

Volume 181
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management Research and Economic Development
R&D investment serves as the primary driver for corporate value enhancement, while executive incentives modulate the efficiency of translating innovation into performance. Utilizing data from China’s A-share listed companies between 2013 and 2022, this study empirically examines the impact of R&D investment on corporate performance and the moderating role of executive incentives. The findings reveal that R&D investment significantly boosts corporate performance. However, compensation incentives exert a negative moderating effect, whereas equity incentives show no significant influence. Notably, R&D investment demonstrates a more pronounced effect on enhancing the performance of state-owned enterprises. To foster innovation, the government should augment fiscal and tax support for corporate R&D, implement differentiated support policies, and invigorate innovation vitality in non-state-owned enterprises. Additionally, corporations should strive to balance long-term and short-term incentive structures to optimize performance outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, Pinduoduo has emerged as one of the most influential platforms in the Chinese e-commerce market through its innovative group-buying model and consumer-focused pricing strategies. Although the majority of previous research has concentrated on Pinduoduo’s business model and logistics, there is a scarcity of studies examining its capital structure, consumer finance products, and credit risk control mechanisms. This gap in research prompts an evaluation of the company’s financial strategies amidst the intensifying market competition and stringent regulatory environment. Through a combination of literature review and case study analysis, the paper examines how Pinduoduo transforms from a traffic-driven platform into a financial innovator. The findings provide insights into the future development of e-commerce finance and offer suggestions for platform operators and policymakers to ensure sustainable financial growth. This research highlights the evolving role of e-commerce platforms in the broader financial landscape and emphasizes the importance of understanding the interplay between innovative business models and financial stability. By analyzing Pinduoduo’s strategic shift, this study contributes to a deeper comprehension of the challenges and opportunities inherent in the integration of e-commerce and financial services.

 View pdf
View pdf


Smart cities are transforming urban landscapes worldwide, integrating digital technologies to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. Despite Japan’s global leadership in technology and innovation, the country struggles to keep pace with international smart city developments, ranking lower than global leaders. This study investigates the institutional, technological, and socio-cultural challenges that hinder Japan’s smart city transformation. This research delineates the fundamental barriers hindering Japan's optimal utilization of digital technologies in urban development, as revealed through an examination of policy documents, global smart city rankings, and governmental initiatives. The findings suggest that while Japan possesses advanced technological capabilities, governance inefficiencies, regulatory complexities, and socio-economic disparities continue to impede its smart city progress. The research culminates by offering suggestions aimed at enhancing policy alignment, fostering public confidence in digital governance, and expediting the incorporation of intelligent technologies into urban service delivery. Addressing these interconnected challenges through an integrated and inclusive approach will be essential for Japan to maximize the benefits of smart city innovations and achieve long-term sustainability in urban development.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of digital economy, as a core resource for enterprises and a critical element of market competition, the balance between the protection and circulation of commercial data has become a key proposition for promoting high-quality economic development. Although the Opinions on Building a Foundation for Data Systems to Better Leverage the Role of Data Elements issued by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council has clarified the framework for foundational data systems, China's Anti-Unfair Competition Law still faces challenges such as ambiguous application of legal provisions, unclear definitions of protection scope, and difficulties in judicial practice recognition. This paper analyzes typical cases such as “Sina Weibo v. Momo” and “Dianping v. Baidu,” dissecting the root causes of dilemmas from perspectives including legal lag, inherent characteristics of commercial data, and insufficient market maturity. In response, this paper proposes solutions such as adding special provisions for commercial data, establishing criteria for object identification, and optimizing the content of the Anti-Unfair Competition Law, drawing on Japan's regulatory experience to fully leverage the “incubator” role of the Anti-Unfair Competition Law. By curbing unfair data competition while promoting data circulation, stimulating innovation momentum, and establishing a systematic and scientific protection mechanism under the Anti-Unfair Competition Law, this study aims to provide a Chinese solution for data governance and safeguard the high-quality development of the digital economy.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on theories of industrial integration and related frameworks, this paper explores the integration of tourism and the low-altitude economy through literature review and case study methods. The two sectors share a solid foundation for integration, with significant potential for synergy in product development, market expansion, and industrial organization. Integration is driven by enterprise collaboration, academia-industry partnerships, and multi-stakeholder coordination. Adhering to the principles of sustainable development is of great significance for promoting industry integration and long-term development. Future efforts should focus on applying new technologies, expanding into international markets, tracking policy developments, and engaging in interdisciplinary research, thus providing stronger support for the growth of this emerging industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines green trade barriers in RCEP countries using an extended gravity model to analyze their impact and mechanisms on Yangtze River Delta agricultural exports, with policy recommendations. Findings show that despite strengthening barriers, exports to some countries saw countercyclical growth: SPS notifications, a key barrier indicator, positively correlate with exports, especially at higher volumes. Mechanism analysis reveals barriers enhance competitiveness via increased organic certifications, improving product quality. Combining SPS/TBT indicators confirms robust results, offering theoretical and practical guidance for addressing barriers, upgrading agriculture, and promoting sustainable regional development.

 View pdf
View pdf


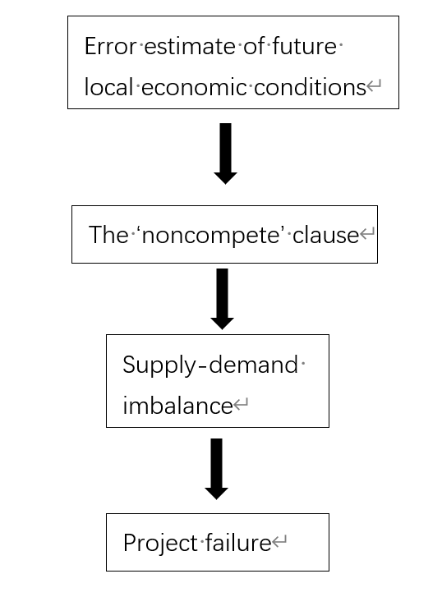
As Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects involve collaboration between the public sector and private enterprises, they are commonly used in infrastructure construction, which is characterized by long durations, substantial investments, and low short-term returns. Those characteristics lead a lot of potential risk for P3 projects. In order to explore why P3 project fail and the risk management optimization plan, this study examines the cases of the "Ghost City" of Ordos in China and SR-91 of California in the US.By employing a literature review and comparative analysis, the study identifies and contrasts the challenges faced by these two cases. Based on the identified problem models in China and the US, the study further extracts a common problem model. The findings suggest that the main reason that impact the failure of P3 project is error estimate of local future economic development and put forward three solutions that multidimensional dynamic analysis, professional assessment and improve the transparency.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper investigates the transformative effects of the digital economy on China's monetary and economic policies, highlighting both the challenges and opportunities presented by this new economic paradigm. The digital economy, driven by advancements in big data, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, has introduced significant disruptions to traditional economic structures and monetary policy mechanisms. This study critically evaluates the adaptability of China's current policies and reviews the innovative measures undertaken to accommodate the demands of the digital economy. By summarizing both the achievements and the challenges associated with policy adjustments and innovations, this paper provides a comprehensive analysis of China's response to digital economic transformation. Furthermore, it highlights the impact of digital currencies, fintech regulatory changes, and strengthened macro-prudential policies on economic growth and financial stability. The findings suggest that future policy improvements should focus on optimizing digital currency promotion strategies, enhancing fintech regulatory systems, and actively participating in international financial cooperation to address cross-border digital financial risks. In conclusion, this paper provides a comprehensive analysis of China's monetary and economic policies in the digital economy era, summarizing the main achievements and existing problems of policy adjustments and innovations.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the complexity and diversity of consumer behavior and decision-making in the context of online food vendors from the perspective of representativeness bias. The research finds that consumers exhibit significant cognitive biases during the online purchase decision-making process, especially in their perceptions of product features and vendor credibility. This leads to the formation of a simplified decision-making model when confronted with information overload. Emotional factors play a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions, with perceived risk and levels of trust significantly influencing consumers' choices of online food. Combining empirical analysis results, the study argues that representativeness bias is prevalent in the consumer information processing and evaluation process. It emphasizes the need for online food vendors to adjust their marketing strategies to adapt to these changes in consumer behavior. The findings of this study not only provide a theoretical basis for understanding online food consumption behavior but also offer practical guidance for vendors to design targeted marketing plans. This promotes positive interactions between consumers and vendors and drives the healthy development of the food e-commerce industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


In an increasingly digitized global economy, the seamless transfer of data across national borders has become integral to facilitating international commerce, digital service delivery, and economic progress. This study critically examines the legal structure established by the European Union (EU) for regulating international transfers of personal data, emphasizing key aspects of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Recognized globally for its rigorous protection standards, GDPR's extraterritorial application and reliance on adequacy determinations have nonetheless intensified global regulatory divergence. Despite widespread adoption, compliance instruments such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) and Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) encounter notable operational difficulties when navigating diverse international legal contexts. The study identifies key challenges—such as lack of international harmonization, enforcement barriers, and the disproportionate compliance burden on SMEs—and offers recommendations to enhance legal interoperability and policy convergence. Through comparative analysis and policy proposals, the paper calls for strengthened international coordination, global standardization of data transfer mechanisms, and integration of SCCs/BCRs into multilateral trade and governance frameworks. These efforts are essential for building a secure, transparent, and legally robust global data protection ecosystem.

 View pdf
View pdf




