1. Introduction
The 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China clearly puts forward the strategy of strengthening the country through education, puts forward important conclusions such as "education is the important plan of the country and the Party" and "the strong youth makes the country strong", and constantly promote the development of higher education. At the same time, the world is involved in the wave of science and technology, and the demand for high-quality innovative talents is increasing. Therefore, it has become the requirement of The Times to continuously promote college students to learn basic knowledge and improve their scientific research ability.
However, the popularity of the Internet makes virtual social networking and online surfing gradually occupy the life of college students, which has a huge impact on their study. Through the survey of 2183 students of Jilin Industry and Business College, involving a total of 10 colleges and four grades (see Figure 1). It is concluded that college students' entertainment will seriously occupy the normal study time [1].
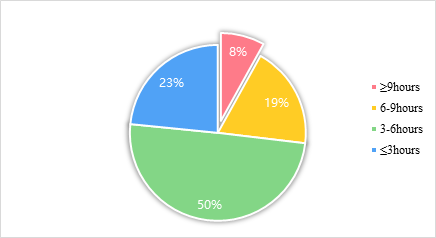
Figure 1: Average recreation time per day.
Hou Yanqin, Zhang Shumin and Zhang Yutong also investigated the relationship between mobile phone entertainment and learning procrastination, which is the most important part of college students' entertainment. Through a survey of 900 students from Cangzhou Medical College, it is concluded that there is a significant positive correlation between the total score of college students' mobile phone dependence questionnaire and the total score of runaway, withdrawal, evasion, inefficiency and the total score of the learning procrastination questionnaire and the completion of homework, review preparation, and independent learning dimension score, indicating that college students' mobile phone dependence has a serious impact on learning delay [2]. This is not only the squeeze of the study time, but also the deterioration of the study habits.
Obviously, learning and entertainment can bring satisfaction to students, but more students choose entertainment. This is worth reflecting on and exploring. From the perspective of pan-entertainment, entertainment is the behavior of pursuing immediate enjoyment; on the contrary, because learning is essentially self-preparation and self-improvement for future life, learning becomes a behavior similar to delayed enjoyment. Taking this as a starting point, this paper starts to analyze the action mechanism of pan-entertainment doctrine, explore the causes of this phenomenon from the perspective of inconsistent time preference, and puts forward corresponding solutions to improve students 'learning motivation and adapt to the trend of the world's demand for high-quality talents.
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Background
What is entertainment? Xu Shen said, "entertainment, is happiness ", and defined entertainment as a means to seek happiness, which points out the motivation of entertainment. Entertainment Psychology believes that entertainment is an experience that is pursued and enjoyed by humans [3]. The Uses and Gratification Theory believes that users choose media based on their utility [4]. When they gain satisfaction by using media, they have the motivation to continuously use media for entertainment. Park points out that using a phone can be motivated for instrumental purposes, namely accessing information and entertainment [5]. The entertainment here also refers to the harvest of happiness. Consumers seem to be choosing entertainment rationally, but there are irrational factors. Epicurus once divided happiness into sensual pleasure and spiritual pleasure, believing that "sensual pleasure itself lies only in the continuous desire, and it disappears once the goal is achieved" [6]. This psychology of entertainment first also seems to be one of the reasons for excessive entertainment.
Traditional economic theory holds that people's time preferences are consistent, but Strotz in 1956 proposed the concept of inconsistent time preferences, pointing out that people's time preferences will change due to the change of time [7]. At the same time, individual learning decisions are also influenced by "time preferences" [8]. Due to the inconsistency of time preference, students will have the psychology of myopic cognitive bias. Using the hyperbolic discount model to describe the myopic cognitive bias, it will be found that students' time preference has the characteristics of high short-term discount rate and low long-term discount rate [9, 10]. This also becomes an important theoretical basis for the analysis.
The marginal contribution of this paper is that although there have been many studies on the interrelationship between learning and entertainment, it does not introduce the analysis perspective of inconsistency between time preference and myopic cognitive bias in the analysis of the influence of entertainment on learning, and lacks further exploration of the influence mechanism of entertainment. This paper makes up for this defect to some extent.
3. Framework and Research Design
3.1. Causes and Action Mechanisms of Entertainment
The development of the information age has provided a fertile ground for entertainment, which has also become an important source of students' addiction to enjoyment. In the information age, the audience is no longer the passive viewer in the traditional media era, but becomes the "prosumer, that is, the unity of entertainment consumers and producers" [11]. This is because big data can accurately capture people's preferences, so while people gradually define their own entertainment, a steady stream of information will "cast them" to attract people’s attention.
The encroachment of entertainment on people's life is also related to people's psychology. The psychology of "entertainment first" enables people to pursue simple sensory happiness. Compared with spiritual pleasure, the simple ease of sensory pleasure lowers the threshold of entertainment. At the same time, people's instinctive pursuit of advantages and avoiding harm make people seek to escape in the pressure of life. The interaction between the two makes people gradually indulge in pleasure and ignore the sense of achievement and satisfaction of realizing the value of life [12].
Pan-entertainment is a capitalized idea. In western culture, including in the Chinese context of Shuo Wen Jie Zi, entertainment refers to the spiritual recreation. However, by cultivating the theory of audience identity, emotional identity, value of identity and identity, etc., the entertainment deeply embedded in real life, to spirituality, to sublime, alienation entertainment concept, even using the network environment of low-cost intensified contradictions and emotional expression, happiness increasingly floating in the form, become a fast food consumption.
3.2. Importance and Motivation of Learning
Learning is a necessary preparation to realize their own sustainable development and create social value. China has clearly highlighted the requirements of "building a learning society" in the 14th Five-Year Plan and the long-term goal of 2035. This is of great significance to adapt to the demand of high-quality talents in the information age, promote the high-quality development of economy and accelerate the social and economic transformation.
This paper wants to explore the means to solve the contradiction between entertainment and learning, to find solutions to urge students to learn, first of all, people must know the motivation of learning. This paper mainly uses the ARCS model (see Figure 2) to analyze the mechanism of action of each element from the perspectives of attention, correlation, confidence and satisfaction [13]. The main role of attention is to shift students' attention to learning, so people need to think about how to make students have a basic interest in learning like entertainment. Correlation refers to the correlation between knowledge and practice. Using the knowledge learned to solve problems in real life can well stimulate students' endogenous learning motivation. Satisfaction refers to the pleasure that students can solve problems independently by learning knowledge. Self-confidence focuses on learning to master enough knowledge and confidence in self-ability. The discount perspective of time preference is to consider the weight given to learning by students and the utility of learning. Therefore, satisfaction will be the focus of this study.
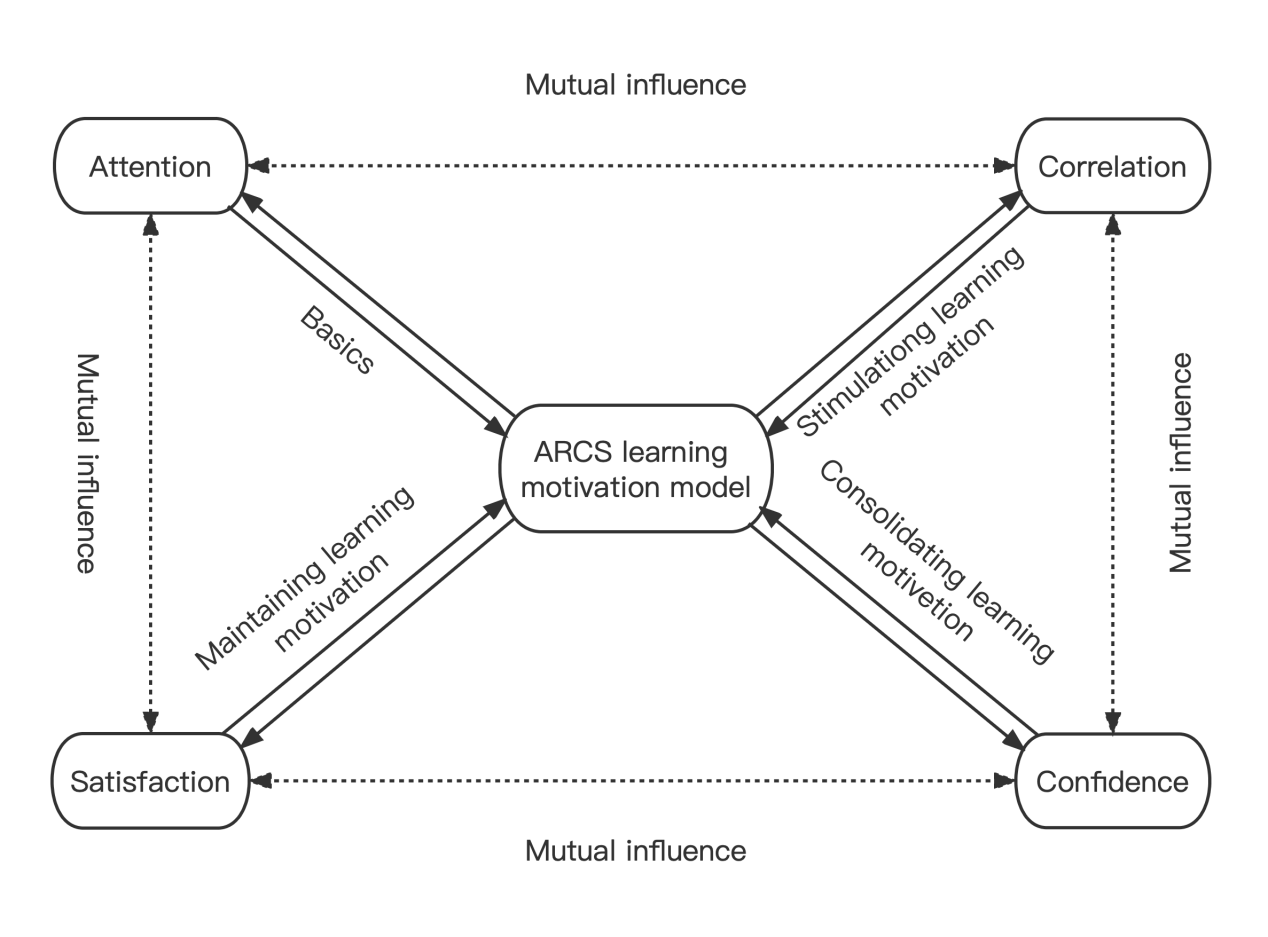
Figure 2: ARCS learning motivation model.
3.3. The Relationship Between Entertainment and Learning
According to the previous analysis, both entertainment and learning can meet the needs of students to a certain extent, and have sufficient utility for students. However, the reality is that students will waste a lot of time to meet their entertainment needs even if they clearly know the importance of learning, thus seriously squeezing their learning time. Moreover, in reality, there is usually a very interesting phenomenon: Someone had promised to follow the future study plan, but when got ready to implement it, the plan was almost unfinished, and most of the time was lost on mobile phones and other entertainment devices. This suggests that preference reversal occurs in people’s inter-temporal decisions. In the short term, people prefer immediate utility, but in the long term, they are more rational and choose to learn.
From the perspective of diminishing patience, people always want to satisfy the utility as soon as possible, and largely refuse to delay the enjoyment. So, when people make a choice between entertainment and learning, people will consider that entertainment can bring people immediate happiness, but most of the utility of learning should be realized in the future, and learning means to separate the present time from the entertainment. As a result, many people are addicted to entertainment and refuse to devote their time to study.
Under the influence of limited willpower, people cannot have complete control over their actions. O'Donoghue, proposed the decision two-system model, which decomposes the decision into the interaction process of two systems, emotional system and rational system [14]. The emotional system dominates and tends to enjoy short-term enjoyment, while the role of the rational system depends on the amount of willpower, balancing short-term and long-term utility. Therefore, the emergence of students' learning problems and their own lack of self-control has a great relationship. In the face of learning, rational people will use their willpower to make the rational system on the emotional system and avoid short-sighted; However, due to the students' weak self-control, the rational system cannot play a greater role, and the emotional system continues to dominate, which makes entertainment seriously hinder the normal study and life.
Loss aversion is another important factor. It is proved that people have loss aversion. This is manifested by a stronger loss of the same degree of loss and gain than the sense of gain, different risk preference for loss and gain, and diminishing marginal sensitivity to utility change [15]. Using the characteristics of decreasing marginal sensitivity, it is easy to analyze the phenomenon mentioned above. Whether for gain or loss, the perception of him decreases away from the reference point, that is, the time to learn. When making a plan, usually there is still a certain time before the implementation of the plan, the study plan is usually only simulated in the mind, will mistakenly estimate the test of learning willpower, the difficulty of learning will be small, people will "swear" that they will study according to the plan. However, when it comes to implement the plan, that is, closer and closer to the reference point, people will gradually feel the pressure of learning, and the degree of impatience will increase. Learning also means the loss of entertainment time, which is much stronger than the sense of gain through learning. At the same time, with the help of the decision-making dual system theory, the willpower at this time can hardly balance the utility of short-term and long-term decisions in the face of the strong emotional system, and people will have a strong impulse to pursue immediate pleasure. Therefore, various factors interact and influence each other, and people will leave their plans behind and become appendages of entertainment.
3.4. Resolution and Measure
This paper analyzes the relationship between entertainment and learning, and points out that entertainment has a serious exclusion effect on learning. However, the purpose of the analysis is to urge students to better devote themselves to their study and life, so this paper proposes the following measures to solve the contradiction between the asymmetry and imbalance between entertainment and study.
3.4.1. Popularization of Mental Health Knowledge
Pay attention to students' psychological adjustment. One of the most important reasons for students' addiction to entertainment is that due to the excessive learning pressure, negative emotions are constantly filled in their hearts, so they turn to entertainment to seek comfort, so as to escape from real life. Therefore, in each school should establish a complete psychological counseling mechanism, equipped with a complete psychological counseling personnel. In addition to providing daily psychological counseling services, also mental health knowledge popularization education should be carried out to guide students to properly relieve pressure and avoid the psychology of negative coping.
3.4.2. Dissemination of Valuable Knowledge
The government should strengthen oversight of digital platforms. The algorithm mechanism of digital platform firmly grasps people's attention. It poisons the hearts of students with meaningless content. "Simple sensory entertainment is not equal to spiritual entertainment." The government should strengthen the restrictions on the content of digital platforms, while pursuing economic benefits, but also pay attention to the dissemination of knowledge, and promote the drainage of knowledge in the platform. At the same time, the platform should be required to limit and remind students' use time to a certain extent, and use mandatory means to enhance their willpower.
3.4.3. Establishment of Effective Learning Evaluation Mechanism
For students, the future achievement and the realization of self-worth are relatively long-term goals, which makes learning become a long-term effect compared with entertainment, resulting in deviation under the psychological influence of inconsistent time preferences. The short-term evaluation mechanism of learning mainly involves academic performance. According to the ARCS learning motivation model, students are satisfied with the acquisition of academic performance. However, the problem is that the students of achievement satisfaction largely from their past achievements and others of contrast, but in the process of achievement evaluation is difficult to achieve absolute fair, achievement is difficult to reflect the various aspects of efforts, the unfair feeling will constantly enlarge, and affect the students' satisfaction. Therefore, teachers should establish a double evaluation mechanism of process and result, include more influencing factors in quantifying the performance, and comprehensively evaluate the whole process. At the same time, in the daily study and life, people should pay attention to the feedback of comments, and give encouragement and affirmation to students, which is an effective means to improve students' satisfaction.
3.4.4. Improvement of Information Collection and Processing Ability
Behavioral economics believes that incomplete and uncertain access to information can make people even more short-sighted [16], pay more attention to the immediate utility, and selectively ignore the long-term interests. As a result, they can only achieve the short-term maximum utility, and it is difficult for them to achieve the optimal planning. Therefore, in the context of the rapid development of information technology, by improving their personal information technology literacy, students can better judge the learning effectiveness and cost, make more reasonable learning decisions, and reduce the impact of entertainment on learning.
3.4.5. Perfection in Learning Reward System
People’s addiction to entertainment is closely related to the weak short-term utility of learning. However, people can decompose the learning goals, and encourage and support to excellent students through a reasonable award evaluation and evaluation system, so as to stimulate students' enthusiasm for learning. At the same time, learning tasks can be set in a gradient. Students who complete the task earlier should have less homework or higher scores, so that students can free themselves from excessive entertainment and transfer their attention to learning.
3.4.6. Cultivation of Students' Self-discipline Quality
In the final analysis, all the measures are only auxiliary, and students should pay attention to learning from the bottom of their hearts, which is the key to solve the learning problems. Students should strengthen the sense of self-discipline and actively resist the temptation. They should realize the importance of learning for their own development ideologically, so as to work hard to contribute to the realization of their own and the development of the motherland.
4. Conclusion
Learning is a necessary means to improve their own quality and adapt to the development of modern society. This paper analyzes the relationship between entertainment and learning through the existing data, and points out the phenomenon of entertainment squeezing the learning time. Then from the perspective of the development of social psychology and entertainment carrier, this paper analyzes the reasons why entertainment can quickly attract students' attention. At the same time, this paper starts from the ARCS learning motivation model, and points out that in addition to the long-term goal of realizing their own value, attention, relevance, satisfaction and self-confidence are the four major starting points to encourage students to devote themselves to learning in the short term. Based on this, it focuses on the theory of inconsistent time preference. This paper combines the explanation of the perspective of diminishing patience, limited willpower and the important view of western economics that students prefer to entertain more in daily life. This paper also puts forward feasible measures for the social psychology of "entertainment first", the upgrading of entertainment carrier, ARCS learning motivation model, time preference inconsistency and other factors affecting students 'learning, and emphasizes the importance of students' self-attention.
Of course, this paper also has deficiencies and defects. For example, in the discussion of entertainment and learning issues, this paper mainly uses the data of Cangzhou Medical College and Jilin Industry and Commerce University to draw a conclusion, and it is not representative from the perspective of data. For “Project 985” and “Project 211” college students, the impact of entertainment on learning may be relatively weakened.
References
[1]. Yu Caixia, Man Siyu, Zhang Tingting. Analysis of the current situation and countermeasures of the Impact of online entertainment on college students' learning and life. Fujian Textile, 2022, (10): 73-76.
[2]. Hou Yanqin, Zhang Shumin, Zhang Yutong. Study on the status of mobile phone dependence of higher vocational college students and its influence on learning delay. Health Vocational Education, 2022, 40(19): 115-117.
[3]. Jennings B, Peter W. Entertainment psychology. Beijing: Communication University of China Press, 2022.
[4]. Lee CS, Ma L. News sharing in social media: The effect of gratifications and prior experience. Computers in Human Behavior, 2012, 28(2): 331-339.
[5]. Park WK. The mobile phone addiction among Korean college students. Korean Society for Journalism & Communication Studies, 2003, 47(2): 250-281.
[6]. Schopenhauer A. The wisdom of life: Counsels and Maxims. Shanghai: Shanghai People's Publishing House, 2016.
[7]. Strotz RH. Myopia and Inconsistency in Dynamic Utility Maximization.Review of Economic Studies, 1956, 23(3): 165-180.
[8]. Yang Yi. Empirical study of delays among college students based on time preferences. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2016.
[9]. Hoch SJ, Loewenstein GF. Time-inconsistent preferences and consumer self-control. The Journal of Consumer Research, 1991, 17(4): 492-507.
[10]. Gheith E, Jaberi NM. The effectiveness of an interactive training program in developing a set of non-cognitive skills in students at university of pet. Higher Education Research, 2017, 13(3): 106-118.
[11]. Christian F. Digital labor and Karl Marx. New York: Routledge, 2014.
[12]. Xing Guozhong, Zhang Min. A psychosocial analysis of pan-atonalism and its coping. Research on Ideological Education, 2022 (05): 106-111.
[13]. Yan Wenfei. Teaching strategy of liberal arts innovation and entrepreneurship course in universities based on ARCS Learning Motivation Model. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Social Science Edition), 2022, 38(05): 59-64.
[14]. Loewenstein G, Donoghue T. Animal spirits: Affective and deliberative processes in economic behavior. Available at SSRN 539843, 2004.
[15]. Kai-Ineman D, Tversky A. Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 363-391.
[16]. Wang Yilin, Chen Xianjie, Sun Rong. Effect of health risk cognitive bias on commercial health insurance purchase decision — Based on behavioral economics perspective. China Soft Science, 2021, (9): 66-74.
Cite this article
Bao,H. (2023). Analysis of the Relationship Between Learning and Entertainment from the Perspective of Behavioral Economics. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,29,41-47.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Yu Caixia, Man Siyu, Zhang Tingting. Analysis of the current situation and countermeasures of the Impact of online entertainment on college students' learning and life. Fujian Textile, 2022, (10): 73-76.
[2]. Hou Yanqin, Zhang Shumin, Zhang Yutong. Study on the status of mobile phone dependence of higher vocational college students and its influence on learning delay. Health Vocational Education, 2022, 40(19): 115-117.
[3]. Jennings B, Peter W. Entertainment psychology. Beijing: Communication University of China Press, 2022.
[4]. Lee CS, Ma L. News sharing in social media: The effect of gratifications and prior experience. Computers in Human Behavior, 2012, 28(2): 331-339.
[5]. Park WK. The mobile phone addiction among Korean college students. Korean Society for Journalism & Communication Studies, 2003, 47(2): 250-281.
[6]. Schopenhauer A. The wisdom of life: Counsels and Maxims. Shanghai: Shanghai People's Publishing House, 2016.
[7]. Strotz RH. Myopia and Inconsistency in Dynamic Utility Maximization.Review of Economic Studies, 1956, 23(3): 165-180.
[8]. Yang Yi. Empirical study of delays among college students based on time preferences. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2016.
[9]. Hoch SJ, Loewenstein GF. Time-inconsistent preferences and consumer self-control. The Journal of Consumer Research, 1991, 17(4): 492-507.
[10]. Gheith E, Jaberi NM. The effectiveness of an interactive training program in developing a set of non-cognitive skills in students at university of pet. Higher Education Research, 2017, 13(3): 106-118.
[11]. Christian F. Digital labor and Karl Marx. New York: Routledge, 2014.
[12]. Xing Guozhong, Zhang Min. A psychosocial analysis of pan-atonalism and its coping. Research on Ideological Education, 2022 (05): 106-111.
[13]. Yan Wenfei. Teaching strategy of liberal arts innovation and entrepreneurship course in universities based on ARCS Learning Motivation Model. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Social Science Edition), 2022, 38(05): 59-64.
[14]. Loewenstein G, Donoghue T. Animal spirits: Affective and deliberative processes in economic behavior. Available at SSRN 539843, 2004.
[15]. Kai-Ineman D, Tversky A. Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 363-391.
[16]. Wang Yilin, Chen Xianjie, Sun Rong. Effect of health risk cognitive bias on commercial health insurance purchase decision — Based on behavioral economics perspective. China Soft Science, 2021, (9): 66-74.









