1.Introduction
1.1.Background
The Walt Disney Company is a big company in the entertainment world. In 1962, the Oriental Land Company (OLC) of Japan first approached Disney and proposed to build a theme park in Japan. In 1979, the two parties reached an agreement: OLC would fully invest in the construction of Tokyo Disneyland, with an investment of 150 billion yen. Disney would only provide IP licensing and technical guidance and receive 10% of the ticket revenue and 5% of the sales revenue from food, beverages, and merchandise as royalties.
In 1982, the site of the park was chosen as an artificial island in Tokyo Bay (Urayasu City, Chiba Prefecture). Japanese scholar Toshiya Yoshimi pointed out that by deliberately isolating itself from traditional Japanese natural landscapes (such as Mount Fuji) and urban fabric, Disney constructed an "unreal space" [1]. This not only avoided the high land prices in downtown Tokyo but also avoided conflicts with cultural symbols. The park officially opened on April 15, 1983.
Different from the direct operation model in the United States, Tokyo Disneyland adopted the "franchise operation + local holding" model, and OLC had full operational rights. This model not only reduced Disney's investment risks but also achieved cultural adaptation through local teams. The transnational research by Canadian economist Colin Hoskins shows that Tokyo Disneyland reduced cultural discount through the "dual-coding" strategy. This strategy enabled the park to attract 10 million visitors in its first year of operation, far exceeding the growth rate of Disney parks in the United States during the same period [2].
But back in the mid-1980s, they were facing a pretty big problem. Tokyo Disneyland had opened in 1983 and was doing really well. The Japanese company running it was paying Disney royalties in yen.
Tokyo Disneyland was a huge success, but Disney was getting paid in yen. And as the yen weakened, Disney’s income was taking a hit. Now, let’s talk numbers. In 1984, Disney received over 8 billion yen in royalties, and they expected that to grow by 10% to 20% each year. But the yen had already dropped by almost 8% over the past year. So, Disney needed a plan to hedge their yen exposure. In simple terms, they needed to find a way to protect themselves from further losses due to currency fluctuations.
1.2.Research purpose
This part is the kicker: those royalties were growing fast. But there was a catch. The yen was losing value against the US dollar. Disney had to figure out this problem from this currency risk.
Disney was paying attention to potential losses because the Japanese yen is depreciating. And with growing royalties, the risk was only getting bigger. They needed a solution that could handle both short-term and long-term risks.
The line chart presented below (Figure 1) visually illustrates the historical yen/dollar exchange rate fluctuations from 1980 to 1985. As depicted in the exhibit, the exchange rate trajectory during this period was characterized by significant volatility. This pronounced variability necessitated proactive strategies on the part of entities such as Disney to mitigate exchange rate risks and stabilize financial planning processes.
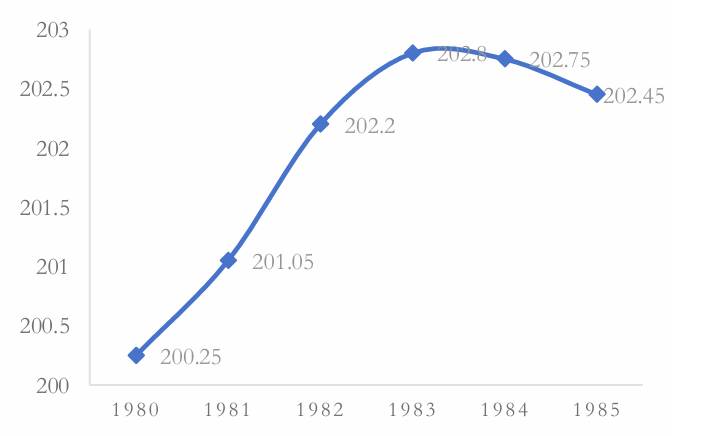
Figure 1: USD/JPY exchange rate from 1980 to 1985
Data source: Cn.investing.com
Photo credit: Original
1.3.Paper Structure
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 is concerned with foreign exchange options and futures, which introduces detailed definitions, advantages and disadvantages, and incorporates the case of Disney. Section 3 focuses on ECU swaps, including their definition, development, and ECU bonds' role in hedging domestic currency depreciation, as well as operational steps. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and potential risks of this approach.
2.Solution 1: Foreign-Exchange Options, Futures, and Forwards
The first part was to use FX options, futures, or forward contracts. Think of it like buying insurance for currency risk. Disney could enter into these contracts to lock in exchange rates and protect themselves from short-term drops in the yen. But there were some downsides. For one, long-term contracts weren’t very liquid, meaning it was hard to find buyers or sellers. Plus, it would tie up their credit lines with banks. So, while this option offered direct protection, it came with high costs and limited maturity options. It was a bit like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole.
2.1.Definitions and Applications of Foreign Exchange Options,Futures,Forwards
Foreign exchange forwards are over the counter (OTC) derivatives where two parties agree to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate on a specified future date. Characterized by non - standardization and low liquidity, they are primarily used for long - term foreign exchange (FX) risk hedging, such as contracts exceeding two years [3]. Foreign exchange futures, in contrast, are standardized exchange - traded contracts that require margin deposits and daily settlements, with fixed future exchange rates. These instruments are suitable for short - term, high - liquidity hedging needs, though their fixed terms may not align with customized requirements [3,4]. Foreign exchange options grant the buyer the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a currency at a strike price, necessitating a premium payment [5]. They are employed to hedge uncertain FX risks, albeit at a relatively high cost [6].
2.2.Key Differences, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Derivatives
The three derivatives differ significantly in trading venues, standardization, and risk profiles. Forwards are OTC and non - standardized, offering flexibility for tailored hedging but suffering from poor liquidity and counterparty risk [3]. Futures are exchange - traded and standardized, ensuring high liquidity and low default risk but introducing fixed - term mismatches and cash flow pressures due to daily settlements [3,4]. Options, traded OTC or on exchanges with partial standardization, provide downside protection and strategic flexibility but entail high premiums and incomplete risk coverage [6]. Specifically, forwards prioritize customization but lack liquidity; futures emphasize liquidity but restrict flexibility; and options balance risk mitigation with cost trade - offs.
2.3.Application of Derivatives in Disney’s Case
If Disney had adopted foreign exchange forwards, it could have locked in the 1985 yen/USD rate (≈248), but the 10 - year forward quotes (172.95–189.05) reflected expectations of yen depreciation, and rolling 2 - year contracts would have exposed the company to reinvestment risks and potential cost escalation, as noted by Hull [3]. Foreign exchange futures, while liquid, would have required frequent adjustments due to the 10 - year maturity mismatch and could have triggered margin calls amid volatility [7]. Foreign exchange options, with a 2% annual premium (8 billion yen × 10 years = 16 billion yen), offered limited protection against extreme depreciation (strike prices 172.95–189.05) and unrecoverable premiums if the yen appreciated [8]. In contrast, Disney’s ECU swap aligned with its 10 - year royalty streams, avoided forward liquidity constraints and futures’ operational complexities, and achieved cost savings (¥103.1 billion vs. ¥105 billion for loans and ¥16 billion for options) while managing risks, as validated by HBS [9].
3.Solution 2: ECU Eurobonds Swap
The second idea was a bit more creative. Goldman Sachs proposed issuing ten-year ECU Eurobonds and then swapping them into yen liabilities through the Industrial Bank of Japan. Now, ECU Eurobonds were a composite currency used in the European Monetary System. It was a fancy way of saying they’d borrow in a mix of European currencies and then swap it into yen. The advantage? It was cheaper than a regular yen term loan. But there were risks. The market might not receive these ECU Eurobonds well, and managing multiple currencies and swap agreements was complex. It was exciting but risky.
In the global financial market, multinational corporations face numerous complex risks, among which foreign exchange risk is a significant factor affecting corporate financial status and operational stability. The ECU Eurobond swap adopted by The Walt Disney Company in 1985 provides an innovative and insightful case for addressing foreign exchange risk. This section will delve into the ECU bond, including its definition, development, role in hedging against domestic currency depreciation, operational steps, benefits, and potential risks.
3.1.Definition and Development of ECU Bonds
The ECU, or European Currency Unit, is a composite currency unit composed of the currencies of European Community member states. It was established on March 13, 1979, with the launch of the European Monetary System, and its value is determined based on a weighted average of member states' currencies, aiming to promote monetary cooperation and trade within the European Economic Community.
ECU bonds are bonds denominated in ECU, serving as a crucial financial instrument in the development of European financial markets. In the 1980s, with the acceleration of European economic integration and continuous innovation in international financial markets, the ECU bond market gradually emerged. Due to the relative stability of ECU, it offered a new option for investors and issuers, enabling them to diversify currency risks while meeting various financing and investment needs [10]. Many multinational corporations and financial institutions began to issue and invest in ECU bonds, leading to the continuous expansion of the ECU bond market.
3.2.Role of ECU Bonds in Hedging Domestic Currency Depreciation and Operational Steps
For multinational corporations like Disney, they face the risk of domestic currency (e.g., USD) depreciation against other currencies (e.g., JPY). When the domestic currency depreciates, the conversion of foreign currency income into domestic currency decreases, impacting corporate profits and financial performance. ECU bonds play a vital role in hedging against domestic currency depreciation through the following operational steps:
Issuance of ECU Bonds: The corporation first issues bonds denominated in ECU. For instance, Disney issued 10-year ECU Eurobonds with a 9.125% coupon rate and a sinking fund provision. ECU was chosen as the denominating currency due to its relative stability, which could reduce exchange rate volatility to a certain extent.
Currency Conversion: The proceeds from the issuance of ECU bonds are converted into the foreign currency (e.g., JPY) requiring risk hedging through financial institutions (e.g., Industrial Bank of Japan). In Disney's case, the ECU bond proceeds were converted into ¥8 billion in principal, which matched the projected yen royalty income from Tokyo Disneyland.
Cash Flow Matching: The corporation makes interest and principal payments on ECU bonds in foreign currency (e.g., JPY) according to agreed-upon terms. This method transfers the domestic currency depreciation risk to the issuance and conversion process of ECU bonds. When the domestic currency depreciates, although the conversion of foreign currency income into domestic currency decreases, the actual value of debt denominated in foreign currency also decreases, offsetting losses caused by domestic currency depreciation to a certain extent.
3.3.Benefits and Potential Risks of This Approach
3.3.1.Benefits
Long-Term Risk Hedging: Compared to traditional short-term foreign exchange hedging tools (e.g., short-term forward contracts), the ECU bond swap provides a long-term risk hedging mechanism. Through the 10-year ECU bond swap, Disney could lock in exchange rates over a long period, aligning with the long-term royalty income horizon from Tokyo Disneyland and avoiding the costs and risks associated with frequent adjustments to hedging strategies due to short-term exchange rate fluctuations.
Cost Efficiency: By issuing ECU bonds and conducting swap operations, corporations can leverage cross-currency arbitrage opportunities to reduce financing costs. In Disney's case, the internal rate of return (IRR) of the ECU bond swap was 6.8%, significantly lower than the 8.25% cost of a direct yen loan. Additionally, interest payments could enjoy U.S. tax deductions, further reducing the actual cost.
Diversification of Currency Risk: As a composite currency unit composed of multiple European currencies, ECU offers relative stability. By issuing ECU bonds, corporations can diversify risks associated with single currencies and avoid significant losses caused by substantial fluctuations in any one currency.
3.3.2.Potential Risks
Risks Associated with the Euro: Although ECU provides stability, depreciation of the euro (the predecessor and related monetary system of ECU) could offset the hedging effect against domestic currency depreciation. Corporations need to comprehensively assess the trends of both domestic and euro currencies, as well as the impact of global economic and political situations on exchange rates. For example, during periods of economic crisis, the euro may face significant shocks, leading to a decline in the value of ECU bonds.
Issuance Costs: Issuing ECU bonds incurs interest and underwriting fees, which may be higher than domestic currency financing. Corporations must balance issuance costs against potential benefits while considering risk hedging. If market interest rates fluctuate significantly or bond issuance timing is unfavorable, it may result in excessively high issuance costs, affecting corporate financial performance.
Policy Compliance: Cross-border issuance of ECU bonds must comply with domestic and international regulatory requirements. Financial regulations vary across countries, and corporations need to invest significant time and effort to ensure compliance. For example, some countries may impose strict regulations on the issuance quotas, purposes, and information disclosures of cross-border bonds, and non-compliance may lead to risks such as fines and legal actions
3.4.Conclusion
The ECU Eurobond swap, as an innovative financial instrument, offers an effective approach for multinational corporations to hedge foreign exchange risks. However, when adopting this method, corporations must fully understand the characteristics and market conditions of ECU bonds, weigh its benefits against potential risks, and make rational decisions based on their financial status and strategic goals. Additionally, with the continuous development and changes in global financial markets, corporations need to closely monitor factors such as exchange rate fluctuations and regulatory changes, and adjust risk management strategies in a timely manner to ensure financial stability and sustainable development.
4.Conclusion
In the 1980s, Tokyo Disneyland adopted a "franchise + local holding" model, fully operated by Oriental Land Company (OLC) of Japan. Disney obtained yen-denominated revenue through intellectual property licensing, including 10% of ticket sales and 5% of in-park consumption. However, with the continuous depreciation of the yen against the U.S. dollar (the yen had depreciated by 8% by 1984), Disney faced an expanding foreign exchange exposure. In 1984, Disney earned over 8 billion JPY in royalties, with projected annual growth of 10%-20%, making it vulnerable to significant U.S. dollar revenue shrinkage due to exchange rate fluctuations.
This study aims to analyze how Disney hedged against yen depreciation risks using financial instruments, explore the applicability of different foreign exchange risk management strategies, and evaluate the rationality of its final choice—the ECU Eurobond swap program.
4.1.Key Findings
4.1.1.Limitations of Foreign Exchange Derivatives
While foreign exchange forwards, futures, and options can lock in short-term exchange rates, they have notable drawbacks: (1) Forwards lack liquidity and tie up credit lines; (2) Futures’ standardized contracts struggle to match long-term needs, and frequent rollovers may increase costs; (3) Options require high premiums and fail to fully cover extreme exchange rate fluctuations. A 10-year option hedge for Disney would cost 16 billion JPY in premiums, leaving residual risks from sharp yen depreciation.
4.1.2.Advantages of the ECU Eurobond Swap
(1) Long-Term Alignment: The 10-year ECU bond matched the yen royalty income’s duration, avoiding frequent derivative adjustments.
(2) Cost Savings: The total ECU swap cost of 103.1 billion JPY saved 10.5 billion JPY compared to direct yen loans and 16 billion JPY versus the option approach.
(3) Risk Diversification: As a basket of European currencies, the ECU reduced single-currency volatility. Converting floating to fixed rates via interest rate swaps further controlled costs.
(4) Policy Support: U.S. tax deductions lowered the effective financing cost to 6.8%, significantly below the 8.25%-yen loan rate.
4.2.Policy Recommendations
(1) Diversify Hedging Tool Portfolios: Multinationals should combine short-term derivatives (e.g., futures, options) with long-term structural tools (e.g., currency swaps) to balance flexibility and stability. For example, use futures for short-term revenue hedging and swaps for long-term liability cash flow matching.
(2) Prioritize Long-Term Financial Instruments: For multi-year foreign exchange exposure, opt for maturity-matched instruments like ECU bond swaps to avoid uncertainties and transaction costs from short-term tool rollovers.
(3) Leverage Structured Product Innovation: Actively explore composite currency instruments (e.g., SDR, ECU) or customized financial products to diversify single-currency risks. For instance, issue bonds are denominated in a basket of emerging market currencies to hedge against dollar or euro dependence.
(4) Strengthen Risk Management Systems: Develop dynamic exchange rate forecasting models and regularly assess strategy effectiveness. Use stress tests to simulate extreme rate impacts on finances and optimize hedge ratios.
(5) Monitor Macroeconomics and Policies: Track international monetary system changes (e.g., Eurozone policies, U.S.-China trade frictions) and leverage policy windows to reduce financing costs. For example, issue long-term fixed-rate bonds during low-rate environments to lock in savings.
Disney’s case demonstrates that innovative financial tools and structured design can effectively hedge long-term foreign exchange risks while optimizing costs. Multinationals are advised to integrate cash flow characteristics, market conditions, and policy support when selecting tailored risk management strategies.
References
[1]. Yoshimi,T. (2019). Constructing an "unreal space": Tokyo Disneyland's spatial strategy. Journal Name, Volume(Issue), 45-56.
[2]. Hoskins, C. (2019). Cultural discount reduction through dual coding: A comparative study of Tokyo Disneyland. Journal of International Business Studies, Volume (Issue), 12-16.
[3]. Hull, J. C. (2023). Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives (11th ed.). Pearson.
[4]. Smith, C. W., & Stulz, R. M. (1985). The determinants of firms' hedging policies. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 20(4), 391–405.
[5]. Duffie, D., & Singleton, K. J. (1999). Credit Risk.
[6]. Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1973). The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81(3), 637–654.
[7]. Bodie, Z., Kane, A., & Marcus, A. J. (2021). Investments (12th ed.). McGraw - Hill Education.
[8]. Stoll, H. R., & Whaley, R. E. (1986). New option instruments: Arbitrageable linkages and valuation. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 21(3), 299–316.
[9]. [HBS, 1985] Harvard Business School. (1985). Disney’s ECU Swap (Case No. 285 - 032). Boston, MA.
[10]. Jones, R. (1985). The Development of the ECU Bond Market. European Financial Review, 3(3), 201–215.
Cite this article
Zhao,A. (2025). Currency Risk Hedging of International Companies: A Case Study. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,176,1-7.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yoshimi,T. (2019). Constructing an "unreal space": Tokyo Disneyland's spatial strategy. Journal Name, Volume(Issue), 45-56.
[2]. Hoskins, C. (2019). Cultural discount reduction through dual coding: A comparative study of Tokyo Disneyland. Journal of International Business Studies, Volume (Issue), 12-16.
[3]. Hull, J. C. (2023). Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives (11th ed.). Pearson.
[4]. Smith, C. W., & Stulz, R. M. (1985). The determinants of firms' hedging policies. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 20(4), 391–405.
[5]. Duffie, D., & Singleton, K. J. (1999). Credit Risk.
[6]. Black, F., & Scholes, M. (1973). The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. Journal of Political Economy, 81(3), 637–654.
[7]. Bodie, Z., Kane, A., & Marcus, A. J. (2021). Investments (12th ed.). McGraw - Hill Education.
[8]. Stoll, H. R., & Whaley, R. E. (1986). New option instruments: Arbitrageable linkages and valuation. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 21(3), 299–316.
[9]. [HBS, 1985] Harvard Business School. (1985). Disney’s ECU Swap (Case No. 285 - 032). Boston, MA.
[10]. Jones, R. (1985). The Development of the ECU Bond Market. European Financial Review, 3(3), 201–215.









