1. Introduction
Many people like drinking coffee every day, making the coffee industry one of the market's most important segments among those for food and beverages [1]. With the increasing material and cultural needs of people, coffee has gradually become a mainstream drink. The famous coffee chain brand Starbucks has occupied most of the market shares with 51%. As learned from the official website, Starbucks currently operate more than 5,400 stores in over 200 cities on the Chinese mainland, employing more than 60,000 partners in 2020. At the same time, the Chinese market also becomes more and more significant to Starbucks. In 2020, it generated $745 million in revenue in China, accounting for more than 10 percent of its global revenue. It is becoming an increasingly significant part of Starbucks' global strategy.
However, recently Starbucks, as an old brand of high-end coffee, has repeatedly encountered problems during the epidemic, such as expired ingredients in stores that continue to be used, and clerks tampering with the shelf life of ingredients. Beyond the decreasing management quality, its sales also face continued decline. According to the latest financial report of Starbucks in 2022, in the first fiscal quarter of the year, the store orders decreased by 14%, and the average transaction price decreased by 9%, resulting in a 6% decline in total store sales. In the second fiscal quarter, the transaction volume of Starbucks China market decreased by 20%, and the average transaction price decreased by 4%. Sales at Starbucks stores in China fell 23%. Despite the impact of the pandemic, other coffee brands such as Luckin have shown smaller reductions. The phenomenon probably reflects that Starbucks is likely to have some internal problems. If these problems are not managed carefully, the failure of the Chinese market may have more serious impacts on the future of Starbucks.
Therefore, we want to explore what problems a successful global brand has encountered in China, and how Starbucks could probably solve them. And we checked many literatures and found that there was no relevant literature on the management problems of Starbucks in China recently, which gives us the direction of this research. The main purpose of this paper is to analyse the dilemma of Starbucks' current business development in China by using theories like organizational behaviour, organizational management, and leadership with trying to provide powerful solutions for Starbucks after analysis with further theories.
For the organization of the essay, the first chapter is about the research meaning and background of the topic. The second chapter analyses the current problems of Starbucks in corporate culture, leadership style, personnel management, and brand positioning, and the third chapter based on the OB theory, analyses how it is applied in the overall structure of Starbucks and how it may be useful in solving issues in marketing and management of Starbucks.
2. Starbucks Background Analysis
In the book Management [2], Robbins mentions that the influence of the external environment on the internal management of the company is indirectly reflected in the management of the company's business. This section will therefore use the five forces method and the PESTLE method to analyse the factors influencing the external environment of a company. This provides a general background for the question-specific assessment section below.
Taiwan was the first country that Starbucks entered, followed by Beijing in January 1999 and Shanghai in May 2000. First and foremost, Starbucks' corporate culture is a brand-new experience cultural environment that enables individuals to have a "third space" where coffee life is situated between home and work, allowing customers to travel as much as possible. The realization of one's own values in accordance with culture is the second. Starbucks has consistently seen its workers as partners. By doing this, Starbucks has in a short period of time come to represent fashion in China. The majority of trendy petty bourgeoisie are familiar with Starbucks' iconic advertising tagline, "I'm not in the office, I'm in Starbucks; I'm not in Starbucks, I'm on the way to Starbucks." It's more than simply a cup of coffee; it's a culture and a brand.
2.1. Five Forces: Analysis of Starbucks’ Model
The Risk from Potential Rivals’ Similar Businesses. In cities where economic conditions have gotten to a certain level, a Starbucks culture starts to spread over the globe. There are many new cafes, some of which are operated by other international businesses, domestic brands, or neighborhood cafes. National and global businesses are much less well-known than Starbucks, while neighborhood small-scale coffee shops pose a stronger challenge to Starbucks. These small-scale cafes are easier for the owner to manage, allowing them to concentrate on creating a Starbucks-like atmosphere for leisurely life, offering a place for friends to chat, relax, and play board games. These cafes cater to the numerous needs of its patrons and their desire to explore new things through their various styles. Additionally, because Starbucks is so well-known in various locations, there are also many of visitors there. Many consumers avoid Starbucks because it is like a vegetable market in a place that should be tranquil. As a result, Starbucks rivals pose a serious danger.
Substitutes in The Form of Fruit Juice, Milk Tea and Other Drinks. Fruit juice, milk tea, and other alternatives to coffee are a threat, but Starbucks now has a special supply of juice and milk tea as well. Even though there are small businesses offering fruit juice and milk tea all over the street, Starbucks sells more than just coffee, juice, etc. These small stores typically only sell drinks and do not have seating. Since beverages are also marketed in a setting and through an experience, the risk of substitutes is minimal.
Buyers’ Low Bargaining Power. Starbucks sells more than just coffee and juice drinks; it also offers experiences, so the money customers spend on coffee covers both the concrete cost of the beverage and its intangible value. Customers have little negotiating leverage because it is difficult to determine whether paying for the coffee experience is cost-effective compared to the standard price of purchasing coffee from a store.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power: Heightened Level of Attention. Exporters are dealt with by Starbucks. The processed coffee beans are sold to exporters by coffee growers. Starbucks directly purchases coffee beans from exporters. Suppliers concentrate on high-quality Arabica beans because they sell for more money, whereas the trade industry uses lower-quality coffee beans. 35% of all Starbucks coffee beans are sourced from the Pacific Rim, 15% are from East Africa, and 50% are from Latin America. extensive standardization Starbucks is a significant client for vendors: Starbucks and suppliers have long maintained a tight relationship because Starbucks frequently works directly with suppliers and trains them. Starbucks is a key client for its suppliers. Finding a reliable coffee source and building a strong working relationship are difficult tasks. As a result, Starbucks will incur significant switching costs when purchasing raw materials. In conclusion, Starbucks places a high value on the goods that its suppliers deliver. As a result of the study above, Starbucks' suppliers are well-positioned to negotiate.
The Competition’s Intensity: Ample and Balanced Competitors. Competition from well-known coffee companies like Costa, Taiwan's 85 degrees C, McDonald's McCafe, Maxwell, and others is growing. 85 degrees C has progressed to the point that there are currently 345 stores in Taiwan, with franchise stores making up roughly 90% of the total number of stores. This growth pace of adding two new stores every year has increased. McDonald's has extended the variety of coffee drinks available in its locations; Maxwell House Coffee, founded in 1892, has always aimed to be "Good to the last drop!" and has grown to be a well-known brand. Drip coffee from McDonald's is more popular than Starbucks in terms of taste and price.
2.2. Potential Risks Analysed Based on PESTLE Framework
Contrary to the Five Forces model, which examines the competitive environment of Starbucks by observing the entire coffee industry, the pestle model identifies the potential risks that Starbucks faces by exploring the macro environment of the company in six dimensions [3].
Political Factors. China has maintained a stable development and an encouraging attitude towards foreign investment in China, which has positively helped the development of Starbucks in China [4]. However, alterations in China's international relations with the United States will have a substantial impact, for example, the mutual boycott between 2019 and 2021, which has prompted the introduction of a bill on countermeasures in China, which has put considerable pressure on foreign companies in the mainland China [5].
Economic Factors. In the context by which the epidemic has struck the global economy, Although Starbucks' market in China has recovered under the effective management of the Chinese government, Starbucks' sales were still down 7% based on the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2021 [6]. This suggests a potential financial risk in the future if their sales do not rebound.
Social Factors. The pandemic has had an unavoidable negative impact. The number of customers has decreased significantly. Some of the workforce was unable to operate normally due to the quarantine policy [7]. Moreover, the addition of new competitors to Starbucks has led to increased pay increases for Starbucks employees, which has led to increased staff turnover and the need to increase pay again in order to retain talent. This again increased Starbucks' staffing costs.
Technological Factors. The delivery industry is growing rapidly in China, and with the epidemic prohibiting people from going out, the delivery market continues to mature. Starbucks has aggressively gone digital, partnering with Alibaba, China's largest internet company, to enable takeaway services [8]. Conversely, from a brick-and-mortar perspective, there is a risk that people will become accustomed to takeaways instead of shops in the aftermath of the epidemic.
Legal Factors. According to the Starbucks impact report in 2021 [9], local legal policies in China have changed and new restrictions on data transfers are now in place, and there is concern about the uncertainty of whether restrictions will increase again in the future, which will result in legal risks and potential additional costs.
Environmental Factors. The emergence of local coffee companies in China in recent years has squeezed the market space, such as Luckin coffee [10]. This has prevented Starbucks from expanding to its current target size and has reduced its profit margins.
3. Problems Encountered by Starbucks in Its Chinese Expansion
3.1. The Problem of Starbucks Experiential Service China
In some Starbucks restaurants in China, many customers come in and sit, and if they don't order, they will be invited to other places. As far as this situation is concerned, Starbucks China has not brought much enjoyment about coffee to Chinese customers. But in the United States, Starbucks is very warm and polite. When entering the store, ordering, picking up coffee, and leaving the store, each say hello and thank you. Sometimes they say sorry when they don't buy things (the cups). Through the comparison of the two parties, it can be seen that Chinese customers and Starbucks employees did not form a good interactive experience, but this does not mean that Starbucks has made a mistake in its value concept in this regard. The reason for the contradiction may be the cultural differences between Europe, America, and China. Italians understand that interpersonal relationships can be connected with coffee, and Americans are warm and open, good at communicating and chatting, but these are just difficult to achieve in China. In fact, customers and Starbucks employees can easily establish a good relationship, but the fact shows that the key problem lies in whether the Chinese customers themselves can understand and enjoy Starbucks' values and positioning services.
3.2. The Potential Threat Behind Transformational Leadership Behaviour
Effective leadership tends to facilitate aggressive business development, and the type and behaviour of leaders has a significant impact on the management of organisations, as leadership is one of the four functions of management [2]. In conjunction with leadership theory, the leadership style of Starbucks in China could be explored. Under this leadership, certain potential management challenges could be observed. The transformational and charismatic leadership is exemplified by Wong's ability to persuade those with a vested interest by her accumulated influence as a general manager and her ability to inspire and support innovative change projects. Her transformational leadership has a positive impact on the staff at the bottom, such as imitation [11]. Because of the increased speed of expansion under the leadership of change, the quality of individual management has not been able to keep up.
3.3. The Issues of Starbucks Personnel Management
It is precisely because of the rapid expansion of business that there have been omissions in personnel management.
Lack of Standardization in Recruitment. Starbucks is very inclusive in recruitment, and the evaluation of Starbucks' recruitment is still relatively one-sided. Because early hiring is not standardized and follow-up work is not evaluated, it is impossible to decide whether to hire qualified employees for the company [12].
Formalism of Performance Assessment. The assessment indicators of the store manager include three aspects. However, due to the rigid assessment system, in order to deal with formalism, the assessment data are good-looking every time the superior checks. For example, in order to report the loss data in Wuxi store, the clerk tampers with the expiration date of ingredients.
Training Defects of Part-Time Personnel. Starbucks has a thorough training program for its employees, but it doesn't appear to cover part-time employees. There is a difference in the level of service provided by each store as a result of part-time employees' reliance on their own subjective opinions and ideas when serving clients [13].
3.4. Starbucks Brand Positioning Predicament
Recently, Starbucks is facing the brand positioning crisis. The old brand definition of "high-end" has been challenged.
The Disenchantment of Starbucks. Mentioned by the Starbucks website, it has more than 5,100 stores in China after the significant expansions. While expanding its market share, Starbucks has gradually become a ubiquitous store on the streets, making its original atmosphere of mystery disappear. Being visible all over the places dilutes the brand's uniqueness, which is likely to be prejudicial to the brand of Starbucks in the long run [14].
The Privation of High-End Sense of Starbucks. The expense of Starbucks was considered as the conspicuous consumption. Cited the word of Padilla and Puertas [15], conspicuous consumption symbolizes ostentatious and material consumption through the purchase of products and services with a higher economic value and that allows their consumers to excel socially. However, the action of Starbucks itself reduces its value as high-end consumption. Starbucks determines to embark on a major brand transformation. Howard Schultz, the CEO of Starbucks stressed that Starbucks' distribution channels will expand beyond coffee stores to supermarkets. Nonetheless, in the long run, it may lead to a change in the brand recognition of Starbucks. "A high-end brand should be known as a brand that offers special treats rather than something consumers can consume every day" [14]. According to Kotler's model, consumers' purchase decision depends on marketing stimulus and internal stimulus, which will combine with consumers' own cognition to make the final decision. Therefore, consumers could be more reluctant to pay a premium after no longer considering Starbucks as a high-end brand.
The Loss of Environmental Immersion of Starbucks. Finally, with the rapid development of China's food delivery industry, the positioning of "The Third Space of The City" of Starbucks was also significantly damaged. During 2020, thirteen percent of Starbucks' orders came from delivery apps. The investors believe Starbuck sells set and time, and consumers go to Starbucks due to valuing its environment, service and atmosphere [16]. However, after home delivery service, people would directly have coffee in their homes, preventing Starbucks from taking advantage of its own ambience. The elitist social interaction it used to provide has disappeared owing to delivery service. Starbucks' offline service has always been dedicated to providing customers with personalized and intimate service, which used to attract loyal customers. None of these merits could be available in the delivery service process. Without the advantages of scene experience and behavioural experience offering the customers, Starbucks may not be capable to clearly distinct from competitors like Luckin.
4. Suggestion
4.1. Use Hierarchy of Needs Theory to Solve Problems in China
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs divide the human needs into five-tier. They are a physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem and self-actualization respectively (see figure 1).
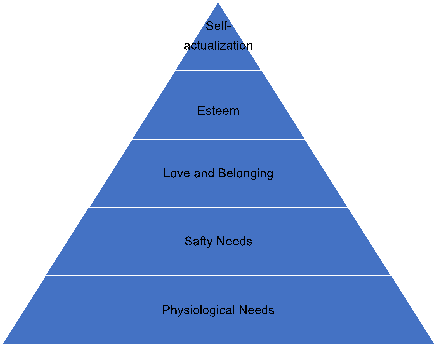
Figure 1: Five-tier of hierarchy of needs.
Leaders in business always try to meet the needs from this pyramid to motivate the workers. In Starbucks, the main reason for experiential service is not available in every Starbucks store is the low motivation of workers. To improve this situation, Starbucks should provide a relatively safe working environment and zero-risk job for workers, so the second tier, the need of safety is met. As subordinates feel comfortable to work in Starbucks, they will be in a better mood at work and thus more motivated. Furthermore, Starbucks should try to build a premium brand, so not only the colleagues but also the consumers there are friendly and well-educated. Workers here feel loved and respected, then the love and belonging needs are met. During the process of meeting their needs, workers may feel needed and motivated, which make the communication and management become easier for leaders.
4.2. Using Multiple-Linkage Model to Solve Troubles in Different Aspects
The multiple-linkage model describes how different types of leader behaviour and different variables jointly influence performance by individual workers’ behaviour and by the leader’s work unit [11]. A larger number of mediating variables are included in this model, which explain the effects of leader behaviours and situational variables, and there is more accurate description of group-level processes can be showed. For different problems caused by Starbucks, it has different solutions to solve them.
Short-Term Actions to Correct Deficiencies. It is a model that suggests some leader actions which can solve any deficiencies in the mediating variables that identify group performance. And Starbucks can use it to solve the problems caused in personnel management and leadership style.
For part-time employees in Starbucks, the low task knowledge and skills are the main challenges. In Multiple-linkage model, leaders can do next four steps to solve that (1) Make clear assignments. Make sure what they need to do and what they need to focus on, which can avoid some unnecessary tasks. Provide more direction and clarification of procedures. Workers in Starbucks could know more about working procedure, so can-do work more efficiently. Provide instruction and coaching when needed to directly increase their knowledge and skills. Find skilled people to do difficult tasks. Skilled workers can do jobs quickly and no need to much supervision. In those cases, low -quality service can be avoided, and workers will get more knowledge about their jobs. Because of the over-expansion, individual management goes wrong, the coordination between subordinates became extremely weak. Leaders in Starbucks need to act to improve this situation. Develop better plans to avoid internal coordination problems. Leaders should focus better on the individual management and make fool proof plan to supervise the workers. Like the special time schedule. (2) Improve internal relations with interdependent units. In Starbucks, workers’ need to work together. For leaders, they should organize more activities to improve them. (3) Monitor closely to detect internal coordination problems quickly. Leaders should also be considered as regulators to make sure their subordinates keep on doing the work. Then, the quality of individual management would increase.
Long-Term Actions to Improve the Situation. Leaders can make larger improvements within the longer time to solve the problems happened during the work time. For the problems happened in brand position and external expansion.
For the problems caused in external expansion, (1) leaders should improve selection procedures to increase the level of employee skills to provide better quality service. For example, Starbucks’ leaders should try to employ some workers which more suitable to work in China. (2) Supervisor need gain more access to resources needed for the work by making better relationships with suppliers, finding substitutes, and reducing dependence on unreliable sources. Like extra seats in Starbucks, or an extra place for people who do not buy products in Starbucks, in that case, there is no need for workers to drive consumers.
For brand challenge, (1) leaders should gain more control over the demand for the unit’s products and services by finding new customers, stop selling products in the market, having more advertisement, and modifying the products or services to be more acceptable to clients and customers. For Starbucks, owners need to keep the price high and advertise the high-end sense of its products. (2) Owners should limit the number of stories in China and stop provide goods to some places which are against the brand positioning. Like stop provide Starbucks coffee in the markets. Solutions should be done to give the sense of mysterious back.
5. Conclusion
According to our research and review of previous literature, Starbucks has developed and expanded its business at a high speed in China in recent years, but at the same time, management loopholes have emerged. We find that Starbucks has many problems in its business model, leadership style, personnel management, and brand positioning. We use Maslow's hierarchy of needs to solve the problem that Starbucks waiters do not provide good service. We mentioned that Starbucks need to take specific measures to meet the needs of two employees to motivate employees. Finally, the multiple link model is used to solve the problems of employee management, brand positioning and external expansion. This model is divided into two parts, one is short-term and the other is long-term. The short-term solution is to solve the problems of employee management and leadership style. The solution includes providing more guidance and procedures, it has long solved the problem of external expansion, such as improve selection procedure. Throughout this study, it is obvious that, we found that the company can also try to find new strategies to organize future plans.
References
[1]. R. Sinha, V. Ganatra, P. Pandey, DLA Deepaa, P. Arumugan, DMH. Kee, G.S. Lekha, N. Kumar, S.D. Kew, A. Dhupad, "Impact of Covid-19 on business performance: A case study of Starbucks”, International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality in Asia Pacific 4(2) (2021) 13-27. DOI: http://doi.org/10.32535/ijthap.v4i2.1054.
[2]. S.P. Robbins, M.A. Coulter, Management, China Renmin University Press, 2017.
[3]. R. Perera, The PESTLE analysis. Nerdynaut, 2017.
[4]. China Daily, (2020). China's development will bring more opportunities for foreign companies. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2022-03/16/content_5679281.htm.
[5]. Centre for China and Organization, (2021). Latest trends in the US-China Relations: Implications for MNCs in China. http://en.ccg.org.cn/archives/74216.
[6]. S. Corporation, (2021). Starbucks Reports Q4 and Full Year Fiscal 2021 Results. https://stories.starbucks.com/press/2021/starbucks-reports-q4-and-full-year-fiscal-2021-results/.
[7]. S. Wang, Different Marketing Strategies Between Starbucks and Luckin Coffee and the Impact of the Epidemic, International Conference on Enterprise Management and Economic Development (ICEMED), Atlantis Press (2021) 1-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.210601.001.
[8]. N. KUMAR, S. BHARDWAJ, S.E. CHU, Starbucks in China: An undisputed leader?, Asian Management Insights 7(1) (2020) 34-41.
[9]. S. Corporation, (2021). S&P Global Impact Report 2021. https://www.spglobal.com/en/who-we-are/corporate-responsibility/impact-report-2021.pdf .
[10]. Q.I.U. Lingyu, The Analysis on the Marketing Strategy of Luckin Coffee in China, 4th International Seminar on Education, Management and Social Sciences (ISEMSS 2020), Atlantis Press (2020) 469-472.
[11]. G. Yukl, W.L. Gardner, Leadership in Organizations, Pearson Education, 2019.
[12]. Q. Xiaohan, Analysis of current enterprise talent recruitment problems and Countermeasures -- Taking Starbucks as an example, The Fortune Times (2015) 172-173. DOI: CNKI: SUN: ZFSD.0.2015-S2-143.
[13]. C. Ruilong, L. Junpeng, X. Zhihao, Research on Starbucks management -- from the aspects of manpower, marketing and service quality (2009) 104. DOI: http://120.106.195.12/handle/310904600Q/5662.
[14]. L. Jing, Z. Yun, A.Ries Get out of the Starbucks-style dilemma, Chinese and foreign management (05) (2011) 88-89. DOI: http: //CNKI: SUN: ZHGN.0.2011-05-037.
[15]. J.Padilla, M.Puertas, (2021). Conspicuous Consumption in Emerging Markets: The Case of Starbucks in Colombia as a Global and Sustainable Brand. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.662950/full.
[16]. W. Xinhao, The midlife crisis of Starbucks, China Brand (11) (2018) 82-8. DOI: http: //CNKI: SUN: ZGPP.0.2018-11-028.
Cite this article
Fu,G.;Meng,R.;Huang,Q.;Tao,H.;Yang,L. (2023). Research On Management Quality of Starbucks in China's Business Expansion. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,9,82-89.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. R. Sinha, V. Ganatra, P. Pandey, DLA Deepaa, P. Arumugan, DMH. Kee, G.S. Lekha, N. Kumar, S.D. Kew, A. Dhupad, "Impact of Covid-19 on business performance: A case study of Starbucks”, International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality in Asia Pacific 4(2) (2021) 13-27. DOI: http://doi.org/10.32535/ijthap.v4i2.1054.
[2]. S.P. Robbins, M.A. Coulter, Management, China Renmin University Press, 2017.
[3]. R. Perera, The PESTLE analysis. Nerdynaut, 2017.
[4]. China Daily, (2020). China's development will bring more opportunities for foreign companies. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2022-03/16/content_5679281.htm.
[5]. Centre for China and Organization, (2021). Latest trends in the US-China Relations: Implications for MNCs in China. http://en.ccg.org.cn/archives/74216.
[6]. S. Corporation, (2021). Starbucks Reports Q4 and Full Year Fiscal 2021 Results. https://stories.starbucks.com/press/2021/starbucks-reports-q4-and-full-year-fiscal-2021-results/.
[7]. S. Wang, Different Marketing Strategies Between Starbucks and Luckin Coffee and the Impact of the Epidemic, International Conference on Enterprise Management and Economic Development (ICEMED), Atlantis Press (2021) 1-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2991/aebmr.k.210601.001.
[8]. N. KUMAR, S. BHARDWAJ, S.E. CHU, Starbucks in China: An undisputed leader?, Asian Management Insights 7(1) (2020) 34-41.
[9]. S. Corporation, (2021). S&P Global Impact Report 2021. https://www.spglobal.com/en/who-we-are/corporate-responsibility/impact-report-2021.pdf .
[10]. Q.I.U. Lingyu, The Analysis on the Marketing Strategy of Luckin Coffee in China, 4th International Seminar on Education, Management and Social Sciences (ISEMSS 2020), Atlantis Press (2020) 469-472.
[11]. G. Yukl, W.L. Gardner, Leadership in Organizations, Pearson Education, 2019.
[12]. Q. Xiaohan, Analysis of current enterprise talent recruitment problems and Countermeasures -- Taking Starbucks as an example, The Fortune Times (2015) 172-173. DOI: CNKI: SUN: ZFSD.0.2015-S2-143.
[13]. C. Ruilong, L. Junpeng, X. Zhihao, Research on Starbucks management -- from the aspects of manpower, marketing and service quality (2009) 104. DOI: http://120.106.195.12/handle/310904600Q/5662.
[14]. L. Jing, Z. Yun, A.Ries Get out of the Starbucks-style dilemma, Chinese and foreign management (05) (2011) 88-89. DOI: http: //CNKI: SUN: ZHGN.0.2011-05-037.
[15]. J.Padilla, M.Puertas, (2021). Conspicuous Consumption in Emerging Markets: The Case of Starbucks in Colombia as a Global and Sustainable Brand. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.662950/full.
[16]. W. Xinhao, The midlife crisis of Starbucks, China Brand (11) (2018) 82-8. DOI: http: //CNKI: SUN: ZGPP.0.2018-11-028.









