1. Introduction
1.1. The Chinese Market for Customized Meal Services
With the rising popularity of light food products, an increasing number of individuals are embracing this nutritious dietary trend. Light foods are broadly characterized as healthy options encompassing a variety of fruits, fresh vegetables, meats, and seafood. These foods play a pivotal role in reducing body fat and maintaining balanced daily nutritional requirements. According to the "China Light-Food Delivery Consumption Report," light food orders experienced a remarkable 98% year-on-year increase in September 2019 [1]. During the November holidays of the same year, light food deliveries surged by an impressive 128% [1]. These statistics underscore the burgeoning demand for light food products within the market [1].
Furthermore, data from the "Light-Food Consumption Big Data Report" for the same year revealed a substantial increase in searches on the Meituan App compared to 2018. The number of searches for four key terms, namely, "light-food," "fat-loss meal," "weight-loss meal," and "healthy meal," surged by 235.8%, 200.6%, 186.4%, and 116.0%, respectively [2]. Many industry experts posit that light foods have evolved into a mainstream healthy dietary lifestyle, transitioning from a niche trend to a popular choice. This healthy lifestyle choice is no longer confined to major Chinese cities but is spreading from first-tier and new first-tier cities to second- and third-tier cities, signifying substantial growth potential. A health-conscious lifestyle is becoming an increasingly favored option.
This vast potential market is drawing a multitude of enterprises. Tianyancha, a prominent Chinese commercial inquiry platform, analyzed market data and reported rapid growth in China's light-food enterprises over the past five years. The annual registration growth rate for related companies has consistently exceeded 40% since 2016. Currently, more than 8,000 Chinese firms are actively involved in relevant business activities. In just the first half of the previous year, over 3,000 companies targeting the light food market were established. Their product offerings predominantly include items such as "zero-calorie, zero-fat, zero-sugar, no-burden" cereals, low-fat shakes, protein bars, and chicken breasts. Additionally, numerous renowned food brands are progressively introducing light food products, and even industries beyond food, such as fitness clubs, are venturing into this market.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge that the light-food market remains a relatively nascent industry. On one hand, some consumers express skepticism regarding the natural efficacy and quality of light foods. On the other hand, issues of high product homogenization and pricing persist, causing concerns among customers. It is important to note that blandishments alone do not lead to windfall profits. Despite some industry insiders estimating these products to yield approximately 150% returns, operators must contend with platform fees, packaging expenses, labor costs, rent outlays, marketing expenditures, and various other overheads. Consequently, the profit margins available to light food companies are relatively modest. These challenges pose significant obstacles to the sustainable development of the fair food market. The imperative task for market participants is to devise comprehensive solutions to address these issues.
1.2. Addressing the Challenges of Diet Management: A Business Model for Chronic Patients
The management of long-term dietary needs for patients with chronic illnesses can be an arduous task for their families in today's fast-paced world. Modern individuals are faced with the challenge of balancing work and personal lives, making it increasingly difficult to provide adequate care for chronically ill family members. Moreover, the dietary requirements for these patients are often complex, necessitating precise nutritional balance tailored to their health conditions. Additionally, a significant portion of the population lacks the professional knowledge required to maintain a nutritious and healthy diet. Consequently, the preparation of specialized meals becomes a significant time and effort investment. Unfortunately, the market has struggled to meet this demand adequately, with only a few companies in China offering nutritional meal customization services for chronic diseases.
These products and services are rooted in the concept of customized healthy food and cater to individuals who are either seeking to lose weight or maintain their body shape. The target demographic is primarily composed of economically stable individuals who live alone and lack the time or inclination to prepare specialized meals. These customers will receive customized, health-conscious meals with dietary ratios carefully calibrated based on their foundational health assessment data, including factors such as exercise habits, physical condition, energy expenditure, gender, height, and weight. The service will only be available through long-term monthly subscriptions via an online platform. In terms of recipe development, periodic body assessments will enable operators to continually update their understanding of customers' daily habits and physical health status.
To provide consumers with a comprehensive experience, physical stores will be established as experiential centers where potential customers can learn about and experience the full range of products and services. These offline locations will feature transparent glass designs to entice customers and maximize product visibility. To optimize manufacturing costs, the business will explore partnerships with local restaurants that meet specific operational criteria rather than pursuing in-house production. As the venture matures, the target audience will expand to include individuals with chronic medical conditions requiring ongoing dietary attention, such as diabetics and hypertensive patients.
As the appeal of a healthy lifestyle continues to grow, various strategies will be employed to expand market reach. A healthy lifestyle is no longer solely defined by dietary habits; it encompasses new lifestyle choices. An increasing number of advocates for healthy living are extending their principles to embrace environmentalism. This presents a unique advertising opportunity, and, therefore, a line of zero-waste sub-products will be introduced during this phase, significantly impacting promotional efforts.
To assess the practical viability of customized healthy food products and identify potential consumers, the study employs multiple logistic regression analysis and cluster analysis to uncover consumer characteristics and market potential. It is evident that a substantial gap exists in China's market for managing the dietary needs of chronic patients. This research can serve as a reference for other businesses seeking to enter this burgeoning market.
2. Literature Review: The Nexus of Nutrition, Health, and Sporting Performance
The inherent connection between good health and nutrition has been extensively documented in scientific literature [3]. The impact of nutrition on sporting performance has emerged as a well-defined field of study, applicable to athletes of all levels, from professional competitors to weekend sports enthusiasts, and even those who engage in daily exercise routines. A nutritionally sound diet serves as the fundamental cornerstone for augmenting performance [3].
Customers aspiring to achieve peak sporting performance must prioritize their nutritional intake, as substantiated by the research of Nguyen and Phan [4]. To attain optimal results, they necessitate a meticulously planned and nutritionally balanced diet, aligning with the vitamin and mineral requirements commonly observed in athletes. Furthermore, Maesen et al. [5] emphasize the importance of incorporating an adequate protein intake to facilitate muscle growth and repair.
Given that the primary target market for these products and services encompasses individuals seeking long-term body management, there is a compelling case for increased consumption [6]. Athletes, in particular, often find themselves in need of customized healthy food options to cater to their unique nutritional requirements and support muscle recovery.
Daily training regimens often demand specific dietary considerations to furnish the requisite energy and nutrients essential for meeting the rigorous demands of exercise and promoting adaptation and recovery between training sessions [4]. Such diets should encompass a diverse array of foods, with a notable emphasis on leafy green vegetables and low-fat dairy products, which contribute to the development of enduring nutritional habits and behaviors [3]. Healthy light-food products can play a pivotal role in assisting individuals in achieving their optimal body weight and fat levels, thereby enhancing their overall performance. Furthermore, these foods provide essential fluids to ensure optimal hydration before, during, and after exercise, thus contributing to the short- and long-term well-being of athletes.
3. Hypotheses and Data Analysis: Investigating Consumer Behavior
3.1. Hypotheses
This section presents and tests three hypotheses related to consumer spending on healthy meal services, monthly income, family size, and exercise habits. It details the data analysis process and unveils the outcomes, providing insights into the relationships between these variables:
Hypothesis 1: Customers who have sports consumption habits and are willing to buy healthy meals will be interested in customized nutrition products.
These healthful food products will be priced affordably, ensuring accessibility for individuals with moderate to high incomes. Nevertheless, the product range will be diverse, catering to the specific needs of a wide clientele, including those with chronic conditions [6]. A common economic principle asserts that an increase in consumers' monthly income typically leads to heightened demand for goods and services, whereas a decrease in income corresponds with a decrease in demand for the same items [7]. However, in the case of inferior goods, an income increase typically reduces demand, while an income decrease raises demand.
Rising monthly incomes indicate greater financial capacity to purchase goods and services, resulting in an increased demand for customized food products [8]. Increased income levels empower consumers to allocate more resources to their health and nutritional requirements, fostering healthier lifestyles. This, in turn, boosts sales profits and business operations. Conversely, a decline in income levels may lead to reduced spending, lower company sales, staff layoffs, and a decrease in overall profitability [9]. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that an increase in consumers' monthly income will drive greater demand for healthy food products, with higher incomes facilitating an increased focus on wellness, nutritional intake, and other factors supporting healthy living. Consequently, an increase in income is expected to positively impact the demand for customized light-food products. Based on this rationale, the second hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 2: Customer groups with higher monthly incomes are more likely to purchase health products and, consequently, are more inclined to acquire light-food customization products and services.
Social factors related to family dynamics, such as family size, religion, and income levels, significantly influence the consumption of healthful food products [10,11]. For instance, families with higher income levels are better positioned to afford health products than those with limited financial resources. Among the primary target customers are individuals with chronic health conditions [6]. Families with members who have chronic health conditions are highly likely to consume customized food products, as these offerings provide the necessary nutritional support to manage their conditions and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Importantly, customized food service providers conduct comprehensive physical assessments of clients to develop personalized recipes with tailored nutritional profiles [6]. Individuals with chronic conditions typically have specific dietary requirements that must be met to effectively manage their health [12]. Families with such members are among the prime consumers of customized meal products, as service providers can assess, prescribe, and supply healthful products tailored to their needs. Thus, the third hypothesis is proposed:
Hypothesis 3: Families with higher incomes and families with special demographics, such as individuals with health issues, are more inclined to purchase health products.
The formulation of these hypotheses is grounded in an exploration of various factors influencing food service selection. To align with the research objectives, three assumptions have been developed:
1. Expenditure on healthy meal services is linked to individuals' monthly incomes.
2. Expenditure on healthy meal services is associated with the number of family members.
3. People's spending on healthy meal services correlates with their spending on exercise.
To test these hypotheses, surveys were administered to a sample of the general population (N=109), categorized into three groups: employed individuals (Nw=65), students (Ns=34), and freelancers (Nf=10), as depicted in Figure 1. These groups were selected as they represent the primary focus of the study, encompassing college students, office workers, and other professionals. Office workers and students constitute the majority, while other professionals are less represented. Participants in the study were aged between 19 and 46 years and reported monthly incomes ranging from 1,100 yuan to 9,400 yuan. The study considered both healthy individuals and those with chronic diseases, with the questionnaire designed to address all three hypotheses. Figure 1 below provides an overview of the study participants.
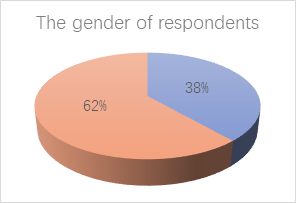
Figure 1: Respondents’ Gender
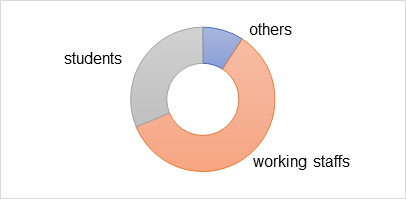
Figure 2: Respondents’ Occupations
3.2. Data Analysis
The data collection process primarily relied on questionnaires, and statistical methods were employed to construct multiple logistic regression models to assess the validity of the hypotheses.
Table 1: Correlations between factors
Correlations | |||||
You are more likely to choose the following types of catering services : |
| Gender | Age | Monthly Income | Monthly expenditure on healthy food |
Pearson's correlation | 0.061 | 0.074 | 0.069 | -0.058 | |
Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.053 | 0.445 | 0.478 | 0.547 | |
N | 109 | 109 | 109 | 109 | |
Whether Have sport/fitness habit or not | Monthly expenditure on sport/fitness | Weekly usge of Delivery services | Family Numbers | ||
Pearson's correlation | 0.148 | -0.200 | 0.015 | -0.008 | |
Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.124 | 0.037 | 0.277 | 0.931 | |
N | 109 | 109 | 109 | 109 | |
Whethter have Chronic disease ornot | The numbers of chronic patients in family | Attention to healthy food | The willingness to earn about the healthy Nutrition management knowledge | ||
Pearson's correlation | -0.027 | -0.039 | -0.042 | -0.030 | |
Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.781 | 0.688 | 0.667 | 0.760 | |
N | 109 | 109 | 109 | 109 | |
The results presented in Table 1 examine the relationships between various factors and how they relate to people's spending on sports. The multiple logistic regression analysis revealed a significant correlation between individuals' expenditure on healthy meal services and their spending on exercise (P<0.05). This finding suggests that the third hypothesis may be valid, indicating that the cost of training could be a direct influencing factor in individuals' decisions to opt for customized meal services.
3.2.1. Exploration of the Possible Mediator
Regrettably, the analysis in Table 2 reveals that people's spending on a fitness diet serves as a partial mediator rather than a complete one. When the variable for monthly healthy food expenditure (T= -0.490, P= 0.625) was introduced alongside the variable for monthly fitness expenditure (T= -2.108, P=0.037), the significance level of the monthly fitness expenditure changed from 0.37 to 0.41. This suggests that the monthly healthy food expenditure factor partially diminishes the significance of exercise spending. In conclusion, the third hypothesis, asserting that people's expenditure on exercise impacts their consumption of customized meal services, remains valid.
Table 2: Coefficients of the Possible Mediator
Coefficients | ||||||||
understandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | 95% Confidence Interval for B | ||||||
Model | B | Std. Error | Bata | t | Sig. | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |
1 | (Constant) | 3.374 | 0.272 | 12.382 | 0.000 | 2.834 | 3.914 | |
Monthly Expenditure onsport/fitness | -0.001 | 0.001 | -0.200 | -2.108 | 0.037 | -0.002 | 0.000 | |
2 | (Constant) | 3.499 | 0.375 | 9.342 | 0.000 | 2.757 | 4.242 | |
Monthly expenditure on sport/ fitness | -0.001 | 0.001 | -0.197 | -2.068 | 0.041 | -0.002 | 0.000 | |
Monthly expenditure on healthy food | -0.059 | 0.121 | -0.047 | -0.490 | 0.625 | -0.300 | 0.181 | |
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis and Characteristics of Potential Customers
Cluster analysis was employed to identify potential customer characteristics that are most likely to be interested in customized meal services. Table 3 illustrates that customized healthy food is more commonly favored by women than men, and it tends to be more popular among individuals aged 24 to 32. Moreover, people with a monthly income of around 5,000 yuan appear to be more inclined to make purchases in this regard. These potential customer characteristics can provide valuable insights to operators, enabling them to enhance the comprehensiveness of related services and continually update their offerings.
Table 3: Result of Cluster Analysis
Cluster category variance analysis difference comparison results | |||
Cluster 1(n=44) | Cluster 2(n=31) | Cluster 3(n=34) | |
Gender | 1.80±0.41 | 1.19±0.40 | 1.76±0.43 |
Age | 29.52±8.78 | 34.90±8.72 | 31.88±7.38 |
Monthly Income | 4381.82±2433.70 | 5851.61±2333.08 | 5182.35±2517.87 |
Monthly expenditure on healthy food | 2.50±1.05 | 2.65±0.88 | 1.50±0.75 |
Whethter have sport/fitness habit or not | 0.73±0.45 | 0.52±0.51 | 0.21±0.41 |
Monthly expenditure on sport/fitness | 386.36±222.66 | 409.68±192.10 | 470.59±222.29 |
Weekly usge of delivry services | 2.36±0.78 | 2.26±0.93 | 3.50±0.66 |
Family Numbers | 4.32±1.12 | 3.16±1.27 | 3.59±1.35 |
Whethter have chronic disease or not | 0.34±0.48 | 0.19±0.40 | 0.29±0.46 |
The numbers of chronic patients in family | 1.41±0.58 | 2.16±0.86 | 1.32±0.47 |
Attention to healthy food | 2.00±0.86 | 2.55±1.31 | 2.88±1.51 |
The willingness to learn about the healthy nutrition management knowledge | 2.55±1.41 | 4.03±0.95 | 3.53±1.28 |
4. Discussion
While conclusive findings have been drawn, it is essential to consider various factors that could have influenced these outcomes. Firstly, the sample size may warrant expansion, potentially impacting the results. A larger sample size might either affirm or negate the hypotheses more definitively. Secondly, it's worth noting that customized light food is not yet widely adopted in the Chinese market. Consequently, individuals, even if they fall within the potential target customer category, may still opt for services that have been more extensively popularized.
The business model encompasses both body-shape management and long-term diet management for chronic patients. Regarding the weight loss segment, the data analysis has provided robust evidence to inform business strategies. The investigation has successfully established a link between healthy food consumption and fitness expenditure. Consequently, a logical approach for entering the market during the initial stages of the business plan would be to focus on individuals who are inclined to spend on fitness-related activities. This strategy can involve forging stable partnerships with local fitness clubs to tap into the initial customer base. Such partnerships can be mutually beneficial and serve as primary marketing channels, creating substantial added value for all parties involved. To further enhance customer engagement and loyalty, diversifying services will be imperative.
While the data analysis did not conclusively demonstrate the feasibility of the long-term diet management market for chronic patients, this segment still holds significant potential. Importantly, the number of chronic patients in China continues to rise. For instance, the prevalence rate of diabetes in China stands at 9.7%, with nearly 100 million individuals afflicted by the condition. Given the substantial market size, it is likely that new entrants will be attracted to this space. However, in many cases, even successful products must adhere to market requirements. The lead user innovation method suggests that some products and services necessitate specialized knowledge not widely understood by the general population. In such cases, specialists must introduce these products and services before market demand becomes evident (Von-Hippel, Eric, 2012 [13]). The long-term diet management market for chronic patients is reliant on expertise in medicine and nutrition. Therefore, products and services in this domain should be introduced even in the absence of widespread market awareness.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, this study delved into the emerging market of customized meal services, particularly focusing on the intersection of healthy light food products and the preferences of potential consumers. As the Chinese market witnesses a burgeoning demand for healthy light food products and services, it becomes increasingly imperative for operators to differentiate themselves in a landscape often characterized by homogeneous offerings. This academic investigation explored several factors that potentially influence the consumption of nutrition customization services in China.
The findings of this study revealed a significant association between individuals' expenditure on physical training and their intention to consume customized light food products. This insight is invaluable for practitioners in related industries as they chart their future market strategies. The results suggest that targeting individuals who are likely to invest in fitness-related activities can be an efficient entry point into the market, with partnerships with local fitness clubs serving as a viable avenue for reaching initial customers.
Additionally, cluster analysis shed light on potential customer characteristics that are most inclined towards customized meal services. The analysis indicated that women, individuals aged 24 to 32, and those with a monthly income of around 5,000 yuan may be more predisposed to purchase such services. Understanding these customer segments can assist operators in fine-tuning their services and ensuring relevance to their target audience.
While this research provides actionable insights for the weight-loss segment of the market, the study also underscores the potential of the long-term diet management market for chronic patients. Despite the lack of conclusive evidence, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases in China, such as diabetes, presents a substantial opportunity for market entrants. These markets, often requiring specialized knowledge, can be tapped into by forward-thinking specialists, even before widespread market awareness.
In essence, this study suggests that operators in the customized meal services industry should adopt a strategic approach that not only targets existing demand but also seeks to shape and create demand. By aligning with the evolving consciousness of a healthier lifestyle and crafting unique solutions, operators can gradually expand their market reach in this dynamic and promising landscape.
References
[1]. Wang,N.(2019).China Light-Food Delivery Consumption Report. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1648163158402429573&wfr=spider&for=pc.
[2]. Meituan takeaway. (2019). Light-Food Consumption Big Data Report.
[3]. Hong, S. P., Rhee, Y. C., & Daihak-gil, G. (2016). Effect of SNS on purchasing intention for sport product. Sport Journal, 20, 1-15. https://thesportjournal.org/article/effect-of-sns-on-purchasing-intention-for-sport-product/
[4]. Nguyen, T. T., & Phan, H. T. T. (2022). Impact of COVID-19 anxiety on functional foods consuming intention: role of electronic word of mouth. Heliyon, 8(11), e11344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11344
[5]. Maesen, S., Lamey, L., ter Braak, A., & Jansen, L. (2022). Going healthy: how product characteristics influence the sales impact of front-of-pack health symbols. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 50(1), 108-130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-021-00796-w.
[6]. SuperLife. (n.d). Project.
[7]. Kathan, W., Matzler, K., & Veider, V. (2016). The sharing economy: Your business model's friend or foe? Business Horizons, 59(6), 663-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2016.06.006
[8]. Henderson, E. (2023, February 24). Scientists investigate the influence of sports on eating habits. News. Retrieved March 22, 2023, from https://www.news-medical.net/news/20210407/Scientists-investigate-the-influence-of-sport-on-eating-habits.aspx
[9]. Li, Y., & Li, G. (2022, June). The Effect of High-Calorie Food Intake and Systematic Physical Activity on Physical Health in Our General Population. In 2022 8th International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research (ICHSSR 2022) (pp. 39-43). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220504.008
[10]. Leddy, Anna M., et al. "A conceptual model for understanding the rapid COVID-19–related increase in food insecurity and its impact on health and healthcare." The American journal of clinical nutrition 112.5 (2020): 1162-1169. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqaa226
[11]. Aday, S., & Aday, M. S. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on the food supply chain. Food Quality and Safety, 4(4), 167-180. https://doi.org/10.1093/fqsafe/fyaa024
[12]. Dominguez-Viera, M. E., van den Berg, M., Donovan, J., Perez-Luna, M. E., Ospina-Rojas, D., & Handgraaf, M. (2022). Demand for healthier and higher-priced processed foods in low-income communities: Experimental evidence from Mexico City. Food Quality and Preference, 95, 104362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104362
[13]. Von-Hippel, Eric., [Openuerinnovation]. (2012, Jun 21). [Lead User Innovation Method (Eric von Hippel)].YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLD4C0E9AEDF085119
Cite this article
Chen,D.;Zhu,C.;Zhang,S. (2023). Exploring the Market Dynamics and Consumer Preferences in Customized Meal Services: A Study in the Emerging Chinese Landscape. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,32,13-22.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Wang,N.(2019).China Light-Food Delivery Consumption Report. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1648163158402429573&wfr=spider&for=pc.
[2]. Meituan takeaway. (2019). Light-Food Consumption Big Data Report.
[3]. Hong, S. P., Rhee, Y. C., & Daihak-gil, G. (2016). Effect of SNS on purchasing intention for sport product. Sport Journal, 20, 1-15. https://thesportjournal.org/article/effect-of-sns-on-purchasing-intention-for-sport-product/
[4]. Nguyen, T. T., & Phan, H. T. T. (2022). Impact of COVID-19 anxiety on functional foods consuming intention: role of electronic word of mouth. Heliyon, 8(11), e11344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11344
[5]. Maesen, S., Lamey, L., ter Braak, A., & Jansen, L. (2022). Going healthy: how product characteristics influence the sales impact of front-of-pack health symbols. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 50(1), 108-130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-021-00796-w.
[6]. SuperLife. (n.d). Project.
[7]. Kathan, W., Matzler, K., & Veider, V. (2016). The sharing economy: Your business model's friend or foe? Business Horizons, 59(6), 663-672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2016.06.006
[8]. Henderson, E. (2023, February 24). Scientists investigate the influence of sports on eating habits. News. Retrieved March 22, 2023, from https://www.news-medical.net/news/20210407/Scientists-investigate-the-influence-of-sport-on-eating-habits.aspx
[9]. Li, Y., & Li, G. (2022, June). The Effect of High-Calorie Food Intake and Systematic Physical Activity on Physical Health in Our General Population. In 2022 8th International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research (ICHSSR 2022) (pp. 39-43). Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220504.008
[10]. Leddy, Anna M., et al. "A conceptual model for understanding the rapid COVID-19–related increase in food insecurity and its impact on health and healthcare." The American journal of clinical nutrition 112.5 (2020): 1162-1169. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqaa226
[11]. Aday, S., & Aday, M. S. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on the food supply chain. Food Quality and Safety, 4(4), 167-180. https://doi.org/10.1093/fqsafe/fyaa024
[12]. Dominguez-Viera, M. E., van den Berg, M., Donovan, J., Perez-Luna, M. E., Ospina-Rojas, D., & Handgraaf, M. (2022). Demand for healthier and higher-priced processed foods in low-income communities: Experimental evidence from Mexico City. Food Quality and Preference, 95, 104362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2021.104362
[13]. Von-Hippel, Eric., [Openuerinnovation]. (2012, Jun 21). [Lead User Innovation Method (Eric von Hippel)].YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLD4C0E9AEDF085119









