1. Introduction and Literature Review
1.1. Introduction
Global IPO market sentiment remained very fragile in the second quarter as market conditions deteriorated, with deal volumes down significantly sequentially, especially compared to last year. As shown in Fig. 1, Global IPO offerings totaled $36.6 billion in Q2 2022, down more than 70% compared to Q2 2021 and even lower than the $43.6 billion in Q2 2020 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, which was the lowest second quarter since 2016 [1]. Since the end of 2014, China's stock market has ushered in a bull market, and the bull market has triggered an upsurge in the listing of small and medium-sized enterprises. Due to the strict requirements for IPO listing, it is inevitable that some companies use financial fraud to achieve the purpose of listing. In the past, there were fraudulent acts of Yinguangxia, Lantian Co., Ltd., and Wanfu Biotechnology. The financial scandals of listed companies have become a hot spot in the market. They concealed the company's true profitability from the majority of investors, and financial fraud has seriously damaged investors and creditors. It weakens the effectiveness of the government's macro-control and the resource allocation function of the market, and at the same time misleads information users, causing them to suffer serious losses and the loss of state-owned assets. The harm of IPO financial fraud is catastrophic, endangering the integrity of the entire social industry and threatening the effective operation.
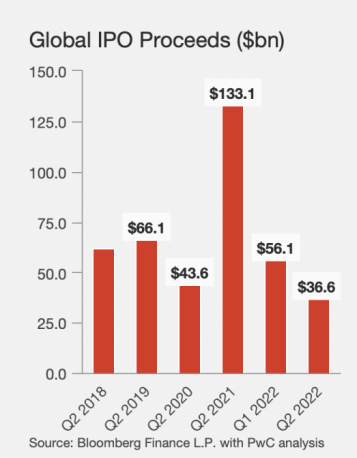
Figure 1: Global IPO proceeds.
It is believed that China’s IPO approval system has many shortcomings compared with the United States. First, the degree of publicity in China's issuance review is relatively small. The materials submitted by the issuing companies to the CSRC and the review opinions of the CSRC have not been made public, while the United States will disclose all the materials and review opinions of the issuing companies; secondly, China's false information on listed companies The stated punishment for violations is low enough to restrict the behavior of the issuing company, which is also caused by the imperfect securities system in China. Many scholars have discussed the role and impact of the delisting system of listed companies on the securities market.
1.2. Literature Review
Previous studies aim at the deficiencies of the delisting mechanism of China’s investment bank market [1-4]. The scholars analyze the impact of the securities market, and points out that the unsound delisting mechanism has caused the resource utilization rate of Chinese listed companies low, abnormal development of the securities market, low internal governance efficiency of listed companies, and increased securities market risks. The lack of delisting mechanism makes the securities market form a situation of "bad money drives out good money", resulting in stock investment. Only by establishing a perfect and efficient delisting system for listed companies can the advantages and disadvantages of the securities market be formed. Elimination mechanism can improve the internal quality of listed companies. Under the perfect delisting mechanism of listed companies, investors only then can one fully understands the systematic and unsystematic risks in the market and form a rational investment situation.
During a company's initial public offering (IPO), the existence of a brokerage as an independent third-party certifies is considered It is an effective solution to alleviate the information asymmetry of IPO [5]. However, there are brokers in order to obtain For example, to assist unqualified companies in issuing and listing by collecting underwriting fees, or to misassess the possibility of IPO enterprise value due to the professional competence of securities companies, how can investors judge the accuracy of the information provided by securities companies? Commitment and Guarantee [6, 7]. Investors believe that reputable securities companies have a strong certification role, so they can judge the quality of the securities companies' professional ethics, service quality and the accuracy of the information provided by virtue of their reputation. As an important intermediary between investors and issuing companies, securities companies can alleviate the problem of information asymmetry in the process of securities issuance by playing the certification function [8, 9]. Baker analyzed the delisted companies on the NYSE and the AMEX and found that more than 40% of the delisted companies had stock prices in the 10 to 1 year before delisting. The value has almost been lost [10].
Since the establishment of the Science and Technology Innovation Board in July 2019, the Science and Technology Innovation Board has changed the approval system to the registration system for the first time, and the pricing mechanism adopts the inquiry system to further marketization. More and more innovative companies choose to go public on the Science and Technology Innovation Board. However, the lowering of the listing threshold requires the support of mature investors and follow-up systems. If there is no mature system and laws as backup support, the interests of small and medium shareholders will be damaged. Amethystum Storage has been listed on the Science and Technology Innovation Board on February 26, 2020. From the suspension of trading on May 6, 2022 to delisting warning (ST*) only take five days, Amethystum Storage may become the first company to be delisted from the China’s Science and Technology Innovation Board. Is the company fraudulent or the sponsor's lack of supervision? this article analyzes the situation before and after the listing of Amethystum Storage, and analyzes the company's financial fraud from the perspectives of illegal pledge and inflated net profit. The Sec. 2 introduces the process of listing and delisting of companies on the Sci-Tech Innovation Board. The Sec. 3 analyzes the situation before and after the listing of the listed company Amethyst Storage. The Sec. 4 analyzes the reasons for the company's imminent delisting from the perspectives of illegal pledge and net profit fraud. In Sec. 5, based on the analysis of Amethyst Storage, some suggestions are given from the perspective of investment banks. The Secs. 6 and 7 illustrate the limitations of this paper and prospects for the future and makes some conclusions.
2. IPO and Delisting Process
In China, the listing process of science and Technology Innovation board companies is shown in Fig. 2. According to the relevant laws and regulations of China. the delisting standards for companies listed on the main board market in China mainly include the following aspects:
• Changes in the company's total share capital and shareholding distribution are no longer eligible for listing;
• The company fails to disclose its financial status in accordance with regulations
• The company has committed major illegal acts;
• The company has suffered losses for the past three consecutive years;
• The company is dissolved or declared bankrupt;
• Other circumstances stipulated by the listing rules of the stock exchange.
In order to ensure that investors have sufficient time to make investment decisions before the company's stocks are terminated from trading, the stock exchange implements "special treatment to warn of the risk of termination of listing" for listed companies that have the risk of termination of stock trading, referred to as "delisting risk warning". The main measure of "delisting risk warning" is to prefix the stock with the word "ST" to remind investors to pay attention to the delisting risk of the stock. For stocks that have been issued a delisting risk warning, if their operating conditions have not improved at a certain stage, they will be suspended from listing when certain conditions are met. Suspension of listing is a situation in which the listing of its securities is suspended for special reasons stipulated by law, rather than a decisive and final denial of the listing qualification of a listed company. The suspension of listing of stocks does not mean that the company will be delisted. The stock exchange will give the listed company a grace period of one year, so that the listed company can revive. If the listed company can achieve profitability within the one-year grace period, it can avoid delisting. When a listed company falls under the circumstances stipulated by law, the exchange may decide to terminate the listing of its stock within the statutory time limit. According to the review opinion of the Listing Committee, decide on whether to terminate the listing of the stock.
Figure 2: STAR Market IPO Schedule.
3. Background
3.1. Amethystum Storage
Founded in 2010, Amethystum Storage is a leading optical storage high-tech enterprise in China. It was listed on SSE STAR MARKET on February 26, 2020 under stock code: 688086. Targeting at big data market, the company promotes intelligent cold-hot tiered data storage management, creates competitive advantages in the full industry chain along the development path of optical storage “media-device-software-solution” and has become a big data storage solution and product provider [11]. On February 26, 2020, Amethystum Storage was listed on the Science and Technology Innovation BoardOn February 26, 2020, Amethyst Storage was listed on the STAR Market. The price evolution of the company is illustrated in Fig. 3.
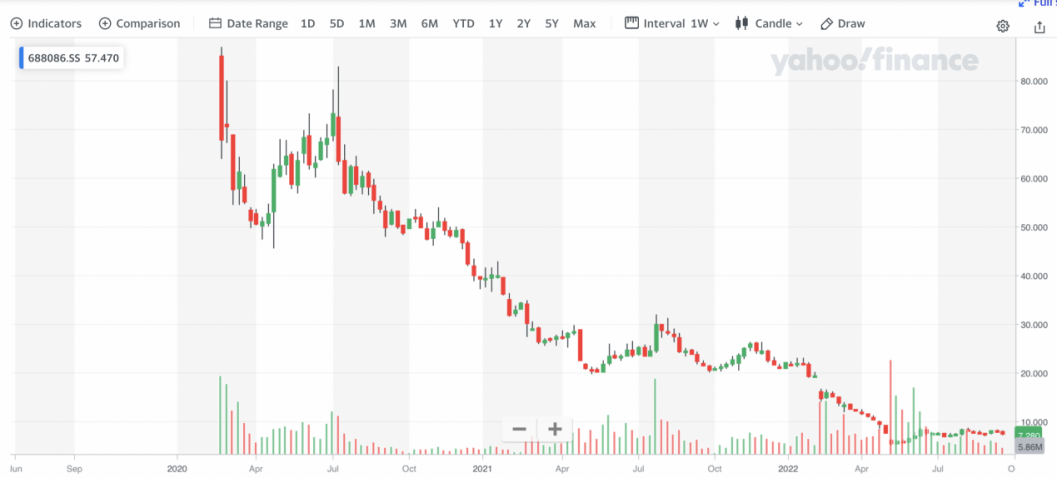
Figure 3: Price evolution of Amethystum Storage.
3.2. Overview of the Company
The issuer’s audited net profit attributable to shareholders of the parent company in 2017 and 2018, before and after deducting non-recurring gains and losses, whichever is lower, were RMB 46,007,500 and RMB 102,413,400, respectively. The financial indicator is not less than RMB 50 million [12]. In November 2018, the company introduced 7 institutional investors. Based on the share price of 9.665 yuan per share, the company's share capital after the capital increase was 142,785,377 yuan, and the estimated post-investment valuation of the company was 1.380 billion yuan. It is expected that after this public offering, the company's market value will not be less than 1 billion yuan. The information about the shareholder is given in Table. 1.
Table 1: Information about the Company's Shareholders.
Time | Event | Registered capital (million) | Shareholder |
2010.4 | Amethystum Storage LLC | 3 | Zheng Mu; Luo Tiewei |
2015.9 | Amethystum Storage Co., Ltd. | 80 | Zichen Investment, Zihui Investment, Okura Investment, He Quyi, Wang Yayu, Chen Dongming, Li Linkai, Gan Yu, etc. |
2015.11 | The first capital increase of the joint-stock company | 92 | Zichen Investment, Zihui Investment, Okura Investment, He Quyi, Wang Yayu, Tianxing Shengshi Investment, Baoding Aiping, Phoebe Investment, Huishi Dinghe Investment, etc. |
2016.9 | The second capital increase of the joint-stock company | 95.9 | Zichen Investment, Zihui Investment, Okura Investment, He Quyi, Wang Yayu, Tianxing Shengshi Investment, Baoding Aiping, Phoebe Investment, Huishi Dinghe Investment, etc. |
2017.2 | The third capital increase of the joint-stock company | 118.988 | Zichen Investment, Zihui Investment, Okura Investment, He Quyi, Wang Yayu, Dachen Venture Capital, etc. |
2018.11 | The forth capital increase of the joint-stock company | 142.785377 | Zichen Investment, Zihui Investment, Okura Investment, He Quyi, Wang Yayu, Fortune Ventures, Price Asset Management, etc. |
The issuer's listing on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations (which also summarized in Table. 2):
• Listing situation. On January 26, 2016, the company obtained the "About Approval of Guangdong Amethystum Storage Information" issued by the National Share Transfer System. The stock is abbreviated as "Amethystum Storage" and the stock code is It is "835870", and the transfer method is agreement transfer.
• Delisting. On July 2, 2018, the company submitted the application materials for the termination of listing of stocks to the National Equities Exchange and Quotations, and the company's shares were terminated from the National Equities Exchange and Quotations on July 18, 2018.
• The issuer has not received any penalty during its listing on the National Equities Exchange and Quotations.
• Current equity of the company. The controlling shareholders of the company are Zichen Investment and Zihui Investment. Mr. Zheng Mu and Mr. Luo Tiewei respectively held 19.54% of the company's equity through Zichen Investment and Zihui Investment respectively, and held a total of 39.08% of the company's equity. the actual controller of the company.
• The specific IPO road of Amethystum Storage Technology Co., Ltd.
Table 2: The specific IPO road of Amethystum Storage Technology Co., Ltd.
Date | Process |
20190403 | Acceptance of listing materials |
20190417 | The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the first round of "Audit Inquiry Letters" |
20190524 | The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the second round of "Audit Inquiry Letters" |
20190620 | The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the third round of "Audit Inquiry Letters" |
20190717 | The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the forth round of "Audit Inquiry Letters" |
20190930 | The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued the fifth round of "Audit Inquiry Letters" |
20191023 | Approved by the Committee |
20200120 | IPO success |
4. Analysis
4.1. Fact Situation Statement
On April 29, 2022, Amethystum Storage disclosed its 2021 annual report. As the current audit institution, Zhongxi Accounting Firm issued an audit report with no opinion on Amethystum Storage. In this annual report, Zhongxi believes that there are five events that form the basis for not being able to express opinions. In response, the Shanghai Stock Exchange subsequently issued an inquiry letter. The first item is the violation guarantee of Amethystum Storage. As of March 10, 2022, Amethystum Storage and its subsidiaries Guangzhou Amethystum Storage and Meizhou Jingkai have illegal pledge guarantees for time deposit certificates, with a total amount of 373 million yuan, a total of 14 A total of 16 guarantees have been provided by third parties.
The second item is Amethystum Storage’s retrospective adjustment to the 2020 financial statements, which offsets the Industrial Cloud Manufacturing (Sichuan) Innovation Center, Hefei Hargong Lubo Robotics Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei Hargong Rongtai Power Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei Rui. The sales contract of Da Robot Co., Ltd. corresponds to the operating income of 71.8478 million yuan, and the corresponding operating cost is 25.1834 million yuan. Offset the advance payment of 87.7874 million yuan corresponding to the technology development supplier related to the prepaid technology development fee, offset the corresponding research and development expenses of 18.2077 million yuan and the cost of 2.6212 million yuan; offset the net amount of Suzhou Nazhitiandi Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. 31.52 million yuan.
The third item is that Amethystum Storage will return a large number of sales in 2021. Zhuhai Biren Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd. and Shenzhen Shenshan Special Cooperation Zone Shenhui Development Co., Ltd. have sales refunds of 51.3274 million yuan and 33.4928 million yuan respectively. However, the relevant return agreement has not been signed, and the inventory has not been returned to the warehouse where Amethystum Storage is stored. The fourth item is the matters in the 2020 annual report that were issued with qualified opinions by the former accountant, including matters concerning prepayments and accounts receivable. The fifth item is the litigation and other matters of Amethystum Storage.
It is worth noting that, from Grant Thornton to Rongcheng to Lixin to Zhongxi, the three-change accounting firm did not bring qualitative changes to Amethystum Storage, but the authenticity of financial reports "deteriorated", from the reservation in 2020 to the 2021 can't express an opinion. At the same time, the law firm of Amethystum Storage has also changed from Guangdong Hengyi Law Firm to Guangdong Guangxin Junda Law Firm. Compared with the repeated changes of accounting firms, CSC, as the sponsor of the IPO, could not easily "get out". It still has to continue to supervise Amethystum Storage, and issue verification opinions on the inquiry letter issued by the supervision.
4.2. Fraudulent Means
On October 8, 2021, Amethystum Storage made it clear in the "Reply Announcement on the Shanghai Stock Exchange's "Information Disclosure Regulatory Inquiry Letter on Amethystum Storage Storage's 2021 Semi-annual Report", which clearly stated that the relevant bank accounts did not exist for any reason. In the case of limited funds due to pledges and guarantees, the sponsor China Securities Co., Ltd. also issued a clear verification opinion.
On March 13 this year, Amethystum Storage Storage blew itself up involving violation guarantees. The company stated that from March 2021 to March 2022, the company had several violations of guarantees. As of March 10, a total of 13 certificates of deposit were pledged, and the amount of guarantee for third parties amounted to 373 million yuan, involving 4 banks and guarantors. Fang 14. China Securities Investment Securities issued an inspection opinion based on the latest progress, saying that Amethystum Storage does have violations of guarantees.
After the "self-destruction" of Amethystum Storage, the Shanghai Stock Exchange once again issued an inquiry letter to Amethystum Storage, asking it to explain the ins and outs of the illegal guarantee, and at the same time requiring the sponsor and annual audit accountant to fully verify and express clear opinions one by one.
In the inquiry letter, the Shanghai Stock Exchange proposed that Amethystum Storage in the "Reply Announcement on Shanghai Stock Exchange's "Information Disclosure Regulatory Inquiry Letter on Amethystum Storage's 2021 Semi-annual Report", clearly stated that the relevant bank account does not exist Due to the limitation of funds due to pledges and guarantees, the sponsor China Securities Investment Corporation issued a clear verification opinion, but there are currently 4 violation guarantees occurred from March to April 2021, involving an amount of 373 million yuan.
To this end, the Shanghai Stock Exchange requires Amethystum Storage storage and sponsor institutions to seriously self-examine and disclose the verification process, implementation procedures and evidence obtained in the previous response to regulatory inquiries, and explain the reasons for the inconsistent information disclosure before and after and who is responsible.
On March 14, CSC stated that the illegal guarantee of Amethystum Storage does exist, and the 100 million yuan of funds deposited in Guangzhou Bank has been transferred to the bank account of Zhejiang Jingchao Trading Co., Ltd. on March 11, 2022, and other guarantees If the party fails to repay the bank debts on time, the rest of the bank deposit certificates used for illegal guarantees also have the risk of being deducted.
CSC acknowledges that due to the above-mentioned violation of guarantees, Amethystum Storage Storage may assume relevant guarantee obligations, which in turn may cause Amethystum Storage Storage to confirm estimated liabilities and losses, which may lead to risks affecting daily normal operations. At the same time, the violation of Amethystum Storage Storage also reflects that there are defects in its internal control that need to be rectified urgently. CSC will also urge the company to make rectification, and at the same time remind investors to pay close attention to operational and internal control risks, and conduct investment activities cautiously.
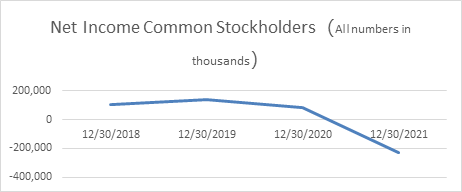
Figure 4: The Income Common Stockholders (all numbers in thousands).
4.3. Payment and Net Profit
Amethystum Storage's four suppliers in Fujian Province either use virtual addresses, or they go to empty buildings, or their office addresses change frequently. According to the supplier's address disclosed in the reply letter of Amethystum Storage Storage (Unit 0118, No. 366, Chengyi Street, Phase III, Xiamen Software Park), it should have been the address of Tumet Intelligence, but it was displayed as Huawei Xiamen DevCloud Innovation Center. When asking the staff of the building whether Tumet Smart was here, the staff said that they "never heard of it", and one of the staff revealed, "It should be a virtual address, and downstairs is Huawei's showroom." Amethystum Storage's two suppliers in Xiamen are missing, and Fujian Yulun and Fuzhou Century Peak in Fuzhou are also difficult to find. In the 2021 annual report, Amethystum Storage's net profit was -229 million, a year-on-year decrease of -379.84, and its performance has changed dramatically after IPO. On May 6, 2022, because the net profit shown by the audit results of the last two fiscal years was negative, Amethystum Storage Storage was issued a delisting risk warning, *ST Amethystum Storage. In June 2022, the actual controller received an investigation letter from the China Securities Regulatory Commission. The results are illustrated in Fig. 4.
4.4. Reasons and Consequences
According to Article 56, when a listed company falls under any of the following circumstances, the stock exchange shall decide to terminate the listing and trading of its stocks:
• The company no longer meets the listing requirements due to changes in its total share capital and equity distribution, and still fails to meet the listing requirements within the time limit specified by the stock exchange;
• The company fails to disclose its financial status in accordance with the regulations, or makes false records in the financial and accounting reports, and refuses to make corrections;
• The company has been losing money for the past three consecutive years, and has not been able to recover profit within the following year;
• The company is dissolved or declared bankrupt;
• Other circumstances prescribed by the listing rules of the stock exchange.
On this basis, the company does not disclose its financial status in accordance with regulations, or makes false records in financial accounting reports, and refuses to correct. The company's performance has been losing money year after year.
5. Suggestions
5.1. Sponsor Liability Issues
Under the background of the registration system of the Science and Technology Innovation Board with information disclosure as the core, the role of the CSRC has been weakened, and the functions and roles of intermediaries have become more prominent. Under this circumstance, although the regulatory authorities advocated stricter and more compacted the responsibilities of intermediaries, and the relevant rules of the Shanghai Stock Exchange have also refined the verification requirements of intermediaries such as sponsors, the relevant regulations have not yet defined the division of responsibilities, responsibility sharing, Respond to issues such as the establishment of a reputation mechanism and the adjustment of punishment standards. In order to make intermediaries return to the role of "gatekeeper", we can learn from relevant regulations in Hong Kong, China and the United States, define the scope of their responsibilities centered on the profession of intermediaries, and differentiate the legal responsibilities between different intermediaries; Reasonable trust” other expert opinions or third-party opinions and other relevant exemptions, appropriately raise the standard of administrative punishment, strengthen law enforcement, implement transparency of sponsorship fees, and comprehensively establish a reputation system for intermediaries [13].
5.2. Delisting Advice
China's securities market is established with the promotion of the government, and the functional orientation of the securities market in the early stage of its establishment is Helping state-owned enterprises solve difficulties and raising funds for the state-owned economy, this initial functional positioning alienates China's securities market The financing function of the market makes it difficult to implement the delisting mechanism of the main board. This alienation of the financing function is first manifested as excessive. The main emphasis is on the use of planned management measures to raise funds for inefficient state-owned enterprises, followed by financing. The non-market-oriented control of operation, and the financing function, as a market-oriented financing channel, is a very low-cost fund. Source channels, and in China, whether it is management, local governments or listed companies, ipo is regarded as a low-cost or even no-cost financing channel. The securities market has become a place for "money misappropriation". Under this guiding ideology, the main board delisting mechanism cannot be implemented.
It is very necessary to establish an efficient delisting system. The lack of a delisting system makes the securities market unable to fully realize the functions of survival of the fittest, rational and effective allocation of resources, and also weakens the role of the external governance mechanism of listed companies. The dominant shareholding structure has led to a long-term slump in the company's control market. Therefore, to ensure the vitality of the securities market, it is necessary to improve the implementation efficiency of the delisting system. In view of the complexity of China's main board market, the regulatory authorities have tried many times, but still have little effect, so they adopted a relatively strict delisting system in the GEM market with relatively simple interests, and improved the implementation efficiency of the delisting system. The delisting mechanism of the main board market is relatively mature, and after accumulating certain experience, the delisting system of the main board market will be further improved. However, it should be noted that the delisting system is actually a systematic system, not just the design of delisting standards and delisting procedures, but also includes issues such as regulatory concepts, investor rights protection, litigation mechanisms, and multi-level capital market construction. If we only make a fuss about delisting standards and delisting procedures, and do not make corresponding reforms in other systems, the delisting rules of the ChiNext board may only be paper rules, which are difficult to achieve the intended purpose, and the efficiency of delisting is still difficult to improve [14].
6. Limitations & Prospects
Amethyst Storage may become the first company to be delisted. The serious treatment of Amethyst Storage is of great deterrent significance to other companies, which reflects the CSRC's determination to vigorously crack down on such behavior and is an important symbol. The weakness of this paper is that it only focuses on the case of Xintai Electric, which may be coincidental. Moreover, what can be collected is public information, which is also limited, and it may be impossible to make a specific interpretation of the subjective reasons that are not obvious. Therefore, the conclusion obtained by exploring the way and reason of its fraud can only be used as a reference in the promotion and use.
7. Conclusion
Amethystum Storage’s first five rounds of inquiries and three rounds of feedback involved a total of 38 issues. The 2020 annual report was issued with reservations. In 2021, it received three inquiries from the Shanghai Stock Exchange. The 2021 annual report was issued and could not express opinions. Due to the large amount of advance payment, accounts receivable and other issues, the annual audit accountant issued a reserved opinion. Reservations mainly involve issues such as prepaid technology development fees, prepaid equipment payments, and the recoverability of accounts receivable. The Science and Technology Innovation Board was originally a financing platform for outstanding technology companies. However, the lack of responsibilities for listing participants has led to the emergence of many "thunder stocks" full of financial problems. To protect the interests of small and medium shareholders, from the perspective of securities companies, the quality of sponsorship should be improved, penalties should be increased, and the cost of fraud should be increased, so as to urge sponsors to clarify their own responsibilities, conscientiously perform sponsorship business, and comprehensively establish a reputation system for intermediaries.
References
[1]. Han Zhiguo, Duan Qiang,Delisting Mechanism: Market Oppression or6 Market Oppression,Economic Science Press,(2002)
[2]. Yang Fan:Financial Crisis Handling and Delisting Legal Protection, China Science Press,(2003)
[3]. Xu Liangping:Innovation in de-lisiting mechanism,securities market guide,66-70,(2004)
[4]. Zhu Caibin,Tang Wenxian:The Impact of Delisting Mechanism on China's Stock Market Function,Finance and Economics, second issue,(2006)
[5]. James R. Booth and Richard Smith:Capital raising, underwriting and the certification hypothesis Journal of Financial Economics, vol. 15, issue 1-2, 261-281,(1986)
[6]. RICHARD CARTER, STEVEN MANASTER:Initial Public Offerings and Underwriter Reputation,The Journal of FinanceVolume 45, Issue 4 p. 1045-1067,(1990)
[7]. Roni Michaely, Wayne H. Shaw:The Pricing of Initial Public Offerings: Tests of Adverse-Selection and Signaling Theories, The Review of Financial Studies, Volume 7, Issue 2, April 1994, Pages 279–319, (1994)
[8]. James R.Booth Richard L.SmithII:Capital raising, underwriting and the certification hypothesis,Journal of Financial Economics Volume 15, Issues 1–2, January–February 1986, Pages 261-281,(1986)
[9]. Tiago Duarte-Silva:The market for certification by external parties: Evidence from underwriting and banking relationships,Journal of Financial Economics,Volume 98, Issue 3, December 2010, Pages 568-582,(2010)
[10]. Tze Chuan 'Chewie' Ang :Understanding the Distress Puzzle: Surprises in the Pre-Delisting Period, 2012 Financial Markets & Corporate Governance Conference,77 Pages,(2012)
[11]. Amethystum Storageum Homepage,https://www.Amethystum Storageum.com/article/type/1002-1.html
[12]. PWC Homepage, https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/audit-assurance/ipo-centre/global-ipo-watch.html
[13]. Zhai Hao:Delisting of Listed Companies, Theoretical Analysis and Institutional Construction, East China University of Political Science and Law, Shanghai,(2012)
[14]. Xue Shuang,Wang Yu:Reply to the IPO review inquiry on the Science and Technology Innovation Board and underpricing,management of the word,the fourth issue, 185-197,(2022)
Cite this article
Zhang,Y. (2023). Analysis of IPO Fraud: Evidence from Amethystum Storage. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,13,262-272.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Han Zhiguo, Duan Qiang,Delisting Mechanism: Market Oppression or6 Market Oppression,Economic Science Press,(2002)
[2]. Yang Fan:Financial Crisis Handling and Delisting Legal Protection, China Science Press,(2003)
[3]. Xu Liangping:Innovation in de-lisiting mechanism,securities market guide,66-70,(2004)
[4]. Zhu Caibin,Tang Wenxian:The Impact of Delisting Mechanism on China's Stock Market Function,Finance and Economics, second issue,(2006)
[5]. James R. Booth and Richard Smith:Capital raising, underwriting and the certification hypothesis Journal of Financial Economics, vol. 15, issue 1-2, 261-281,(1986)
[6]. RICHARD CARTER, STEVEN MANASTER:Initial Public Offerings and Underwriter Reputation,The Journal of FinanceVolume 45, Issue 4 p. 1045-1067,(1990)
[7]. Roni Michaely, Wayne H. Shaw:The Pricing of Initial Public Offerings: Tests of Adverse-Selection and Signaling Theories, The Review of Financial Studies, Volume 7, Issue 2, April 1994, Pages 279–319, (1994)
[8]. James R.Booth Richard L.SmithII:Capital raising, underwriting and the certification hypothesis,Journal of Financial Economics Volume 15, Issues 1–2, January–February 1986, Pages 261-281,(1986)
[9]. Tiago Duarte-Silva:The market for certification by external parties: Evidence from underwriting and banking relationships,Journal of Financial Economics,Volume 98, Issue 3, December 2010, Pages 568-582,(2010)
[10]. Tze Chuan 'Chewie' Ang :Understanding the Distress Puzzle: Surprises in the Pre-Delisting Period, 2012 Financial Markets & Corporate Governance Conference,77 Pages,(2012)
[11]. Amethystum Storageum Homepage,https://www.Amethystum Storageum.com/article/type/1002-1.html
[12]. PWC Homepage, https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/audit-assurance/ipo-centre/global-ipo-watch.html
[13]. Zhai Hao:Delisting of Listed Companies, Theoretical Analysis and Institutional Construction, East China University of Political Science and Law, Shanghai,(2012)
[14]. Xue Shuang,Wang Yu:Reply to the IPO review inquiry on the Science and Technology Innovation Board and underpricing,management of the word,the fourth issue, 185-197,(2022)









