1. Introduction
In recent years, data analysis technology has shown great potential and application value in modern school student management. Through the analysis of multidimensional data such as student behavior, academic performance and mental health, it provides scientific basis for educational administrators, so as to achieve more accurate and personalized management strategies. An important advantage of data analysis is to help schools build a "student portrait", provide individualized teaching support through in-depth understanding of students' learning habits, interests and academic needs, and improve education quality and student satisfaction [1]. In addition, data analysis technology also improves the efficiency and science of school management. By integrating students' study, life and behavior data, schools can monitor students' status in real time, quickly discover potential problems and adjust policies in time, so as to optimize the allocation of Educational resources [2]. At the same time, data analysis also provides new perspectives for educational decision-making, for example, through the analysis of students' behavior patterns at school, schools can reveal the key factors affecting students' academic performance and mental health. It provides data support for formulating Education policies [3]. These applications not only significantly enhance the school's management capabilities, but also promote the personalized development of students, enabling them to grow in a more balanced educational environment.
This study aims to comprehensively analyze the impact of students' lifestyle variables on academic performance (GPA) and mental health (stress level), and reveal the relationship between lifestyle variables and students' school experience and future development. Specifically, through in-depth analysis of students' daily behavior data, the study will explore the direct or indirect impact of variables such as study time, extracurricular activity time, sleep time, social time, and physical activity time on academic performance and mental health.
In addition, the study attempts to propose feasible, scientific school intervention strategies by discovering potential correlations between these variables. These strategies can not only help students improve their academic performance, but also effectively relieve psychological stress and promote physical and mental health, thereby optimizing the overall school experience for students. This study hopes to provide data-driven decision support for education administrators to help formulate more rational and efficient education policies and lay the foundation for students' all-round development and future growth.
2. Review of relevant works
In recent years, the application of data analysis techniques in modern school student management has become increasingly widespread, providing education decision-makers with an efficient evidence-based tool. Data analysis helps schools develop more scientific and accurate management strategies by comprehensively mining and quantifying the potential relationship between students' behavior patterns, academic performance and psychological states. First, in terms of academic intervention, data analysis can identify the key drivers of student academic performance and provide empirical support for the improvement of learning efficiency. Nonis & Hudson pointed out that by analyzing students' study time allocation and study efficiency, schools can develop personalized study support plans for students with poor academic performance, thus effectively improving their GPA [4]. At the same time, Carrell & West emphasized that data analysis can help schools optimize curriculum design and assignment arrangement, reduce students' academic burden, and avoid wasting learning time due to repetitive tasks [5]. This data-driven approach gives schools the flexibility to adjust the allocation of teaching resources for efficient management. In mental health management, data analysis provides quantifiable insight into a student's mental state. For example, Wheaton et al. showed that by analyzing students' rest and rest data, schools can optimize the class schedule and delay the morning start time, thereby improving students' sleep quality and mental health [6]. At the same time, Cain & Gradisar pointed out that by tracking and analyzing students' stress levels and sleep habits, schools can design appropriate interventions, such as reducing class load or introducing sleep education [7]. These data-based interventions significantly reduced students' psychological stress and improved overall well-being. In the management of extra-curricular activities and sports activities, data analysis helps to assess the actual effects of these activities on student development. Eccles & Barber found through data analysis that diversified extracurricular activities not only improved students' social skills and mental health, but also provided indirect support for their academic performance [8]. The study of Afonso et al. showed that regular physical activity significantly improved students' sleep quality and stress level [9]. By quantifying the frequency and effectiveness of students' participation in extracurricular activities and physical exercise, schools can more scientifically design and optimize the content of activities to ensure that they meet the needs of students' interests without incurring too much academic time. The application of data analysis in students' social behavior management shows its unique value. Ryan & Deci emphasized that analyzing the relationship between students' social time and academic performance can help schools find a balance between academic and social needs [10]. At the same time, Kalpidou et al. pointed out that by tracking students' social network data, schools can design activities that promote healthy social interaction and enhance students' overall well-being and social adaptability [11]. All in all, data analytics provides a powerful tool for modern schools by optimizing academic interventions, psychological support, extracurricular activity design, and social behavior management. This data-based approach to student management not only improves management efficiency, but also significantly improves students' academic performance, mental health and overall well-being, laying a solid foundation for their future development.
3. Research method
The research method in this paper follows the following three steps: determine the analysis target - process the data - data analysis
a. Determine the analysis objective: This step is mainly to determine the choice of independent and dependent variables. According to the data set, there is Student ID, Study Hours Per Day, Extracurricular Hours. Per Day Sleep Hours. Per Day, Social Hours Per. Day, Physical Activity Hours Per. Day, GPA, Stress Level These eight items Dependent variable: For school management, GPA and Stress Level are important indicators to measure students' school performance and psychological state. Therefore, these two fields are selected as dependent variables for focus analysis. Independent variables: The remaining six indicators (study time, extracurricular activity time, sleep time, etc.) represent student behavior patterns and lifestyle habits, and can also improve student performance through school intervention and policy changes. Therefore, these variables are regarded as independent variables and their influence on dependent variables is explored in subsequent analysis.
b. Processing data: In this step, the main task is to prepare the data for further analysis, and to clean and preprocess the data for analysis. The data for this dataset was collected by SUMIT KUMAR and made available on Kaggle in the form of "Student lifestyle dataset". This dataset uses a Google form survey that asks questions about daily study time, sleep patterns, extracurricular activities, physical exercise, social time, and stress levels. It is important to note that this dataset focuses on students in India and other South Asian countries. A total of 2,000 students participated in the survey, and the responses were collected in one academic year (August 2023 to May 2024).
The following data cleaning and preprocessing procedures were adopted:
Deduplication: Deletes duplicate data and abnormal data from a data set
Delete missing value: Deletes a record with missing data
Numerical presentation of stress levels: Since stress levels are expressed in the data set as low, medium and high, this is not conducive to subsequent data analysis in this report. Therefore, this report deals with the variable pressure level and expresses the pressure level in numerical form. In this report, low pressure, medium pressure and high pressure correspond to the three values of 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
Check data consistency: Make sure the units and ranges of each variable are correct. For example, unify time units into hours and check if the data range is reasonable (e.g., sleep time should be between 0-24 hours).
c. Data analysis: In this study, the ordinary least squares (OLS) regression model was used to analyze the relationship between independent variables and dependent variables, and to evaluate confidence intervals. Since the data set used does not have the concept of time, it is not possible to perform panel data operations such as random effects analysis or fixed effects analysis, so only the basic OLS regression model is used in this report. The specific operation is: OLS regression is performed in Python using statsmodels.api, and OLS regression is performed using all independent variables and two dependent variables respectively. Then use python to draw correlation heat maps and data distribution maps.
Table 1: GPA regression result
Variable | Coefficient | Standard Error | t-value | P-value | [0.025 | 0.975] |
constant | 0.0232 | 0.000 | 154.922 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.024 |
Study_Hours_Per_Day | 0.2371 | 0.003 | 96.302 | 0.000 | 0.232 | 0.242 |
Extracurricular_Hours_Per_Day | 0.0752 | 0.004 | 19.51 | 0.000 | 0.068 | 0.083 |
Sleep_Hours_Per_Day | -0.0781 | 0.002 | 32.396 | 0.000 | 0.073 | 0.083 |
Social_Hours_Per_Day | 0.084 | 0.003 | 33.187 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.089 |
Physical_Activity_Hours_Per_Day | 0.0827 | 0.002 | 52.546 | 0.000 | 0.080 | 0.086 |
Table 2:Stress Level
Variable | Coefficient | Standard Error | t-value | P-value | [0.025 | 0.975] |
constant | 0.0151 | 0.000 | 47.389 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.016 |
Study_Hours_Per_Day | 0.4111 | 0.005 | 47.389 | 0.000 | 0.401 | 0.421 |
Extracurricular_Hours_Per_Day | 0.0282 | 0.008 | 47.389 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.044 |
Sleep_Hours_Per_Day | -0.1299 | 0.005 | -25.245 | 0.000 | -0.140 | -0.120 |
Social_Hours_Per_Day | 0.0239 | 0.005 | 4.433 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.035 |
Physical_Activity_Hours_Per_Day | 0.0303 | 0.003 | 9.015 | 0.000 | 0.024 | 0.037 |
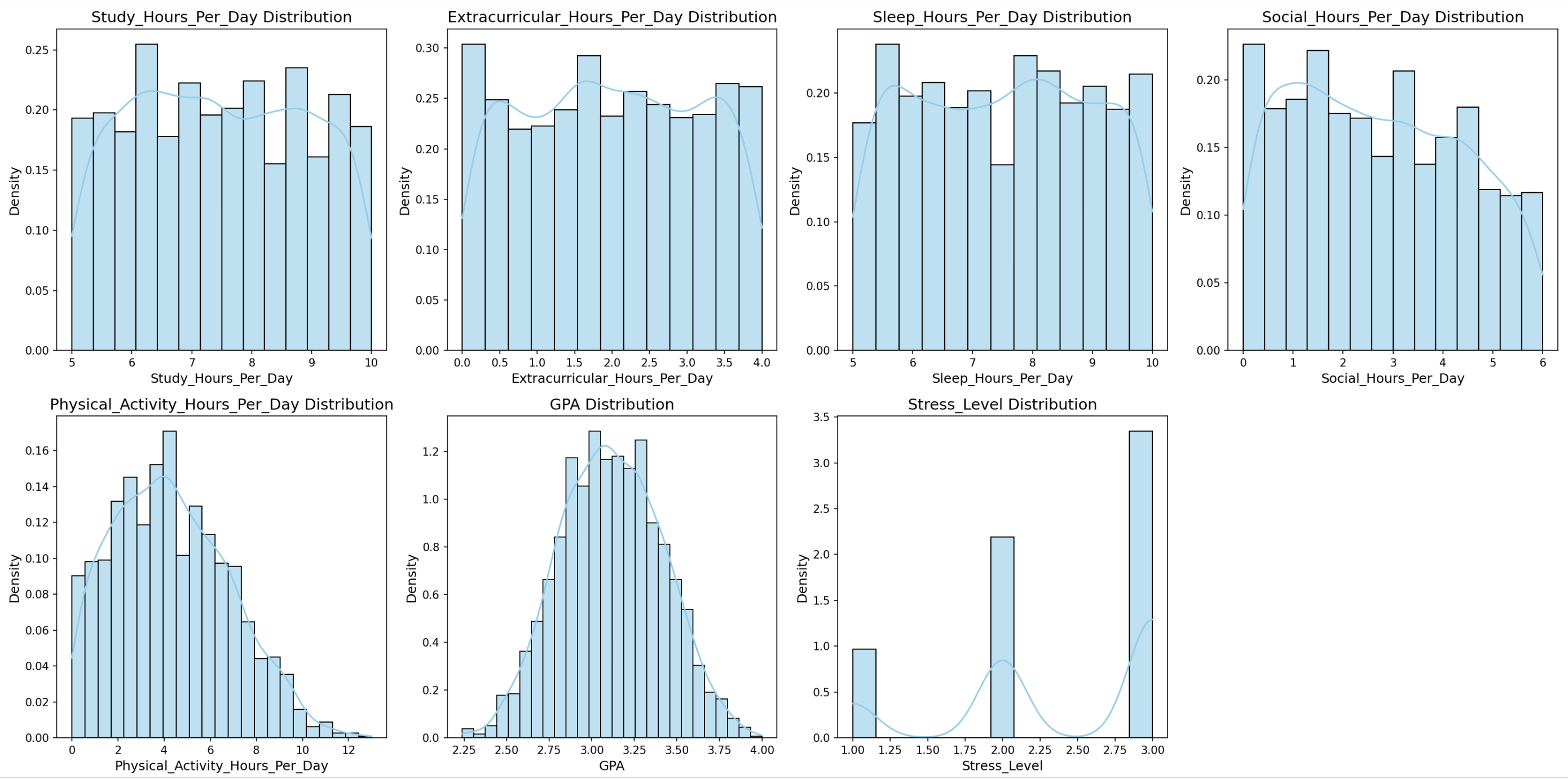
Figure 1: Distribution characteristics of students' lifestyle variables
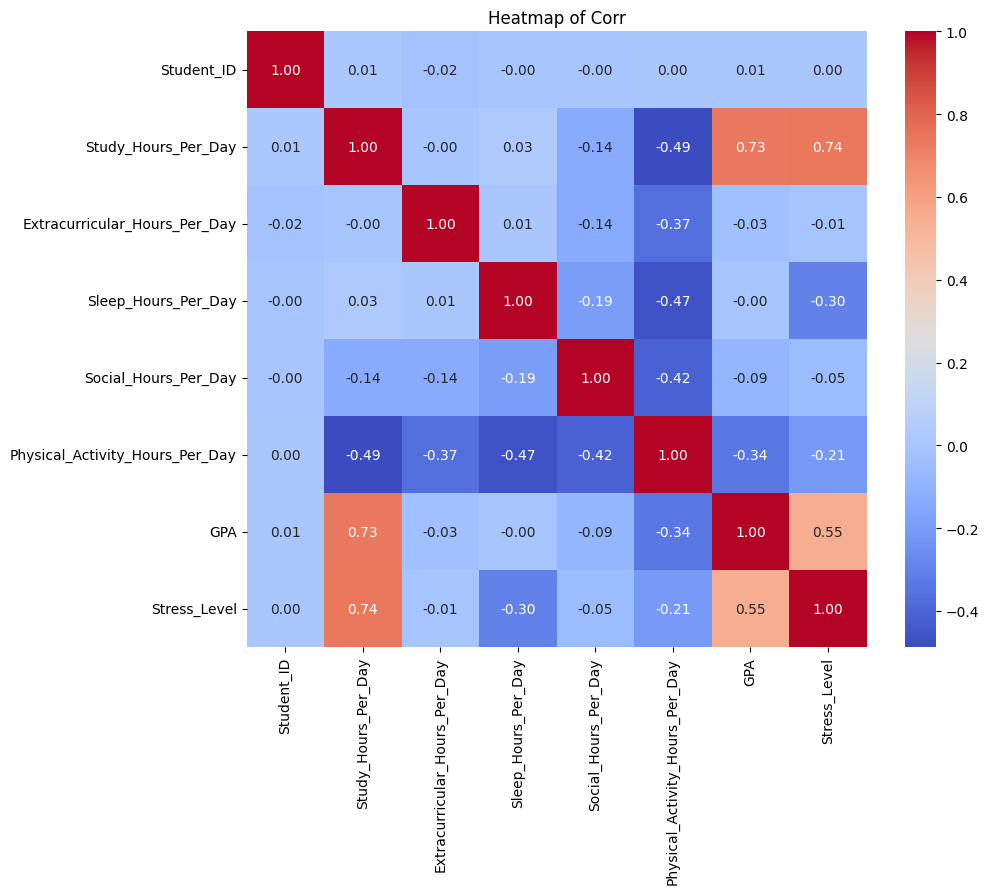
Figure 2: Heatmap of correlation
Result analysis and discussion:
Except the P-value of Extracurricular Hours Per Day on Stress Level, the P-value of all independent variables is 0, which indicates that all independent variables have a very significant impact on GPA and Stress Level. According to the correlation heat map, the correlation coefficient between studying time (Study Hours Per Day) and GPA is 0.73, while the correlation coefficient between learning time and Stress Level is 0.74. This indicates that there is a significant positive correlation between study time and GPA and stress levels, that is, increasing study time may improve GPA, but also lead to higher stress levels. However, excessive extension of study time is not the only way to improve academic performance and can have a negative impact on students' mental health. Therefore, schools should take a scientific approach to improve students' academic performance, pay attention to their mental health, optimize the school experience, and lay a solid foundation for students' future development. Academic pressure is an important factor affecting students' mental health, and excessive pressure may lead to anxiety, depression and other problems [12]. Therefore, schools should take measures to relieve students' academic pressure, such as psychological counseling or other decompression activities, while increasing students' academic hours to improve academic performance. There is a significant negative correlation between students' sleep time and their stress level, that is, the longer the sleep time, the lower the stress level.
Sleep time (Sleep Hours Per Day) has a weak negative correlation with stress level (correlation coefficient is -0.30), indicating that adequate sleep can effectively reduce students' stress level. while
The correlation between sleep duration and GPA was close to zero, suggesting that more sleep had no significant effect on academic performance, but had an important effect on mental health. This means that increasing sleep time helped lower students' stress levels, but had little effect on academic performance. Therefore, the report recommends that schools do more to ensure that students get enough sleep. Wheaton et al. found that delayed start time was associated with significant improvements in students' sleep duration and mental health [6]. Therefore, schools can appropriately delay the morning start time and adjust the start time to 8:30 am or later to meet the needs of teenagers' biological rhythms. Cain & Gradisar pointed out that reducing academic burden has a direct impact on extending students' sleep time [7]. Schools can appropriately reduce students' homework to relieve students' stress and help them get more sleep. However, it should be noted that the increase in study time can significantly improve students' GPA, so schools should balance the amount of work and student pressure.
Time spent in extracurricular activities (Extracurricular Hours Per Day) had a weak effect on GPA and stress levels, with a near zero correlation coefficient, suggesting that it may not have a direct effect on academic performance or mental health. Therefore, schools can appropriately reduce the time for extracurricular activities and increase the time for study to help students better improve their GPA. It is also possible to end the day earlier and allow students to go home earlier to complete homework and rest to reduce students' stress levels.
The correlation coefficient between physical activity time (Physical Activity Hours Per Day) and stress level is -0.21, indicating that moderate physical activity can help relieve stress, which is consistent with the conclusion reached by Afonso et al. [9]. That is, regular physical exercise can improve the quality of sleep and psychological state of teenagers. However, the correlation with GPA was -0.34, which may indicate that physical activity may distract from study time and thus affect academic performance. However, we note that time spent in physical activity has a greater impact on GPA than stress level. Studies have shown that moderate physical activity has a positive impact on students' cognitive function and mental health, but excessive exercise can increase physical and psychological stress, which in turn can negatively impact academic performance. Therefore, this report recommends that students should set a daily or weekly physical activity time according to their age and academic load to ensure that the amount of physical activity is moderate and avoid overtraining.
The association between Social Hours Per Day and GPA and stress levels was low (-0.09 and -0.05, respectively), indicating a small direct impact on overall student performance. But social interaction plays an important role in a student's overall well-being. Studies have shown that positive peer relationships can improve learning motivation and academic performance, while the improvement of social skills can improve students' mental health and social ability, which is very important for students' future development. Therefore, this report suggests that appropriate social time and opportunities should be given to students to help them develop better.
4. Conclusion
This study highlights the critical role of data analytics in modern school management and explores its application in optimizing student academic performance and mental health. Through a systematic analysis of variables such as study time, sleep patterns, extracurricular activities, physical exercise, and social behavior, the study revealed the impact of these factors on GPA and stress levels. With data analytics, schools are able to transfer evidence-based, personalized strategies to better meet the diverse needs of students. Data analysis helps schools identify hidden patterns and associations, providing a scientific basis for decisions about curriculum design, resource allocation, and support services. In addition, based on data-driven insights, schools are able to design interventions that both improve learning outcomes and enhance the overall well-being of students, thus ensuring a well-rounded educational experience for students. This study calls for a broader application of data analytics to address contemporary challenges in student development. By incorporating data analytics into daily practice, schools can not only improve operational efficiency, but also help students reach their full potential and lay a solid foundation for their future development. Although this study demonstrates the importance of data analysis in modern school management by analyzing the relationship between student lifestyle variables (such as study time, sleep patterns, extracurricular activities, physical exercise, and social behavior) and GPA and stress levels, there are certain limitations. First of all, the data sources of the study are mainly limited to specific regions and cultural backgrounds, and it may be difficult to fully reflect the behavior patterns of students in different education systems and social environments. Second, the variable coverage of this study is limited, and other possible factors such as family background, technology use and emotion management are not included, which may lead to insufficient comprehensiveness of the results. The research method in this report is mainly correlation analysis between variables, and fails to reveal causality, which limits the understanding of specific influencing mechanisms. At the same time, this report adopts the most basic OLS regression model, and there may be better and more suitable models that can be used to obtain more accurate results.
References
[1]. Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Professional\Common7\IDEPredicting Student Performance Using Data Mining and Learning Analytics: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 237. Retrieved from (mdpi.com)
[2]. Utilising Learning Analytics to Support Study Success in Higher Education: A Systematic Review. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68(4), 1961–1990. Retrieved from (link.springer.com)
[3]. Data Science for Analyzing and Improving Educational Processes. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 33(1), 1–20. Retrieved from (link.springer.com)
[4]. Nonis, S., & Hudson, G. I. (2010). Performance of college students: Impact of study time and other factors. Journal of Education for Business, 85(4), 229–238.
[5]. Carrell, S. E., & West, J. E. (2010). Does professor quality matter? Evidence from random assignment of students to professors. Journal of Political Economy, 118(3), 409–432.
[6]. Wheaton, A. G., Ferro, G. A., & Croft, J. B. (2016). School start times for middle school and high school students — United States, 2011–12 school year. Journal of School Health, 86(6), 452–457.
[7]. Cain, N., & Gradisar, M. (2010). Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Journal of Adolescence, 33(5), 795–807.
[8]. Eccles, J. S., & Barber, B. L. (1999). Student council, volunteering, basketball, or marching band: What kind of extracurricular involvement matters? Journal of Adolescent Research, 14(1), 10–43.
[9]. Afonso, R. F., et al. (2019). Mindfulness-based interventions for improving sleep quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 48, 101212.
[10]. Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68–78.
[11]. Kalpidou, M., Costin, D., & Morris, J. (2011). The relationship between Facebook and the well-being of undergraduate college students. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 14(4), 183–189.
[12]. Academic tress Interventions in High Schools: A Systematic Literature Review. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10578-024-01667-5
Cite this article
Pan,J. (2025). Data-driven School Management: An Analysis of Pathways to Enhancing Student Academic Performance and Mental Health. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,162,125-131.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Professional\Common7\IDEPredicting Student Performance Using Data Mining and Learning Analytics: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 237. Retrieved from (mdpi.com)
[2]. Utilising Learning Analytics to Support Study Success in Higher Education: A Systematic Review. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68(4), 1961–1990. Retrieved from (link.springer.com)
[3]. Data Science for Analyzing and Improving Educational Processes. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 33(1), 1–20. Retrieved from (link.springer.com)
[4]. Nonis, S., & Hudson, G. I. (2010). Performance of college students: Impact of study time and other factors. Journal of Education for Business, 85(4), 229–238.
[5]. Carrell, S. E., & West, J. E. (2010). Does professor quality matter? Evidence from random assignment of students to professors. Journal of Political Economy, 118(3), 409–432.
[6]. Wheaton, A. G., Ferro, G. A., & Croft, J. B. (2016). School start times for middle school and high school students — United States, 2011–12 school year. Journal of School Health, 86(6), 452–457.
[7]. Cain, N., & Gradisar, M. (2010). Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Journal of Adolescence, 33(5), 795–807.
[8]. Eccles, J. S., & Barber, B. L. (1999). Student council, volunteering, basketball, or marching band: What kind of extracurricular involvement matters? Journal of Adolescent Research, 14(1), 10–43.
[9]. Afonso, R. F., et al. (2019). Mindfulness-based interventions for improving sleep quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 48, 101212.
[10]. Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55(1), 68–78.
[11]. Kalpidou, M., Costin, D., & Morris, J. (2011). The relationship between Facebook and the well-being of undergraduate college students. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 14(4), 183–189.
[12]. Academic tress Interventions in High Schools: A Systematic Literature Review. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10578-024-01667-5









