1. Introduction
1.1. History of Evergrande Development
China Evergrande Group (hereinafter referred to as "Evergrande"), founded by Jiayin Xu in 1996 in Guangzhou, is one of the world's top 500 enterprise groups integrating real estate, finance, health, tourism and sports. With total assets of trillion yuan, annual sales scale of more than 400 billion yuan, 80000 employees, 1.3 million jobs and 500 real estate projects in more than 180 cities across the country. Evergrande has been the world's first real estate enterprise for four consecutive years. Evergrande has eight major industries under its umbrella, such as Evergrande Real Estate, Evergrande New Energy Vehicles and so on.
With the cessation of the housing allocation system more than a decade ago and the implementation of the commercial housing policy, Evergrande first used the strategy of “small area, low price, and low cost” to seize the opportunity, and then quickly established itself in the real estate market with the strategies of “three highs and one low” and “fast in and fast out”. The three highs refer to high debt, high leverage, and high turnover. Low refers to low cost. Fast in and fast out refer to low land prices, fast construction, fast opening, and late payment [1]. Trough these strategies, Evergrande has stood out from more than 2,000 real estate enterprises in Guangzhou, become one of the top 10 real estate enterprises in Guangzhou, then become one of the top three real estate enterprises in China, and finally become the first real estate enterprise in the world. During this period, Evergrande not only held an absolute leading position in the real estate industry, but also achieved diversified layouts in other fields, becoming a multinational enterprise that integrates six business sectors: real estate, finance, health, culture, tourism, and sports [2].
1.2. The Current Situation of Evergrande
Today, Evergrande has a debt of 1.97 trillion yuan and is facing bankruptcy. Because Evergrande's scale is too large and involves too many individuals and groups, its decline will bring serious economic problems [3]. From the perspective of microeconomics, the decline of Evergrande has resulted in unemployment of workers and loss of money for suppliers and buyers. From a macro perspective, it will have a severe impact on China's financial system and may lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
2. Evergrande's Debt Problem
There are three main reasons for Evergrande's high debt problem: high leverage profit model, blind diversified expansion, and high dividend salaries for senior executives of the company.
2.1. High Leverage Profit Model
Evergrande's high leverage profit model has led to increasing pressure on its loan repayment, ultimately leading to a debt crisis due to the rupture of its funding chain. The reason why Evergrande has been able to grow into a global leading real estate enterprise in just over 20 years is that Evergrande has been aggressively expanding through leverage. Evergrande maintains cash flow operations by borrowing new and repaying old, and banks and investors are also willing to hand over funds to leading real estate companies like Evergrande. If the regulatory environment does not change, Evergrande's funding game can be maintained continuously. But there’s no forever free lunch in the world. When Evergrande's business is too large, any slight improper turnover of funds can lead to the rupture of the capital chain.
The entire business model of Evergrande is closely related to high leverage. In order to maintain and increase commercial scale, Evergrande mainly uses five layers of leverage. The first level of leverage is to borrow money from the bank to buy land, then mortgage the land to the bank to borrow money for the development and construction of the land. After the house is built and sold, Evergrande repays the money to the bank with interest and principal. The second level of leverage is that during the construction process, Evergrande will allow construction units and suppliers to advance funds, and issue merchant tickets to leverage supplier funds. The third layer of leverage is that after the construction is completed, Evergrande obtains a large amount of pre-sale funds from the buyer in advance through pre-sale of the house, which is used for working capital, interest repayment for the bank, and daily turnover. The fourth level of leverage is to use the listed platform to issue stocks and bonds, for example the 116 billion yuan of perpetual bonds as of 2016, to attract public investment through high interest rates. The final layer of leverage is the issuance of high return financial products, leveraging internal employee funds and binding employees [4,5]. These five layers of leverage are combined, and in the short term, Evergrande almost does not need to spend any capital costs throughout the entire construction and sales process, but instead uses all external funds, which is later known as leverage and liabilities. Throughout the entire process, the biggest cost for Evergrande was the money for buying land, and most of the land was hoarded at low prices more than a decade ago. When the current prices rise, houses are built and sold to earn a price difference. Evergrande only talks about the payment method and not the price, usually agreeing on installment payments. In one transaction, the down payment of the land transfer fee, which was originally over 100 million yuan, was only given to the 5 million yuan borrowed from the bank, equivalent to 20 times the leverage. By doing so, Evergrande achieved a leverage of ten thousand times with ten thousand yuan, and with the rapid increase in land and housing prices, profits soared instantly [6].
However, leverage can amplify a company's profits while also increasing its risks. From the Fig.1 [7], it can be seen that since 2010, Evergrande's operating cash flow has been negative, indicating that Evergrande's business operations cannot bring cash to Evergrande. Evergrande's overall cash flow is supported by a large amount of financing, covering the net expenses of operating and investment cash flows. At this point, once external financing encounters policy changes and other factors that tighten, the risk of fund chain rupture will rapidly increase.
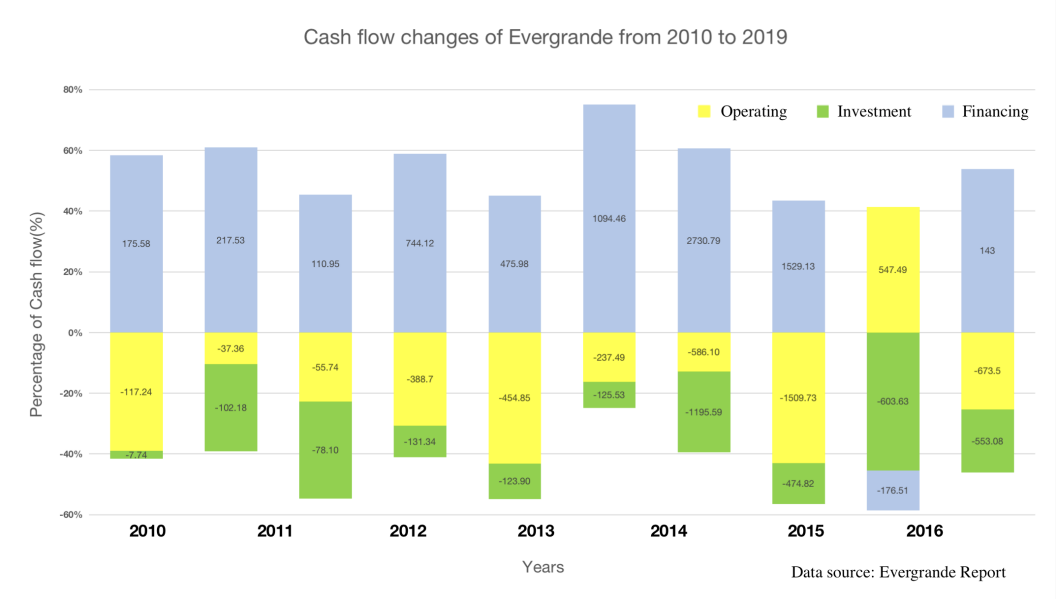
Figure 1: Cash flow changes of Evergrande from 2010 to 2016.
In 2016, China first proposed the concept of “housing without speculation”, and at that time, real estate developers such as Evergrande did not pay special attention. Finally, in 2018, the “Three Red Lines” were introduced, which refer to the three indicators for regulating the financing of real estate enterprises. They required the regulation of the growth of interest bearing liabilities of real estate enterprises and the establishment of three red lines. The first red line is that the asset liability ratio excluding prepayments shall not exceed 70%. The second red line is that the net debt ratio shall not exceed 100%. The third red line is that the ratio of cash to short-term debt shall not be less than one time. Evergrande's high leverage operation mode unexpectedly hits all three red lines.
The first red line, According to Fig. 2. [7,8], Evergrande’s debt ratio excluding accounts received in advance has been above 70% since 2012, exceeding the requirements of the first red line. The net debt ratio has exceeded 100% since 2012. The decline in net return in 2013 was due to Evergrande's issuance of perpetual bonds, which are reflected in equity rather than liabilities on the balance sheet. Perpetual bonds are not included in the numerator of net debt ratio, but have added the denominator - consolidated equity. Nevertheless, since 2014, the net debt ratio has risen again, exceeding the requirements of the second red line. According to Fig.3 [7], Evergrande's cash reserves have been insufficient to cope with short-term debt since 2012, and the cash to short-term debt ratio of the third red line during this period has also not met the standard [8,9]. In the end, Evergrande was unable to increase its interest bearing liabilities due to hitting three red lines, in other words, it could no longer borrow from banks. However, the majority of Evergrande's funds come from operational liabilities, which has led to the rupture of Evergrande's funding chain, resulting in many projects not being delivered on time and ultimately resulting in the current situation.
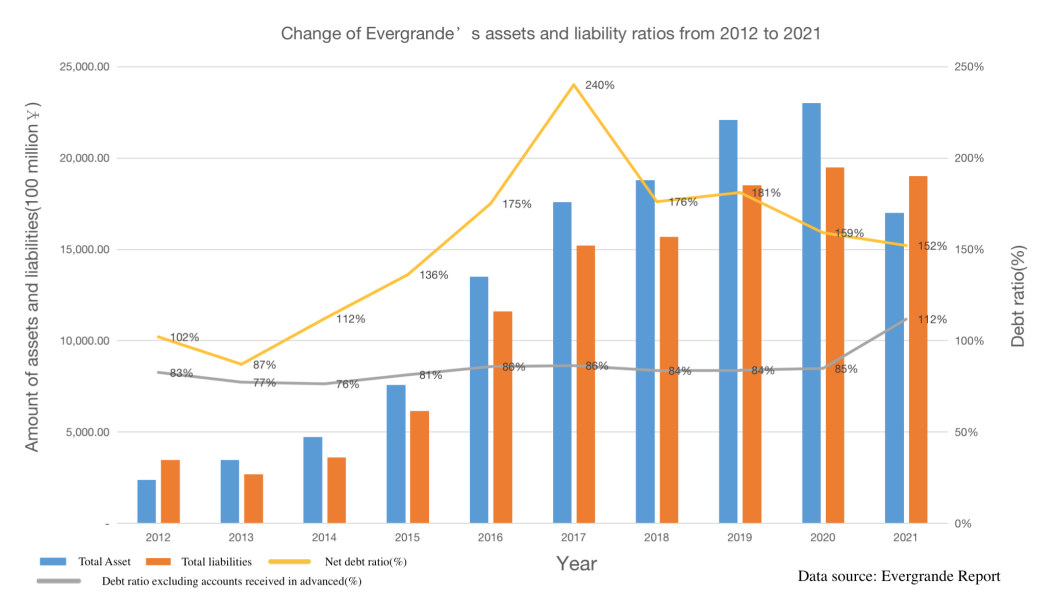
Figure 2: Changes in total assets, liabilities, debt ratio and net debt ratio of Evergrande from 2012 to 2021.
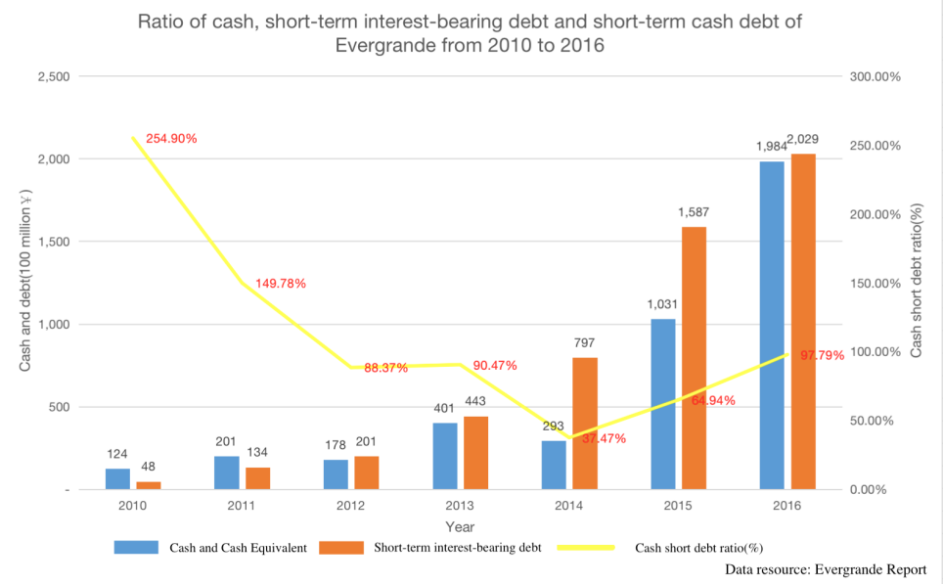
Figure 3: Ratio of cash, short-term interest-bearing debt and short-term cash debt of Evergrande from 2010 to 2016.
Return on assets (ROA)=Net profit/Total average assets x 100%
It can be seen from Fig. 4 [7] that since 2011, Evergrande's ROA has been lower than the borrowing rate, and the Price scissors gap between the two has become larger and larger. If ROA is lower than the borrowing rate, it means that for every yuan of performance or asset growth, the income brought by that yuan is lower than its production loan interest.
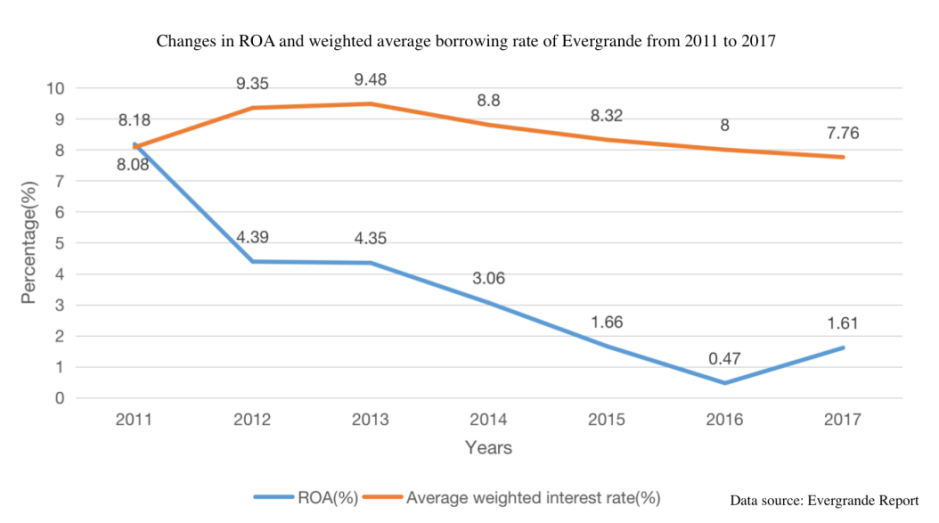
Figure 4: Changes in ROA and weighted average borrowing rate of Everande from 2011 to 2017.
In other words, all the money earned by Evergrande is now used to pay interest. In 2016, Evergrande topped the sales performance table of Chinese real estate enterprises with a sales revenue of 373.4 billion yuan. As shown in Table 1[7], in the same year, Evergrande's ROA and borrowing rate Price scissors reached the peak, with a total net profit of 17.6 billion yuan, up 1.6% year on year. However, the net profit attributable to shareholders of listed companies was only 5.09 billion yuan, and 10.6 billion yuan was used to repay the interest on perpetual bonds, down 51.3% year on year, accounting for 29% of the total net profit [10]. It can be seen that the core of Evergrande's problem is that the interest bearing debt is too high, which affects Evergrande's normal operation and profit settlement.
Table 1: Statement of changes in comprehensive equity of Evergrande.
Consolidated statement of changes in equity (Unit: RMB million yuan) | ||||||||
Capital stock | Share premium | Reserve | Retained earnings | Total | Permanent capital instrument | Non-controlling interest | Total | |
Balance at January 1, 2016 | 971 | — | 7,637 | 42,398 | 51,006 | 75,737 | 15,399 | 142,142 |
Overall income Annual profit | — | — | — | 5,091 | 5,091 | 10,646 | 1,880 | 17,617 |
Other comprehensive income Changes in the value of financial assets available for sale | — | — | (3,039) | — | (3,039) | — | — | (3,039) |
An investment accounted for by the equity method Other comprehensive income | — | — | (2,688) | — | (2,688) | — | — | (2,688) |
Table 1: (continued). | ||||||||
Foreign currency conversion difference | — | — | 835 | — | 835 | — | — | 835 |
Total income | — | — | (4,892) | 5,091 | 199 | 10,646 | 1,880 | 12,725 |
2.2. Diversified Development
After making certain achievements in the real estate industry, Evergrande has embarked on a path of diversified development in order to continue to increase its market share, increase its visibility, enhance its brand value and effectiveness. However, due to Evergrande's investment in some unrelated diversified industries, this indicates that the company is about to enter unfamiliar business areas, which will lead to the company being unfamiliar with new industries and resulting in information asymmetry. If a detailed investigation cannot be conducted in this situation, enterprise managers are likely to be overly optimistic about the profit expectations of the newly established business based on existing information, making incorrect decisions, and there is a high risk of failure in investment decisions, which will also diversify the enterprise's resources to a certain extent.
Evergrande first entered the fast-moving consumer goods industry, such as mineral water, grain and oil, dairy products, and other daily fast-moving consumer goods with a wide audience and diverse audience, the most famous of which is Evergrande Ice Spring. Evergrande Bingquan is a large-scale product operation with sufficient financial strength, product strength, and dissemination power. However, it ultimately resulted in a huge loss of 2.37 billion yuan in one year and a cumulative loss of 4 billion yuan [8, 11]. There are many reasons for the failure of Evergrande Bingquan, mainly due to unclear product positioning, lack of brand stories in advertising, high endorsement costs, and an overly urgent overall operational pace. In addition, Evergrande has also developed industries such as sports, finance, and automobiles, creating a large and virtual commercial empire. In recent years, the trend of new energy vehicles has been very strong, and Evergrande Group has also participated in the queue of car manufacturing in order to have a sip of soup. Due to unfamiliarity with car manufacturing technology, Evergrande directly purchased the core technology of the entire car manufacturing line and acquired and cooperated with many automobile companies. After a series of international mergers and acquisitions and cooperation, Evergrande has gradually completed the entire industrial chain layout from vehicle research and development and manufacturing, powertrain, power batteries, smart charging, to automobile sales [12]. However, the actual situation is far from what was expected. A car goes through many stages from development to launch, and each stage involves a considerable amount of accumulated technology and experience. After the car is manufactured, there is also consumer recognition, which involves marketing and brand building, each step of which is extremely complex and requires manufacturers to be extremely familiar with the entire production chain. However, Evergrande has faced such a refined operation of the automotive market in a simple and crude manner, always using the real estate approach to produce cars, thinking that through acquisition and cooperation, it can bind the industry chain, and as long as cars can be made, they can be sold. In the end, Evergrande Motors has a market value of HKD 500 billion since 2020, and now faces the risk of production suspension. Evergrande Automobile has spent over 50 billion yuan in total, but only produced 9 "model cars".
The only successful example of Evergrande's cross industry success is the Guangzhou Evergrande football team. When Evergrande operated the football industry, it introduced many professional talents from the football field to do professional things, introduced many well-known coaches and players, and ultimately achieved a record - winning the Chinese Super League five times and the Asian Championship twice. However, even so, according to a report by the Securities Times, from 2013 to the first half of 2020, Evergrande Football suffered a total loss of over 8.635 billion yuan [8,13].
Overall, the diversified development and brand extension of Evergrande Group have dispersed the resources of the enterprise, and a large amount of funds have been consumed due to the exploration of new business areas. Ultimately, not only did the investment fail due to unfamiliarity with the new areas, but it also resulted in Evergrande not having the energy to operate its main business and perform well in the business.
2.3. Excessive Dividend Distribution
It is understood that Hui Ka Yan's annual salary is only 251000 yuan, which is very small for the person in charge of an enterprise, even less than the annual salary of Huawei employees. But Hui Ka Yan's dividend reached 50 billion yuan from 2011 to 2021. In addition to Hui Ka Yan, other senior executives of Evergrande Group are also highly paid. Xia Haijun, the CEO of Evergrande Group, has an annual salary of 205 million yuan, reaching 1.2 billion yuan after cashing out his bonds in 2021. The annual salary of other executives is mostly over ten million yuan. Ren Zeping, an economist hired by Hui Ka Yan, earned 15 million yuan a year [8]. Evergrande's behavior is known as the "Ponzi scheme". It uses the money of new investors to pay interest and short-term returns to old investors, so as to create the illusion of making money, and then cheat more investment. In the end, when the new investment was insufficient, Evergrande faced a funding chain fracture, which led to the current problems.
3. Solution
Firstly, Evergrande needs to optimize its capital structure.
The root cause of Evergrande's debt problem is its own capital structure, which means that before Evergrande implemented its diversified development strategy, the high leverage business strategy implemented by the enterprise had already buried hidden dangers. The impact of policies and markets on the real estate industry only brought forward the outbreak of the Evergrande crisis. At this point, Evergrande needs to adjust its business strategy and change its "borrowing new to repay old" state [9]. Therefore, Evergrande needs to control the total scale of corporate debt by reducing interest bearing liabilities, opening up sources and reducing costs, and optimize its capital structure by adjusting debt maturities and other means, adjusting corporate debt to a reasonable level to cope with uncertain market environments [14].
Secondly, Evergrande needs to clarify its development direction and strengthen industrial connections.
Evergrande's concept of diversified development is correct, but it needs to change its expansion strategy. At present, Evergrande's diversification strategy direction is not very clear, and its layout is relatively scattered. The unfamiliar business segments have greatly reduced its competitive advantage. Evergrande should scientifically formulate its development direction, which should rely on the strategic development direction to clarify the distribution of industrial structure, extend the industrial chain on existing businesses and products, expand service coverage, strengthen diversified industrial connections, and reduce investment risks. According to official reports, Evergrande will sell its equity in Evergrande Automobile and Evergrande Property to cope with the current crisis. This includes the sale of a portion of Hengteng Network's equity to recover a total of HKD 7.7 billion, and the sale of Jiakai City to recover approximately RMB 2.5 billion in funds. In addition, Evergrande Property and Evergrande Motors have also reported high-quality capital taking over, allowing Evergrande to obtain a large amount of cash to solve the problem of the capital chain [15].
Finally, Evergrande needs to reduce the cost of personnel salaries and dividends, and allocate more funds to its business.
According to the financial reports of Evergrande Group in the past five years, Evergrande mainly uses a single cash dividend as its main distribution method and maintains a high dividend amount. This dividend strategy will cause a significant outflow of cash from the company. When the company needs cash for subsequent development, due to insufficient reserves of its own funds, it will need to carry out new fundraising activities, which increases fundraising costs and affects the normal operation of the company.
4. Conclusion
Nowadays, Evergrande has fallen into a serious debt crisis, which has also triggered a series of butterfly effects. However, we don't need to worry too much. We believe that with the unremitting efforts of Evergrande Group and the joint efforts of the Chinese government to take corresponding measures, the entire real estate market will soon be on the right track, the foam will soon burst, and the house price will gradually return to normal, reaching a real balance between supply and demand. I also hope that Evergrande can get rid of the debt crisis as soon as possible and prevent more people from being affected by this crisis.
References
[1]. Warton.: China Evergrande Group: Strategic Repositioning Toward a Sustainable Growth Model. Available at: https://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/china-evergrande-group-strategic-repositioning-toward-sustainable-growth-model/ Last accessed: 2023/4/21.
[2]. Popuplartime line.com.: History of Evergrande Group in timeline. Available at: https://populartimelines.com/timeline/Evergrande-Group. Last accessed: 2023/4/19.
[3]. CBS, News.: Struggling Evergrande Group says it will make bond payment this week. Available at: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/deutsche-bank-shares-down/. Last accessed: 2023/4/21.
[4]. Grabar, H.: Why evergrande is causing panic in stock markets everywhere, Slate Magazine. Slate. Available at: https://slate.com/business/2021/09/evergrande-china-markets-real-estate-contagion.html. Last accessed: 2023/4/12.
[5]. Xun, J.: Evergrande, born leverage, die of leverage. Available at: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1722641043164539508&wfr=spider&for=pc. Last accessed: 2023/4/11.
[6]. Zhiyuan, F., Ao, L., Wei Y.: Zhong Guo Heng da Zhi Teng Fei: Shang Ye Chuan Qi Xu Jia Yin. Guang zhou: Guang dong jing ji chu ban she. Guangdong economy Publishing House. Guangdong. P12-130. (2019).
[7]. Evergrande.: Evergrande Group document.write .Evergrande Group - Investor Relations - Annual Report/Interim Report .Available at: https://www.evergrande.com/ir/sc/reports.asp. Last accessed: 2023/4/18.
[8]. Morningstar, Inc.: China Evergrande Group EGRNF valuation. Available at: https://www.morningstar.com/stocks/pinx/egrnf/valuation. Last accessed: 2023/4/16. .
[9]. Kaimeng, Z.: Financial crisis and Prevention of real estate enterprises -- Taking Evergrande Group as an example [J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics. 11(7): 4411-4418. (2022).
[10]. Ling, W.: Xu Jia Yin: Di Chan,Zu Qiu,Heng da De Shi Jie. Beijing, pp30-49. Tai hai Publishing House. Beijing (2019).
[11]. Sanwan W.: Evergrande Bingquan, spent 6 billion advertising loss 4 billion yuan, helpless rout left the game. Available at: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1732526428583018915&wfr=spider&for=pc. Last accessed: 2023/4/16.
[12]. Li Rongjin, Wang Zhen.: Research on Financial Risk and Prevention of Real estate enterprises [J]. Friends of Accounting (mid-day issue) (12) : 96-97 (2010).
[13]. Laura H.: Evergrande Group announces long-awaited debt restructuring deal after 2021 collapse. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/03/23/investing/china-evergrande-debt-restructuring-deal-intl-hnk/index.html#. Last accessed: 2023/4/9.
[14]. Weifeng Z.: New perspective of safe financial management: Financial crisis operation [J]. Productivity Research (8): 144-145 (2007).
[15]. Ying, S.:Evergrande plans to sell some assets of Evergrande Automobile and Evergrande Real Estate.Available at: http://news.winshang.com/html/068/8811.html. Last accessed: 2023/4/6.
Cite this article
Han,J. (2023). The Debt Problem of Evergrande. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,34,83-91.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Warton.: China Evergrande Group: Strategic Repositioning Toward a Sustainable Growth Model. Available at: https://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/china-evergrande-group-strategic-repositioning-toward-sustainable-growth-model/ Last accessed: 2023/4/21.
[2]. Popuplartime line.com.: History of Evergrande Group in timeline. Available at: https://populartimelines.com/timeline/Evergrande-Group. Last accessed: 2023/4/19.
[3]. CBS, News.: Struggling Evergrande Group says it will make bond payment this week. Available at: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/deutsche-bank-shares-down/. Last accessed: 2023/4/21.
[4]. Grabar, H.: Why evergrande is causing panic in stock markets everywhere, Slate Magazine. Slate. Available at: https://slate.com/business/2021/09/evergrande-china-markets-real-estate-contagion.html. Last accessed: 2023/4/12.
[5]. Xun, J.: Evergrande, born leverage, die of leverage. Available at: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1722641043164539508&wfr=spider&for=pc. Last accessed: 2023/4/11.
[6]. Zhiyuan, F., Ao, L., Wei Y.: Zhong Guo Heng da Zhi Teng Fei: Shang Ye Chuan Qi Xu Jia Yin. Guang zhou: Guang dong jing ji chu ban she. Guangdong economy Publishing House. Guangdong. P12-130. (2019).
[7]. Evergrande.: Evergrande Group document.write .Evergrande Group - Investor Relations - Annual Report/Interim Report .Available at: https://www.evergrande.com/ir/sc/reports.asp. Last accessed: 2023/4/18.
[8]. Morningstar, Inc.: China Evergrande Group EGRNF valuation. Available at: https://www.morningstar.com/stocks/pinx/egrnf/valuation. Last accessed: 2023/4/16. .
[9]. Kaimeng, Z.: Financial crisis and Prevention of real estate enterprises -- Taking Evergrande Group as an example [J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics. 11(7): 4411-4418. (2022).
[10]. Ling, W.: Xu Jia Yin: Di Chan,Zu Qiu,Heng da De Shi Jie. Beijing, pp30-49. Tai hai Publishing House. Beijing (2019).
[11]. Sanwan W.: Evergrande Bingquan, spent 6 billion advertising loss 4 billion yuan, helpless rout left the game. Available at: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1732526428583018915&wfr=spider&for=pc. Last accessed: 2023/4/16.
[12]. Li Rongjin, Wang Zhen.: Research on Financial Risk and Prevention of Real estate enterprises [J]. Friends of Accounting (mid-day issue) (12) : 96-97 (2010).
[13]. Laura H.: Evergrande Group announces long-awaited debt restructuring deal after 2021 collapse. Available at: https://edition.cnn.com/2023/03/23/investing/china-evergrande-debt-restructuring-deal-intl-hnk/index.html#. Last accessed: 2023/4/9.
[14]. Weifeng Z.: New perspective of safe financial management: Financial crisis operation [J]. Productivity Research (8): 144-145 (2007).
[15]. Ying, S.:Evergrande plans to sell some assets of Evergrande Automobile and Evergrande Real Estate.Available at: http://news.winshang.com/html/068/8811.html. Last accessed: 2023/4/6.









