1. Introduction
Against the backdrop of today's economic globalization and the maturation of financial systems, the foreign exchange derivatives market plays a pivotal role in the global financial hedging system [1]. This market provides global financial institutions and industries with opportunities to seek profits and mitigate risks in the volatility of foreign exchange markets, thereby playing a crucial role in maintaining financial market stability and meeting the risk management needs of investors. With the innovative development of financial technology and the expansion of the derivatives market, the global foreign exchange derivatives market is experiencing new dynamics and environmental changes, greatly influenced by the European and American financial markets [2].
As one of the world's largest financial markets, the European and American regions possess not only a substantial number of participants and trading volumes in the foreign exchange market but also a leading position in financial innovation and regulatory policies [2]. The fluctuations in these regions' financial markets and policy changes often have direct and profound effects on other regions globally, especially in innovative derivative markets such as foreign exchange derivatives (as of March 2023, derivatives traded on European and American exchanges account for 94.2% of the global market) [3].
This study delves into the new trends and evolving environment of the global foreign exchange derivatives market by examining the categories of innovative mainstream foreign exchange derivative instruments, changes in open interest and market shares; the types, quantity changes, and diversification trends of participants in foreign exchange derivative trading; as well as a series of specific research directions such as the changes in marginal earnings and associated costs for market participants using foreign exchange derivative instruments. The aim is to track the forefront of market development and address the current lack of research in the academic community concerning innovation in the foreign exchange derivatives market (current research primarily focuses on traditional futures, contract derivative markets, and localized market studies, e.g., George Allayannis, Eli Ofek, 2001, Stephen D. Makar, Stephen P. Huffman, 2001 [4]). Simultaneously, this research offers valuable insights for global financial institutions to innovate foreign exchange derivative instruments. Moreover, it aims to provide reference value for enterprises participating in the foreign exchange market to enhance their risk management capabilities through the reasonable use of foreign exchange derivatives, and on a macro level, to offer policy suggestions for regulators in the financial derivatives industry, including governments and international associations.
The structure of this paper is as follows: The first section analyzes "Market Changes in Mainstream European and American Foreign Exchange Derivative Products" and "Changes in Derivatives Market Participants." The second section elaborates on the "Overall Summary of Changes in the European and American Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market," and the third section provides "Relevant Recommendations for Derivative Buyers and Sellers," presenting a comprehensive analysis of the global foreign exchange derivatives market.
2. Analysis
2.1. Analysis of Changes in Foreign Exchange Derivative Products
The foreign exchange derivative market in Europe and the United States, as the birthplace of these financial instruments in the field, has evolved into a comprehensive system covering major global currencies, catalyzed by significant events such as the establishment of the Chicago Mercantile Exchange and the International Monetary Fund, as well as the adoption of the floating exchange rate system at the Jamaica Conference [5]. The popular foreign exchange products in the European and American financial markets have expanded from simple spot forex trading to a diverse range of exchange-traded and over-the-counter derivative products with enhanced functionalities. According to publicly available research data from the Bank for International Settlements [6], over-the-counter trading products include spot transactions, outright forwards, forex swaps, currency swaps, options, and other derivatives; exchange-traded products include forex futures and on-exchange currency options.
Between 2010 and 2022, the total open interest of foreign exchange instruments (settled in USD) in over-the-counter trading products increased by 88.98%, with substantial growth observed in various sub-products. Notably, in the distribution of the share of total turnover of foreign exchange derivatives over-the-counter between 2010 and 2022, only outright forwards and currency swaps experienced an increase in their share, while the rest saw a decline. I believe that the rise of innovative products like non-deliverable forwards (NDFs) in Forward foreign exchange agreement transactions (FXAs) has contributed to this trend. Due to the continuous innovation and customization of foreign exchange derivative products, the share of spot transactions in the total over-the-counter trading volume decreased by nearly 10% from 2010 to 2022, reflecting the overall trend of increased complexity and diversification in foreign exchange derivative products.
Exchange-traded products also generally showed an increase in total open interest, with trends in the distribution of various product types adjusting from 2021 to 2023. Between 2016 and 2019, the trading of interest rate derivatives in the over-the-counter market more than doubled, far surpassing the growth in exchange-traded transactions. According to the BIS, this rapid expansion was attributed to an increase in non-market-facing transactions, such as back-to-back and compression trades (The evolution of OTC interest rate derivatives markets, BIS, 2019). As indicated by data in Table 2, the total open interest of exchange-traded products also achieved an annual growth rate of 7.5% from 2021 to 2022 (in the North American and European markets). In terms of weight distribution, the gap between futures and options products' total open interest gradually widened, with options products experiencing significant growth from 2022 to 2023, with the most substantial contribution coming from short-term interest rate options. Based on an analysis of product open interest and daily average turnover data, it reflects significant growth in liquidity and overall market size for both exchange-traded and over-the-counter trading products, indicating favorable prospects for the foreign exchange derivative product market in Europe and the United States.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that the turnover rate of short-term interest rate derivative instruments has increased rapidly from a temporal perspective. The increased volatility of mainstream currency exchange rates in the European and American markets has contributed to the higher proportion of short-term interest rate derivative instruments. Particularly, the gradual interest rate hikes in the US have further propelled this trend towards shorter-term instruments.
Table 1: OTC foreign exchange turnover by instrument from 2010 to 2022.
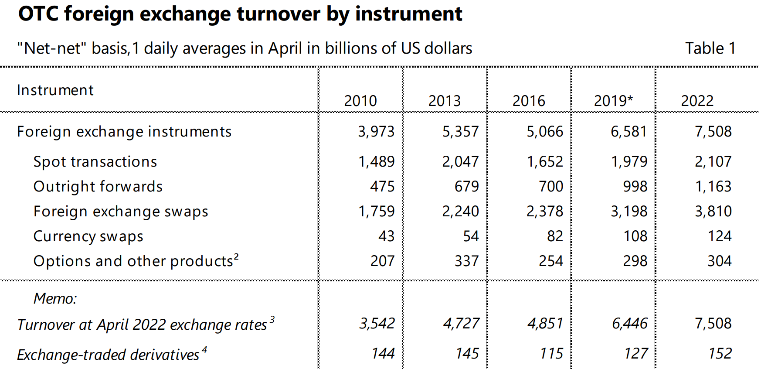
Source: Annex tables: OTC foreign exchange turnover in April 2022, BIS.
Table 2: Exchange-traded futures and options, by location of exchange.
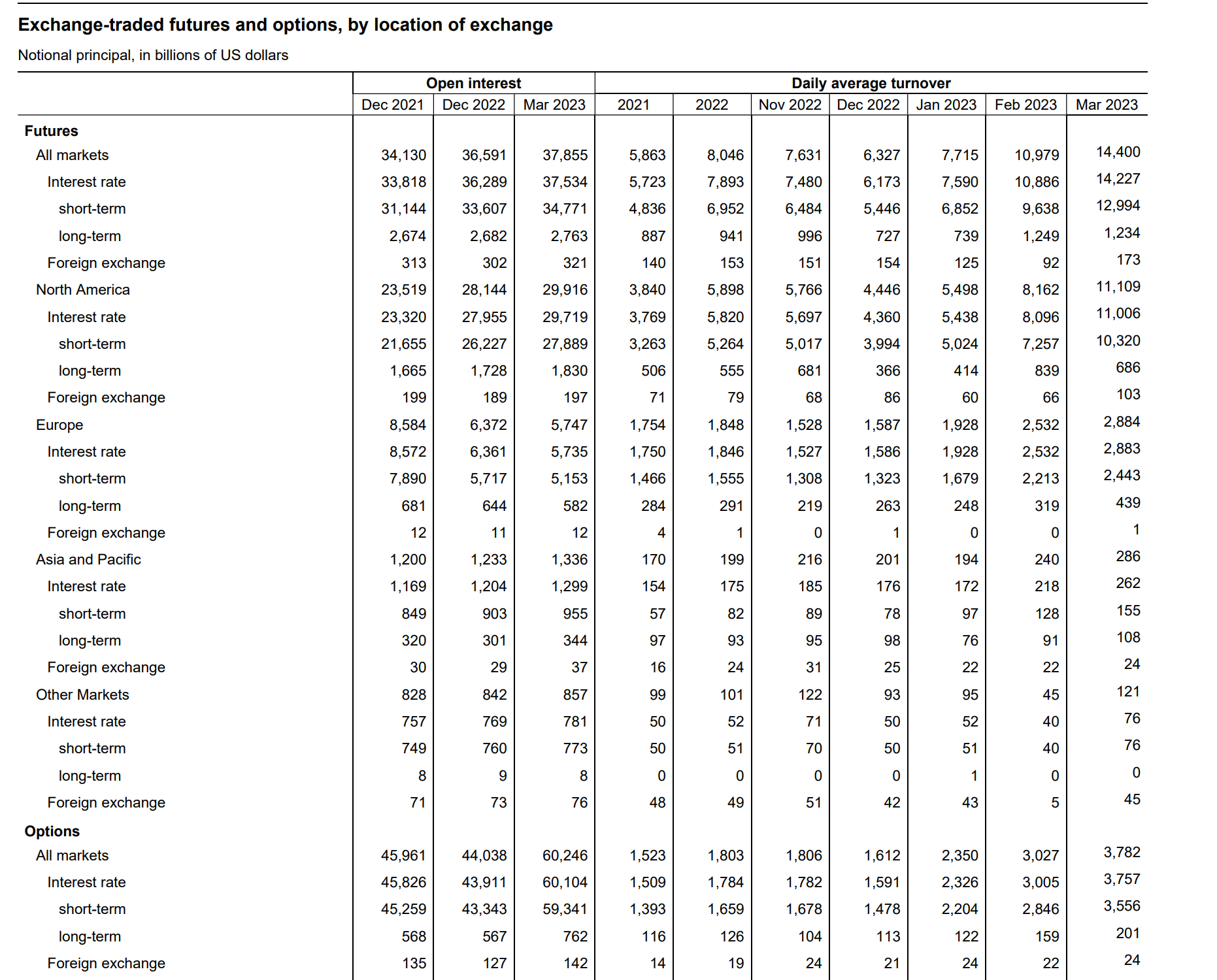
Source: BIS statistics explorer (http://stats.bis.org/statx/).
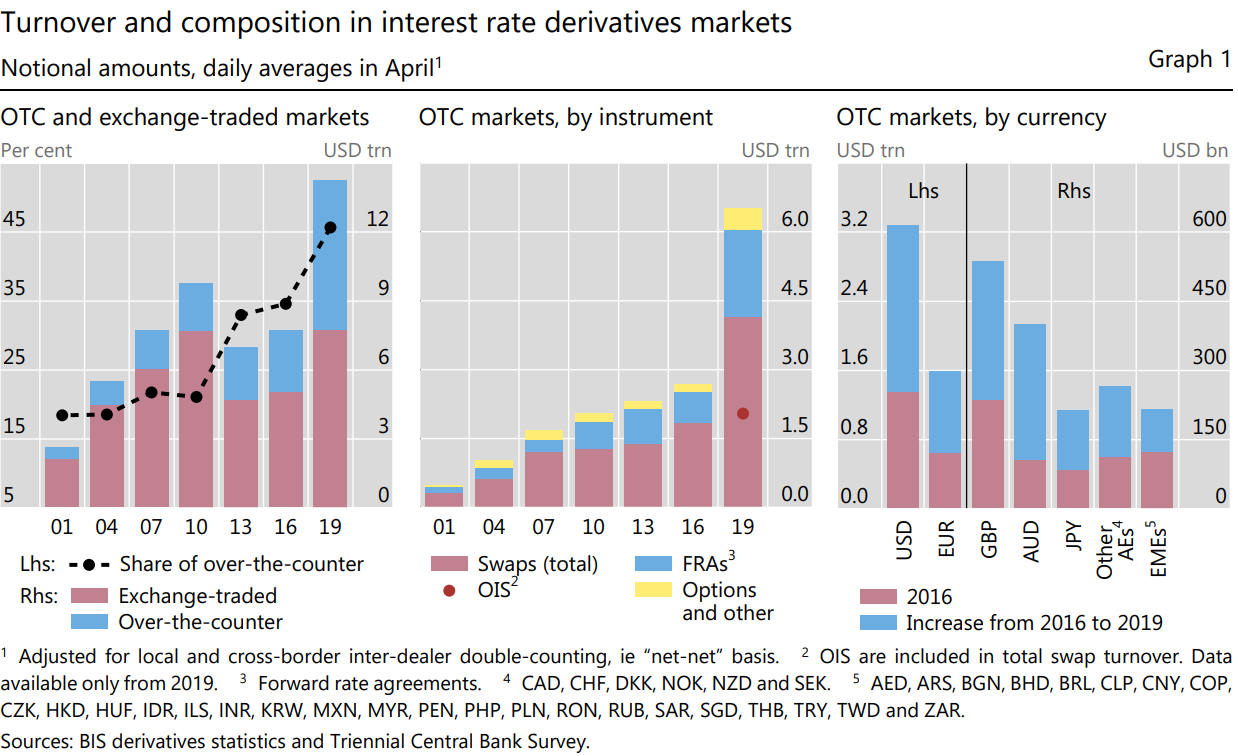
Figure 1: Previous change of Turnover and Composition in Interest Rate Derivatives Markets Notional amounts.
Source: BIS Derivatives Statistics and Triennial Central Bank Survey.
2.2. Analysis of Participant Transformations in the Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market
Over time, the trading landscape in the foreign exchange market has shown a clear trend of diversification, comprehensive development, and segmentation, as strongly validated by data from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). According to BIS classifications, participants in the foreign exchange market are categorized as eligible reporting dealers, other financial institutions, and non-financial institutions, each category playing distinct roles and functions in the market.
Eligible reporting dealers, typically comprising large commercial banks, investment firms, and securities companies, hold a vital position in the foreign exchange market. Data from April 2022 indicates that the weight of these reporting dealers in forex trading in the United States and the United Kingdom is approximately 60.36% and 52.48% of the total trading volume, respectively. Compared to 2019 data (BIS, Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange and Over-The-Counter (OTC) derivatives markets, 2019. [7]), there has been an increase of about 62.46% in the trading share of eligible reporting dealers in the US and an increase of about 28.15% in the UK. This signifies a steady enhancement of reporting dealers' roles in market liquidity and pricing.
An emerging trend of note is the rise of other financial institutions, encompassing smaller-scale commercial banks, securities firms, fund companies, corporate finance departments, and central banks, among others, as active participants in the growing forex derivatives market. Based on the 2022 BIS Triennial Survey data, the weights of these institutions in US forex trading for that year were: Non-reporting banks (approximately 14.05% of total trading volume), Institutional investors (approximately 8.72%), and Hedge funds and PTFs (approximately 8.16%). In the UK, the corresponding weights were: Non-reporting banks (approximately 18.41%), Institutional investors (approximately 9.18%), and Hedge funds and PTFs (approximately 8.14%). The combined share of other financial institutions in total trading volume in the US and UK in 2022 was 36% and 45.52%, respectively.
Compared to 2019, the total trading volume of other financial institutions in the US increased by approximately 20.2%, institutional investors grew by about 7.86%, and non-financial customers declined by 20%. Conversely, in the UK, the total trading volume of other financial institutions decreased by around 17.28%, institutional investors' share decreased by about 19.51%, and non-financial customers' share decreased by approximately 57.6%. This trend underscores the redistribution of weight among European and American financial institutions, with the growth of other financial institutions primarily concentrated in the US market. Although non-reporting bank financial institutions (other financial institutions) might have a smaller share in total trading volume data compared to traditional reporting bank financial institutions, their impact is equally noteworthy.
In conclusion, the data changes from 2019 to 2022 reveal an overarching trend of diversification, comprehensive development, and segmentation in the European and American foreign exchange derivatives market participants, with the emerging trend of other financial institutions' growth predominantly focused on the US. The dynamic shifts in structure and participants in the European and American foreign exchange derivatives market also offer valuable insights for the future development of the global forex derivatives financial market.
Table 3: Foreign exchange turnover by country and counterparty sector, "net-gross" basis, daily averages in 2022, in millions of US dollars.
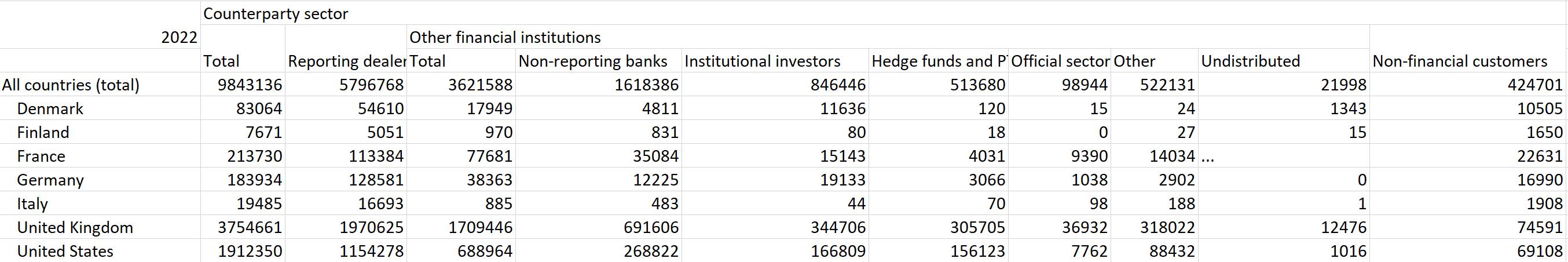
Source: Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange and Over-The-Counter (OTC) derivatives markets in 2022.
Table 4: Foreign exchange turnover by country and counterparty sector, "net-gross" basis, daily averages in 2019, in millions of US dollars.
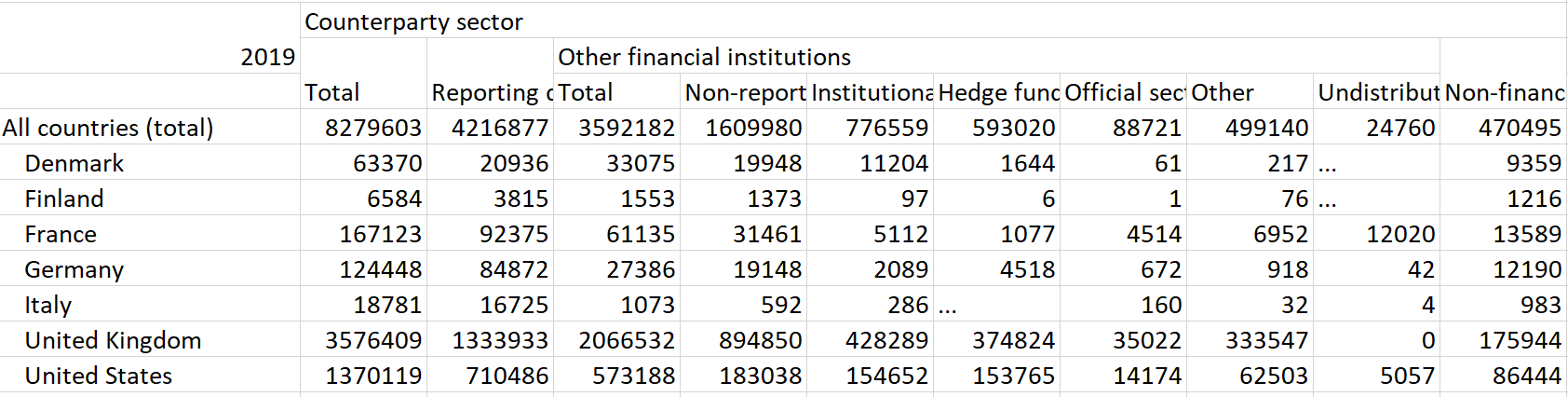
Source: Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange and Over-The-Counter (OTC) derivatives markets in 2019.
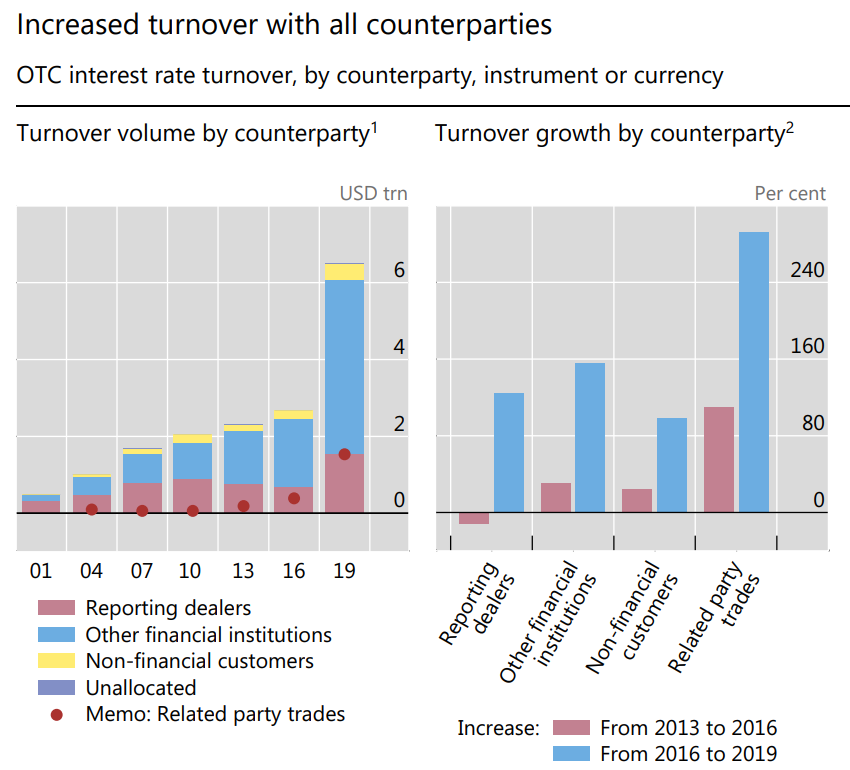
Figure 2: Previous change of turnover with all counterparties from 2013 to 2016.
Source: BIS derivatives statistics and Triennial Central Bank Survey, (2019).
3. Summary and Attribution Analysis of Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market Changes in Europe and the United States
3.1. The Scale of the Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market Continues to Expand, the Share of the OTC Market has Increased Significantly, and Structural Changes Continue to Evolve
In the development of European and American foreign exchange derivatives markets in the past decade, structural changes, and other changes, including central clearing and regulatory changes, have continued to evolve, and have intensified over time. The above development trends have profoundly affected the development of the OTC market, resulting in a significant increase in the size and trading volume of the OTC market in the past decade, and also making the OTC market increasingly attractive in the eyes of foreign exchange derivatives traders, as shown below:
First and foremost, as an important feature of the current structural changes in the OTC market, central clearing is an inevitable trend in the current market environment. After experiencing the major financial crisis such as the subprime mortgage crisis in 2008 and the black swan event such as the outbreak of new coronavirus pneumonia, the financial market participants' sensitivity to risk has greatly increased and their perspective on risk assessment has significantly increased. A large number of market participants tend to choose more conservative investment strategies; The clearing and portfolio compression services hosted by large-scale, reputable, and stable market makers and large institutions in the OTC market have also brought the stability, security, and reliability of many traditional exchanges to the OTC market.
In addition, in recent years, the proportion of automated transactions in over-the-counter transactions has increased, which has greatly reduced the threshold of market access, effectively reduced the transaction costs of many links, achieved the result of attracting new market players to the market, and increasing the total transaction volume, and promoted the continuous evolution of structural changes in the over-the-counter market. These technological advances have also promoted the implementation of many investment strategies that use new algorithms and enjoy the benefits of electronic and automated technological progress.
3.2. The Relationship Between the Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market and Monetary Policy is Increasingly Close, and the Trend is to Choose Shorter-term Trading Instruments
In recent years, frequent fluctuations in the general environment have led to an increase in changes in monetary policy, which has brought more risks and uncertainties than ever before, resulting in more frequent fluctuations in sentiment and trading strategies in the foreign exchange derivatives market, and increasingly tightening the relationship between the foreign exchange derivatives market and monetary policy. At the same time, due to speculative reasons and the need to hedge against potential changes in short-term interest rates, many market players will choose to build positions on both sides, objectively promoting the further increase of trading volume and turnover.
Similarly, in consideration of market expectations and the current high-risk situation, market players, in addition to choosing more stable, safe, and conservative investment strategies, also prefer to diversify funds through trading instruments with shorter terms and complete the required transactions with more frequent trading opportunities. So as to reduce the transaction risk. Macroscopically, it also promoted the growth of trading volume and turnover of the entire foreign exchange derivatives market.
4. Conclusion: Recommendations for Forex Derivatives Buyers and Sellers
4.1. For Forex Derivatives Buyers
To address the dynamic interest rate environment and meet institutional risk control needs, institutions must possess the ability to select suitable interest rate derivatives and effectively utilize them for profit. Considering the current overarching trend, customized derivative products offered on the OTC market are increasingly attractive to most financial and non-financial institution buyers. Ongoing innovations in OTC products provide buyers with more refined options.
However, due to innovative changes in benchmark rates, such as the transition to new overnight risk-free rates (RFRs), the complexity of new derivative instruments, and the lack of reference pose challenges that elevate search costs for buyers when selecting products. This underscores the proactive approach for forex derivatives buyers to establish their own hedging and arbitrage systems, along with the requisite strategies and teams.
Furthermore, before engaging in forex derivatives trading, buyers need to comprehensively assess their currency risk exposure. Subsequently, they should formulate clear risk management strategies based on diverse business activities and market expectations, considering the costs, liquidity, and risk characteristics of selected products.
4.2. For Forex Derivatives Sellers
Adapting to the rapid growth trend of the OTC market necessitates innovation and customization as essential strategies. Sellers should focus on continuously innovating and customizing forex derivative products to meet the evolving risk management needs of buyers. Beyond product focus, sellers should align with the trend of automated trading. Recent years have witnessed a rise in automated trading across all derivative markets. Advanced trading technology platforms and services are imperative.
Forex derivatives sellers currently demand user-friendliness, stability, and security. In contrast to buyers, sellers should realign innovation and sales strategies in accordance with market orientation, utilizing emerging trends in product and participant changes in the global forex derivatives market to further business development.
Notably, while innovating forex derivative products, sellers should strictly adhere to regulatory requirements and compliance standards. Providing transparency and reliability to buyers is essential. Regulatory scrutiny of the forex derivatives market is increasing, necessitating sellers to ensure their products and trading processes comply with regulations and market norms. This not only supports the health of the market but also enhances buyer confidence in the market.
References
[1]. George Allayannis, Eli Ofek, Exchange rate exposure, hedging, and the use of foreign currency derivatives, Journal of International Money and Finance (2001).
[2]. William C. Dudley, Principles for financial regulatory reform, Global Finance Journal (2019).
[3]. Data source: Table D1, Exchange-traded derivatives statistics, Bank for International Settlements (2023).
[4]. Stephen D. Makar, Stephen P. Huffman, Foreign exchange derivatives, exchange rate changes, and the value of the firm: U.S. multinationals’ use of short-term financial instruments to manage currency risk, Journal of Economics and Business, (2001).
[5]. BIS, OTC derivatives outstanding, Bank for International Settlements (2023).
[6]. BIS, derivatives statistics, and Triennial Central Bank Survey. (2022).
[7]. BIS, Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange and Over-The-Counter (OTC) derivatives markets, (2019).
Cite this article
Peng,C.;Zhao,Z. (2023). Exploring New Trends in the Global Foreign Exchange Derivatives Market Based on the European and American Financial Markets. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences,53,188-194.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. George Allayannis, Eli Ofek, Exchange rate exposure, hedging, and the use of foreign currency derivatives, Journal of International Money and Finance (2001).
[2]. William C. Dudley, Principles for financial regulatory reform, Global Finance Journal (2019).
[3]. Data source: Table D1, Exchange-traded derivatives statistics, Bank for International Settlements (2023).
[4]. Stephen D. Makar, Stephen P. Huffman, Foreign exchange derivatives, exchange rate changes, and the value of the firm: U.S. multinationals’ use of short-term financial instruments to manage currency risk, Journal of Economics and Business, (2001).
[5]. BIS, OTC derivatives outstanding, Bank for International Settlements (2023).
[6]. BIS, derivatives statistics, and Triennial Central Bank Survey. (2022).
[7]. BIS, Triennial Central Bank Survey of foreign exchange and Over-The-Counter (OTC) derivatives markets, (2019).









