1. Introduction
The global supply chain of agricultural products is facing unprecedented challenges. According to the data of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the global food waste is as high as 1.3 billion tons every year, accounting for one third of the global food production [1]. This not only caused huge losses in economy, but also had a serious negative impact on the environment. In addition, the agricultural supply chain suffers from issues such as information asymmetry, lack of transparency and food safety. For example, FAO report points out that about 600 million people get sick every year, of which 420 thousand die, because of eating contaminated food [2]. The source lies in the limitation of traditional supply chain management, failing to effectively track and monitor the circulation process of agricultural products.
Blockchain technology, a decentralized and tamper-proof distributed ledger, has been widely concerned in agricultural product supply chain. Researches shows that it significantly improves the transparency and traceability of the supply chain, effectively reducing food waste and safety problems [3]. For example, the IBM Food Trust platform uses blockchain to successfully trace the whole process from farm to table, significantly improving the efficiency and trust of the supply chain. In addition, blockchain technology can also automatically execute various transactions and contracts in the supply chain through smart contracts, reducing human intervention and errors.
However, most existing researches focus on the advantages of the technology itself, ignoring the strategic trade-off under cost constraints. Implementing blockchain involves high initial investment and continuous maintenance costs, posing challenges for many small and medium-sized enterprises. Therefore, determining the optimal supply chain strategy under cost constraints is a critical research gap. In addition, different supply chain structures, such as centralized, distributed and hybrid, have different cost sensitivities to blockchain technology. However, existing researches lack the differential cost sensitivity analysis of different supply chain structures.
Based on this, this study discusses the strategic trade-offs under different cost constraints, aiming at filling the gaps in the existing research. Through in-depth analysis of the dynamic influence of blockchain technology cost on the strategic choice of agricultural product supply chain, this study provides a new perspective for related theories and practical strategic suggestions for enterprises in agricultural product supply chain.
2. Literature Review
In recent years, the application of blockchain technology in the traceability system of agricultural product supply chain has been widely concerned. A notable example is IBM Food Trust platform, which utilizes blockchain to achieve comprehensive traceability from farm to table, greatly enhancing supply chain transparency [4]. Researches show that the blockchain traceability systems effectively reduce food waste problems and enhance consumers' trust in the supply chain [5]. For example, consumers can obtain detailed information on the production, processing and transportation of agricultural products in real time, thus ensuring the safety and quality of food [6]. The non-tampering of blockchain technology guarantees the authenticity of data in the supply chain and further improves the reliability of traceability system [7].
As one of the core functions of blockchain technology, smart contract has made remarkable progress in the application research of agricultural product supply chain in recent years. Blockchain smart contracts connect multiple parties in the supply chain, such as manufacturers, distributors, retailers, etc. (as shown in Figure 1). Smart contracts significantly reduce the transaction time and cost in the supply chain of agricultural products by automatically executing the transaction terms [8]. For example, in agricultural products auctions and wholesale transactions, smart contracts can automatically complete payment and logistics arrangements, reducing human intervention and errors [9]. The application of smart contract in cross-border agricultural trade can significantly reduce the incidence of transaction disputes and improve the overall efficiency of supply chain [10].
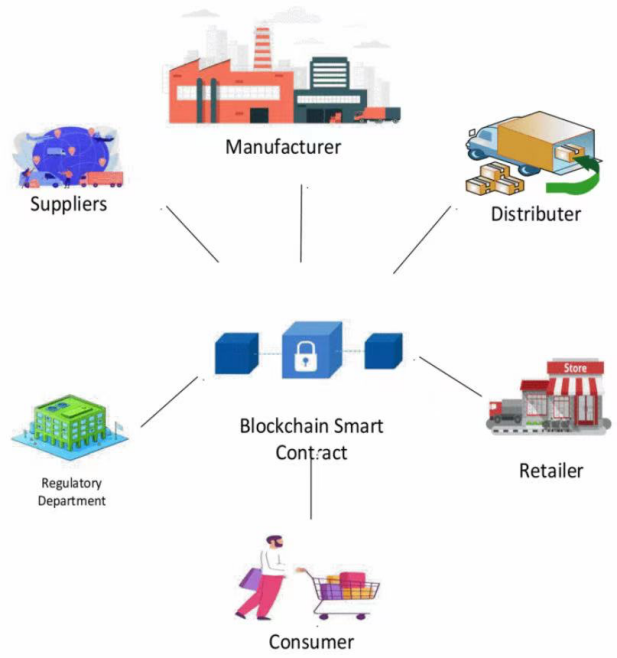
Figure 1: Intelligent Contract Supply Chain Based on Blockchain [11]
Regarding the dynamic mechanism of cost and strategy, blockchain technology has different technical cost structures, leading to different supply chain strategies. Enterprises will implement initial, medium-term and long-term strategies according to technical costs. Different strategies will consume different costs and enterprises will optimize according to their cost consumption. There is a dynamic correlation mechanism between enterprise cost variables and strategy selection.
Despite significant advancements in researching blockchain technology in agricultural product supply chains, important gaps persist. The dynamic correlation mechanism between cost variables and strategy selection has not been quantified. The existing research mostly focuses on technical functions, but ignores the strategic trade-off under cost constraints.
3. Case Study
Carrefour, founded in France in 1959, opened its first mass-market store in 1963 and merged into the first retail group in Europe and the second largest in the world in 1999 in Promodes. To enhance supply chain transparency and consumer trust, Carrefour introduced the IBM Food Trust blockchain platform in 2018, initially applied to its "Carrefour Quality Certification" chicken products. Then it extended to organic eggs, salmon, milk and other categories, allowing consumers to trace product data from farm to shelf by scanning code.
3.1. Technical Cost
The cost of the enterprise blockchain technology includes two parts: initial investment and operating cost. The initial investment includes access fees for the IBM Food Trust platform, ranging from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per year, depending on the access node size. Meanwhile, the enterprise face data integration costs for connecting the data of farms, processing plants, logistics and other links into the blockchain, which account for about 30% of the total investment. The initial investment also includes hardware and equipment costs. The farm side needs to be equipped with IoT sensors to upload data in real time, as well as training costs, such as training suppliers and employees to use the blockchain system. The second part is the operating cost. Each participating node of blockchain technology needs to pay an annual fee, which is the node maintenance fee. After the application of blockchain technology, its distributed storage and consensus mechanism will bring higher computing cost. Compliance costs also arise to ensure that the data complies with privacy regulations such as GDPR of the European Union.
Strategy selection is driven by technology cost structure. The high initial investment leads to significant fixed costs, prompting enterprises to pilot on a small scale to mitigate risks [12]. For example, Carrefour initially only selected chicken products for pilot projects to control costs and reduce risks. The marginal cost of blockchain technology is decreasing in the later stage. With the expansion of technology application scope, the marginal cost of new nodes is significantly reduced, such as API interface reuse and platform license fee sharing. For example, Carrefour expanded the blockchain to organic eggs, salmon and other categories in the medium term. What’s more, it reused the existing technical framework, reducing the unit product cost.
3.2. Supply Chain Strategy
The supply chain strategy can be divided into three stages: initial stage, medium stage and long stage. The initial strategy is a small-scale pilot to verify the cost-effectiveness. At this stage, the enterprise verifies whether the blockchain can enhance consumer trust in a single category of chicken, expecting to reduce the cost of quality disputes and achieve cost constraints. The initial investment is concentrated on the core suppliers with close cooperation, limiting the number of nodes to control expenses. Following this strategy, the traceability of blockchain shortens the response time of supply chain by 40% and increases the scanning rate of consumers by 25%, with sales growth helping to cover technical costs. The medium-term strategy is to expand the application scope and share the fixed cost. The goal is to expand the blockchain to more high value-added categories like organic eggs and salmon. It reused the existing IBM platform framework, reducing the marginal cost of new categories. Also, the reuse rate of API interface is over 60%, realizing cost optimization. At the same time, the company made strategic adjustments, requiring new suppliers to access the blockchain system; otherwise the cooperation will be cancelled and the upstream technology of the supply chain will be upgraded. The long-term strategy is to drive the whole chain integration with the reduction of technology cost, with the intention of deeply combining blockchain with AI and IoT to realize the predictive management of supply chain. With the maturity of technology, the cost of blockchain operation and maintenance has dropped by 12% annually, which is the scale effect of IBM Food Trust. At this stage, enterprises upgrade their strategies and attract more ecological partners through blockchain data sharing. For example, insurance companies develop agricultural insurance products based on trusted data.
3.3. Cost Optimization
Strategy selection promotes cost optimization. In the pilot stage, which is the initial stage, enterprises verify the actual benefits of blockchain technology through pilot projects, such as enhancing consumer trust and reducing the cost of quality disputes. After Carrefour's pilot, it was found that blockchain shortened the response time of supply chain by 40% and increased the scanning rate of consumers by 25%, which verified the feasibility of the technology. In the expansion stage, which is the middle stage, enterprises force more suppliers to access the blockchain system and promote the upstream technology upgrade of the supply chain. Carrefour dilutes fixed costs through large-scale application, and eliminates suppliers with backward technology to enhance the concentration of supply chain. In the ecological stage, which is the long term, enterprises open the blockchain data ecology, attract more partners to join, and further share the technology cost. Carrefour upgraded the blockchain from a "traceability tool" to a "supply chain intelligent hub" through data sharing and cross-border cooperation.
3.4. Dynamic Cycle
The dynamic association mechanism has a positive cycle. The initial high fixed cost drives enterprises to choose a small-scale pilot strategy to verify the technical effect. With the maturity of technology and cost reduction, enterprises gradually expand the scope of application and promote the upgrading of supply chain strategy. At the same time, large-scale application and ecological synergy significantly reduce the unit product cost. Carrefour reduces the blockchain operation and maintenance cost by 12% annually by reusing the technical framework and attracting ecological partners. In addition, the cost reduction makes enterprises more motivated to expand the application scope of blockchain and form a positive cycle. Carrefour finally transformed the blockchain technology from the cost center to the core competitiveness of supply chain value-added. With the promotion of strategy, enterprises further dilute the technology cost through large-scale application and ecological synergy, forming a positive cycle of "technology investment → strategy upgrade → cost optimization → larger-scale investment".
4. Enlightenment
4.1. Enterprise Management
Enterprises should adopt a small-scale pilot strategy in the initial stage to verify the actual benefits of blockchain technology while managing the risks associated with high fixed costs. Through the pilot, enterprises can evaluate the feasibility and lay the foundation for the subsequent expansion strategy. With the maturity of technology and the decline of cost, enterprises should gradually expand the application scope of blockchain technology and dilute the technical cost through large-scale application and ecological synergy. Enterprises can force suppliers to access the blockchain system, promote the upstream technology upgrade of the supply chain and enhance the concentration of the supply chain. Enterprises should open the blockchain data ecosystem, attract more partners to join, and further share the technology costs. Through data sharing and cross-border cooperation, enterprises can upgrade the blockchain from a "traceability tool" to a "supply chain intelligent hub" to enhance the overall efficiency and competitiveness of the supply chain.
4.2. Policy Formulation
The government should set up a blockchain technology pilot fund to provide financial support for small and medium-sized enterprises. They should encourage them to try blockchain technology in the supply chain and provide tax incentives and subsidies to enterprises participating in the pilot to reduce the initial technology input cost. In addition, it is also possible to formulate blockchain data interface standards and promote data interoperability between different supply chain nodes. Also, they can encourage industry associations or technology alliances to develop open source blockchain frameworks and lower the threshold for enterprise technology access. The government should also establish a supply chain blockchain cooperation platform, promote the technical cooperation between core enterprises and upstream and downstream suppliers, and then provide financing support and technical training for suppliers actively participating in blockchain application.
5. Conclusion
By studying the case of Carrefour’s agricultural product supply chain, this study discusses the dynamic influence of blockchain technology cost on the strategic choice. The research results show that the cost structure of blockchain directly affects the enterprise strategy. In the initial stage, enterprises tend to experiment in a small scale to verify the technical effect. As technology matures and costs decline, the application scope is gradually expanded. The technical cost is further diluted through large-scale application and ecological synergy. The Carrefour case shows that blockchain technology not only improves the transparency and traceability of supply chain, but also optimizes supply chain management through intelligent contract and data analysis. Finally, it transforms blockchain technology from cost center to core competitiveness of supply chain value-added, providing a theoretical basis for enterprises to choose the optimal supply chain strategy under cost constraints. In addition, this study puts forward a positive feedback mechanism of "technology investment → strategy upgrade → cost optimization → larger-scale investment", explaining how enterprises optimize technology costs through strategy adjustment and offering a theoretical framework for the wide application of blockchain technology in supply chain.
However, this study still has some limitations. The case data of this study mainly come from Carrefour's public reports and existing research materials, lacking the support of first-hand data. In the future, more first-hand data can be obtained through field research and interviews to further verify the research conclusions.
Looking ahead, future technological progress may further reduce the technical cost and change the strategic choice of enterprises. Future research can continuously track the development of blockchain technology and update the cost-benefit analysis model. The policy environment has an important impact on the application of blockchain technology. It can also explore the adoption strategies of blockchain technology under different policy environments and provide more targeted suggestions for policy makers.
References
[1]. FAO. (2020). The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020. Rome: FAO. https://www.fao.org/family-farming/detail/en/c/1308354/
[2]. FAO. (2011). Global Food Losses and Food Waste. Rome: FAO. https://www.fao.org/4/mb060e/mb060e00.htm
[3]. IBM. (2019). From seed to shelf: How IBM innovations will transform every stage of the food supply chain within the next five years. Armonk, NY: IBM. https://research.ibm.com/blog/ibm-research-5-in-5-2019-food?mhsrc=ibmsearch_a&mhq=transforming%20the%20food%20supply%20chain
[4]. IBM. (2023). World Food Safety Day: How blockchain helps serve safer salads. Armonk, NY: IBM. https://www.ibm.com/blog/world-food-safety-day-how-blockchain-helps-serve-safer-salads/?mhsrc=ibmsearch_a&mhq=food%20supply%20chain
[5]. Zheng, Y., Xu, Y., & Qiu, Z. (2023). Blockchain Traceability Adoption in Agricultural Supply Chain Coordination: An Evolutionary Game Analysis. Agriculture, 13(1), 184.
[6]. Demestichas, K., Peppes, N., Alexakis, T., & Adamopoulou, E. (2020). Blockchain in Agriculture Traceability Systems: A Review. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4113.
[7]. Mwewa, T.., Lungu, G., Turyasingura, B. ., Umer, Y. ., & Chavula, P. (2024). Blockchain Technology: A Review Study on Improving Efficiency and Transparency in Agricultural Supply Chains. Jurnal Galaksi, 1(3), 178–190.
[8]. Daraghmi, E., Jayousi, S., Daraghmi, Y., Daraghmi, R., & Fouchal, H. (2024). Smart Contracts for Managing the Agricultural Supply Chain: A Practical Case Study. Ieee Access.
[9]. Bayramova, A., Edwards, D. J., & Roberts, C. (2021). The Role of Blockchain Technology in Augmenting Supply Chain Resilience to Cybercrime. Buildings, 11(7), 283.
[10]. Chang, Y., Iakovou, E., & Shi, W. (2019). Blockchain in global supply chains and cross border trade: a critical synthesis of the state-of-the-art, challenges and opportunities. International Journal of Production Research, 58(7), 2082–2099.
[11]. Eletter, S. F., Elrefae, G. A., Yasmin, T., Qasem, A., Alshehadeh, A. R., & Belarbi, A. (2022, November). Leveraging Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts in the Management of Supply Chain: Evidence from Carrefour UAE. In 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
[12]. R, T., Priya, V.K.A., Raja, V. et al. (2024). Blockchain Technology and Advancements in the Agri-food Industry. J. Biosyst. Eng. 49, 120–134.
Cite this article
Zhang,Z. (2025). Dynamic Influence of Blockchain Technology Cost on Strategic Choice of Agricultural Product Supply Chain. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,177,44-49.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. FAO. (2020). The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020. Rome: FAO. https://www.fao.org/family-farming/detail/en/c/1308354/
[2]. FAO. (2011). Global Food Losses and Food Waste. Rome: FAO. https://www.fao.org/4/mb060e/mb060e00.htm
[3]. IBM. (2019). From seed to shelf: How IBM innovations will transform every stage of the food supply chain within the next five years. Armonk, NY: IBM. https://research.ibm.com/blog/ibm-research-5-in-5-2019-food?mhsrc=ibmsearch_a&mhq=transforming%20the%20food%20supply%20chain
[4]. IBM. (2023). World Food Safety Day: How blockchain helps serve safer salads. Armonk, NY: IBM. https://www.ibm.com/blog/world-food-safety-day-how-blockchain-helps-serve-safer-salads/?mhsrc=ibmsearch_a&mhq=food%20supply%20chain
[5]. Zheng, Y., Xu, Y., & Qiu, Z. (2023). Blockchain Traceability Adoption in Agricultural Supply Chain Coordination: An Evolutionary Game Analysis. Agriculture, 13(1), 184.
[6]. Demestichas, K., Peppes, N., Alexakis, T., & Adamopoulou, E. (2020). Blockchain in Agriculture Traceability Systems: A Review. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4113.
[7]. Mwewa, T.., Lungu, G., Turyasingura, B. ., Umer, Y. ., & Chavula, P. (2024). Blockchain Technology: A Review Study on Improving Efficiency and Transparency in Agricultural Supply Chains. Jurnal Galaksi, 1(3), 178–190.
[8]. Daraghmi, E., Jayousi, S., Daraghmi, Y., Daraghmi, R., & Fouchal, H. (2024). Smart Contracts for Managing the Agricultural Supply Chain: A Practical Case Study. Ieee Access.
[9]. Bayramova, A., Edwards, D. J., & Roberts, C. (2021). The Role of Blockchain Technology in Augmenting Supply Chain Resilience to Cybercrime. Buildings, 11(7), 283.
[10]. Chang, Y., Iakovou, E., & Shi, W. (2019). Blockchain in global supply chains and cross border trade: a critical synthesis of the state-of-the-art, challenges and opportunities. International Journal of Production Research, 58(7), 2082–2099.
[11]. Eletter, S. F., Elrefae, G. A., Yasmin, T., Qasem, A., Alshehadeh, A. R., & Belarbi, A. (2022, November). Leveraging Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts in the Management of Supply Chain: Evidence from Carrefour UAE. In 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
[12]. R, T., Priya, V.K.A., Raja, V. et al. (2024). Blockchain Technology and Advancements in the Agri-food Industry. J. Biosyst. Eng. 49, 120–134.









