship between information sharing and firm performance (p<0.001), that is, hypothesis H5 is supported. Supplier trust has a significant positive impact on firm performance (p<0.001), that is, assuming that H6 is supported. There is a significant positive relationship between supply chain integration and firm performance (p<0.001), that is, hypothesis H7 is supported. Supply chain governance has a significant positive impact on firm performance (p<0.001), that is, hypothesis H8 is supported. Information sharing, supplier trust and supply chain integration all play partial mediating roles between supply chain governance and firm performance (p<0.05), that is, assuming that H9, H10 and H11 are all supported. This study hypothesized that government support plays a positive moderate role between supply chain governance and supply chain integration, and proved it empirically (p<0.05), that is, hypothesis H4 is supported.
5.2. Research Conclusions
This paper takes enterprises in Sichuan Province as the research object, and discusses the influence mechanism of supply chain governance on enterprise performance. Through the empirical analysis of more than 200 valid questionnaires collected from some enterprises in Sichuan province, it is concluded that there is a positive relationship between supply chain governance and enterprise performance, in which information sharing, supplier trust and supply chain integration play a partial intermediary role, and the indirect impact of supply chain governance on enterprise performance through intermediary is greater than the direct impact. Government support plays a positive moderate role between supply chain governance and supply chain integration. This is a powerful supplement to the existing research system on the validity of supply chain governance, and makes up for the shortcomings of existing research to a certain extent. At the same time, it also provides necessary reference for enterprises with inefficient supply chain governance.
6. Implication and future prospect
6.1. Implication
Supply chain governance has an important impact on enterprise performance, and the mediating factors such as information sharing, supplier trust and supply chain integration, as well as the regulatory role of government support, cannot be ignored. The establishment of the research hypothesis has the following implications for enterprises and governments:
For enterprises, we should attach great importance to supply chain governance. First of all, contract governance should be strictly standardized, such as the development of clear governance processes and standards, distinct and consistent goals and responsibilities, clear rights and obligations of both parties, and formulate emergency response plans. By standardizing the contract terms, the communication between the two sides of the enterprise will be closer as the plan progresses, thus promoting the speed and quality of information sharing. The higher the frequency of information sharing, the threat of information asymmetry will be effectively reduced, the innovation ability of employees will continue to improve according to the market demand reflected by the information and improve the market competitiveness of the enterprise, the enhancement of employees' sense of belonging to the enterprise after receiving the information will make the improvement of work efficiency, and the precision of high-level decision-making will greatly benefit the improvement of enterprise management performance. Under the digital background, the establishment of a more efficient information platform can not only promote the validity of information sharing, but also monitor and evaluate the internal integration of enterprises to provide targeted guidance. The improvement of the supply chain integration process plays an important role in improving the management efficiency and operational efficiency of enterprises. In addition, a contract that sets out the rights and obligations of both parties and estimates the benefits of cooperation and the distribution of benefits can help suppliers who put profits first to build a stronger long-term trust in the company.
Secondly, efficient relationship governance should be innovated, such as promoting the personal relationship between executives and the interpersonal relationship between border personnel. A stable personal relationship between senior executives is conducive to the rapid improvement of trust with suppliers. On the premise of having a high degree of trust from suppliers, the quality of products and services can be urged to improve, which can enhance the competitiveness and long-term benefits of enterprises. Stable personal relationship cultivation lays the foundation for the subsequent formation of long-term stable partnership, and can also promote the integration of suppliers, providing a certain guarantee for the long-term benefits of enterprises. The cultivation of the relationship between ordinary employees and customers can help enterprises classify customers, position their value, and provide customized services for them, thus enhancing customer loyalty and corporate reputation, which in turn encourages employees to innovate and improve product and service quality, thus contributing to the improvement of business profits. The cultivation of the personal relationship between executives can help them get the internal information of the other company, and the idle chat with border personnel can also not be ignored. The gossip of the company, such as the change of reputation and development status, is often reflected in the status of ordinary employees. The acquisition of the above key information of the company can provide support or warning for the subsequent cooperation with the other party. This makes contributions to the scientific decision-making and management efficiency of enterprises.
For the government, by formulating relevant policies and regulations, it can ensure that all enterprises have equal opportunities to operate in the supply chain, can reduce the pressure on enterprises to conduct risk management, can help enterprises effectively use resources, and help enterprises to integrate suppliers and improve internal integration efficiency. In the case of the prevailing concept of sustainable development, government support can supervise and manage the supply chain, improve product quality and safety standards, provide further guarantee for the sustainable development of supply chain governance, and help improve customer satisfaction, thus promoting customer integration. Government support plays a supporting role in guiding enterprises to adopt more environmentally friendly and sustainable governance, which provides a good prerequisite for the integration of supply chain resources.
6.2. Research limitations and future prospects
There are still several shortcomings in this study: (1) The measurement of enterprise economic performance in this paper is based on questionnaire survey, which is subjective and lacks of persuasion. Future research data can be obtained through enterprise financial statements for comparative study and more objective and practical conclusions. (2) In this paper, information sharing is not divided in a deep level, and is limited to inventory level information and order processing information at the basic operation level, while important management level and strategic level are not considered. In the future, multi-level information sharing types can be considered to further verify its mediating role between supply chain governance and enterprise performance. (3) The object of this study is limited to enterprises in Sichuan, and the development status of cities in different regions of China is different, which limits the promotion of the conclusions of this study. In the future, it can be considered to expand the regional scope of enterprise research, so as to make the conclusions more universal.
References
[1]. Li J Q, Sikora R, Shaw M J, et al. A strategic analysis of inter organizational information sharing[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2006,42(1):251-2.
[2]. Gao J, Lee J D, Zhang Y. A dynamic model of interaction between reliance on automation and cooperation in multi-operator multi-automation situations[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2006,36 (5):511-526.
[3]. LEE H L,WHANG S. Information Sharing in a Supply Chain[J].International Journal of Technology Management, 2000, 20(3) :373-387.
[4]. Morgan R.M., Hunt S.D. The Commitment-Trust Theory of Relationship Marketing[J]. Journal of Marketing,1994,58(3): 20-38.
[5]. McAllister, Daniel J. “Affect - and Cognition - based Trust as Foundations for Interpersonal Cooperation in Organizations”, Academy of Management Journal, 1995,38 ( 1), pp. 24.
[6]. Mayer, R., Davis, J. and Schoorman, F. ”An Integrative Model of Organizational Trust”, Academy of Management Review, 1995,20 (3), pp.709~34.
[7]. Ganesan, S. “Determinants of Long- term Orientation in Buyer- Seller Relationships”, Journal of Marketing, 1994,58 ( April) , pp.1~8.
[8]. Doney, P. M. and Cannon, J. P. ”An Examination of the Nature of Trust in Buyer- Seller Relationships”, Journal of Marketing, 1997,61( April) , pp.35~51.
[9]. Zhao X, Huo B, Flynn B B, et al. The impact of power and relationship commitment on the integration between manufacturers and customers in a supply chain[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2008, 26(3): 368-388.
[10]. Devaraj S, Krajewski L, Wei J C. Impact of eBusiness technologies on operational performance: the role of production information integration in the supply chain[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2007, 25(6): 1199-1216.
[11]. Flynn B B, Huo B, Zhao X. The impact of supply chain integration on performance: A contingency and configuration approach[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2010, 28(1): 58-7
[12]. Eckerd S,Sweeney K. The role of dependence and information sharing on governance decisions regarding conflict[J].The International Journal of Logistics Management, 2018, 29(1):409-434.
[13]. Ferguson J R ,Paulin M ,Möslein K , et al. Relational governance, communication and the performance of biotechnology partnerships[J].Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 2005, 12(3):395-408.
Cite this article
Yuan,J. (2024). Study on the Indirect Effect Mechanism of Supply Chain Governance on Firm Performance. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,124,190-203.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Li J Q, Sikora R, Shaw M J, et al. A strategic analysis of inter organizational information sharing[J]. Decision Support Systems, 2006,42(1):251-2.
[2]. Gao J, Lee J D, Zhang Y. A dynamic model of interaction between reliance on automation and cooperation in multi-operator multi-automation situations[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2006,36 (5):511-526.
[3]. LEE H L,WHANG S. Information Sharing in a Supply Chain[J].International Journal of Technology Management, 2000, 20(3) :373-387.
[4]. Morgan R.M., Hunt S.D. The Commitment-Trust Theory of Relationship Marketing[J]. Journal of Marketing,1994,58(3): 20-38.
[5]. McAllister, Daniel J. “Affect - and Cognition - based Trust as Foundations for Interpersonal Cooperation in Organizations”, Academy of Management Journal, 1995,38 ( 1), pp. 24.
[6]. Mayer, R., Davis, J. and Schoorman, F. ”An Integrative Model of Organizational Trust”, Academy of Management Review, 1995,20 (3), pp.709~34.
[7]. Ganesan, S. “Determinants of Long- term Orientation in Buyer- Seller Relationships”, Journal of Marketing, 1994,58 ( April) , pp.1~8.
[8]. Doney, P. M. and Cannon, J. P. ”An Examination of the Nature of Trust in Buyer- Seller Relationships”, Journal of Marketing, 1997,61( April) , pp.35~51.
[9]. Zhao X, Huo B, Flynn B B, et al. The impact of power and relationship commitment on the integration between manufacturers and customers in a supply chain[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2008, 26(3): 368-388.
[10]. Devaraj S, Krajewski L, Wei J C. Impact of eBusiness technologies on operational performance: the role of production information integration in the supply chain[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2007, 25(6): 1199-1216.
[11]. Flynn B B, Huo B, Zhao X. The impact of supply chain integration on performance: A contingency and configuration approach[J]. Journal of Operations Management, 2010, 28(1): 58-7
[12]. Eckerd S,Sweeney K. The role of dependence and information sharing on governance decisions regarding conflict[J].The International Journal of Logistics Management, 2018, 29(1):409-434.
[13]. Ferguson J R ,Paulin M ,Möslein K , et al. Relational governance, communication and the performance of biotechnology partnerships[J].Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 2005, 12(3):395-408.









