1 Introduction and Literature Review
A major epidemic of the century, which has been accelerated and deeply influenced by the great changes not seen in a century and the world's economic development is facing many uncertainties and fluctuations. In recent years, China has made great efforts to cultivate market players and stimulate social creativity and market vitality. The shorter the negative list, the wider the door of reform and opening-up policy. It is precise because of China's growth potential that China's actual use of foreign capital has increased against the trend against the background of the current decline in global transnational investment.
Judging from the latest research, a large number of studies on the main factors contributing to China’s FDI have been done by many scholars. First of all, [1] Through the factor analysis method of three public factors: internal balance, domestic economic development level, and external balance, Sun Gangqiang, Gan Qi, and Wang Wenyu found that the decisive factor of China's foreign direct investment is the level of domestic economic development; to observe panel data of provinces in mainland China, [2] Zou Zhiming and Chen Xun got FDI technology spillover effect shows a significant impact. [3]And Lv Zheng, Hu chenpei research shows that FDI has a positive technology spillover on the transnational impact of labor productivity ;[4] Aiming at the spillover of FDI level and the impact of independent R & D on industrial output, Zhou Xuan, Tan Jianhua, Guo Pibin and Du Wei found that the level of independent R & D and the promotion of FDI on human capital flow and competition, demonstration and imitation were positively correlated with industrial output.[5] Shen Kun and Rong gengqiang used the research methods of econometric test and found that the uneven distribution of FDI had different effects on endogenous growth. [6]Li Minjie and Wang Jian found significant spatial autocorrelation of FDI in logistics industry through nuclear density estimation; [7] Scholars Li Jian and Wu Min found regional heterogeneity in the moderating effect of FDI on dual environmental regulation.
The above-mentioned scholars have done a lot of research on the factors affecting FDI. But at present, with the global epidemic still continuing and China's rapid economic recovery after controlling the epidemic, FDI has become an important carrier deeply embedded in the global value chain system and an important link for foreign high-quality factors to promote the domestic cycle Our inquiry should not only focus on the impact of FDI but also clarify the main factors contributing to China's FDI.
2 Description of Current Status
The article summarizes the current status of FDI in China, presenting the distributions across provinces.
Table 1. Panels and provinces.
Panels | Provinces |
Northeast Comprehensive Economic Region(N) | Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang |
Northern coastal comprehensive Economic Region (NC) | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong |
Eastern coastal comprehensive Economic Region (EC) | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang |
Southern coastal Economic Region (SC) | Fujian, Guangdong, Hainan |
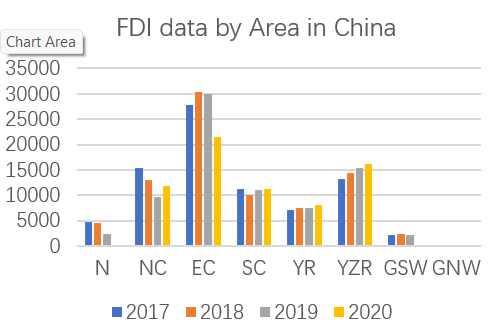
Fig. 1 FDI data by Area in China.
From the geographical view, Statistics from the Chinese Ministry of Commerce show that there are significant differences in the regional distribution of foreign direct investment. To give a better contrast, 31 provinces and municipalities used in this paper are artificially divided into 8 panels, which are shown in Table 1.
Figure1 shows the FDI data of different region in different years. To get rid of the effect of the number of provinces within different regions, each FDI data is represented by average FDI of provinces. From Figure1, the regions can be divided into classes according to their FDI data from the largest to the smallest. The highest FDI amount is in the Eastern coastal comprehensive Economic Region (EC), which includes Shanghai, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu provinces, with an average FDI of 30,000 million USD in 2018. The second tier is NC, SC, YZR, where the average FDI in each province is between 10,000-15,000 million USD. The lowest bracket is N, YR, GSW, where the average figure is less than USD 10,000.
In general, the distribution of foreign direct investment in China by province is characterized by the following:
1. decreasing from east to west. Most of the first and second ranking provinces are located in the eastern coastal region of China, while the data of the western provinces have a significant gap with the east.
2. Concentration with major economic regions. The major economic regions in China (Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei) are in the first and second rank in terms of FDI data and have good performance.
Still, a more precise evaluation of the factors influencing the FDI distribution in China is required.
3 Data and Analysis
3.1 Data Source
The dataset is a balanced panel that consists of observations for 31provinces covering the period 2017–2020, with a sample of 121 observations. The provincial-level data are collected from the Chinese National Bureau of Statistics, China Statistical Yearbook, and the Wind data.
3.2 Data Description
Table 2.Data description.
Abbreviation | Definition | Unites | N | Mean | S.D | Min | Max |
FDI | Foreign Direct Investment | Dollar | 121 | 9104.9 | 9982.67 | 4.46 | 50253 |
Pop | population | - | 121 | 45.3 | 29.845 | 3.49 | 126.24 |
Inter | Number of international firms | - | 121 | 19318.6 | 33134.5 | 252 | 179268 |
imEX | Ratio of import and export | % | 121 | 0.231 | 1.05 | 0.17 | 4.95 |
Trade ratio | Share of trade to GDP | % | 121 | 1.15 | 0.23 | 0.0076 | 0.976 |
Dummy variables | |||||||
TW | If there is trade war between US and China. | ||||||
Covid | If there is Covid-19. | ||||||
Based on annual data, this project analyses the macro-level relationship among urbanization, energy consumption, trade openness, and GDP per capital using panel data econometric methods. The results are showed in Table 2.
China has rapid economic growth. Population, as one of the main drivers of development, plays an important role in economic growth, which is also a factor that cannot be ignored that it makes a great contribution to attracting international capital. The number of international companies in a province can reflect the local foreign trade operation. If the number of multinational companies is large, it can reflect the frequent foreign trade activities, which has a positive effect on foreign direct investment, so it is included as the research object. From the ratio of imports and exports, it can be seen that the local economy is relatively active to a certain extent. The higher the number, the more it can reflect the more foreign investment.
There are two dummy variables in our model: Tw、Covid. By comparing the years before and after the epidemic and the trade war, we can get the impact of these two dummy variables on our research objects. The variables are FDI, Population, the number of international firms, the ratio of imports and esports, The ratio of foreign trade to GDP, the trade war between the US and China, and COVID-19.
3.3 Empirical Analysis
This study introduces factors (population, the number of firms, the ratio of imports and esports, the ratio of imports and esports, the ratio of foreign trade to GDP, trade war and covid pandemic) influence FDI. The specific model is described as follows.
\( ln{(FDI)}=α+{β_{1}}ln{(Pop)}+{β_{2}}ln{(Inter)+{β_{3}}ln{(ImEx){+β_{4}}ln{(Trade ratio)+{D_{Tw}}+{D_{covid}}}}} \) [1]
Table 3. Factors affecting.
Variables | Coefficient | Standard Error | t stat | P-value | ||
Intercept | 1.2828 | 1.8496 | 0.6935 | 0.4893 | ||
In(Pop) | 0.6756 | 0.2048 | 3.2981 | 0.0012 | ||
In(inter) | 0.5997 | 0.2137 | 2.8053 | 0.0059 | ||
In(Imex) | -0.0205 | 0.1499 | -0.1371 | 0.8911 | ||
In(Trade) | 0.4461 | 0.2359 | 1.8908 | 0.0611 | ||
Dummy variables | ||||||
Tw | -0.687 | 0.2368 | -0.7127 | 0.4774 | ||
Covid | -0.1 | 0.2469 | -0.405 | 0.6861 | ||
R-square | Adj. R-square | S.E. | ||||
0.7102 | 0.6949 | 1.0706 | ||||
After doing the statistical analysis, the results of the overall regression in table 3 offers more information. Compared with the results of annual regression, the statistic test for overall regression has a larger sample size (over 30). Thus, the results of the overall regression can offer more reliable information. First of all, according to the statistics report in table3, six variables can explain around 70% of the change of FDI. For all variables, only the ratio of exports and imports has a negative correlation with FDI, but it is not important for FDI. In fourth column, the ratio of foreign trade to GDP, population, and the number of international firms has a positive significant effect on FDI at a 5% significant level. This is because the number of international firms shows the international trade strength. There are some situations that the FDI and trade do not move in the same direction, but in the model the FDI in China and foreign trade increases at the same time. This is because China has a strong trade power and plays a key role in the world economy. [8]China has already been the largest supplier for EU since 2006 and the third destination for EU exports. [8]The largest bilateral deficit in trade happened between China and EU since 2000. The number of international firms shows the potential investment market and internalization of a country. Under a strict investment policy environment such as trade war or covid-19 period, international firms can establish a presence through FDI. The population has the most important effect on FDI. This is because the change in human capital can affect the form and number of domestic investments. It also means the population in China is a potential consumption market. The composition of total consumer demand determines the investment opportunity. To be more specific, when the ln foreign trade to GDP increases 1%, the ln FDI will increase by 0.236 million dollars. The ten thousand increases in ln population will add 0.675 million dollars in ln FDI, and the one unit increase in ln number of international companies will add 0.599 million dollars in ln FDI. Since the overall regression is based on data across different years, two dummy variables are useful for finding the change in FDI with fluctuation. Although these two variables are not significant for FDI, the coefficient of the two variables are both negative. It indicates both trade war and the covid-19 pandemic have a negative influence on FDI. This result also matches the report of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development that [9] FDI flows to developing countries are expected to drop more due to severely effect by the covid-19 pandemic. Other fact is that [10]the FDI form China to US fell more than 90 percent in the first half of 2017 due to trade war. The result also indirectly reveals that[10] foreign investors prefer the investment market with economic opportunities and political stability.
In addition, although annual regressions are less reliable than overall regression, we still can get something the results. Population has positive significant effect for FDI in 2017. The number of international companies has positive important impact on FDI in 2018. Foreign trade to GDP has positive significant effect in 2020. These results indirectly show foreign trade to GDP, population and the number of international firms have significant effect on FDI. Besides, comparing with other variables, population has more effect in 2017, 2019 and 2020. However, in 2020, the population became a negative effect for FDI. This is partly because covid-19 shock reduces labor supply in international business.
4 Conclusion and Expectation
4.1 Conclusion
From 2017 to 2020, Data analysis shows that in the overall multiple linear regression, only the ratio of exports and imports has a negative correlation with FDI, the ratio of foreign trade to GDP, population, and the number of international firms has positive. The trade war between US and China and the covid-19 pandemic are not significant for FDI, the coefficient of the two variables are both negative. For the multiple linear regression by year, the significant influencing factors in different years are different and show volatility.
4.2 Policy Recommendations
At the national level, the article suggests that it should Focus on balanced development among regions and enhance cross-regional economic cooperation. Focus on FDI hotspots and spread to neighboring regions. Through economic cooperation, transfer of enterprises, and starting from upstream and downstream of foreign enterprises, we will transform the advantages of internationalization of a single region into an organic linkage of multiple regions and drive the economic development and internationalization of inland regions to start and advance. Insist on implementing the 'One Belt, One Road' policy to drive more provincial cities to 'go out and 'look out to keep up with the wave of globalization.
At the level of the provinces, Provinces should actively participate in the internationalization process to attract foreign direct investment and promote economic and people's living standards. Work on the introduction of talents to ensure the population advantage while attracting high-quality talents with complex backgrounds to transform the population advantage into economic advantage. Also, introduce corresponding subsidy support policies to actively and positively attract excellently, multinational enterprises with high technology, increase the number of multinational enterprises, and strengthen internationalization.
References
[1]. Sun, G.,Gan, Q., Wang, W.Analysis of factors affecting China's foreign direct investment [J] Hebei finance, 2021 (03): 14-18 DOI:10.14049/j.cnki. hbjr. 2021.03.005.
[2]. Zou, Z., Chen, X.Research on the impact mechanism of FDI on China's high-quality economic development under the constraints of environmental regulation -- An Empirical Analysis Based on intermediary effect and threshold effect [J / OL] Scientific and technological progress and Countermeasures: 1-10 [2022-02-17] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1224.g3.20220121.1335.006.html.
[3]. Zhou, X., Tan, J., Guo, P., Du, W. The impact of FDI level spillover and independent R & D on industrial output -- a multidimensional threshold effect test based on the panel data of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao Bay Area [J / OL] Resources and Industry: 1-20 [2022-02-17] DOI:10.13776/j.cnki. resourcesindustries. 20211221.012.
[4]. Shen, K., Geng, Q. Foreign direct investment, technology spillover, and endogenous economic growth -- econometric test and empirical analysis of Chinese data [J] Chinese Social Sciences, 2001 (05): 82-93 + 20
[5]. Shen, K., Geng, Q. Foreign direct investment, technology spillover, and endogenous economic growth -- econometric test and empirical analysis of Chinese data [J] Chinese Social Sciences, 2001 (05): 82-93 + 20
[6]. Li Minjie, WANG Jian. Space-time evolution characteristics of China's logistics industry FDI and its driving mechanism analysis [J]. Journal of statistics and decision, 2022, 38 (01) : 85-89. The DOI: 10.13546 / j.carol carroll nki tjyjc. 2022.01.018.
[7]. Li Jian, Wu min Dual environmental regulation, FDI and green Total Factor Productivity -- a case study of three urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River economic belt [J] East China economic management, 2022,36 (01): 31-41 DOI:10.19629/j.cnki. 34-1014/f.210818002.
[8]. 2013 Edition International Trade and Foreign - Europa. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3930297/5969114/KS-FO-12-001-EN.PDF.
[9]. “Foreign Direct Investment Flows in the Time of Covid-19.” OECD, 4 May 2020, https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/foreign-direct-investment-flows-in-the-time-of-covid-19-a2fa20c4/.
[10]. Bborzyko. “The Dire Ripple Effect from a US-China Trade War: A Drop in Foreign Investment Worldwide.” CNBC, CNBC, 6 July 2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2018/07/05/ripple-effect-from-pending-us-china-trade-war-drop-in-fdi-worldwide.html.
Cite this article
Gao,Z.;Li,X.;Mo,Y.;Wang,J. (2023). The Main Factors Contributing to China’s FDI. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,3,147-153.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Economic Management and Green Development (ICEMGD 2022), Part Ⅰ
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Sun, G.,Gan, Q., Wang, W.Analysis of factors affecting China's foreign direct investment [J] Hebei finance, 2021 (03): 14-18 DOI:10.14049/j.cnki. hbjr. 2021.03.005.
[2]. Zou, Z., Chen, X.Research on the impact mechanism of FDI on China's high-quality economic development under the constraints of environmental regulation -- An Empirical Analysis Based on intermediary effect and threshold effect [J / OL] Scientific and technological progress and Countermeasures: 1-10 [2022-02-17] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1224.g3.20220121.1335.006.html.
[3]. Zhou, X., Tan, J., Guo, P., Du, W. The impact of FDI level spillover and independent R & D on industrial output -- a multidimensional threshold effect test based on the panel data of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao Bay Area [J / OL] Resources and Industry: 1-20 [2022-02-17] DOI:10.13776/j.cnki. resourcesindustries. 20211221.012.
[4]. Shen, K., Geng, Q. Foreign direct investment, technology spillover, and endogenous economic growth -- econometric test and empirical analysis of Chinese data [J] Chinese Social Sciences, 2001 (05): 82-93 + 20
[5]. Shen, K., Geng, Q. Foreign direct investment, technology spillover, and endogenous economic growth -- econometric test and empirical analysis of Chinese data [J] Chinese Social Sciences, 2001 (05): 82-93 + 20
[6]. Li Minjie, WANG Jian. Space-time evolution characteristics of China's logistics industry FDI and its driving mechanism analysis [J]. Journal of statistics and decision, 2022, 38 (01) : 85-89. The DOI: 10.13546 / j.carol carroll nki tjyjc. 2022.01.018.
[7]. Li Jian, Wu min Dual environmental regulation, FDI and green Total Factor Productivity -- a case study of three urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River economic belt [J] East China economic management, 2022,36 (01): 31-41 DOI:10.19629/j.cnki. 34-1014/f.210818002.
[8]. 2013 Edition International Trade and Foreign - Europa. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3930297/5969114/KS-FO-12-001-EN.PDF.
[9]. “Foreign Direct Investment Flows in the Time of Covid-19.” OECD, 4 May 2020, https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/foreign-direct-investment-flows-in-the-time-of-covid-19-a2fa20c4/.
[10]. Bborzyko. “The Dire Ripple Effect from a US-China Trade War: A Drop in Foreign Investment Worldwide.” CNBC, CNBC, 6 July 2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2018/07/05/ripple-effect-from-pending-us-china-trade-war-drop-in-fdi-worldwide.html.









