1. Introduction
As the primary industry in China, agriculture plays a vital role in the national basic economic construction. In the process of developing agriculture, there are many scientific methods and laws that need to be followed in order to increase crop yield, reduce costs and thus obtain more profits. The law of diminishing marginal returns is a widely used theory in the agricultural field. Although the effects of the law of diminishing marginal returns are widely counted and understood, such as crop failures caused by excessive application of fertilizer, few studies have linked the phenomenon to an economic concept known as the law of diminishing marginal returns. This paper will study the embodiment and influence of the law of diminishing marginal returns on some important factors in agricultural production, specifically exploring whether the relationship between crop planting density, fertilizer application rate, the number of the employed labor force, crop yield, and profit follows the law of diminishing marginal returns. The research method adopted in this paper is empirical research, and specific data are used as case tests. This paper hopes to integrate the economic concept of diminishing marginal returns into positive agricultural production as a scientific production method to maximize profits.
2. The Concept of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns and Its Causes
The law of diminishing marginal returns is an important concept of short-term production in economics, also known as Gorsen's first law. Ceteris paribus, the marginal utility will increase at the beginning when the input increases, that is, the total utility will increase greatly, but after accumulating a substantial increment, the increment of the product provided will decrease, so the marginal utility will gradually decrease. If marginal utility remains positive, it means that total utility continues to increase, but at a gradual rate. When the input quantity accumulates to saturation and marginal utility drops to 0, it means that the total utility will not increase cumulatively and the total utility reaches the maximum. If marginal utility goes down to a negative value, total utility goes down [1]. The law of diminishing marginal returns reflects the inverse relationship between production factors and returns, and the reason behind it lies in the fact that, with the increase of variable factor input, the proportion between variable factor input and fixed factor input is changing. In the initial stage of the increase of variable factor input, compared with the fixed factor input, the variable factor input is too small. Therefore, with the increase of variable factor input, the marginal product increases. When the proportion of variable factor and fixed factor is appropriate, the marginal product reaches the maximum. If the variable factor input continues to increase, because the quantity of other factors is fixed, the variable factor will be relatively too much, so the marginal product will inevitably decrease. It is important to note that in agricultural production, marginal utility is unlikely to be negative because the produce is always available for sale. But when the utility from the addition of the product is less than the cost of the input, the profit is still reduced.
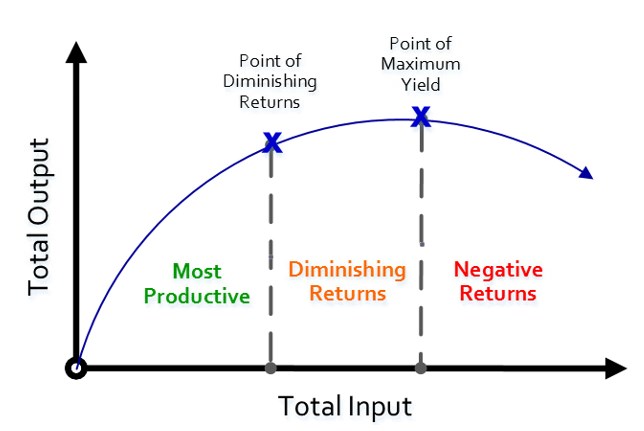
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the law of diminishing marginal returns.
3. The Embodiment of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns in Planting Density
In agriculture, because of the scarcity of land available for cultivation, it is important to maximize the yield of crops in a limited space to expand profits. One of the important ways is reasonable dense planting. Although increasing the planting density will indeed increase the yield per mu of crops at the beginning, due to the limitation of land fertility, the increase of yield per mu will continuously decrease with the increase of planting density, and eventually stop or even turn negative because this increase can affect individual plant production.
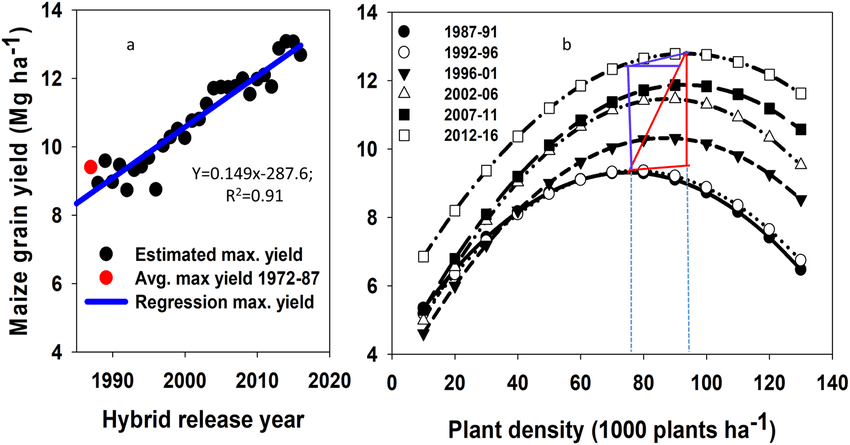
Figure 2: Plot of relationship between corn grain yield and planting density in different years in North America.
Figure 2 shows the relationship between corn planting density and grain yield for several years in North America [2]. It can be seen that although yield increases with year and technology development in all planting densities, the trend between corn planting density and yield does not change much, and still follows the law of diminishing marginal returns. In any given year, as planting density increases, corn yields also increase, with a positive marginal return. Then the increase is smaller and smaller, until the density increases to 80,000 to 100,000 plants per hectare, where the increase in corn yield becomes zero, where the yield peaks, and where the marginal revenue is zero. After that, if the planting density continues to increase, the yield starts to show negative growth due to the excessive amount of input, and the marginal revenue is negative. (This is because too dense planting will not get enough nutrients, which will greatly reduce the yield.) Therefore, planting should make proper and full use of land, light, heat, water and fertilizer resources to determine the density and obtain the ideal yield. Neither too thin nor too dense.
4. The Embodiment of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns in Fertilizer Application Rate
In agriculture, it is sometimes not the total yield but the total yield that needs to be considered. It is assumed that other factors are constant in short-term agricultural production and only the amount of fertilizer applied is changed. Based on the fertilizer application rate and formula of wheat in different areas of Henan Province, the following two figures [3] [4] respectively calculated the relationship between total wheat income, fertilization cost, net income and nitrogen application rate under different soils. And the relationship between total wheat income, cost and net income of K application and K application amount under different soil K supply levels. It can be seen that no matter whether nitrogen or potassium is applied, the total return obtained by planting wheat follows the law of diminishing marginal return: at the beginning, the amount of fertilizer applied from zero to zero, the marginal return has been positive and continuously decreased, and the total income is also increasing. Until the marginal return from increasing the amount of fertilizer is reduced to zero, the total benefit from growing wheat is maximum at that amount of fertilizer [5]. After the fertilization rate, the amount of fertilizer continued to be increased. Although the yield of wheat was still increasing at this time, the total return showed a downward trend due to the continuous increase of fertilization cost, and the marginal return became negative, that is, the marginal return was decreasing [6]. It can be seen that in short-term agricultural production, in order to get the highest income, we should not simply pursue the maximization of output, but look for the law in practice, consider the cost, follow the law of diminishing marginal returns, scientifically control the amount of fertilizer to obtain the maximum profit.
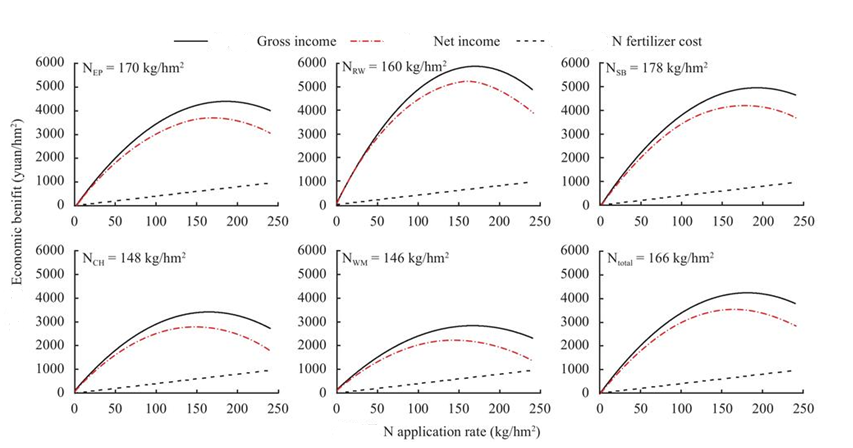
Figure 3: Relationships between gross income, N fertilizer cost and net return and N application rates of wheat.
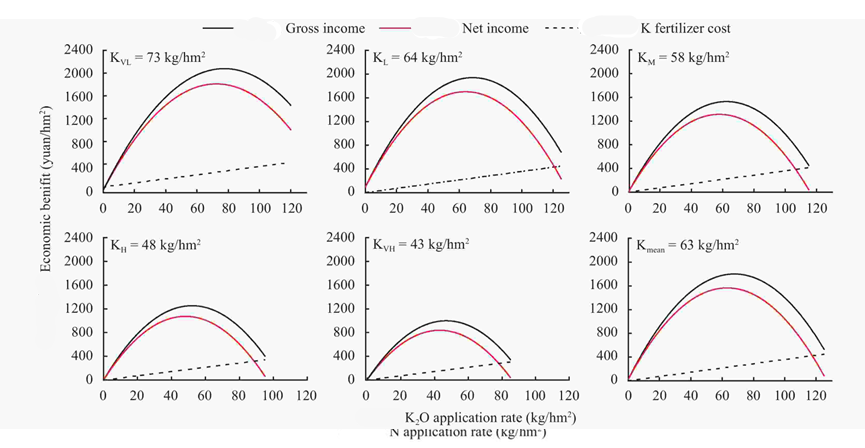
Figure 4: The gross and net return of wheat under different K fertilizer rates in fields with different soil K levels.
5. The Embodiment of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns in Quantity of Labor Force
In agricultural production, many human factors also have an impact on agricultural production, such as the amount of farm labor input. Other things being equal, less labor input will make the crop yield unable to reach the maximum, and increasing labor input will make the profit increase. The marginal reward is positive until it reaches saturation. When it reaches saturation, increasing labor input and increasing expenditure will not increase output, so profits will be reduced, and marginal returns will be negative and decreasing. The main reason for this phenomenon is that farmers, as labor factors, have low efficiency and low output when cooperating with other factors and resources, which means they cannot meet the needs of the market and the development of agriculture itself, and its essence lies in the diminishing marginal return of labor. In terms of quantity, the number of labor factors is relatively large compared with other factors, resulting in the so-called surplus rural labor force, or the relative shortage of other factors such as land. Compared with the rural labor population, Chinese soil and water resources are limited At the same time, in the process of industrialization and urbanization, more land and water resources will continue to be occupied, which will further aggravate the contradiction between factors and further lead to the diminishing marginal return of labor. Since the quality of laborers and marginal product of labor can not meet the needs of modern agricultural development, we can say that it is imperative to reasonably control the number of labor force and cultivate a new type of agricultural management subject with high quality and high production efficiency.
6. Conclusion
Through the above research, it is concluded that the agricultural production in the planting density and fertilizer application, and the relationship between labor input and producing profits are to follow the law of diminishing marginal returns, the producers should be charged with the law, a reasonable increase in input to ensure that the marginal benefit of those factors is greater than or equal to the marginal cost to maximize profit rather than blindly increasing the input. The current deficiency of this paper is that in the third part of the analysis of labor input following the diminishing marginal return, due to the limited data, it does not take out the data of hired labor and marginal product of agricultural products to prove, but simply uses a lot of theoretical knowledge to explain. I should consult some farmers for data on farm labor and productivity, and calculate the relationship between unit labor input and incremental marginal product.
Acknowledgement
First of all, I would like to thank teaching Assistant Yang for the inspiration of my thesis topic. He suggested that I should write a paper on the practical application of the law of diminishing marginal returns. This gave me the idea to study the application of the law of diminishing marginal returns in agriculture. Secondly, I would like to thank foreign Professor F. Lf for his support of my knowledge of economic theory. He let me know what is the law of diminishing marginal returns and its application in some fields, which is the basis of this paper. Finally, I would like to thank my thesis teacher, Ms. Huang, for her constructive modification suggestions on my finished thesis, which makes my thesis more perfect.
References
[1]. The Peak Performance Center, The Law of Diminishing Rule
[2]. Yared Assefa, Analysis of Long Term Study Indicates Both Agronomic Optimal Plant Density and Increase Maize Yield per Plant Contributed to Yield Gain, Scientific Reports, March 2018.
[3]. Zhu Z L. On the methodology of recommendation for the application rate of chemical fertilizer nitrogen to crops[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2006, 12(1): 1–4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2006.01.001
[4]. Zhao Y N, Su M M, Lü Y, et al. Wheat yield, nutrient use efficiencies and soil nutrient balance under reduced fertilizer rate[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017, 23(4): 864–873. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16417
[5]. Chuan L M. Methodology of fertilizer recommendation based on yield response and agronomic efficiency for wheat[D]. Beijing: PhD Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013.
[6]. Zhao Y N, Xu X, Huang Y F, et al. Nitrogen requirement and saving potential for wheat and maize in Henan Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(14): 2747–2757. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.14.012
Cite this article
Liang,X. (2023). Research on the Influence of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns in Agriculture. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,8,262-267.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. The Peak Performance Center, The Law of Diminishing Rule
[2]. Yared Assefa, Analysis of Long Term Study Indicates Both Agronomic Optimal Plant Density and Increase Maize Yield per Plant Contributed to Yield Gain, Scientific Reports, March 2018.
[3]. Zhu Z L. On the methodology of recommendation for the application rate of chemical fertilizer nitrogen to crops[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2006, 12(1): 1–4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2006.01.001
[4]. Zhao Y N, Su M M, Lü Y, et al. Wheat yield, nutrient use efficiencies and soil nutrient balance under reduced fertilizer rate[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2017, 23(4): 864–873. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16417
[5]. Chuan L M. Methodology of fertilizer recommendation based on yield response and agronomic efficiency for wheat[D]. Beijing: PhD Dissertation of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013.
[6]. Zhao Y N, Xu X, Huang Y F, et al. Nitrogen requirement and saving potential for wheat and maize in Henan Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2018, 51(14): 2747–2757. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.14.012









